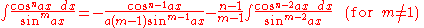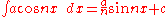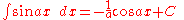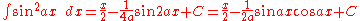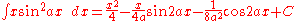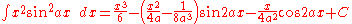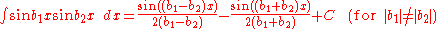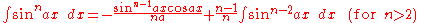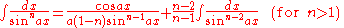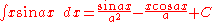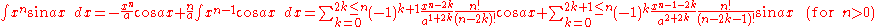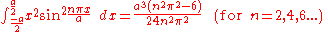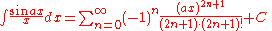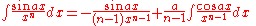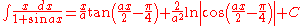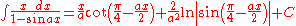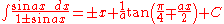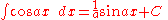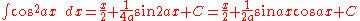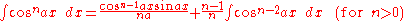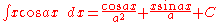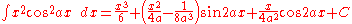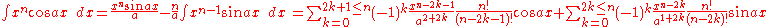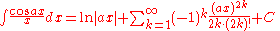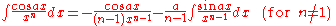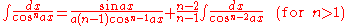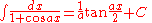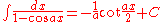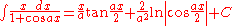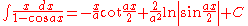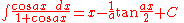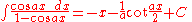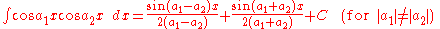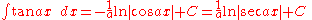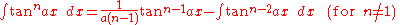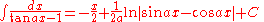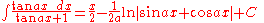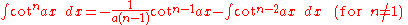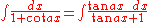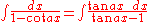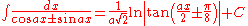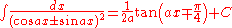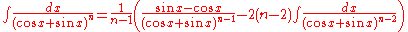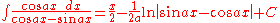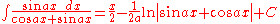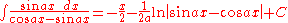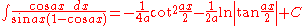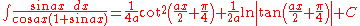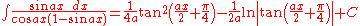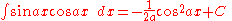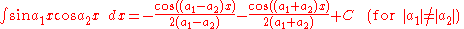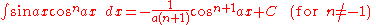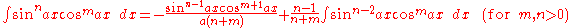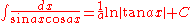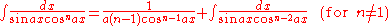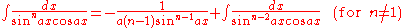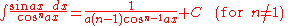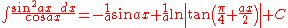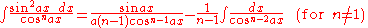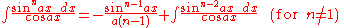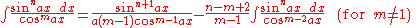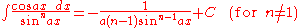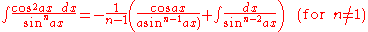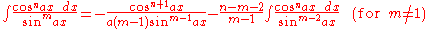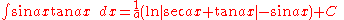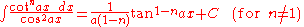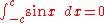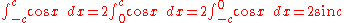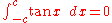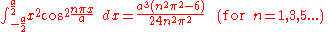List of integrals of trigonometric functions
Encyclopedia
The following is a list of integral
s (antiderivative
function
s) of trigonometric functions. For antiderivatives involving both exponential and trigonometric functions, see List of integrals of exponential functions. For a complete list of antiderivative functions, see lists of integrals. See also trigonometric integral
.
Generally, if the function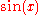 is any trigonometric function, and
is any trigonometric function, and 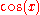 is its derivative,
is its derivative,
In all formulas the constant a is assumed to be nonzero, and C denotes the constant of integration.
Integrals involving only sine
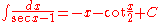
Integrands involving only secant
In the 17th century, the integral of the secant function was the subject of a well-known conjecture posed in the 1640s by Henry Bond. The problem was solved by Isaac Barrow
. It was originally for the purposes of cartography
that this was needed. See Integral of the secant function
.

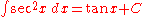
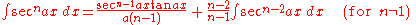

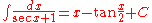


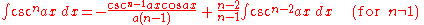
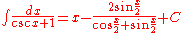
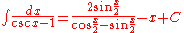
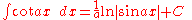
Integrands involving both sine
Integrands involving both sine
Integrands involving both cosine and tangent
Integrals containing both sine
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
s (antiderivative
Antiderivative
In calculus, an "anti-derivative", antiderivative, primitive integral or indefinite integralof a function f is a function F whose derivative is equal to f, i.e., F ′ = f...
function
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the argument of the function, also known as the input, with another quantity, the value of the function, also known as the output. A function assigns exactly one output to each input. The argument and the value may be real numbers, but they can...
s) of trigonometric functions. For antiderivatives involving both exponential and trigonometric functions, see List of integrals of exponential functions. For a complete list of antiderivative functions, see lists of integrals. See also trigonometric integral
Trigonometric integral
In mathematics, the trigonometric integrals are a family of integrals which involve trigonometric functions. A number of the basic trigonometric integrals are discussed at the list of integrals of trigonometric functions.-Sine integral:...
.
Generally, if the function
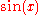 is any trigonometric function, and
is any trigonometric function, and 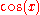 is its derivative,
is its derivative,In all formulas the constant a is assumed to be nonzero, and C denotes the constant of integration.
Integrals involving only sineSineIn mathematics, the sine function is a function of an angle. In a right triangle, sine gives the ratio of the length of the side opposite to an angle to the length of the hypotenuse.Sine is usually listed first amongst the trigonometric functions....
Integrands involving only cosine
Integrands involving only tangent
Integrands involving only secantSecantSecant is a term in mathematics. It comes from the Latin secare . It can refer to:* a secant line, in geometry* the secant variety, in algebraic geometry...
In the 17th century, the integral of the secant function was the subject of a well-known conjecture posed in the 1640s by Henry Bond. The problem was solved by Isaac BarrowIsaac Barrow
Isaac Barrow was an English Christian theologian, and mathematician who is generally given credit for his early role in the development of infinitesimal calculus; in particular, for the discovery of the fundamental theorem of calculus. His work centered on the properties of the tangent; Barrow was...
. It was originally for the purposes of cartography
Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
that this was needed. See Integral of the secant function
Integral of the secant function
The integral of the secant function of trigonometry was the subject of one of the "outstanding open problems of the mid-seventeenth century", solved in 1668 by James Gregory. In 1599, Edward Wright evaluated the integral by numerical methods – what today we would call Riemann sums...
.

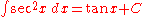
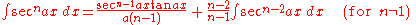

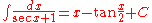

Integrands involving only cosecant


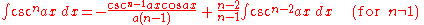
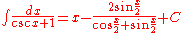
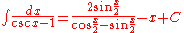
Integrands involving only cotangent
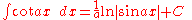
Integrands involving both sineSineIn mathematics, the sine function is a function of an angle. In a right triangle, sine gives the ratio of the length of the side opposite to an angle to the length of the hypotenuse.Sine is usually listed first amongst the trigonometric functions....
and cosine
- also:

- also:
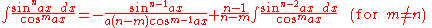
- also:
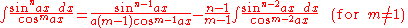
- also:

- also: