
Leipzig–Dresden Railway Company
Encyclopedia
The Leipzig-Dresden Railway Company (Leipzig-Dresdner Eisenbahn-Compagnie) or LDE was a private railway company in the Kingdom of Saxony
, now a part of Germany
. Amongst other things, it operated the route between Leipzig and Dresden, opened in 1839, and which was the first long-distance railway line in Germany. On 1 July 1876 the company was nationalised and became part of the Royal Saxon State Railways
.

 The idea of building a railway to link Leipzig with Strehla
The idea of building a railway to link Leipzig with Strehla
(on the river Elbe), had already been put forward before 1830 by the Leipzig merchant, Carl Gottlieb Tenner. Tenner's idea gained new impetus after the state economist in Leipzig, Friedrich List
, publicised his plans for a German railway system in 1833, in which it was envisaged that Leipzig would function as a central hub. That same year, a railway committee was founded which, on 20 November 1833, submitted a petition to the lower house of the Saxon Parliament (Sächsischer Landtag) in Dresden for the construction of a railway from Leipzig to Dresden .
In 1835, the Leipzig-Dresden Railway Company was founded as a private company by twelve citizens of Leipzig, including: Albert Dufour-Féronce (1798–1861), Gustav Harkort (1795–1865), Carl Lampe (1804–1889) and Wilhelm Theodor Seyfferth (1807–1881). At the Easter trade fair in 1835 the shares of the company (nominally valued at 100 thaler
) were fully subscribed within just a few hours, making a capital sum of over one million thalers available. On 6 May 1835 the Saxon state government authorised the construction and operation of the line as well as the issue of non-interest bearing bonds to the value of 500,000 thalers. The total capital generated thus amounted to 1.5 million thalers.
In October 1835 the English engineers Sir James Walker und Hawkshaw surveyed the proposed routes and recommended the northern route via Strehla (estimated cost: 1,808,500 thalers) over the route via Meißen (1,956,000 thalers). On 16 November 1835 the purchase of land began for the section between Leipzig and the Mulde bridge north of Wurzen. On 1 March 1836 the first sod was cut. Oversight for the entire project lay in the hands of the Saxon Senior Waterways Construction Engineer (Oberwasserbaudirektors), Karl Theodor Kunz.
Then however the town council of Strehla rejected the building of the railway. So the line was re-routed over the river Elbe
7 km further south at Riesa
. On 7 April 1839 the first train ran over the Elbe railway bridge at Riesa.
The route was taken into operation in several stages:
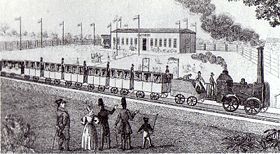
On 7 April 1839, on the completion of the Elbe bridge at Riesa, the entire route from Leipzig to Dresden was finally opened. A second track was built immediately afterwards and the route was then operated with traffic running on the left, in line with English practice until 1884!
From 1851 to 1878 a single-tracked, 5 km long, connecting railway was operated in Leipzig, that branched off from the Saxon-Bavarian Railway, ran eastwards around the city in a large curve and finally entered the Dresden railway north of Dresden station.
On 1 December 1860 the Leipzig-Dresden Railway opened a side line that branched off the main line in Coswig and ran to Meißen. On 14 May 1866 it opened services on another side line, which branched off the main route in Borsdorf and initially ran as far as Grimma
; then on 28 October 1867 to Leisnig
, on 2 June 1868 to Döbeln
, on 25 October 1868 to Nossen
and on 22 December 1868 it was finally extended as far as Meißen, so that a parallel southern route was established between Borsdorf and Coswig.
The Großenhain
branch, opened on 14 October 1862, went into to the ownership of the LDE on 1 July 1869.
On 15 October 1875 the LDE opened a connecting route from Riesa to Elsterwerda
(since 1815 part of the Kingdom of Prussia
), that from 17 July 1875 was linked to Berlin and Dresden.
The route from Nossen to Freiberg – as part of the line from Nossen to Moldau
- was completed on 15 July 1873, and extended as far as Mulda/Sa. by 2 November 1875. On 15 August 1876 the route reached the Bohemian border at Moldau
.
After the collapse of the Elbe bridge at Riesa, the general assembly of the shareholders decided on 29 March 1876 to sell the Dresden railway to the state of Saxony. On 1 July 1876 the operation and management of the Leipzig-Dresden Railway was transferred to the Royal Saxon State Railways
.
The 'railway monument' in Leipzig, erected in 1878, commemorates the development of the Dresden railway from its emergence as a private initiative of Leipzig citizens to its nationalisation.

Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony , lasting between 1806 and 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. From 1871 it was part of the German Empire. It became a Free state in the era of Weimar Republic in 1918 after the end of World War...
, now a part of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. Amongst other things, it operated the route between Leipzig and Dresden, opened in 1839, and which was the first long-distance railway line in Germany. On 1 July 1876 the company was nationalised and became part of the Royal Saxon State Railways
Royal Saxon State Railways
The Royal Saxon State Railways were the state-owned railways operating in the Kingdom of Saxony from 1869 to 1918...
.
History


Strehla
Strehla is a place in the district of Meißen, Saxony, Germany. It is located at the Elbe north of Riesa. This place name means arrow in Sorbian.-History:...
(on the river Elbe), had already been put forward before 1830 by the Leipzig merchant, Carl Gottlieb Tenner. Tenner's idea gained new impetus after the state economist in Leipzig, Friedrich List
Friedrich List
Georg Friedrich List was a leading 19th century German economist who developed the "National System" or what some would call today the National System of Innovation...
, publicised his plans for a German railway system in 1833, in which it was envisaged that Leipzig would function as a central hub. That same year, a railway committee was founded which, on 20 November 1833, submitted a petition to the lower house of the Saxon Parliament (Sächsischer Landtag) in Dresden for the construction of a railway from Leipzig to Dresden .
In 1835, the Leipzig-Dresden Railway Company was founded as a private company by twelve citizens of Leipzig, including: Albert Dufour-Féronce (1798–1861), Gustav Harkort (1795–1865), Carl Lampe (1804–1889) and Wilhelm Theodor Seyfferth (1807–1881). At the Easter trade fair in 1835 the shares of the company (nominally valued at 100 thaler
Thaler
The Thaler was a silver coin used throughout Europe for almost four hundred years. Its name lives on in various currencies as the dollar or tolar. Etymologically, "Thaler" is an abbreviation of "Joachimsthaler", a coin type from the city of Joachimsthal in Bohemia, where some of the first such...
) were fully subscribed within just a few hours, making a capital sum of over one million thalers available. On 6 May 1835 the Saxon state government authorised the construction and operation of the line as well as the issue of non-interest bearing bonds to the value of 500,000 thalers. The total capital generated thus amounted to 1.5 million thalers.
In October 1835 the English engineers Sir James Walker und Hawkshaw surveyed the proposed routes and recommended the northern route via Strehla (estimated cost: 1,808,500 thalers) over the route via Meißen (1,956,000 thalers). On 16 November 1835 the purchase of land began for the section between Leipzig and the Mulde bridge north of Wurzen. On 1 March 1836 the first sod was cut. Oversight for the entire project lay in the hands of the Saxon Senior Waterways Construction Engineer (Oberwasserbaudirektors), Karl Theodor Kunz.
Then however the town council of Strehla rejected the building of the railway. So the line was re-routed over the river Elbe
Elbe
The Elbe is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Krkonoše Mountains of the northwestern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia , then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, 110 km northwest of Hamburg...
7 km further south at Riesa
Riesa
Riesa is a town in the district of Meißen in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is located at the river Elbe, approx. 40 km northwest of Dresden.The world's first 110 kV power line was inaugurated between Riesa and Lauchhammer in 1912....
. On 7 April 1839 the first train ran over the Elbe railway bridge at Riesa.
The route was taken into operation in several stages:

- 1837, 24 April: Leipzig–Althen (10.60 km)
- 1837, 12 November: Althen–BorsdorfBorsdorfBorsdorf is a municipality in the Leipzig district in Saxony, Germany....
–Gerichshain (4.32 km) - 1838, 11 May: Gerichshain–Machern (2.93 km)
- 1838, 19 July: Weintraube–Dresden (8.18 km)
- 1838, 31 July: MachernMachernMachern is a town in the Leipzig district in Saxony, Germany. It is in the vicinity of the city of Leipzig.- Geography and Transport :Machern lies 20 km east of Leipzig, about 10 km west of Wurzen over the Mulda river...
–Wurzen (8.00 km) - 1838, 16 September: WurzenWurzenWurzen is a town in the Leipzig district, in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the river Mulde, here crossed by two bridges, 25 km east of Leipzig, by rail N.E. of Leipzig on the main line to Dresden...
–Dahlen (17.53 km) - 1838, 16 September: OberauOberauOberau is a municipality in the district of Garmisch-Partenkirchen, in Bavaria, Germany....
–CoswigCoswigCoswig can refer to two towns in Germany, both on the river Elbe:*Coswig, Saxony, in the district of Meißen, Saxony*Coswig, Anhalt, in the district of Wittenberg, Saxony-Anhalt...
–Weintraube (13.44 km) - 1838, 3 November: Dahlen–Oschatz (9.56 km)
- 1838, 21 November: OschatzOschatzOschatz is a town in the district Nordsachsen, in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is located 60 km east of Leipzig and 60 km west of Dresden.- Site and Climate :...
–Riesa (13.07 km) - 1839, 7 April: Riesa–Oberau (28.45 km)
On 7 April 1839, on the completion of the Elbe bridge at Riesa, the entire route from Leipzig to Dresden was finally opened. A second track was built immediately afterwards and the route was then operated with traffic running on the left, in line with English practice until 1884!
From 1851 to 1878 a single-tracked, 5 km long, connecting railway was operated in Leipzig, that branched off from the Saxon-Bavarian Railway, ran eastwards around the city in a large curve and finally entered the Dresden railway north of Dresden station.
On 1 December 1860 the Leipzig-Dresden Railway opened a side line that branched off the main line in Coswig and ran to Meißen. On 14 May 1866 it opened services on another side line, which branched off the main route in Borsdorf and initially ran as far as Grimma
Grimma
Grimma is a town in the Free State of Saxony, Germany on the left bank of the Mulde, southeast of Leipzig. Founded in c. 1170, it is part of the Leipzig district.- Location :...
; then on 28 October 1867 to Leisnig
Leisnig
Leisnig is a small town in the district of Mittelsachsen, federal Free State of Saxony in Germany.-History:A settlement in this location was first mentioned in 1046. The town features Mildenstein Castle which is over 1000 years old. The house Markt 13 shows the coat of arms of the family...
, on 2 June 1868 to Döbeln
Döbeln
Döbeln is a town in the Free State of Saxony, Germany, part of the Mittelsachsen district, located at both banks of the river Freiberger Mulde.-History:It was founded in the 10th century, the first written proof of its existence dates back to the year 981....
, on 25 October 1868 to Nossen
Nossen
Nossen is a town in the district of Meißen, in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is part of the Dresden region, and located 80 km southeast of Leipzig. The town is dominated by a large Renaissance castle.- History :...
and on 22 December 1868 it was finally extended as far as Meißen, so that a parallel southern route was established between Borsdorf and Coswig.
The Großenhain
Großenhain
Großenhain is a Große Kreisstadt in the district of Meißen, Saxony, Germany.-History:...
branch, opened on 14 October 1862, went into to the ownership of the LDE on 1 July 1869.
On 15 October 1875 the LDE opened a connecting route from Riesa to Elsterwerda
Elsterwerda
Elsterwerda is a town in the Elbe-Elster district, in southwestern Brandenburg, Germany. It is situated on the river Schwarze Elster, 48 km northwest of Dresden, and 11 km southeast of Bad Liebenwerda.-External links:...
(since 1815 part of the Kingdom of Prussia
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
), that from 17 July 1875 was linked to Berlin and Dresden.
The route from Nossen to Freiberg – as part of the line from Nossen to Moldau
Moldau
The German word Moldau may refer to:*The historical region of Moldavia*Vltava, river in the Czech Republic*"The Moldau", a symphonic poem by Bedřich Smetana named after the Vltava...
- was completed on 15 July 1873, and extended as far as Mulda/Sa. by 2 November 1875. On 15 August 1876 the route reached the Bohemian border at Moldau
Moldava
Moldava may refer to:*Moldavia, historical region in Eastern Europe*Moldava nad Bodvou, town in Slovakia*Moldava , village in the Czech Republic- See also :*Republic of Moldova, a country in the south-east of Europe....
.
After the collapse of the Elbe bridge at Riesa, the general assembly of the shareholders decided on 29 March 1876 to sell the Dresden railway to the state of Saxony. On 1 July 1876 the operation and management of the Leipzig-Dresden Railway was transferred to the Royal Saxon State Railways
Royal Saxon State Railways
The Royal Saxon State Railways were the state-owned railways operating in the Kingdom of Saxony from 1869 to 1918...
.
The 'railway monument' in Leipzig, erected in 1878, commemorates the development of the Dresden railway from its emergence as a private initiative of Leipzig citizens to its nationalisation.
The routes

- Leipzig–Dresden (*1839)
- Leipzig Bavarian station–Leipzig Dresden station (1851–1878)
- Borsdorf–Coswig (*1860/1868)
- Priestewitz–Großenhain (procured in 1868)
- Riesa–Elsterwerda (*1875)
- Nossen–Freiberg–Moldau (*1876)
The locomotives
The following list is incomplete:| Lokomotives of the Leipzig-Dresden Railway Company | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDE-Designation | Quantity | Manufacturer | Years of manufacture | Axle arrangement UIC classification The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is set out in the International Union of Railways "Leaflet 650 - Standard designation of axle arrangement on locomotives and multiple-unit sets". It is used in much... |
Royal Saxon St. Rly. No. |
| Comet and Faust LDE – Comet The German locomotives Comet, Faust, Blitz and Windsbraut were four of the first locomotives on the Leipzig-Dresden Railway . They were four-coupled engines, that Rothwell and Company had built in Manchester between 1835 and 1838.Comet was the first locomotive to be delivered to Saxony... |
2 | Rothwell Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell was an engineering company in Bolton, England.Set up in 1830, the partners became interested in the production of steam locomotives after the Rainhill Trials... |
1835, 1838 | B-n2 / B1-n2 | |
| Blitz and Windsbraut LDE – Comet The German locomotives Comet, Faust, Blitz and Windsbraut were four of the first locomotives on the Leipzig-Dresden Railway . They were four-coupled engines, that Rothwell and Company had built in Manchester between 1835 and 1838.Comet was the first locomotive to be delivered to Saxony... |
2 | Rothwell Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell was an engineering company in Bolton, England.Set up in 1830, the partners became interested in the production of steam locomotives after the Rainhill Trials... |
1836, 1837 | B-n2 / B1-n2 | |
| Columbus LDE – Columbus Columbus was a tender locomotive operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway .- History :The locomotive was sent to the LDE on the recommendation of the Saxon consul in the USA. Similar locomotives had already proven themselves on the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. Columbus was a tender locomotive... |
1 | Winans Ross Winans Ross Winans was an American inventor, mechanic, and builder of locomotives and railroad machinery. He is also noted for design of pioneering cigar-hulled ships. Winans, one of the United States' first multi-millionaires, was involved in politics and was a vehement states' rights advocate... |
1835 | B-n2 | |
| Renner to Greif LDE – Renner to Greif The German locomotive series Renner to Greif comprised passenger train, tender locomotives operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway .- History :The five locomotives were delivered in 1837 and 1839 by Kirtley, Warrington/England to the LDE... |
5 | Kirtley Matthew Kirtley Matthew Kirtley was an important early locomotive engineer. His brother Thomas Kirtley was also a locomotive engineer as was his nephew, William Kirtley, who served as locomotive superintendent on the London, Chatham and Dover Railway, 1874-1898.Kirtley was born in February 1813 at Tanfield,... |
1837–1838 | 1A1-n2 | |
| Edward Bury to Pfeil LDE – Edward Bury to Pfeil The EDWARD BURY to PFEIL series of early German locomotives were tender engines operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway .- History :... |
4 | Bury | 1838 | B-n2 | |
| Peter Rothwell to Nordlicht LDE – Peter Rothwell to Nordlicht The Peter Rothwell to Nordlicht series of steam engines were early, passenger train, tender locomotivess operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway in Germany.- History :... |
6 | Rothwell Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell was an engineering company in Bolton, England.Set up in 1830, the partners became interested in the production of steam locomotives after the Rainhill Trials... |
1838–1840 | 1A1-n2 | |
| Robert Stephenson LDE – Robert Stephenson The Robert Stephenson was an early, passenger train, tender locomotive operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway or LDE.The locomotive was delivered to the LDE in 1838 by Robert Stephenson & Co., Newcastle upon Tyne, England with factory number 205... |
1 | Stephenson Robert Stephenson and Company Robert Stephenson and Company was a locomotive manufacturing company founded in 1823. It was the first company set up specifically to build railway engines.- Foundation and early success :... |
1838 | 1A1-n2 | |
| Brüssel LDE – Brüssel The BRÜSSEL was an early German, steam locomotive. It was used by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway for hauling passenger trains.The locomotive was delivered to the LDE in 1842 by Renard of Brussels in Belgium with works number 11... |
1 | Renard | 1842 | 1A1-n2 | |
| Dresden to Riesa LDE – Dresden to Riesa The DRESDEN to RIESA series of early German steam engines, were tender locomotives operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway .- History :The three locomotives were delivered in 1844 and 1846 to the LDE by Hawthorn of Newcastle upon Tyne, England... |
3 | Hawthorn R and W Hawthorn R and W Hawthorn Ltd was a locomotive manufacturer in Newcastle upon Tyne, England from 1817 until 1880.-Locomotive building:Robert Hawthorne first began business at Forth Bank Works in 1817, building marine and stationary steam engines. In 1820, his brother joined him and the firm became R and W... |
1844–1846 | 1B-n2 | |
| Saxonia and Phoenix Saxonia (locomotive) The locomotive Saxonia was operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway Company and was the first practical working steam locomotive built in Germany. Its name means Saxony in Latin.- History :... |
2 | Maschinenbauanstalt Übigau Maschinenbauanstalt Übigau The Maschinenbauanstalt Übigau was a German engineering firm based in the present-day district of Übigau in the city of Dresden, Germany.- History :... |
1838–1840 | B1-n2 | |
| Pegasus LDE – Pegasus The Pegasus was an early, passenger train tender locomotive operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway or LDE. She was one of the first locomotives to be built in Germany.- History :... |
1 | Sächsische Maschinenfabrik Sächsische Maschinenfabrik The Sächsische Maschinenfabrik in Chemnitz was one of the most important engineering companies in Saxony in the second half of the 19th century and the first two decades of the 20th century. Including its various predecessor businesses, the firm existed from 1837 until its liquidation in 1930, and... |
1839 | 1A1n2 | |
| Wurzen and Oschatz LDE – Wurzen and Oschatz The locomotives WURZEN and OSCHATZ were early German steam engines operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway for mixed duties. They were tender locomotives.- History :The two locomotives were delivered in 1847 by Borsig in Berlin to the LDE.... |
2 | Borsig | 1847 | 1B-n2 | |
| Elbe to Hayn LDE – Elbe to Hayn The ELBE to HAYN series of early, German, steam locomotives were equipped with tenders and operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway .- History :... |
5 | Borsig | 1848–1850 | 1A1n2 | |
| Richard Hartmann to Zwickau LDE – Richard Hartmann to Zwickau The RICHARD HARTMANN to ZWICKAU series of early German locomotives were express train tender locomotives operated by the Leipzig-Dresden Railway .- History :... |
3 | Hartmann BMAG *Birmingham Museum & Art Gallery*Berliner Maschinenbau AG - German manufacturer of locomotives... |
1849 | 1A1n2 | |
| LDE - Gustav Harkort etc. Saxon VIa - External links :* There is a relevant English-language forum at... |
1848–1868 | 1A1-n2 |
Sources
- Udo Becher: Die Leipzig-Dresdner Eisenbahn-Compagnie. transpress VEB Verlag für Verkehrswesen, Berlin 1981.
- Die Leipzig-Dresdner Eisenbahn, Anfänge und Gegenwart einer 150-jährigen, hrsg. v. Fritz Borchert, transpress VEB Verlag für Verkehrswesen, Berlin 1989, ISBN 3-344-00354-2
- Panorama der Eisenbahn zwischen Leipzig und Dresden, Koedition der Verlage transpress, Berlin und Tourist, Berlin/Leipzig, 1989, Hrsg. Gerhard Schlegel, ISBN 3-344-00348-8, Reprint eines Originals von 1839
External links
- The Leipzig-Dresden railway line through time
- There is a relevant English-language forum at Railways of Germany

