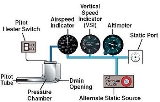
Pitot-static system
Overview
System
System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
of pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
-sensitive instruments that is most often used in aviation to determine an aircraft's airspeed
Airspeed
Airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are: indicated airspeed , calibrated airspeed , true airspeed , equivalent airspeed and density airspeed....
, Mach number
Mach number
Mach number is the speed of an object moving through air, or any other fluid substance, divided by the speed of sound as it is in that substance for its particular physical conditions, including those of temperature and pressure...
, altitude
Altitude
Altitude or height is defined based on the context in which it is used . As a general definition, altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The reference datum also often varies according to the context...
, and altitude trend. A pitot-static system generally consists of a pitot tube
Pitot tube
A pitot tube is a pressure measurement instrument used to measure fluid flow velocity. The pitot tube was invented by the French engineer Henri Pitot Ulo in the early 18th century and was modified to its modern form in the mid-19th century by French scientist Henry Darcy...
, a static port, and the pitot-static instruments. This equipment is used to measure the forces acting on a vehicle as a function of the temperature, density, pressure and viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
of the fluid in which it is operating.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

