
Linear induction motor
Encyclopedia
A linear induction motor (LIM) is an AC asynchronous linear motor
that works by the same general principles as other induction motor
s but which has been designed to directly produce motion in a straight line.
Linear motors frequently run on a 3 phase power supply.
Their uses include magnetic levitation
, linear propulsion, and linear actuators. They have also been used for pumping liquid metals.
at King's College
in London, but Wheatstone's model was too inefficient to be practical. A feasible linear induction motor is described in the US patent 782312 ( 1905 - inventor Alfred Zehden of Frankfurt-am-Main ), for driving trains or lifts. The German engineer Hermann Kemper built a working model in 1935. In the late 1940s, professor Eric Laithwaite
of Imperial College in London
developed the first full-size working model.
In a single sided version the magnetic field can create repulsion forces that push the conductor away from the stator, levitating it, and carrying it along in the direction of the moving magnetic field. Laithewaite called the later versions of it magnetic river
. These versions of the linear induction motor use a principle called transverse flux where two opposite poles are placed side by side. This permits very long poles to be used, which permits high speed and efficiency.
Because of these properties, linear motors are often used in maglev
propulsion, as in the Japanese Linimo
magnetic levitation train line near Nagoya. However, linear motors have been used independently of magnetic levitation, as in Bombardier
's Advanced Rapid Transit
systems worldwide and a number of modern Japanese subways, including Tokyo
's Toei Oedo Line
.
Similar technology is also used in some roller coaster
s with modifications but, at present, is still impractical on street running tram
s, although this, in theory, could be done by burying it in a slotted conduit.
 Outside of public transportation, vertical linear motors have been proposed as lifting mechanisms in deep mine
Outside of public transportation, vertical linear motors have been proposed as lifting mechanisms in deep mine
s, and the use of linear motors is growing in motion control
applications. They are also often used on sliding doors, such as those of low floor tram
s such as the Citadis
and the Eurotram. Dual axis linear motors also exist. These specialized devices have been used to provide direct X-Y motion for precision laser cutting of cloth and sheet metal, automated drafting
, and cable forming. Mostly used linear motors are LIM (linear induction motor), LSM (linear synchronous motor). Linear DC motors are not used as it includes more cost and linear SRM suffers from poor thrust. So for long run in traction LIM is mostly preferred and for short run LSM is mostly preferred.
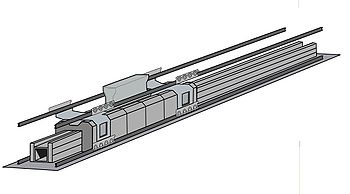 Linear induction motors have also been used for launching aircraft, the Westinghouse Electropult system in 1945 was an early example and the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) was due to be delivered in 2010.
Linear induction motors have also been used for launching aircraft, the Westinghouse Electropult system in 1945 was an early example and the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) was due to be delivered in 2010.
The secondary is frequently a sheet of aluminum, often with an iron backing plate. Some LIMs are double sided, with one primary either side of the secondary, and in this case no iron backing is needed.
Two sorts of linear motor exist, short primary, where the coils are truncated shorter than the secondary, and a short secondary where the conductive plate is smaller. Short secondary LIMs are often wound as parallel connections between coils of the same phase, whereas short primaries are usually wound in series.
The primaries of transverse flux LIMs have a series of twin poles lying transversely side-by-side, with opposite winding directions.
acting on conductors in the field. Any conductor, be it a loop, a coil or simply a piece of plate metal, that is placed in this field will have eddy current
s induced
in it thus creating an opposing magnetic field, in accordance with Lenz's law
. The two opposing fields will repel each other, thus creating motion as the magnetic field sweeps through the metal.
With a short secondary, the behaviour is almost identical to a rotary machine, provided it is at least two poles long, but with a short primary reduction in thrust occurs at low slip (below about 0.3) until it is eight poles or longer.
However, because of end effect, linear motors cannot 'run light'- normal induction motors are able to run the motor with a near synchronous field under low load conditions. Due to end effect this creates much more significant losses with linear motors.
Linear motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor "unrolled" so that instead of producing a torque it produces a linear force along its length...
that works by the same general principles as other induction motor
Induction motor
An induction or asynchronous motor is a type of AC motor where power is supplied to the rotor by means of electromagnetic induction. These motors are widely used in industrial drives, particularly polyphase induction motors, because they are robust and have no brushes...
s but which has been designed to directly produce motion in a straight line.
Linear motors frequently run on a 3 phase power supply.
Their uses include magnetic levitation
Magnetic levitation
Magnetic levitation, maglev, or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields...
, linear propulsion, and linear actuators. They have also been used for pumping liquid metals.
History
The history of linear electric motors can be traced back at least as far as the 1840s, to the work of Charles WheatstoneCharles Wheatstone
Sir Charles Wheatstone FRS , was an English scientist and inventor of many scientific breakthroughs of the Victorian era, including the English concertina, the stereoscope , and the Playfair cipher...
at King's College
King's College London
King's College London is a public research university located in London, United Kingdom and a constituent college of the federal University of London. King's has a claim to being the third oldest university in England, having been founded by King George IV and the Duke of Wellington in 1829, and...
in London, but Wheatstone's model was too inefficient to be practical. A feasible linear induction motor is described in the US patent 782312 ( 1905 - inventor Alfred Zehden of Frankfurt-am-Main ), for driving trains or lifts. The German engineer Hermann Kemper built a working model in 1935. In the late 1940s, professor Eric Laithwaite
Eric Laithwaite
Eric Roberts Laithwaite was a British electrical engineer, known as the "Father of Maglev" for his development of the linear induction motor and maglev rail system.- Biography :...
of Imperial College in London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
developed the first full-size working model.
In a single sided version the magnetic field can create repulsion forces that push the conductor away from the stator, levitating it, and carrying it along in the direction of the moving magnetic field. Laithewaite called the later versions of it magnetic river
Magnetic river
Magnetic river is an electrodynamic suspension magnetic levitation system designed by Eastham and Eric Laithwaite in 1974.It consists of a thin conductive plate on an AC linear induction motor...
. These versions of the linear induction motor use a principle called transverse flux where two opposite poles are placed side by side. This permits very long poles to be used, which permits high speed and efficiency.
Because of these properties, linear motors are often used in maglev
Magnetic levitation
Magnetic levitation, maglev, or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields...
propulsion, as in the Japanese Linimo
Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi, Japan, near the city of Nagoya. While primarily built to serve the Expo 2005 fair site, the line is still operating to serve the local community.Linimo is owned and operated by...
magnetic levitation train line near Nagoya. However, linear motors have been used independently of magnetic levitation, as in Bombardier
Bombardier Transportation
Bombardier Transportation is the rail equipment division of the Canadian firm, Bombardier Inc. Bombardier Transportation is one of the world's largest companies in the rail-equipment manufacturing and servicing industry. Its headquarters are in Berlin, Germany....
's Advanced Rapid Transit
Bombardier Advanced Rapid Transit
Advanced Rapid Transit or ART is the current name given to a rapid transit system manufactured by Bombardier Transportation. The original versions look like small subway cars that typically run in two-, four- or six-car trains, but the latest versions are more streamlined two-car articulated...
systems worldwide and a number of modern Japanese subways, including Tokyo
Tokyo
, ; officially , is one of the 47 prefectures of Japan. Tokyo is the capital of Japan, the center of the Greater Tokyo Area, and the largest metropolitan area of Japan. It is the seat of the Japanese government and the Imperial Palace, and the home of the Japanese Imperial Family...
's Toei Oedo Line
Toei Oedo Line
The is a subway line in Tokyo, Japan operated by the Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation . It commenced full operations on December 12, 2000; using the Japanese calendar this reads "12/12/12" as the year 2000 equals Heisei 12...
.
Similar technology is also used in some roller coaster
Roller coaster
The roller coaster is a popular amusement ride developed for amusement parks and modern theme parks. LaMarcus Adna Thompson patented the first coasters on January 20, 1885...
s with modifications but, at present, is still impractical on street running tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
s, although this, in theory, could be done by burying it in a slotted conduit.

Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
s, and the use of linear motors is growing in motion control
Motion control
Motion control is a sub-field of automation, in which the position or velocity of machines are controlled using some type of device such as a hydraulic pump, linear actuator, or an electric motor, generally a servo...
applications. They are also often used on sliding doors, such as those of low floor tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
s such as the Citadis
Citadis
The Citadis is a low-floor tram built by Alstom in La Rochelle, France, and Barcelona, Spain. 1,140 Citadis are currently in use in 28 cities, among others: Bordeaux, Grenoble, Lyon, Montpellier, Orléans, the Paris area, and Barcelona, Dublin, Gdańsk, Katowice, Adelaide, Melbourne, Jerusalem and...
and the Eurotram. Dual axis linear motors also exist. These specialized devices have been used to provide direct X-Y motion for precision laser cutting of cloth and sheet metal, automated drafting
Technical drawing
Technical drawing, also known as drafting or draughting, is the act and discipline of composing plans that visually communicate how something functions or has to be constructed.Drafting is the language of industry....
, and cable forming. Mostly used linear motors are LIM (linear induction motor), LSM (linear synchronous motor). Linear DC motors are not used as it includes more cost and linear SRM suffers from poor thrust. So for long run in traction LIM is mostly preferred and for short run LSM is mostly preferred.

Construction
A linear electric motor's primary typically consists of a flat magnetic core (generally laminated) with transverse slots which are often straight cut with coils laid into the slots.The secondary is frequently a sheet of aluminum, often with an iron backing plate. Some LIMs are double sided, with one primary either side of the secondary, and in this case no iron backing is needed.
Two sorts of linear motor exist, short primary, where the coils are truncated shorter than the secondary, and a short secondary where the conductive plate is smaller. Short secondary LIMs are often wound as parallel connections between coils of the same phase, whereas short primaries are usually wound in series.
The primaries of transverse flux LIMs have a series of twin poles lying transversely side-by-side, with opposite winding directions.
Moving magnetic field
In this design of electric motor, the force is produced by a moving linear magnetic fieldMagnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
acting on conductors in the field. Any conductor, be it a loop, a coil or simply a piece of plate metal, that is placed in this field will have eddy current
Eddy current
Eddy currents are electric currents induced in conductors when a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field; due to relative motion of the field source and conductor or due to variations of the field with time. This can cause a circulating flow of electrons, or current, within the body of...
s induced
Electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electric current across a conductor moving through a magnetic field. It underlies the operation of generators, transformers, induction motors, electric motors, synchronous motors, and solenoids....
in it thus creating an opposing magnetic field, in accordance with Lenz's law
Lenz's law
Lenz's law is a common way of understanding how electromagnetic circuits must always obey Newton's third law and The Law of Conservation of Energy...
. The two opposing fields will repel each other, thus creating motion as the magnetic field sweeps through the metal.
Thrust
The drive generated by linear induction motors are somewhat similar to conventional induction motors, the drive forces show a roughly similar characteristic shape relative to slip, albeit modulated by end effects.End effect
Unlike a circular induction motor, a linear induction motor shows end effects.With a short secondary, the behaviour is almost identical to a rotary machine, provided it is at least two poles long, but with a short primary reduction in thrust occurs at low slip (below about 0.3) until it is eight poles or longer.
However, because of end effect, linear motors cannot 'run light'- normal induction motors are able to run the motor with a near synchronous field under low load conditions. Due to end effect this creates much more significant losses with linear motors.

