
LocoScript
Encyclopedia
Word processing
Word processing is the creation of documents using a word processor. It can also refer to advanced shorthand techniques, sometimes used in specialized contexts with a specially modified typewriter.-External links:...
software package
Software package
Software package may refer to:* A piece of application software or utility software** A software suite, or collection of related application or utility software* A software library...
LocoScript by Locomotive Software
Locomotive Software
Locomotive Software was a small British software house which did most of its development for Amstrad's home and small business computers of the 1980s....
was introduced as one of the programs bundled with the Amstrad PCW
Amstrad PCW
The Amstrad PCW series was a range of personal computers produced by British company Amstrad from 1985 to 1998, and also sold under licence in Europe as the "Joyce" by the German electronics company Schneider in the early years of the series' life. When it was launched, the cost of a PCW system was...
, a personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
launched in 1985. Early versions of LocoScript were noted for combining a wide range of facilities with outstanding ease of use. This and the low price of the hardware made it one of the best-selling word processors of the late 1980s. Four versions of LocoScript were published for the PCW, and two for IBM-compatible
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
PCs running under MS-DOS
MS-DOS
MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers. It was the most commonly used member of the DOS family of operating systems, and was the main operating system for IBM PC compatible personal computers during the 1980s to the mid 1990s, until it was gradually superseded by operating...
. LocoScript's market share didn't expand with the PC versions, which were not released until after Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
became the dominant PC operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
.
Background and reception
LocoScript's developers, Locomotive SoftwareLocomotive Software
Locomotive Software was a small British software house which did most of its development for Amstrad's home and small business computers of the 1980s....
, had produced Locomotive BASIC
Locomotive BASIC
Locomotive Basic is a proprietary dialect of the BASIC programming language written by Locomotive Software used only on the Amstrad CPC...
for Amstrad
Amstrad
Amstrad is a British electronics company, now wholly owned by BSkyB. As of 2006, Amstrad's main business is manufacturing Sky Digital interactive boxes....
's CPC 464 home computer, introduced in 1984. For the Amstrad PCW
Amstrad PCW
The Amstrad PCW series was a range of personal computers produced by British company Amstrad from 1985 to 1998, and also sold under licence in Europe as the "Joyce" by the German electronics company Schneider in the early years of the series' life. When it was launched, the cost of a PCW system was...
, introduced in 1985, Locomotive produced the LocoScript word processor
Word processor
A word processor is a computer application used for the production of any sort of printable material....
and Mallard BASIC
Mallard BASIC
Mallard BASIC is a BASIC interpreter for CP/M written by Locomotive Software and supplied with the Amstrad PCW range of small business computers, the ZX Spectrum +3 version of CP/M Plus, and the Acorn BBC Micro Z80 second Processor....
, and also wrote the PCW's User Guide. These programs and a dot matrix printer
Dot matrix printer
A dot matrix printer or impact matrix printer is a type of computer printer with a print head that runs back and forth, or in an up and down motion, on the page and prints by impact, striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the paper, much like the print mechanism on a typewriter...
were included in the price of the PCW, which was £399 plus value added tax
Value added tax
A value added tax or value-added tax is a form of consumption tax. From the perspective of the buyer, it is a tax on the purchase price. From that of the seller, it is a tax only on the "value added" to a product, material or service, from an accounting point of view, by this stage of its...
for the base model. The PCW, regarded as extremely good value for money, gained 60% of the UK home computer market, and 20% of the European personal computer market. According to Personal Computer World, the PCW "got the technophobes using computers".
LocoScript was regarded as easier to use than Wordstar
WordStar
WordStar is a word processor application, published by MicroPro International, originally written for the CP/M operating system but later ported to DOS, that enjoyed a dominant market share during the early to mid-1980s. Although Seymour I...
and WordPerfect
WordPerfect
WordPerfect is a word processing application, now owned by Corel.Bruce Bastian, a Brigham Young University graduate student, and BYU computer science professor Dr. Alan Ashton joined forces to design a word processing system for the city of Orem's Data General Corp. minicomputer system in 1979...
, which in the mid-1980s were the dominant word processors on IBM-compatible
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
PCs, and many users needed no additional information beyond what the manual's "first 20 minutes" introductory chapter provided. The PCW's keyboard offered clearly labelled, one-press special keys for many common LocoScript functions, including cut, copy, and paste, while LocoScript's competitors required a wide range of key combinations that the user had to remember. Most of the program's other features were presented via a pull-down menu bar
Menu bar
A menu bar is a region of a screen or application interface where drop down menus are displayed. The menu bar's purpose is to supply a common housing for window- or application-specific menus which provide access to such functions as opening files, interacting with an application, or displaying...
in which the top-level options were activated by function key
Function key
A function key is a key on a computer or terminal keyboard which can be programmed so as to cause an operating system command interpreter or application program to perform certain actions...
s. The menu system had two structures, one for beginners and the other for experienced users. Locomotive Software's slogan for the product was "Everything you need, nothing you don't." However LocoScript version 1 was regarded as relatively slow.
When the PCW product line was discontinued in 1998, The Daily Telegraph
The Daily Telegraph
The Daily Telegraph is a daily morning broadsheet newspaper distributed throughout the United Kingdom and internationally. The newspaper was founded by Arthur B...
said that the range of independently produced add-on software for LocoScript had contributed to the series' longevity.
LocoScript faded into obscurity because its developers were slow to produce a version for IBM-compatible PCs. By the time they released a version that ran under MS-DOS
MS-DOS
MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers. It was the most commonly used member of the DOS family of operating systems, and was the main operating system for IBM PC compatible personal computers during the 1980s to the mid 1990s, until it was gradually superseded by operating...
, Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
was becoming the dominant operating system. The developers of WordPerfect made a similar mistake, releasing their first Windows version in 1991, shortly after the second Windows version of Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processor designed by Microsoft. It was first released in 1983 under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms including IBM PCs running DOS , the Apple Macintosh , the AT&T Unix PC , Atari ST , SCO UNIX,...
.
As late as 1993, a journalist found "special characters" much easier to produce on Locoscript than on PC word processing software.
Version 1
LocoScript 1 was bundled with the PCW 8256 and 8526, both launched in 1985. LocoScript did not run under the control of a standard operating systemOperating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
but booted directly from a floppy disk. Users had to reboot
Booting
In computing, booting is a process that begins when a user turns on a computer system and prepares the computer to perform its normal operations. On modern computers, this typically involves loading and starting an operating system. The boot sequence is the initial set of operations that the...
if they wanted to switch between LocoScript and a CP/M
CP/M
CP/M was a mass-market operating system created for Intel 8080/85 based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc...
application, unless they used a utility called "Flipper", which could allocate separate areas of RAM
Ram
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
to LocoScript and CP/M.
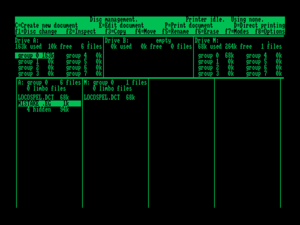
On start-up LocoScript displayed a file management menu, like WordStar
WordStar
WordStar is a word processor application, published by MicroPro International, originally written for the CP/M operating system but later ported to DOS, that enjoyed a dominant market share during the early to mid-1980s. Although Seymour I...
but unlike WordPerfect
WordPerfect
WordPerfect is a word processing application, now owned by Corel.Bruce Bastian, a Brigham Young University graduate student, and BYU computer science professor Dr. Alan Ashton joined forces to design a word processing system for the city of Orem's Data General Corp. minicomputer system in 1979...
, Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processor designed by Microsoft. It was first released in 1983 under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms including IBM PCs running DOS , the Apple Macintosh , the AT&T Unix PC , Atari ST , SCO UNIX,...
and other modern word processors, which start with an empty document. LocoScript enabled users to divide documents into groups, display all the groups on a disk and then the documents in the selected group, and set up a template
Template
Template may mean:*a stencil, pattern or overlay used in graphic arts and sewing to replicate letters, shapes or designs...
for each group. File names were restricted to the "8.3" format, but the edit facilities enabled users to add summaries up to 90 characters long, which they could display from the file menu. The "limbo
Limbo
In the theology of the Catholic Church, Limbo is a speculative idea about the afterlife condition of those who die in original sin without being assigned to the Hell of the damned. Limbo is not an official doctrine of the Roman Catholic Church or any other...
file" facility enabled users to recover accidentally deleted documents until the disk ran out of space, when the software would permanently delete files from "limbo" to make room for new ones. Journalist Dave Langford published a collection of his articles about the PCW, and titled it "The Limbo Files". LocoScript was designed to accommodate add-on programs, which could be selected via the file manager.
LocoScript 1 supported 150 characters. For each language supported by the PCW, the keyboard and LocoScript were configured so that users could easily type all of the normal character set. Various other languages' characters could be typed by holding down the ALT or EXTRA key, along with the SHIFT key if capitals were required. LocoScript could also display mathematical and technical symbols. All these characters and symbols could be printed, unless the printer was a daisy wheel
Daisy wheel printer
Daisy wheel printers use an impact printing technology invented in 1969 by David S. Lee at Diablo Data Systems. It uses interchangeable pre-formed type elements, each with typically 96 glyphs, to generate high-quality output comparable to premium typewriters such as the IBM Selectric, but two to...
unit. LocoScript's menu system enabled users to add, singly or in combination, a range of typographical effects: monospaced or proportional character spacing; normal or double width characters and spacing; various font sizes; bold, underline, italics, subscript or superscript, and reverse video. All of these except those that affected font size and spacing were displayed on the screen. Reverse video was an on-screen reminder to the user and was never printed, while the other effects were printed, except on daisy wheel printers.
Users could optionally set up to two page headers and footers, and could tell LocoScript whether to use one header or footer on odd pages and the other on even pages, or one header or footer for the first or last page and another for all the rest,or to omit a header or footer on the first or last page. The program provided codes for the current page number and total number of pages, and aligning them to the left, centre or right, and for decorations such as leading and trailing hyphens (e.g. "-9-"). LocoScript automatically avoided widows and orphans, ensuring that, if a paragraph of four or more lines split across pages at least two line appeared on each page. Users could also tell LocoScript to keep a group of lines or paragraphs together on the same page, or to avoid splitting paragraphs throughout a document, and could force page breaks.
Users could control placement of text by means of: margins; indentation
Indentation
An indentation may refer to:* A notch, or deep recesses; for instance in a coastline, or a carving in rock* The placement of text farther to the right to separate it from surrounding text....
; normal tab stop
Tab stop
A tab stop on a typewriter is a location where the carriage movement is halted by mechanical gears. Tab stops are set manually, and pressing the tab key causes the carriage to go to the next tab stop...
s; decimal tab stops, which set the position of the decimal point rather than the start of a number; and left, right or full justification
Justification (typesetting)
In typesetting, justification is the typographic alignment setting of text or images within a column or "measure" to align along both the left and right margin...
. Different combinations of these settings, called "layouts", were automatically numbered, which made it possible to re-use layouts and to make changes that applied to all parts of a document where a specified layout was used. These facilities could be used for presenting tables.
LocoScript's cut, copy and paste facility provided 10 paste buffers ("blocks"), each of which was designated by a number and could be saved for re-use in a different document. Users could also save up to 26 short phrases, identified by letters, although the size of individual phrases and of the whole collection of phrases was limited. Both phrases and paste blocks could be inspected via a menu option. In addition, users could insert whole files, which could be either LocoScript documents or ASCII
ASCII
The American Standard Code for Information Interchange is a character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet. ASCII codes represent text in computers, communications equipment, and other devices that use text...
text files. The "find" and "find and replace" facilities could operate on a whole document, or small sections of one, and "find and replace" ("exchange" in the manual's terminology) had an option to confirm each change or just go ahead.
The program did not immediately reflow text after major insertions or deletions, but did this when the user pressed the RELAY key, or automatically if the user moved the cursor through the changed passage.
LocoScript allowed the user to edit one document while printing another, so that the relative slowness of the bundled dot matrix printer
Dot matrix printer
A dot matrix printer or impact matrix printer is a type of computer printer with a print head that runs back and forth, or in an up and down motion, on the page and prints by impact, striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the paper, much like the print mechanism on a typewriter...
seldom caused difficulties. Users could ask for all of a document to be printed or a range of pages, set the print quality to "high quality" or "draft", and set the paper used to single-sheet or continuous stationery
Continuous stationery
Continuous stationery or Continuous form paper is paper which is designed for use with dot-matrix printers and line printers. Other names for continuous stationery include fan-fold paper, sprocket feed paper, burst paper, tractor-feed paper, and pin feed paper...
. LocoScript automatically adjusted the size of margins so that the same number of lines per page appeared on both single-sheet and continuous stationery. Since the printer only accepted one sheet of single-sheet paper at a time, LocoScript displayed a prompt at the end of each page when in single-sheet mode. The program also had the ability to resume at a specified page after a paper jam. In addition to printing LocoScript documents, the program had a "direct printing" mode which operated like a typewriter, printing each piece of text after the user pressed RETURN. This could be used for completing forms.
LocoScript version 1 had no spell checker
Spell checker
In computing, a spell checker is an application program that flags words in a document that may not be spelled correctly. Spell checkers may be stand-alone capable of operating on a block of text, or as part of a larger application, such as a word processor, email client, electronic dictionary,...
or mail merge
Mail merge
Mail merge is a software function which allows to create multiple documents from a single template form and a structured data source.-History:This technique of merging data to create gave rise to the term mail merge....
facilities.
Version 2
LocoScript 2 was bundled with the Amstrad PCWAmstrad PCW
The Amstrad PCW series was a range of personal computers produced by British company Amstrad from 1985 to 1998, and also sold under licence in Europe as the "Joyce" by the German electronics company Schneider in the early years of the series' life. When it was launched, the cost of a PCW system was...
9512, introduced in 1987. This version was significantly faster, included a spell checker
Spell checker
In computing, a spell checker is an application program that flags words in a document that may not be spelled correctly. Spell checkers may be stand-alone capable of operating on a block of text, or as part of a larger application, such as a word processor, email client, electronic dictionary,...
and supported non-Amstrad printers. It could also format
Disk formatting
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a hard disk drive or flexible disk medium for data storage. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems...
, copy and verify disks for itself, instead of requiring the user to switch to CP/M and use the Disckit utility. However copying via LocoScript was much slower because the word processor occupied more RAM
Ram
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
than the CP/M system, leaving less space for the RAM disk
RAM disk
A RAM disk or RAM drive is a block of RAM that a computer's software is treating as if the memory were a disk drive...
and therefore forcing the copy to be done in smaller, more numerous stages. LocoScript 2 increased its character set to 400, and allowed users to define up to 16 of their own characters.
Version 3
LocoScript 3 includes the ability to print text at any size using scalable "LX" fontFont
In typography, a font is traditionally defined as a quantity of sorts composing a complete character set of a single size and style of a particular typeface...
s, and to use multiple fonts in a document. According to the vendors, LocoScript 3 also includes the ability to include pictures and draw boxes within documents, a facility to print odd-numbered and even-numbered pages separately, and a word counter. The vendors recommend LocoScript 3 for PCW models with only 512 KB
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information...
of RAM
Ram
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
.
Add-on utilities including LocoSpell (spell check), LocoMail (mail merge), LocoFile (database) and a Printer Support Pack were available but these are no longer sold separately.
Version 4
According to the vendors, LocoScript 4 adds a wider range of fontFont
In typography, a font is traditionally defined as a quantity of sorts composing a complete character set of a single size and style of a particular typeface...
s, support for colour printing and (with the optional extra Printer Support Pack) hundreds of printers (excluding those that require Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
), and a label-printing facility. Version 4 also interfaces with the mail merge
Mail merge
Mail merge is a software function which allows to create multiple documents from a single template form and a structured data source.-History:This technique of merging data to create gave rise to the term mail merge....
program LocoMail and the LocoFile database.
LocoScript PC Easy
According to the vendors, this is equivalent to LocoScript 2 on the Amstrad PCWAmstrad PCW
The Amstrad PCW series was a range of personal computers produced by British company Amstrad from 1985 to 1998, and also sold under licence in Europe as the "Joyce" by the German electronics company Schneider in the early years of the series' life. When it was launched, the cost of a PCW system was...
,
LocoScript PC Pro
According to the vendors, this is equivalent to LocoScript 4 and runs under MS-DOSMS-DOS
MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers. It was the most commonly used member of the DOS family of operating systems, and was the main operating system for IBM PC compatible personal computers during the 1980s to the mid 1990s, until it was gradually superseded by operating...
version 3.0 or higher, as supplied with Windows 3, Windows 95, Windows 98 and Windows XP. Some issues exist with it being compatible with Windows Vista or Windows 7. It supports only printers that can connect via a parallel printer port, such as most HP Deskjets and which can run under MS-DOS; it does not support printers that require a USB connection or are labelled "Windows only".
External links
- LocoScript Software – LocoScript official homepage

