
Leukocoria
Encyclopedia
Leukocoria is an abnormal white reflection from the retina
of the eye. Leukocoria resembles eyeshine
, but leukocoria can occur in humans and other animals that lack eyeshine because their retina lacks a tapetum lucidum
.
Leukocoria is a medical sign
for a number of conditions, including Coats disease
, congenital cataract
s, corneal scarring, melanoma
of the ciliary body
, Norrie disease
, ocular toxocariasis
, persistence of the tunica vasculosa lentis (PFV/PHPV), retinoblastoma
, and retrolental fibroplasia.
Because of the potential life threatening nature of retinoblastoma
, a cancer
, that condition is usually considered in the evaluation of leukocoria.
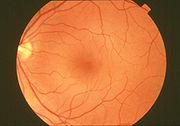
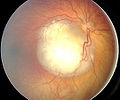 On photographs taken using a flash
On photographs taken using a flash
, instead of the familiar red-eye effect
leukocoria can cause a bright white reflection in an affected eye. Leukocoria may appear also in low indirect light, similar to eyeshine.
Leukocoria can be detected by a routine eye exam (see Ophthalmoscopy
). For screening purposes, the red reflex
test is used. In this test, when a light is shone briefly through the pupil, an orange red reflection is normal. A white reflection is leukocoria.
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
of the eye. Leukocoria resembles eyeshine
Tapetum lucidum
The tapetum lucidum is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrate animals....
, but leukocoria can occur in humans and other animals that lack eyeshine because their retina lacks a tapetum lucidum
Tapetum lucidum
The tapetum lucidum is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrate animals....
.
Leukocoria is a medical sign
Medical sign
A medical sign is an objective indication of some medical fact or characteristic that may be detected by a physician during a physical examination of a patient....
for a number of conditions, including Coats disease
Coats disease
Coats’ disease, , is a very rare congenital, nonhereditary eye disorder, causing full or partial blindness, characterized by abnormal development of blood vessels behind the retina.It can have a similar presentation to that of retinoblastoma.-Presentation:Coats’ usually...
, congenital cataract
Cataract
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope, varying in degree from slight to complete opacity and obstructing the passage of light...
s, corneal scarring, melanoma
Melanoma
Melanoma is a malignant tumor of melanocytes. Melanocytes are cells that produce the dark pigment, melanin, which is responsible for the color of skin. They predominantly occur in skin, but are also found in other parts of the body, including the bowel and the eye...
of the ciliary body
Ciliary body
The ciliary body is the circumferential tissue inside the eye composed of the ciliary muscle and ciliary processes. It is triangular in horizontal section and is coated by a double layer, the ciliary epithelium. This epithelium produces the aqueous humor. The inner layer is transparent and covers...
, Norrie disease
Norrie disease
Norrie Disease is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the eye and almost always leads to blindness. In addition to the congenital ocular symptoms, some patients suffer from a progressive hearing loss starting mostly in their 2nd decade of life, while another portion may be mentally...
, ocular toxocariasis
Toxocariasis
-History of discovery:Werner described a parasitic nematode in dogs in 1782 which he named Ascaris canis. Johnston determined that what Werner had described was actually a member of the genus Toxocara established by Stiles in 1905. Fữlleborn speculated that T canis larvae might cause granulomatous...
, persistence of the tunica vasculosa lentis (PFV/PHPV), retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rapidly developing cancer that develops in the cells of retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. In the developed world, Rb has one of the best cure rates of all childhood cancers , with more than nine out of every ten sufferers surviving into...
, and retrolental fibroplasia.
Because of the potential life threatening nature of retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rapidly developing cancer that develops in the cells of retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. In the developed world, Rb has one of the best cure rates of all childhood cancers , with more than nine out of every ten sufferers surviving into...
, a cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, that condition is usually considered in the evaluation of leukocoria.
Diagnosis


Flash (photography)
A flash is a device used in photography producing a flash of artificial light at a color temperature of about 5500 K to help illuminate a scene. A major purpose of a flash is to illuminate a dark scene. Other uses are capturing quickly moving objects or changing the quality of light...
, instead of the familiar red-eye effect
Red-eye effect
The red-eye effect in photography is the common appearance of red pupils in color photographs of eyes. It occurs when using a photographic flash very close to the camera lens , in ambient low light. The effect appears in the eyes of humans and animals that have no tapetum lucidum, hence no...
leukocoria can cause a bright white reflection in an affected eye. Leukocoria may appear also in low indirect light, similar to eyeshine.
Leukocoria can be detected by a routine eye exam (see Ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope . It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part of a routine physical examination...
). For screening purposes, the red reflex
Red reflex
The red reflex refers to the reddish-orange reflection from the eye's retina that is observed when using an ophthalmoscope or retinoscope from approximately 30 cm / 1 foot...
test is used. In this test, when a light is shone briefly through the pupil, an orange red reflection is normal. A white reflection is leukocoria.
External links
- PHPV Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous
- Retinoblastoma MedPix Images

