Mac OS X v10.5
Encyclopedia
Mac OS X Leopard is the sixth major release of Mac OS X, Apple's desktop and server operating system
for Macintosh computers. Leopard was released on 26 October 2007 as the successor of Tiger (version 10.4), and is available in two variants: a desktop
version suitable for personal computer
s, and a server
version, Mac OS X Server
. Steve Jobs stated at Macworld
2008 that over 20% of Macs use Leopard as their operating system. Leopard was superseded by Snow Leopard (version 10.6). Leopard is the final version of Mac OS X to support the PowerPC
architecture as Snow Leopard functions solely on Intel based Macs.
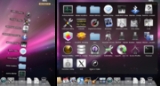
According to Apple, Leopard contains over 300 changes and enhancements over its predecessor, Mac OS X Tiger, covering core operating system components as well as included applications and developer tools. Leopard introduces a significantly revised desktop, with a redesigned Dock, Stacks
, a semitransparent menu bar
, and an updated Finder that incorporates the Cover Flow visual navigation interface first seen in iTunes
. Other notable features include support for writing 64-bit
graphical user interface
applications, an automated backup utility called Time Machine
, support for Spotlight
searches across multiple machines, and the inclusion of Front Row and Photo Booth
, which were previously included with only some Mac models.
Apple missed Leopard's release time frame as originally announced by Apple's CEO Steve Jobs
. When first discussed in June 2005, Jobs had stated that Apple intended to release Leopard at the end of 2006 or early 2007. A year later, this was amended to Spring 2007; however on 12 April 2007, Apple issued a statement that its release would be delayed until October 2007 because of the development of the iPhone
.
Library Randomization: Leopard implements library randomization
, which randomizes the locations of some libraries in memory. Vulnerabilities that corrupt program memory often rely on known addresses for these library routines, which allow injected code to launch processes or change files. Library randomization is presumably a stepping-stone to a more complete implementation of address space layout randomization at a later date.
Application Layer Firewall
Sandboxes: Leopard includes kernel-level support for role-based access control (RBAC). RBAC is intended to prevent, for example, an application like Mail from editing the password database.
Application Signing: Leopard provides a framework to use public key signatures
for code signing
to verify, in some circumstances, that code has not been tampered with. Signatures can also be used to ensure that one program replacing another is truly an "update", and carry any special security privileges across to the new version. This reduces the number of user security prompts, and the likelihood of the user being trained to simply clicking "OK" to everything.
Secure Guest Account: Guests can be given access to a Leopard system with an account that the system erases and resets at logout.
Security features in Leopard have been criticized as weak or ineffective, with the publisher Heise Security
documenting that the Leopard installer downgraded firewall protection and exposed services to attack even when the firewall was re-enabled. Several researchers noted that the Library Randomization feature added to Leopard was ineffective compared to mature implementations on other platforms, and that the new "secure Guest account" could be abused by Guests to retain access to the system even after the Leopard log out process erased their home directory.
Leopard’s retail version was not released in separate versions for each type of processor, but instead consisted of one universal release
that could run on both PowerPC and Intel processors. However, the install discs that ship with Intel-based Macs only contain Intel binaries.
Processor type and speed are checked during installation and installation halted if insufficient; however, Leopard will run on slower G4 processor machines (e.g., a 733mhz Quicksilver) if the installation is performed on a supported Mac and its hard-drive then moved to a slower/unsupported one (the drive may either be an internal mechanism or a Firewire
external).
(used for installing earlier releases of Mac OS X on unsupported G3 and pre-G3 Macs) that uses the Mac’s Open Firmware to tell Leopard that the machine does have a CPU meeting the 867 MHz minimum requirement that the Installer checks for before installation is allowed to commence, when in reality the CPU is slower. Currently, LeopardAssist only runs on slower G4s and many people have installed Leopard successfully on these older machines.
Users who have access to supported hardware have installed Leopard on the supported machine then simply moved the hard drive to the unsupported machine. Alternatively, the Leopard Installation DVD was booted on a supported Mac, then installed on an unsupported Mac via Firewire Target Disk Mode. Leopard is only compiled for AltiVec-enabled PowerPC processors (G4 and G5) though, as well as Intel, so both of these methods will only work on Macs with G4 or later CPUs. While some of the earlier beta releases were made to run on some later G3 machines (mostly later 800–900 MHz iBooks), no success with the retail version has been officially reported on G3 Macs except for some later iMacs and "Pismo" PowerBook G3s with G4 processor upgrades installed.
For a number of months after Leopard's release it appeared that the only G3 Macs on which Leopard could be run were those with both an aftermarket G4 processor and an AGP graphics card, as failures with the OS partially booting before crashing were reported on older Macs such as the original tray-loading iMacs and the Beige and Blue & White Power Mac G3 (all with G4 upgrades as Leopard will not even begin to load without one) whereas it would boot fine on newer Macs where the Installer restriction had been circumvented. However, more recently it has been reported that with some more work and use of kernel extensions from XPostFacto, Tiger and beta builds of Leopard, the OS can be made to run on G4-upgraded Macs as old as the Power Macintosh 9500
, despite the lack of AGP-based graphics. While Leopard can be run on any Mac with a G4 or later processor, some functionality such as Front Row or Time Machine fails to work without a Quartz Extreme-capable graphics card, which many of the earlier G4s did not include in their factory specification.
Since Apple moved to using Intel processors in their computers, the OSx86
project has developed and now also allows Mac OS X Tiger, Leopard, and Snow Leopard to be installed and run successfully on non-Apple x86-based computers, albeit in violation of Apple's licensing agreement for OS X. A variety of installation processes can be used, the most common being to use modified Darwin bootloaders commonly known as "Boot 132" designed to trick the retail, or vanilla
, operating system into thinking that it is running on an EFI
-based Mac
. This method of installation allows the use of an unmodified Apple installation DVD and the updating of the operating system from the built-in Software Update utility, but will work only on Intel Core-based PCs, unless a modified kernel is added to the pre-boot CD. Modified installation DVDs are also available illegally which offer a more outdated approach to installing.
cover, making the X appear to float above a purple galaxy, somewhat resembling the default Leopard desktop wallpaper.
(APE), from Unsanity
which is incompatible with Leopard; many users do not know, APE had been installed silently on many Macs by Logitech as part of their mouse drivers. However, only the users who did not have the latest version of APE installed (2.0.3 at that time) were affected. Apple published a knowledge base article on how to solve this problem.
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
for Macintosh computers. Leopard was released on 26 October 2007 as the successor of Tiger (version 10.4), and is available in two variants: a desktop
Desktop computer
A desktop computer is a personal computer in a form intended for regular use at a single location, as opposed to a mobile laptop or portable computer. Early desktop computers are designed to lay flat on the desk, while modern towers stand upright...
version suitable for personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s, and a server
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
version, Mac OS X Server
Mac OS X Server
Mac OS X Server is a Unix server operating system from Apple Inc. The server edition of Mac OS X is architecturally identical to its desktop counterpart, except that it includes work group management and administration software tools...
. Steve Jobs stated at Macworld
Macworld Conference & Expo
Produced by Boston-based IDG World Expo, Macworld | iWorld is a trade-show with conference tracks dedicated to the Apple Macintosh platform. It is held annually in the United States, usually during the second week of January...
2008 that over 20% of Macs use Leopard as their operating system. Leopard was superseded by Snow Leopard (version 10.6). Leopard is the final version of Mac OS X to support the PowerPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
architecture as Snow Leopard functions solely on Intel based Macs.
According to Apple, Leopard contains over 300 changes and enhancements over its predecessor, Mac OS X Tiger, covering core operating system components as well as included applications and developer tools. Leopard introduces a significantly revised desktop, with a redesigned Dock, Stacks
Stacks (software)
Stacks are a feature first found in Apple's operating system, Mac OS X v10.5 "Leopard". As the name implies, they "stack" files into a small organized folder on the Dock...
, a semitransparent menu bar
Menu bar
A menu bar is a region of a screen or application interface where drop down menus are displayed. The menu bar's purpose is to supply a common housing for window- or application-specific menus which provide access to such functions as opening files, interacting with an application, or displaying...
, and an updated Finder that incorporates the Cover Flow visual navigation interface first seen in iTunes
ITunes
iTunes is a media player computer program, used for playing, downloading, and organizing digital music and video files on desktop computers. It can also manage contents on iPod, iPhone, iPod Touch and iPad....
. Other notable features include support for writing 64-bit
64-bit
64-bit is a word size that defines certain classes of computer architecture, buses, memory and CPUs, and by extension the software that runs on them. 64-bit CPUs have existed in supercomputers since the 1970s and in RISC-based workstations and servers since the early 1990s...
graphical user interface
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
applications, an automated backup utility called Time Machine
Time Machine (Apple software)
Time Machine is a backup utility developed by Apple. It is included with Mac OS X and was introduced with the 10.5 "Leopard" release of Mac OS X. The software is designed to work with the Time Capsule as well as other internal or external drives.-Overview:...
, support for Spotlight
Spotlight (software)
Spotlight is a system-wide desktop search feature of Apple's Mac OS X operating system. Spotlight is a selection-based search system, which creates a virtual index of all items and files on the system. It is designed to allow the user to quickly locate a wide variety of items on the computer,...
searches across multiple machines, and the inclusion of Front Row and Photo Booth
Photo Booth
Photo Booth is a small software application for taking photos and videos with an iSight camera by Apple Inc. for Mac OS X and iOS .-Photo Booth:...
, which were previously included with only some Mac models.
Apple missed Leopard's release time frame as originally announced by Apple's CEO Steve Jobs
Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs was an American businessman and inventor widely recognized as a charismatic pioneer of the personal computer revolution. He was co-founder, chairman, and chief executive officer of Apple Inc...
. When first discussed in June 2005, Jobs had stated that Apple intended to release Leopard at the end of 2006 or early 2007. A year later, this was amended to Spring 2007; however on 12 April 2007, Apple issued a statement that its release would be delayed until October 2007 because of the development of the iPhone
IPhone
The iPhone is a line of Internet and multimedia-enabled smartphones marketed by Apple Inc. The first iPhone was unveiled by Steve Jobs, then CEO of Apple, on January 9, 2007, and released on June 29, 2007...
.
End-user features
Apple advertises that Mac OS X Leopard has 300+ new features, including:- A new and improved Automator, with easy starting points to easily start a workflow. It also can quickly create or edit workflows with new interface improvements. Now it can use a new action called "Watch Me Do" that lets you record a user action (like pressing a button or controlling an application without built-in Automator support) and replay as an action in a workflow. It can create more useful Automator workflows with actions for RSS feeds, iSight camera video snapshots, PDF manipulation, and much more.
- Back to My MacBack to My MacBack to My Mac is a feature introduced with Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard that uses Wide-Area Bonjour to securely discover services across the Internet and automatically configure ad hoc, on-demand, point-to-point encrypted connections between computers using IPSec...
, a feature for MobileMeMobileMeMobileMe was a subscription-based collection of online services and software offered by Apple Inc. Originally launched on January 5, 2000, as iTools, a free collection of Internet-based services for users of Mac OS 9, Apple relaunched it as .Mac on July 17, 2002, when it became a paid subscription...
users that allows users to access files on their home computer while away from home via the internet. - Boot Camp, a software assistant allowing for the installation of other operating systems, such as Windows XPWindows XPWindows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
(SP2 or later) or Windows VistaWindows VistaWindows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
, on a separate partition (or separate internal drive) on Intel-based Macs. - Dashboard enhancements, including Web Clip, a feature that allows users to turn a part of any Web page displayed in SafariSafari (web browser)Safari is a web browser developed by Apple Inc. and included with the Mac OS X and iOS operating systems. First released as a public beta on January 7, 2003 on the company's Mac OS X operating system, it became Apple's default browser beginning with Mac OS X v10.3 "Panther". Safari is also the...
into a live Dashboard widget, and DashcodeDashcodeDashcode is a software application created by Apple Inc. that is included with Mac OS X Leopard and facilitates the development of widgets for Dashboard...
to help developers code widgetsWeb widgetIn computing a web widget is a software widget for the web. It's a small application that can be installed and executed within a web page by an end user. They are derived from the idea of code reuse. Other terms used to describe web widgets include: portlet, gadget, badge, module, webjit, capsule,...
. - New Desktop, comprises a redesigned 3-D dockDock (computing)The Dock is a prominent feature of the graphical user interface of the Mac OS X operating system. It is used to launch applications and switch between running applications...
with a new grouping feature called StacksStacks (software)Stacks are a feature first found in Apple's operating system, Mac OS X v10.5 "Leopard". As the name implies, they "stack" files into a small organized folder on the Dock...
, which displays files in either a "fan" style, "grid" style, or (since 10.5.2) a "list" style. R.L. Prior, on the ThinkMac blog, criticized the shelf-like Dock along with a number of other changes to the user interface.
- DictionaryDictionary (software)Dictionary is an application developed by Apple for its Macintosh computers. It was introduced with Mac OS X v10.4 "Tiger", and provides definitions and synonyms from the New Oxford American Dictionary, 2nd Edition and Oxford American Writer's Thesaurus, 2nd Edition...
can now search WikipediaWikipediaWikipedia is a free, web-based, collaborative, multilingual encyclopedia project supported by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. Its 20 million articles have been written collaboratively by volunteers around the world. Almost all of its articles can be edited by anyone with access to the site,...
, and a dictionary of Apple terminology as well. Also included is the Japanese-language dictionary DaijisenDaijisenThe is a general-purpose Japanese dictionary published by Shogakukan in 1995 and 1998. It was designed as an "all-in-one" dictionary for native speakers of Japanese, especially high school and university students.-History:...
, Progressive E-J and Progressive J-E dictionaries, and the 25000-word thesaurus , all of which are provided by the Japanese publisher ShogakukanShogakukanis a Japanese publisher of dictionaries, literature, manga, non-fiction, DVDs, and other media in Japan.Shogakukan founded Shueisha which founded Hakusensha. These are three separate companies, but are together called the Hitotsubashi Group, one of the largest publishing groups in Japan...
. - A redesigned FinderMacintosh FinderThe Finder is the default file manager used on Mac OS and Mac OS X operating systems; it is responsible for the overall user-management of files, disks, network volumes and the launching of other applications...
, with features similar to those seen in iTunesITunesiTunes is a media player computer program, used for playing, downloading, and organizing digital music and video files on desktop computers. It can also manage contents on iPod, iPhone, iPod Touch and iPad....
7, including Cover Flow and a Source list-like sidebar. - Front Row has been reworked to closely resemble the interface of the original Apple TV.
- iCalICaliCal is a personal calendar application made by Apple Inc. that runs on the Mac OS X operating system. iCal was the first calendar application for Mac OS X to offer support for multiple calendars and the ability to publish/subscribe calendars to WebDAV server....
calendar sharing and group scheduling as well as syncing event invitations from Mail. The icon also reflects the current date even when the application is not running. In previous versions of Mac OS X, the icon would show 17 July in the icon any time the application was not running but the current date when the application was running. - iChatIChatiChat is an instant messaging software application developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its Mac OS X operating system. It has audio, video and screen-sharing capabilities as well as text messaging...
enhancements, including multiple logins, invisibility, animated icons, and tabbed chats, similar to features present in PidginPidgin (software)Pidgin is an open-source multi-platform instant messaging client, based on a library named libpurple. Libpurple has support for many commonly used instant messaging protocols, allowing the user to log into various services from one application.The number of Pidgin users was estimated to be over 3...
, AdiumAdiumAdium is a free and open source instant messaging client for Mac OS X that supports multiple IM networks, including Windows Live Messenger, Yahoo! Messenger, Google Talk, AIM, ICQ, and XMPP. It supports many protocols through the libraries libezv , MGTwitterEngine , and libpurple...
and the iChat plugin Chax; iChat TheaterIChatiChat is an instant messaging software application developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its Mac OS X operating system. It has audio, video and screen-sharing capabilities as well as text messaging...
, allowing users to incorporate images from iPhotoIPhotoiPhoto is a digital photograph manipulation software application developed by Apple Inc. and released with every Macintosh personal computer as part of the iLife suite of digital life management applications...
, presentations from KeynoteKeynote (software)Keynote is a presentation software application developed as a part of the iWork productivity suite by Apple Inc. Keynote 5 was announced on January 6, 2009, and is the most recent version for the Macintosh. It adds new themes, transitions and animations, and the ability to control the slideshow...
, videos from QuickTimeQuickTimeQuickTime is an extensible proprietary multimedia framework developed by Apple Inc., capable of handling various formats of digital video, picture, sound, panoramic images, and interactivity. The classic version of QuickTime is available for Windows XP and later, as well as Mac OS X Leopard and...
, and other Quick Look features into video chats; and Backdrops, which are similar to chroma keyChroma keyChroma key compositing is a technique for compositing two images together. A color range in the top layer is made transparent, revealing another image behind. The chroma keying technique is commonly used in video production and post-production...
s, but use a real-time difference matte technique which does not require a green or blue screen. iChat also implements screen sharing, a feature previously available with Apple Remote DesktopApple Remote DesktopApple Remote Desktop is a Macintosh application produced by Apple Inc., first released on March 14, 2002, that replaced a similar product called Apple Network Assistant...
. - MailMail (application)Mail is an email program included with Apple Inc.'s Mac OS X operating system. Originally developed by NeXT as NeXTMail, a part of their NeXTSTEP operating system, it was adapted, following Apple's acquisition of NeXT, to become OS X's Mail application.Mail uses the SMTP, POP3, and IMAP protocols,...
enhancements including the additions of RSS feedsRSS-Mathematics:* Root-sum-square, the square root of the sum of the squares of the elements of a data set* Residual sum of squares in statistics-Technology:* RSS , "Really Simple Syndication" or "Rich Site Summary", a family of web feed formats...
, Stationery, Notes, and to-dos. To-dos use a system-wide service that is available to all applications. - Network file sharing improvements include more granular control over permissions, consolidation of AFPApple Filing ProtocolThe Apple Filing Protocol is a network protocol that offers file services for Mac OS X and original Mac OS. In Mac OS X, AFP is one of several file services supported including Server Message Block , Network File System , File Transfer Protocol , and WebDAV...
, FTPFile Transfer ProtocolFile Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another host over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet. FTP is built on a client-server architecture and utilizes separate control and data connections between the client and server...
and SMBServer Message BlockIn computer networking, Server Message Block , also known as Common Internet File System operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used to provide shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an...
sharing into one control panel, and the ability to share individual folders, a feature that had not been available since Mac OS 9Mac OS 9Mac OS 9 is the final major release of Apple's Mac OS before the launch of Mac OS X. Introduced on October 23, 1999, Apple positioned it as "The Best Internet Operating System Ever," highlighting Sherlock 2's Internet search capabilities, integration with Apple's free online services known as...
. - Parental controlsParental controlsParental controls are features which may be included in digital television services, computer and video games, mobile phones and computer software...
now include the ability to place restrictions on use of the Internet and to set parental controls from anywhere using remote setup. - Photo BoothPhoto BoothPhoto Booth is a small software application for taking photos and videos with an iSight camera by Apple Inc. for Mac OS X and iOS .-Photo Booth:...
enhancements, including video recording with real-time filters and blue/green-screen technology. - Podcast CapturePodcast CapturePodcast Capture was introduced with Mac OS X 10.5 , and allows users to record and distribute podcasts. The software requires a connection to a computer running Mac OS X Server with Podcast Producer....
, an application allowing users to record and distribute podcasts. It requires access to a computer running Mac OS X ServerMac OS X ServerMac OS X Server is a Unix server operating system from Apple Inc. The server edition of Mac OS X is architecturally identical to its desktop counterpart, except that it includes work group management and administration software tools...
with Podcast ProducerPodcast ProducerPodcast Producer is a component of Mac OS X Server v10.5 and v10.6 which can assist in the creation and distribution of Podcasts. Podcast Producer requires an Intel processor, 1GB + 512MB per processor core of RAM, and a Quartz Extreme capable video chipset....
. - PreviewPreview (software)Preview is Mac OS X's application for displaying images and Portable Document Format documents. Like Mac OS X itself, it comes from NeXT's OPENSTEP operating system....
adds support for annotation, graphics, extraction, search, markup, Instant Alpha and size adjustment tools. - Quick LookQuick LookQuick Look is a quick preview feature developed by Apple which was introduced in their operating system, Mac OS X v10.5 "Leopard". It was announced and demonstrated at Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference 2007.-Overview:...
, a framework allowing documents to be viewed without opening them in an external application and can preview it in full screen. Plug-ins are available for Quick LookQuick LookQuick Look is a quick preview feature developed by Apple which was introduced in their operating system, Mac OS X v10.5 "Leopard". It was announced and demonstrated at Apple's Worldwide Developers Conference 2007.-Overview:...
so that you can also view other files, such as Installer Packages.
- SafariSafari (web browser)Safari is a web browser developed by Apple Inc. and included with the Mac OS X and iOS operating systems. First released as a public beta on January 7, 2003 on the company's Mac OS X operating system, it became Apple's default browser beginning with Mac OS X v10.3 "Panther". Safari is also the...
3, which includes Web Clip. - SpacesSpaces (software)Spaces was a virtual desktop feature of Mac OS X, introduced in version 10.5 "Leopard". It was announced by Steve Jobs during the opening keynote at the Worldwide Developers Conference on August 7, 2006...
, an implementation of virtual desktopVirtual desktopIn computing, a virtual desktop is a term used with respect to user interfaces, usually within the WIMP paradigm, to describe ways in which the size of a computer's desktop environment is expanded beyond the physical limits of the screen's real estate through the use of software, This saves space...
s (individually called "Spaces"), allows multiple desktops per user, with certain applications and windows in each desktop. Users can organize certain Spaces for certain applications (e.g., one for work-related tasks and one for entertainment) and switch between them. ExposéExposé (Mac OS X)Exposé is a feature of the Mac OS X operating system. First previewed on 23 June 2003 at the Apple Worldwide Developers Conference as a feature of the then forthcoming Mac OS X v10.3, Exposé allows a user to quickly locate an open window, or to hide all windows and show the desktop without the need...
works inside Spaces, allowing the user to see at a glance all desktops on one screen.) Users can create and control up to 16 spaces, and applications can be switched between each one, creating a very large workspace. The auto-switching feature in SpacesSpaces (software)Spaces was a virtual desktop feature of Mac OS X, introduced in version 10.5 "Leopard". It was announced by Steve Jobs during the opening keynote at the Worldwide Developers Conference on August 7, 2006...
has annoyed some of its users. Apple added a new preference in 10.5.2 which disabled this feature, but there were still bugs found while switching windows. In 10.5.3, this problem was addressed and was no longer an issue. - SpotlightSpotlight (software)Spotlight is a system-wide desktop search feature of Apple's Mac OS X operating system. Spotlight is a selection-based search system, which creates a virtual index of all items and files on the system. It is designed to allow the user to quickly locate a wide variety of items on the computer,...
incorporates additional search capabilities such as Boolean operators, as well as the ability to search other computers (with permissions). - Time MachineTime Machine (Apple software)Time Machine is a backup utility developed by Apple. It is included with Mac OS X and was introduced with the 10.5 "Leopard" release of Mac OS X. The software is designed to work with the Time Capsule as well as other internal or external drives.-Overview:...
, an automated backup utility which allows the user to restore files that have been deleted or replaced by another version of a file. Though generally lauded in the press as a step forward for data recovery, Time Machine has been criticized in multiple publications for lacking the capabilities of third-party backup software. Analyzing the feature for TidBITSTidBITSTidBITS is an influential electronic newsletter and web site dealing primarily with Apple Computer and Macintosh-related topics.-Internet publication:...
, Joe Kissell pointed out that Time Machine does not create bootable copies of backed-up volumes, does not back up to AirPort Disk hard drives and will not back up FileVault encrypted home directories until the user logs out, concluding that the feature is "pretty good at what it does" but he will only use it as part of a "broader backup strategy". One of these issues has been resolved, however; On 19 March 2008, updates were released for AirPort and Time Machine, allowing for Time Machine to use a USB hard disk which has been connected to an AirPort Extreme Base Station. - Universal AccessUniversal AccessApple Universal Access is a component of the Mac OS X operating system that provides computing abilities to the blind, deaf, and handicapped.- Components :Universal Access is a preference pane of the System Preferences application...
enhancements: significant improvements to applications including VoiceOverVoiceOverVoiceOver is a screen reader built into Apple Inc.'s Mac OS X, iOS and iPod operating systems. By using VoiceOver, the user can access their Macintosh or iOS device based on spoken descriptions and, in the case of the Mac, the keyboard. The feature is designed to increase accessibility for blind...
, along with increased support for BrailleBrailleThe Braille system is a method that is widely used by blind people to read and write, and was the first digital form of writing.Braille was devised in 1825 by Louis Braille, a blind Frenchman. Each Braille character, or cell, is made up of six dot positions, arranged in a rectangle containing two...
, closed captioningClosed captioningClosed captioning is the process of displaying text on a television, video screen or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information to individuals who wish to access it...
and a new high‐quality Speech synthesis voice. - Many changes to the user interfaceUser interfaceThe user interface, in the industrial design field of human–machine interaction, is the space where interaction between humans and machines occurs. The goal of interaction between a human and a machine at the user interface is effective operation and control of the machine, and feedback from the...
, such as a transparent menu bar, new icons, and a 3D Dock. As well as this, the Apple icon is now black instead of blue. R.L. Prior, on the ThinkMac blog, criticized a number of changes to Leopard's user interface, including the transparent menu bar and the new folder icons. Decreased transparency of the menu bar, along with the ability to disable the menu bar transparency were added with the 10.5.2 release on 11 February 2008. - Russian language support, bringing the total to 18 languages.
- Leopard removes support for ClassicClassic (Mac OS X)Classic, or Classic Environment, was a hardware and software abstraction layer in Mac OS X that allowed applications compatible with Mac OS 9 to run on the Mac OS X operating system...
applications.
Developer technologies
- Native support by many libraries and frameworks for 64-bit64-bit64-bit is a word size that defines certain classes of computer architecture, buses, memory and CPUs, and by extension the software that runs on them. 64-bit CPUs have existed in supercomputers since the 1970s and in RISC-based workstations and servers since the early 1990s...
applications, allowing 64-bit CocoaCocoa (API)Cocoa is Apple's native object-oriented application programming interface for the Mac OS X operating system and—along with the Cocoa Touch extension for gesture recognition and animation—for applications for the iOS operating system, used on Apple devices such as the iPhone, the iPod Touch, and...
applications. Existing 32-bit32-bitThe range of integer values that can be stored in 32 bits is 0 through 4,294,967,295. Hence, a processor with 32-bit memory addresses can directly access 4 GB of byte-addressable memory....
applications using those libraries and frameworks should continue to run without the need for emulationEmulatorIn computing, an emulator is hardware or software or both that duplicates the functions of a first computer system in a different second computer system, so that the behavior of the second system closely resembles the behavior of the first system...
or translation. - Leopard offers the Objective-CObjective-CObjective-C is a reflective, object-oriented programming language that adds Smalltalk-style messaging to the C programming language.Today, it is used primarily on Apple's Mac OS X and iOS: two environments derived from the OpenStep standard, though not compliant with it...
2.0 runtime, which includes new features such as garbage collectionGarbage collection (computer science)In computer science, garbage collection is a form of automatic memory management. The garbage collector, or just collector, attempts to reclaim garbage, or memory occupied by objects that are no longer in use by the program...
. XcodeXcodeXcode is a suite of tools, developed by Apple, for developing software for Mac OS X and iOS. Xcode 4.2, the latest major version, is available on the Mac App Store for free for Mac OS X 10.7 , and on the Apple Developer Connection website for free to registered developers Xcode is a suite of tools,...
3.0 supports the updated language and was itself rewritten with it. - A new framework, Core AnimationCore AnimationCore Animation is a data visualization API used by Mac OS X 10.5 and later as well as iOS to produce animated user interfaces.-Overview:Core Animation provides a way for developers to produce animated user interfaces via an implicit animation model as well as an "explicit" model...
, allows a developer to create complex animations while specifying only a "start" and a "goal" space. The main goal of Core Animation is to enable the creation of complex animations with small amounts of program code. - Apple integrates DTraceDTraceDTrace is a comprehensive dynamic tracing framework created by Sun Microsystems for troubleshooting kernel and application problems on production systems in real time...
from the OpenSolarisOpenSolarisOpenSolaris was an open source computer operating system based on Solaris created by Sun Microsystems. It was also the name of the project initiated by Sun to build a developer and user community around the software...
project and adds a graphical interface called InstrumentsInstruments (application)Instruments is an application performance analyzer and visualizer, integrated in Xcode 3.0 and later versions of Xcode. It is a developer tool included in Apple Mac OS X v10.5 and later versions of Mac OS X, built on top of the DTrace tracing framework from OpenSolaris and ported to Mac OS...
(previously Xray). DTrace provides tools that users, administrators and developers can use to tune the performance of the operating system and the applications that run on it. - The new Scripting Bridge allows programmers to use PythonPython (programming language)Python is a general-purpose, high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Python claims to "[combine] remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive...
and RubyRuby (programming language)Ruby is a dynamic, reflective, general-purpose object-oriented programming language that combines syntax inspired by Perl with Smalltalk-like features. Ruby originated in Japan during the mid-1990s and was first developed and designed by Yukihiro "Matz" Matsumoto...
to interface with the Cocoa frameworks. - Ruby on RailsRuby on RailsRuby on Rails, often shortened to Rails or RoR, is an open source web application framework for the Ruby programming language.-History:...
is included in the default install. - Leopard’s OpenGLOpenGLOpenGL is a standard specification defining a cross-language, cross-platform API for writing applications that produce 2D and 3D computer graphics. The interface consists of over 250 different function calls which can be used to draw complex three-dimensional scenes from simple primitives. OpenGL...
stack has been updated to version 2.1, and uses LLVMLow Level Virtual MachineThe Low Level Virtual Machine is a compiler infrastructure written in C++ that is designed for compile-time, link-time, run-time, and "idle-time" optimization of programs written in arbitrary programming languages...
to increase its vertex processing speed. Apple has been working to get LLVM integrated into GCCGNU Compiler CollectionThe GNU Compiler Collection is a compiler system produced by the GNU Project supporting various programming languages. GCC is a key component of the GNU toolchain...
; LLVM’s use within other operating system facilities has not been announced. - The Graphics and Media State of the Union address confirmed many other features are possible because of Core Animation, such as live desktops, improvements to Quartz ComposerQuartz ComposerQuartz Composer is a node-based visual programming language provided as part of the Xcode development environment in Mac OS X for processing and rendering graphical data....
with custom patches, a new PDF Kit for developers, and improvements to QuickTimeQuickTimeQuickTime is an extensible proprietary multimedia framework developed by Apple Inc., capable of handling various formats of digital video, picture, sound, panoramic images, and interactivity. The classic version of QuickTime is available for Windows XP and later, as well as Mac OS X Leopard and...
APIs. - The
FSEventsframework allows applications to register for notifications of changes to a given directory tree.FSEventsThe FSEvents API in Mac OS X allows applications to register for notifications of changes to a given directory tree. Whenever the filesystem is changed, the kernel passes notifications via the special device file /dev/fsevents to a userspace process called fseventsd... - Leopard includes a read-only implementation of the ZFSZFSIn computing, ZFS is a combined file system and logical volume manager designed by Sun Microsystems. The features of ZFS include data integrity verification against data corruption modes , support for high storage capacities, integration of the concepts of filesystem and volume management,...
file system.
-
- In mid-December 2006 a pre-release version of Leopard appeared to include support for Sun’s ZFS. Jonathan SchwartzJonathan I. SchwartzJonathan Ian Schwartz is the co-founder and Chief Executive Officer of Picture of Health. He was formerly the President and CEO of Sun Microsystems prior to its acquisition by Oracle, and previously the founder and Chief Executive Officer of Lighthouse Design, Ltd., a software company focused on...
, CEO and President of Sun MicrosystemsSun MicrosystemsSun Microsystems, Inc. was a company that sold :computers, computer components, :computer software, and :information technology services. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982...
, boasted on 6 June 2007 that ZFS has become "the file system" for Leopard. However, the senior project marketing director for Mac OS X stated on 11 June 2007 that the existing HFS+HFS PlusHFS Plus or HFS+ is a file system developed by Apple Inc. to replace their Hierarchical File System as the primary file system used in Macintosh computers . It is also one of the formats used by the iPod digital music player...
, not ZFS, will be used in Leopard. Apple later clarified that a read-only version of ZFS would be included.- Leopard includes drivers for UDFUniversal Disk FormatUniversal Disk Format is an implementation of the specification known as ISO/IEC 13346 and ECMA-167 and is an open vendor-neutral file system for computer data storage for a broad range of media. In practice, it has been most widely used for DVDs and newer optical disc formats, supplanting ISO 9660...
2.5, necessary for reading HD DVDHD DVDHD DVD is a discontinued high-density optical disc format for storing data and high-definition video.Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format...
and Blu-rayBlu-ray DiscBlu-ray Disc is an optical disc storage medium designed to supersede the DVD format. The plastic disc is 120 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick, the same size as DVDs and CDs. Blu-ray Discs contain 25 GB per layer, with dual layer discs being the norm for feature-length video discs...
discs using third-party drives, but the included DVD Player software can only play HD DVDs authored by DVD Studio ProDVD Studio ProDVD Studio Pro was a high-end software tool published by Apple Inc. to allow users to create DVD masters to be sent out for replication at production houses. Its tight integration with other Apple applications allows users to take Final Cut Pro and Motion projects and render them into the DVD...
. - Leopard includes a framework implementing latent semantic mappingLatent semantic mappingLatent semantic mapping is a data-driven framework to model globally meaningful relationships implicit in large volumes of data. It is a generalization of latent semantic analysis...
for classifying (e.g. textual) data. - Leopard is the first operating system with open source BSD code to be certified as fully UNIXUnixUnix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
compliant. Certification means that software following the Single UNIX SpecificationSingle UNIX SpecificationThe Single UNIX Specification is the collective name of a family of standards for computer operating systems to qualify for the name "Unix"...
can be compiled and run on Leopard without the need for any code modification. The certification only applies to Leopard when run on Intel processors. - Leopard includes J2SE 5.0.
- Leopard includes drivers for UDF
- In mid-December 2006 a pre-release version of Leopard appeared to include support for Sun’s ZFS. Jonathan Schwartz
Security enhancements
New security features intend to provide better internal resiliency to successful attacks, in addition to preventing attacks from being successful in the first place.Library Randomization: Leopard implements library randomization
Address space layout randomization
Address space layout randomization is a computer security method which involves randomly arranging the positions of key data areas, usually including the base of the executable and position of libraries, heap, and stack, in a process's address space.- Benefits :Address space randomization hinders...
, which randomizes the locations of some libraries in memory. Vulnerabilities that corrupt program memory often rely on known addresses for these library routines, which allow injected code to launch processes or change files. Library randomization is presumably a stepping-stone to a more complete implementation of address space layout randomization at a later date.
Application Layer Firewall
- Leopard ships with two firewall engines: the original BSD IPFWIpfirewallipfirewall or ipfw is a FreeBSD IP packet filter and traffic accounting facility. Its ruleset logic is similar to many other packet filters except IPFilter. ipfw is authored and maintained by FreeBSD volunteer staff members. Its syntax enables use of sophisticated filtering capabilities and thus...
, which was present in earlier releases of Mac OS X, and the new Leopard Application Layer Firewall. Unlike IPFW, which intercepts and filters IP datagrams before the kernel performs significant processing, the Application Layer Firewall operates at the socket layer, bound to individual processes. The Application Layer Firewall can therefore make filtering decisions on a per-application basis. Of the two-firewall engines, only the Application Layer Firewall is fully exposed in the Leopard user interface. The new firewall offers less control over individual packet decisions (users can decide to allow or deny connections system wide or to individual applications, but must use IPFW to set fine-grained TCP/IP header level policies). It also makes several policy exceptions for system processes: neither mDNSResponder nor programs running with superuserSuperuserOn many computer operating systems, the superuser is a special user account used for system administration. Depending on the operating system, the actual name of this account might be: root, administrator or supervisor....
privileges are filtered.
Sandboxes: Leopard includes kernel-level support for role-based access control (RBAC). RBAC is intended to prevent, for example, an application like Mail from editing the password database.
Application Signing: Leopard provides a framework to use public key signatures
Public-key cryptography
Public-key cryptography refers to a cryptographic system requiring two separate keys, one to lock or encrypt the plaintext, and one to unlock or decrypt the cyphertext. Neither key will do both functions. One of these keys is published or public and the other is kept private...
for code signing
Code signing
Code signing is the process of digitally signing executables and scripts to confirm the software author and guarantee that the code has not been altered or corrupted since it was signed by use of a cryptographic hash....
to verify, in some circumstances, that code has not been tampered with. Signatures can also be used to ensure that one program replacing another is truly an "update", and carry any special security privileges across to the new version. This reduces the number of user security prompts, and the likelihood of the user being trained to simply clicking "OK" to everything.
Secure Guest Account: Guests can be given access to a Leopard system with an account that the system erases and resets at logout.
Security features in Leopard have been criticized as weak or ineffective, with the publisher Heise Security
Heinz Heise
Heinz Heise is a publishing house based in Germany.- History :Heise was created in Hanover in 1949 as an address and telephone directory publisher, then later expanded to include magazines and loose leaf collections. In 2001, the company was divided into separate enterprises, all of which came...
documenting that the Leopard installer downgraded firewall protection and exposed services to attack even when the firewall was re-enabled. Several researchers noted that the Library Randomization feature added to Leopard was ineffective compared to mature implementations on other platforms, and that the new "secure Guest account" could be abused by Guests to retain access to the system even after the Leopard log out process erased their home directory.
System requirements
Apple states the following basic Leopard system requirements, although, for some specific applications and actions (such as iChat backdrops) an Intel processor is required:- Processor must be any Intel, PowerPC G5PowerPC 970The PowerPC 970, PowerPC 970FX, PowerPC 970GX, and PowerPC 970MP, are 64-bit Power Architecture processors from IBM introduced in 2002. When used in Apple Inc. machines, they were dubbed the PowerPC G5....
or G4PowerPC G4PowerPC G4 is a designation used by Apple Computer to describe a fourth generation of 32-bit PowerPC microprocessors. Apple has applied this name to various processor models from Freescale, a former part of Motorola....
(867 MHz and faster) - DVD drive (for installation of the operating system)
- At least 512 MB of RAM (additional RAM (1 GB) is recommended for development purposes)
- At least 9 GB of disk space available.
Leopard’s retail version was not released in separate versions for each type of processor, but instead consisted of one universal release
Universal binary
A universal binary is, in Apple parlance, an executable file or application bundle that runs natively on either PowerPC or Intel-manufactured IA-32 or Intel 64-based Macintosh computers; it is an implementation of the concept more generally known as a fat binary.With the release of Mac OS X Snow...
that could run on both PowerPC and Intel processors. However, the install discs that ship with Intel-based Macs only contain Intel binaries.
Processor type and speed are checked during installation and installation halted if insufficient; however, Leopard will run on slower G4 processor machines (e.g., a 733mhz Quicksilver) if the installation is performed on a supported Mac and its hard-drive then moved to a slower/unsupported one (the drive may either be an internal mechanism or a Firewire
IEEE 1394 interface
The IEEE 1394 interface is a serial bus interface standard for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer, frequently used by personal computers, as well as in digital audio, digital video, automotive, and aeronautics applications. The interface is also known by the brand...
external).
Supported machines
Leopard can run on the later flat panel iMac G4s, the first iMac G5, second iMac G5 (with the ambient light sensor), third iMac G5 (with iSight), iMac Intel Core Duo and (present day) iMac Intel Core 2 Duo, PowerBook G4, Power Mac G4, Power Mac G5, iBook G4, MacBook, MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, Mac Pro, Mac Mini, Xserve, Xserve G5, Xserve RAID, Macintosh Server G4, and later eMac models. Leopard can run on older hardware as long as they have a G4 upgrade installed running at the 867 MHz or faster, have at least 9 GB free of hard drive space, 512 MB RAM and have a DVD drive. Leopard however will not run on the 900 MHz iBook G3 models even though they exceed the minimum 867 MHz requirement. This is due to the lack of AltiVec in the G3 line of processors and the fact that most pre-G4 and early G4 systems do not have video hardware capable of supporting Core Image, two technologies Leopard relies upon heavily, among others. Leopard can be "hacked" (see below) to install on these G3 and pre-867 MHz G4 machines but the system may behave erratically and many of the programs, features, and functions may not work properly or at all. As of Mid 2010, some Apple computers have firmware factory installed which will no longer allow installation of Mac OS X Leopard. These computers only allow installation and running of Mac OS X Snow Leopard.Usage on unsupported hardware
Some ways of running Leopard on certain unsupported hardware, primarily PowerPC G4 computers with CPU speeds lower than the official requirement of 867 MHz, have been discovered. A common way is use of the program LeopardAssist, which is a bootloader similar in some respects to XPostFactoXPostFacto
XPostFacto is an open source utility that enables the installation of PowerPC versions of Mac OS X up to Mac OS 10.4 , and Darwin on some PowerPC-based Apple Macintosh systems that are not officially supported for them by Apple....
(used for installing earlier releases of Mac OS X on unsupported G3 and pre-G3 Macs) that uses the Mac’s Open Firmware to tell Leopard that the machine does have a CPU meeting the 867 MHz minimum requirement that the Installer checks for before installation is allowed to commence, when in reality the CPU is slower. Currently, LeopardAssist only runs on slower G4s and many people have installed Leopard successfully on these older machines.
Users who have access to supported hardware have installed Leopard on the supported machine then simply moved the hard drive to the unsupported machine. Alternatively, the Leopard Installation DVD was booted on a supported Mac, then installed on an unsupported Mac via Firewire Target Disk Mode. Leopard is only compiled for AltiVec-enabled PowerPC processors (G4 and G5) though, as well as Intel, so both of these methods will only work on Macs with G4 or later CPUs. While some of the earlier beta releases were made to run on some later G3 machines (mostly later 800–900 MHz iBooks), no success with the retail version has been officially reported on G3 Macs except for some later iMacs and "Pismo" PowerBook G3s with G4 processor upgrades installed.
For a number of months after Leopard's release it appeared that the only G3 Macs on which Leopard could be run were those with both an aftermarket G4 processor and an AGP graphics card, as failures with the OS partially booting before crashing were reported on older Macs such as the original tray-loading iMacs and the Beige and Blue & White Power Mac G3 (all with G4 upgrades as Leopard will not even begin to load without one) whereas it would boot fine on newer Macs where the Installer restriction had been circumvented. However, more recently it has been reported that with some more work and use of kernel extensions from XPostFacto, Tiger and beta builds of Leopard, the OS can be made to run on G4-upgraded Macs as old as the Power Macintosh 9500
Power Macintosh 9500
The Power Macintosh 9500 was a high-end Macintosh personal computer which was designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer from May 1995 until early 1997. It was powered by a PowerPC 604 processor, a second-generation PowerPC chip which was faster than the earlier PowerPC 601 chip...
, despite the lack of AGP-based graphics. While Leopard can be run on any Mac with a G4 or later processor, some functionality such as Front Row or Time Machine fails to work without a Quartz Extreme-capable graphics card, which many of the earlier G4s did not include in their factory specification.
Since Apple moved to using Intel processors in their computers, the OSx86
OSx86
OSx86 is a collaborative hacking project to run the Mac OS X computer operating system on non-Apple personal computers with x86 architecture and x86-64 compatible processors...
project has developed and now also allows Mac OS X Tiger, Leopard, and Snow Leopard to be installed and run successfully on non-Apple x86-based computers, albeit in violation of Apple's licensing agreement for OS X. A variety of installation processes can be used, the most common being to use modified Darwin bootloaders commonly known as "Boot 132" designed to trick the retail, or vanilla
Vanilla software
Vanilla software is computer software that is not customized from its delivered form - i.e. it is used without any customizations applied to it...
, operating system into thinking that it is running on an EFI
Extensible Firmware Interface
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware...
-based Mac
Macintosh
The Macintosh , or Mac, is a series of several lines of personal computers designed, developed, and marketed by Apple Inc. The first Macintosh was introduced by Apple's then-chairman Steve Jobs on January 24, 1984; it was the first commercially successful personal computer to feature a mouse and a...
. This method of installation allows the use of an unmodified Apple installation DVD and the updating of the operating system from the built-in Software Update utility, but will work only on Intel Core-based PCs, unless a modified kernel is added to the pre-boot CD. Modified installation DVDs are also available illegally which offer a more outdated approach to installing.
Packaging
The retail packaging for Leopard is significantly smaller than that of previous versions of Mac OS X (although later copies of Tiger also came in the new smaller box). It also sports a lenticularLenticular printing
Lenticular printing is a technology in which a lenticular lens is used to produce images with an illusion of depth, or the ability to change or move as the image is viewed from different angles...
cover, making the X appear to float above a purple galaxy, somewhat resembling the default Leopard desktop wallpaper.
Release history
| Version | Build | Date | OS name Uname uname is a software program in Unix and Unix-like computer operating systems that prints the name, version and other details about the current machine and the operating system running on it... |
Notes | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.5 | 9A581 | October 26, 2007 | Darwin Darwin (operating system) Darwin is an open source POSIX-compliant computer operating system released by Apple Inc. in 2000. It is composed of code developed by Apple, as well as code derived from NeXTSTEP, BSD, and other free software projects.... 9.0 |
Original retail DVD release | |
| 10.5.1 | 9B18 | November 15, 2007 | Darwin 9.1 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.1 Update; Second retail DVD release | Mac OS X 10.5.1 Update |
| 10.5.2 | 9C31, 9C7010 | February 11, 2008 | Darwin 9.2 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.2 Update | Mac OS X 10.5.2 Combo Update |
| 10.5.3 | 9D34 | May 28, 2008 | Darwin 9.3 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.3 Update | Mac OS X 10.5.3 Update |
| 10.5.4 | 9E17 | June 30, 2008 | Darwin 9.4 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.4 update; Third retail DVD release | Mac OS X 10.5.4 Update |
| 10.5.5 | 9F33 | September 15, 2008 | Darwin 9.5 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.5 Update | Mac OS X 10.5.5 Update |
| 10.5.6 | 9G55 | December 15, 2008 | Darwin 9.6 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.6 Update | Mac OS X 10.5.6 Update |
| 9G66 | January 6, 2009 | Fourth retail DVD release (part of Mac Box Set) | |||
| 10.5.7 | 9J61 | May 12, 2009 | Darwin 9.7 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.7 Update | Mac OS X 10.5.7 Update |
| 10.5.8 | 9L30 | August 5, 2009 | Darwin 9.8 | About the Mac OS X 10.5.8 Update | Mac OS X 10.5.8 Update |
Compatibility
After Leopard’s release, there were widely-reported incidents of new Leopard installs hanging during boot on the blue screen that appears just before the login process starts. Apple attributed these problems to an outdated version of an unsupported add-on extension called Application EnhancerApplication Enhancer
Application Enhancer is a software program released by Unsanity for Apple's Mac OS X operating system. Application Enhancer provides a framework that allows third-party developers to write "haxies" for OS X. It also provides a daemon to load haxies when certain applications are launched. These...
(APE), from Unsanity
Unsanity
Unsanity is a Mac OS X shareware software developer founded in May 2000, notable for coining the term "haxie".Their most popular software includes ShapeShifter and WindowShade, utilising their freeware Application Enhancer module...
which is incompatible with Leopard; many users do not know, APE had been installed silently on many Macs by Logitech as part of their mouse drivers. However, only the users who did not have the latest version of APE installed (2.0.3 at that time) were affected. Apple published a knowledge base article on how to solve this problem.
External links
- 2006 WWDC keynote presentation at Apple.com
- 2007 WWDC keynote presentation at Apple.com
- Mac OS X Leopard review at Ars TechnicaArs TechnicaArs Technica is a technology news and information website created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, science, technology policy, and video games. Ars Technica is known for its features, long articles that go...

