
Machmeter
Encyclopedia

Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
pitot-static system
Pitot-static system
A pitot-static system is a system of pressure-sensitive instruments that is most often used in aviation to determine an aircraft's airspeed, Mach number, altitude, and altitude trend. A pitot-static system generally consists of a pitot tube, a static port, and the pitot-static instruments...
flight instrument that
shows the ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
of the true airspeed
True airspeed
True airspeed of an aircraft is the speed of the aircraft relative to the airmass in which it is flying. True airspeed is important information for accurate navigation of an aircraft.-Performance:...
to the speed of sound
Speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled during a unit of time by a sound wave propagating through an elastic medium. In dry air at , the speed of sound is . This is , or about one kilometer in three seconds or approximately one mile in five seconds....
,
a dimensionless quantity
Dimensionless quantity
In dimensional analysis, a dimensionless quantity or quantity of dimension one is a quantity without an associated physical dimension. It is thus a "pure" number, and as such always has a dimension of 1. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and...
called Mach number
Mach number
Mach number is the speed of an object moving through air, or any other fluid substance, divided by the speed of sound as it is in that substance for its particular physical conditions, including those of temperature and pressure...
. This is shown on a Machmeter as a decimal fraction.
An aircraft flying at the speed of sound is flying
at a Mach number of one, expressed as Mach 1.
Use
As an aircraft in transonicTransonic
Transonic speed is an aeronautics term referring to the condition of flight in which a range of velocities of airflow exist surrounding and flowing past an air vehicle or an airfoil that are concurrently below, at, and above the speed of sound in the range of Mach 0.8 to 1.2, i.e. 600–900 mph...
flight approaches the speed of sound,
it first reaches its critical mach number, where air flowing
over low-pressure areas of its surface locally reaches the
speed of sound, forming shock wave
Shock wave
A shock wave is a type of propagating disturbance. Like an ordinary wave, it carries energy and can propagate through a medium or in some cases in the absence of a material medium, through a field such as the electromagnetic field...
s. The indicated airspeed
Indicated airspeed
Indicated airspeed is the airspeed read directly from the airspeed indicator on an aircraft, driven by the pitot-static system. IAS is directly related to calibrated airspeed , which is the IAS corrected for instrument and installation errors....
for this condition changes with ambient pressure,
which in turn changes with altitude
Altitude
Altitude or height is defined based on the context in which it is used . As a general definition, altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The reference datum also often varies according to the context...
.
Therefore, indicated airspeed is not entirely adequate to
warn the pilot of the impending problems. Mach number is
more useful, and most high-speed aircraft
High-speed flight
In high-speed flight the assumptions of incompressibility of the air used in low-speed aerodynamics no longer apply. In subsonic aerodynamics, the theory of lift is based upon the forces generated on a body and a moving gas in which it is immersed...
are limited to a maximum operating Mach number, also known as MMO.
For example, if the MMO is Mach 0.83, then at 30000 feet (9,144 m) where the speed of sound under standard conditions
Standard atmosphere
Standard atmosphere may refer to:* A standard reference value for air pressure:** Atmosphere , an approximation of the value at sea level** Atmospheric pressure, other reference values* A model of how atmospheric pressure varies with altitude:...
is 590 knots (321 m/s), the true airspeed
True airspeed
True airspeed of an aircraft is the speed of the aircraft relative to the airmass in which it is flying. True airspeed is important information for accurate navigation of an aircraft.-Performance:...
at MMO is 489 knots (266 m/s). The speed of sound increases with air temperature, so at Mach 0.83 at 10000 feet (3,048 m) where the air is much warmer than at 30000 feet (9,144 m), the true airspeed at MMO would be 530 knots (289 m/s).
Operation
Some older mechanical Machmeters use an altitude aneroid and an airspeedAirspeed indicator
The airspeed indicator or airspeed gauge is an instrument used in an aircraft to display the craft's airspeed, typically in knots, to the pilot.- Use :...
capsule which together convert pitot-static pressure into Mach number. Modern electronic Machmeters use information from an air data computer system.
Calibration
In subsonic flow the Mach meter can be calibrated according to: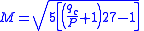
where:
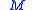 is Mach number
is Mach number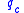 is impact pressure
is impact pressureImpact pressure
In compressible fluid dynamics, impact pressure is the difference between total pressure and static pressure. In aerodynamics notation, this quantity is denoted as q_c or Q_c....
and
 is static pressure
is static pressureStatic pressure
In fluid mechanics the term static pressure has several uses:* In the design and operation of aircraft, static pressure is the air pressure in the aircraft’s static pressure system....
- and assuming the ratio of specific heatsHeat capacity ratioThe heat capacity ratio or adiabatic index or ratio of specific heats, is the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure to heat capacity at constant volume . It is sometimes also known as the isentropic expansion factor and is denoted by \gamma or \kappa . The latter symbol kappa is...
is 1.4
When a shock wave forms across the pitot tube the required formula is derived from the Rayleigh
Rayleigh number
In fluid mechanics, the Rayleigh number for a fluid is a dimensionless number associated with buoyancy driven flow...
Supersonic Pitot equation, and is solved iteratively:
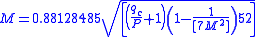
where:
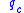 is now impact pressure measured behind a normal shock.
is now impact pressure measured behind a normal shock.Note that the inputs required are impact pressure (or total pressure
Stagnation pressure
In fluid dynamics, stagnation pressure is the static pressure at a stagnation point in a fluid flow.At a stagnation point the fluid velocity is zero and all kinetic energy has been converted into pressure energy . Stagnation pressure is equal to the sum of the free-stream dynamic pressure and...
) and static pressure. Air temperature input is not required.

