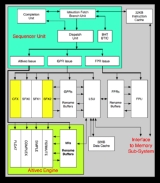
PowerPC G4
Encyclopedia
PowerPC G4 is a designation used by Apple Computer
to describe a fourth generation of 32-bit PowerPC
microprocessor
s. Apple has applied this name to various (though closely related) processor models from Freescale
, a former part of Motorola
.
Macintosh computers such as the PowerBook G4
and iBook G4
laptops and the Power Mac G4
and Power Mac G4 Cube
desktops all took their name from the processor. A PowerPC G4 was also used in the eMac
, first-generation Xserve
s, first-generation Mac Mini
s, and the flat-panel iMac before the introduction of the PowerPC 970
.
Apple completely phased out the G4 series for desktop models after it selected the 64-bit IBM-produced PowerPC 970 processor as the basis for its PowerPC G5 series. The last desktop model that used the G4 was the Mac Mini which now comes with an Intel processor. The last portable to use the G4 was the iBook
G4 but was replaced by the Intel-based MacBook
. The PowerBook G4 has been replaced by the Intel-based MacBook Pro
.
The PowerPC G4 processors are also popular in other computer systems, such as Amiga
clones, like the Pegasos
from Genesi
. Besides desktop computers the PowerPC G4 is popular in embedded environments, like routers, telecom switches, imaging, media processing, avionics and military applications, where one can take advantage of the AltiVec
and its SMP
capabilities.
measures 83 mm² and features copper interconnects
.
Motorola had promised Apple to deliver parts with speed up to 500 MHz, but yields proved too low initially. This forced Apple to take back the advertised 500 MHz models of PowerMac G4. The Power Mac series was downgraded abruptly from 400, 450, and 500 MHz processor speeds to 350, 400, and 450 MHz while problems with the chip were ironed out. The incident generated a rift in the Apple-Motorola relationship, and reportedly caused Apple to ask IBM for assistance to get the production yields up on the Motorola 7400 series line. The 500 MHz model was reintroduced on February 16, 2000.
and IBM
. IBM, the third member of the AIM alliance
, did design the chip together with Motorola in its Somerset design center, but chose not to manufacture it, because it did not see the need back then for the Vector Processing Unit. Ultimately, the G4 architecture design contained a 128-bit vector processing unit labelled AltiVec
by Motorola while Apple marketing referred to it as the "Velocity Engine".
The PowerPC 970
(G5) was the first IBM-manufactured CPU to implement VMX/AltiVec
, for which IBM reused the old 7400 design they still had from the design they did with Motorola in Somerset. The Xenon
CPU in the Xbox 360
also features VMX, with added proprietary extensions made especially for Microsoft. POWER6
, introduced in 2007, is IBMs first "big iron
" CPU to also implement VMX.
With the AltiVec unit, the 7400 microprocessor can do four-way single precision (32-bit) floating point math, or 16-way 8-bit, 8-way 16-bit or four-way 32-bit integer math in a single cycle. Furthermore, the vector processing unit is superscalar
, and can do two vector operations at the same time. Compared to Intel's x86 microprocessors at the time, this feature offered a substantial performance boost to applications designed to take advantage of the AltiVec unit. Some examples are Adobe Photoshop which utilises the AltiVec unit for faster rendering of effects and transitions, and Apple's iLife
suite which takes advantage of the unit for importing and converting files on the fly.
Additionally, the 7400 has enhanced support for symmetric multiprocessing
(SMP) thanks to an improved cache coherency protocol (MERSI
) and a 64-bit floating point unit
(FPU), derived in part from the 604 series. The 603 series had a 32-bit FPU, which took two clock cycles to accomplish 64-bit floating point
arithmetic.
The PowerPC G4 family supports two bus technologies, the older 60x bus which it shares with the PowerPC 600
and PowerPC 7xx families, and the more advanced MPX bus. Devices that utilize the 60x bus can be made compatible with either 6xx or 7xx processors, enabling a wide variety of offerings and a clear and cheap upgrade path while keeping compatibility issues at a minimum. There are primarily two companies manufacturing system controllers for 7xx and 7xxx computers, Tundra
with their Tsi1xx controllers and Marvell
with their Discovery controllers.
on 9 January 2001.
The chip added the ability to use all or half of its cache as high-speed, non-cached memory mapped to the processor's physical address space as desired. This feature was used by embedded system
s vendors such as Mercury Computer Systems
.

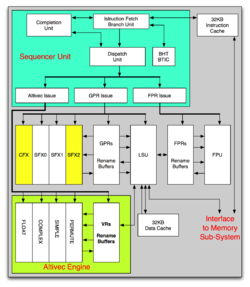 The PowerPC 7450 "Voyager"/"V'ger" was the only major redesign of the G4 processor. The 33-million transistor chip added one extra pipeline stage to the 7400's six-stage pipeline to increase clock rates, 256 KB on-chip L2 cache, and introduced an external L3 cache (up to 2 MB). The AltiVec unit was improved with the 7450; instead of dispatching one permute instruction and one VALU instruction per cycle like its predecessors, the 7450 and its Motorola/Freescale-followers can dispatch two arbitrary AltiVec instructions simultaneously. It was introduced with the 733 MHz Power Mac G4
The PowerPC 7450 "Voyager"/"V'ger" was the only major redesign of the G4 processor. The 33-million transistor chip added one extra pipeline stage to the 7400's six-stage pipeline to increase clock rates, 256 KB on-chip L2 cache, and introduced an external L3 cache (up to 2 MB). The AltiVec unit was improved with the 7450; instead of dispatching one permute instruction and one VALU instruction per cycle like its predecessors, the 7450 and its Motorola/Freescale-followers can dispatch two arbitrary AltiVec instructions simultaneously. It was introduced with the 733 MHz Power Mac G4
on 9 January 2001. Motorola followed with an interim release, the 7451, codenamed "Apollo 6", just like the 7455.
The enhancements to the 745x design gave it the nicknames G4e or G4+ but these were never official designations.
or 180 Nanometers HiPerMOS process with copper interconnects and SOI
. It was the first processor in an Apple computer to pass the 1 GHz mark.
The 7445 is the same chip without the L3 cache interface.
The 7455 is used in the AmigaOne
XE G4, and the dual 1 GHz Power Mac G4 (Quicksilver 2002)
process with SOI, hence drawing less power. It has 58 million transistors. With the 7447A, which introduced an integrated thermal diode as well as DFS (dynamic frequency scaling
) Freescale was able to reach a slightly higher clock. The 7457 has an additional L3 cache interface. However, its frequency scaling stagnated when Apple chose to use the 7447 instead of the L3 cache-enabled 7455 they used before.
The only companies that offer the 7457 in the form of upgrades for the Power Mac G4
and Power Mac G4 Cube
are Giga Designs, Sonnet Technology, Daystar Technology (they use the 7457 only for iMac G4 upgrades) and PowerLogix. The Pegasos
computer platform from Genesi
also uses 7447 in its Pegasos-II/G4.
PowerPC 7448 users are:
devices, and introduced a new naming scheme, MPC86xx. The 7448 was to be the last pure G4 and it formed the base of the new e600 core with a seven-stage, three-issue pipeline, and a powerful branch prediction unit which handles up to sixteen instructions out-of-order. It has an enhanced AltiVec unit capable of limited out-of-order execution
and a 1 MB L2 cache.
Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs and markets consumer electronics, computer software, and personal computers. The company's best-known hardware products include the Macintosh line of computers, the iPod, the iPhone and the iPad...
to describe a fourth generation of 32-bit PowerPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
s. Apple has applied this name to various (though closely related) processor models from Freescale
Freescale Semiconductor
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. is a producer and designer of embedded hardware, with 17 billion semiconductor chips in use around the world. The company focuses on the automotive, consumer, industrial and networking markets with its product portfolio including microprocessors, microcontrollers,...
, a former part of Motorola
Motorola
Motorola, Inc. was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois, which was eventually divided into two independent public companies, Motorola Mobility and Motorola Solutions on January 4, 2011, after losing $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009...
.
Macintosh computers such as the PowerBook G4
PowerBook G4
The PowerBook G4 are a series of notebook computers that were manufactured, marketed, and sold by Apple, Inc. between 2001 and 2006 as part of its PowerBook line. It uses the PowerPC G4 processor, initially produced by Motorola and later by Freescale, after Motorola spun off its semiconductor...
and iBook G4
IBook
The iBook was a line of laptop computers sold by Apple Computer from 1999 to 2006. The line targeted the consumer and education markets, with lower specifications and prices than the PowerBook, Apple's higher-end line of laptop computers....
laptops and the Power Mac G4
Power Mac G4
The Power Mac G4 was a series of personal computers that was designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple between 1999 and 2004. They used the PowerPC G4 series of microprocessors. They were heralded by Apple to be the first personal supercomputers, reaching speeds of 4 to 20 Gigaflops...
and Power Mac G4 Cube
Power Mac G4 Cube
The Power Mac G4 Cube was a small form factor Macintosh personal computer from Apple Inc. It was sold from 2000 to 2001. Its cube shape is reminiscent of the NeXTcube from NeXT, acquired by Apple in 1996. The machine was designed by Apple industrial designer Jonathan Ive...
desktops all took their name from the processor. A PowerPC G4 was also used in the eMac
EMac
The eMac, short for education Mac, was a Macintosh desktop computer made by Apple Inc. It was originally aimed at the education market, but was later made available as a cheaper mass market alternative to Apple's second-generation LCD display iMac....
, first-generation Xserve
Xserve
Xserve was a line of rack unit computers designed by Apple Inc. for use as servers. When the Xserve was introduced in 2002, it was Apple's first designated server hardware design since the Apple Network Server in 1996...
s, first-generation Mac Mini
Mac Mini
The Mac Mini is a small form factor desktop computer manufactured by Apple Inc. Like earlier mini-ITX PC designs, it is uncommonly small for a desktop computer: 7.7 inches square and 1.4 inches tall. It weighs 2.7 pounds...
s, and the flat-panel iMac before the introduction of the PowerPC 970
PowerPC 970
The PowerPC 970, PowerPC 970FX, PowerPC 970GX, and PowerPC 970MP, are 64-bit Power Architecture processors from IBM introduced in 2002. When used in Apple Inc. machines, they were dubbed the PowerPC G5....
.
Apple completely phased out the G4 series for desktop models after it selected the 64-bit IBM-produced PowerPC 970 processor as the basis for its PowerPC G5 series. The last desktop model that used the G4 was the Mac Mini which now comes with an Intel processor. The last portable to use the G4 was the iBook
IBook
The iBook was a line of laptop computers sold by Apple Computer from 1999 to 2006. The line targeted the consumer and education markets, with lower specifications and prices than the PowerBook, Apple's higher-end line of laptop computers....
G4 but was replaced by the Intel-based MacBook
MacBook
The MacBook was a brand of Macintosh notebook computers built by Apple Inc. First introduced in May 2006, it replaced the iBook and 12-inch PowerBook series of notebooks as a part of the Apple–Intel transition. Positioned as the low end of the MacBook family, the Apple MacBook was aimed at the...
. The PowerBook G4 has been replaced by the Intel-based MacBook Pro
MacBook Pro
The MacBook Pro is a line of Macintosh portable computers introduced in January 2006 by Apple. It replaced the PowerBook G4 and was the second model, after the iMac, to be announced in the Apple–Intel transition...
.
The PowerPC G4 processors are also popular in other computer systems, such as Amiga
Amiga
The Amiga is a family of personal computers that was sold by Commodore in the 1980s and 1990s. The first model was launched in 1985 as a high-end home computer and became popular for its graphical, audio and multi-tasking abilities...
clones, like the Pegasos
Pegasos
Pegasos is a MicroATX motherboard powered by a PowerPC 750CXe or PowerPC 7447 microprocessor, featuring three PCI slots, one AGP slot, two Ethernet ports , USB, DDR, AC'97 sound, and FireWire...
from Genesi
Genesi
Genesi is computer company focused on building Power Architecture and ARM architecture computers. The organization is split into two units, Genesi USA, Inc. working out of Texas operating as the primary front-end for sales, customers and developers, and bplan GmbH based in Germany as the primary...
. Besides desktop computers the PowerPC G4 is popular in embedded environments, like routers, telecom switches, imaging, media processing, avionics and military applications, where one can take advantage of the AltiVec
AltiVec
AltiVec is a floating point and integer SIMD instruction set designed and owned by Apple, IBM and Freescale Semiconductor, formerly the Semiconductor Products Sector of Motorola, , and implemented on versions of the PowerPC including Motorola's G4, IBM's G5 and POWER6 processors, and P.A. Semi's...
and its SMP
Symmetric multiprocessing
In computing, symmetric multiprocessing involves a multiprocessor computer hardware architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single shared main memory and are controlled by a single OS instance. Most common multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture...
capabilities.
PowerPC 7400
The PowerPC 7400 (code-named "Max") debuted in August 1999 and was the first processor to carry the "G4" moniker. The chip operates at speeds ranging from 350 to 500 MHz and contains 10.5 million transistors, manufactured using Motorola's 0.20 μm HiPerMOS6 process. The dieDie (integrated circuit)
A die in the context of integrated circuits is a small block of semiconducting material, on which a given functional circuit is fabricated.Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer of electronic-grade silicon or other semiconductor through processes such as...
measures 83 mm² and features copper interconnects
Copper-based chips
Copper-based chips are semiconductor integrated circuits, usually microprocessors, which use copper for interconnections. Since copper is a better conductor than aluminium, chips using this technology can have smaller metal components, and use less energy to pass electricity through them...
.
Motorola had promised Apple to deliver parts with speed up to 500 MHz, but yields proved too low initially. This forced Apple to take back the advertised 500 MHz models of PowerMac G4. The Power Mac series was downgraded abruptly from 400, 450, and 500 MHz processor speeds to 350, 400, and 450 MHz while problems with the chip were ironed out. The incident generated a rift in the Apple-Motorola relationship, and reportedly caused Apple to ask IBM for assistance to get the production yields up on the Motorola 7400 series line. The 500 MHz model was reintroduced on February 16, 2000.
Design
Much of the 7400 design was done by Motorola in close co-operation with AppleApple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs and markets consumer electronics, computer software, and personal computers. The company's best-known hardware products include the Macintosh line of computers, the iPod, the iPhone and the iPad...
and IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
. IBM, the third member of the AIM alliance
AIM alliance
The AIM alliance was an alliance formed on October 2, 1991, between Apple Inc. , IBM, and Motorola to create a new computing standard based on the PowerPC architecture. The stated goal of the alliance was to challenge the dominant Wintel computing platform with a new computer design and a...
, did design the chip together with Motorola in its Somerset design center, but chose not to manufacture it, because it did not see the need back then for the Vector Processing Unit. Ultimately, the G4 architecture design contained a 128-bit vector processing unit labelled AltiVec
AltiVec
AltiVec is a floating point and integer SIMD instruction set designed and owned by Apple, IBM and Freescale Semiconductor, formerly the Semiconductor Products Sector of Motorola, , and implemented on versions of the PowerPC including Motorola's G4, IBM's G5 and POWER6 processors, and P.A. Semi's...
by Motorola while Apple marketing referred to it as the "Velocity Engine".
The PowerPC 970
PowerPC 970
The PowerPC 970, PowerPC 970FX, PowerPC 970GX, and PowerPC 970MP, are 64-bit Power Architecture processors from IBM introduced in 2002. When used in Apple Inc. machines, they were dubbed the PowerPC G5....
(G5) was the first IBM-manufactured CPU to implement VMX/AltiVec
AltiVec
AltiVec is a floating point and integer SIMD instruction set designed and owned by Apple, IBM and Freescale Semiconductor, formerly the Semiconductor Products Sector of Motorola, , and implemented on versions of the PowerPC including Motorola's G4, IBM's G5 and POWER6 processors, and P.A. Semi's...
, for which IBM reused the old 7400 design they still had from the design they did with Motorola in Somerset. The Xenon
Xenon (processor)
Xenon is a CPU that is used in the Xbox 360 game console. The processor, internally codenamed "Waternoose", which was named after Henry J. Waternoose III in Monsters Inc. by IBM and XCPU by Microsoft, is based on IBM's PowerPC instruction set architecture, consisting of three independent processor...
CPU in the Xbox 360
Xbox 360
The Xbox 360 is the second video game console produced by Microsoft and the successor to the Xbox. The Xbox 360 competes with Sony's PlayStation 3 and Nintendo's Wii as part of the seventh generation of video game consoles...
also features VMX, with added proprietary extensions made especially for Microsoft. POWER6
POWER6
The POWER6 is a microprocessor developed by IBM that implemented the Power ISA v.2.03. When it became available in systems in 2007, it succeeded the POWER5+ as IBM's flagship Power microprocessor...
, introduced in 2007, is IBMs first "big iron
Big iron
Big iron, as the hacker's dictionary the Jargon File defines it, "refers to large, expensive, ultra-fast computers. It is used generally for number crunching supercomputers such as Crays, but can include more conventional big commercial IBM mainframes"....
" CPU to also implement VMX.
With the AltiVec unit, the 7400 microprocessor can do four-way single precision (32-bit) floating point math, or 16-way 8-bit, 8-way 16-bit or four-way 32-bit integer math in a single cycle. Furthermore, the vector processing unit is superscalar
Superscalar
A superscalar CPU architecture implements a form of parallelism called instruction level parallelism within a single processor. It therefore allows faster CPU throughput than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate...
, and can do two vector operations at the same time. Compared to Intel's x86 microprocessors at the time, this feature offered a substantial performance boost to applications designed to take advantage of the AltiVec unit. Some examples are Adobe Photoshop which utilises the AltiVec unit for faster rendering of effects and transitions, and Apple's iLife
ILife
iLife is a suite of software applications developed by Apple for organizing, editing, and publishing photos, movies, and music. The suite comprises five applications: iPhoto, iMovie, iDVD, GarageBand, and iWeb, all of which run on the Mac OS X operating system....
suite which takes advantage of the unit for importing and converting files on the fly.
Additionally, the 7400 has enhanced support for symmetric multiprocessing
Symmetric multiprocessing
In computing, symmetric multiprocessing involves a multiprocessor computer hardware architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single shared main memory and are controlled by a single OS instance. Most common multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture...
(SMP) thanks to an improved cache coherency protocol (MERSI
MERSI protocol
The MERSI protocol is a cache coherency and memory coherence protocol used by the PowerPC G4. The protocol consists of five states, Modified , Exclusive , Read Only or Recent , Shared and Invalid . The M, E, S and I states are the same as in the MESI protocol...
) and a 64-bit floating point unit
Floating point unit
A floating-point unit is a part of a computer system specially designed to carry out operations on floating point numbers. Typical operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square root...
(FPU), derived in part from the 604 series. The 603 series had a 32-bit FPU, which took two clock cycles to accomplish 64-bit floating point
Floating point
In computing, floating point describes a method of representing real numbers in a way that can support a wide range of values. Numbers are, in general, represented approximately to a fixed number of significant digits and scaled using an exponent. The base for the scaling is normally 2, 10 or 16...
arithmetic.
The PowerPC G4 family supports two bus technologies, the older 60x bus which it shares with the PowerPC 600
PowerPC 600
The PowerPC 600 family was the first family of PowerPC processors built. They were designed at the Somerset facility in Austin, Texas, jointly funded and staffed by engineers from IBM and Motorola as a part of the AIM alliance. Somerset was opened in 1992 and its goal was to make the first PowerPC...
and PowerPC 7xx families, and the more advanced MPX bus. Devices that utilize the 60x bus can be made compatible with either 6xx or 7xx processors, enabling a wide variety of offerings and a clear and cheap upgrade path while keeping compatibility issues at a minimum. There are primarily two companies manufacturing system controllers for 7xx and 7xxx computers, Tundra
Tundra Semiconductor
Tundra Semiconductor Corporation supplies communications, computing and storage companies with System Interconnect products, intellectual property and design services backed by customer service and technical support...
with their Tsi1xx controllers and Marvell
Marvell Technology Group
Marvell is an American producer of storage, communications and consumer semiconductor products.Founded in 1995, Marvell Technology Group Ltd. has operations worldwide and approximately 5,700 employees. Marvell’s U.S. operating subsidiary is based in Santa Clara, California and Marvell has...
with their Discovery controllers.
PowerPC 7410
The PowerPC 7410 "Nitro" is a low-power version of the 7400 but it was manufactured at 180 nm instead of 200 nm. Like the 7400 it has 10.5 million transistors. It debuted in the PowerBook G4PowerBook G4
The PowerBook G4 are a series of notebook computers that were manufactured, marketed, and sold by Apple, Inc. between 2001 and 2006 as part of its PowerBook line. It uses the PowerPC G4 processor, initially produced by Motorola and later by Freescale, after Motorola spun off its semiconductor...
on 9 January 2001.
The chip added the ability to use all or half of its cache as high-speed, non-cached memory mapped to the processor's physical address space as desired. This feature was used by embedded system
Embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal...
s vendors such as Mercury Computer Systems
Mercury Computer Systems
Mercury Computer Systems, Inc. provides high-performance embedded, real-time digital signal and image processing solutions.Mercury designs and builds embedded multicomputers, which may be considered to be either loosely coupled NUMA computers or tightly coupled clusters. Despite being marketed as...
.
PowerPC 7450


Power Mac G4
The Power Mac G4 was a series of personal computers that was designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple between 1999 and 2004. They used the PowerPC G4 series of microprocessors. They were heralded by Apple to be the first personal supercomputers, reaching speeds of 4 to 20 Gigaflops...
on 9 January 2001. Motorola followed with an interim release, the 7451, codenamed "Apollo 6", just like the 7455.
The enhancements to the 745x design gave it the nicknames G4e or G4+ but these were never official designations.
PowerPC 7445 and 7455
The PowerPC 7455 "Apollo 6" was introduced in January 2002. It came with a wider, 256-bit on-chip cache path, and was fabricated in Motorola's 0.18 µm MicrometreMicrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
or 180 Nanometers HiPerMOS process with copper interconnects and SOI
Silicon on insulator
Silicon on insulator technology refers to the use of a layered silicon-insulator-silicon substrate in place of conventional silicon substrates in semiconductor manufacturing, especially microelectronics, to reduce parasitic device capacitance and thereby improving performance...
. It was the first processor in an Apple computer to pass the 1 GHz mark.
The 7445 is the same chip without the L3 cache interface.
The 7455 is used in the AmigaOne
AmigaOne
AmigaOne is a series of computers intended to run AmigaOS 4 developed by Hyperion Entertainment. Earlier models were produced by Eyetech, and were based on the Teron series of PowerPC POP mainboards...
XE G4, and the dual 1 GHz Power Mac G4 (Quicksilver 2002)
PowerPC 7447 and 7457
The PowerPC 7447 "Apollo 7" is slightly improved from the 7450/55, it has a 512 KiB on-chip L2 cache and was manufactured in a 130 nm130 nanometer
The 130 nm process refers to the level of semiconductor process technology that was reached in the 2000–2001 timeframe, by most leading semiconductor companies, like Intel, Texas Instruments, IBM, and TSMC....
process with SOI, hence drawing less power. It has 58 million transistors. With the 7447A, which introduced an integrated thermal diode as well as DFS (dynamic frequency scaling
Dynamic frequency scaling
Dynamic frequency scaling is a technique in computer architecture whereby the frequency of a microprocessor can be automatically adjusted "on the fly," either to conserve power or to reduce the amount of heat generated by the chip...
) Freescale was able to reach a slightly higher clock. The 7457 has an additional L3 cache interface. However, its frequency scaling stagnated when Apple chose to use the 7447 instead of the L3 cache-enabled 7455 they used before.
The only companies that offer the 7457 in the form of upgrades for the Power Mac G4
Power Mac G4
The Power Mac G4 was a series of personal computers that was designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple between 1999 and 2004. They used the PowerPC G4 series of microprocessors. They were heralded by Apple to be the first personal supercomputers, reaching speeds of 4 to 20 Gigaflops...
and Power Mac G4 Cube
Power Mac G4 Cube
The Power Mac G4 Cube was a small form factor Macintosh personal computer from Apple Inc. It was sold from 2000 to 2001. Its cube shape is reminiscent of the NeXTcube from NeXT, acquired by Apple in 1996. The machine was designed by Apple industrial designer Jonathan Ive...
are Giga Designs, Sonnet Technology, Daystar Technology (they use the 7457 only for iMac G4 upgrades) and PowerLogix. The Pegasos
Pegasos
Pegasos is a MicroATX motherboard powered by a PowerPC 750CXe or PowerPC 7447 microprocessor, featuring three PCI slots, one AGP slot, two Ethernet ports , USB, DDR, AC'97 sound, and FireWire...
computer platform from Genesi
Genesi
Genesi is computer company focused on building Power Architecture and ARM architecture computers. The organization is split into two units, Genesi USA, Inc. working out of Texas operating as the primary front-end for sales, customers and developers, and bplan GmbH based in Germany as the primary...
also uses 7447 in its Pegasos-II/G4.
PowerPC 7448
The PowerPC 7448 "Apollo 8" is an evolution of the PowerPC 7447A announced at the first Freescale Technology Forum in June 2005. Improvements were higher clock rates (up to 2 GHz), a larger 1 MB L2 cache, a faster 200 MHz front side bus, and lower power consumption (18 W at 1.7 GHz). It was fabricated in a 90 nm process with copper interconnects and SOI.PowerPC 7448 users are:
- Daystar for their Aluminum PowerBook G4 upgrades
- NewerTech for their Power Mac G4 upgrades
- PowerLogix for their Power Mac G4 Cube upgrade
e600
In 2004, Freescale renamed the G4 core to e600 and changed its focus from general CPUs to high-end embedded SoCSystem-on-a-chip
A system on a chip or system on chip is an integrated circuit that integrates all components of a computer or other electronic system into a single chip. It may contain digital, analog, mixed-signal, and often radio-frequency functions—all on a single chip substrate...
devices, and introduced a new naming scheme, MPC86xx. The 7448 was to be the last pure G4 and it formed the base of the new e600 core with a seven-stage, three-issue pipeline, and a powerful branch prediction unit which handles up to sixteen instructions out-of-order. It has an enhanced AltiVec unit capable of limited out-of-order execution
Out-of-order execution
In computer engineering, out-of-order execution is a paradigm used in most high-performance microprocessors to make use of instruction cycles that would otherwise be wasted by a certain type of costly delay...
and a 1 MB L2 cache.

