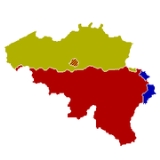
Languages of Belgium
Encyclopedia
The Kingdom of Belgium has three official languages: Dutch
, French
, and German
. A number of non-official, minority languages and dialects are spoken as well.
 Close to 60% of the country's population speaks Dutch as their primary (Belgian) language. Though the standard form of Dutch used in Belgium is almost identical to that spoken in the Netherlands and the different dialects spread across the border, it is often colloquially called "Flemish
Close to 60% of the country's population speaks Dutch as their primary (Belgian) language. Though the standard form of Dutch used in Belgium is almost identical to that spoken in the Netherlands and the different dialects spread across the border, it is often colloquially called "Flemish
".
Dutch is the official language of the Flemish Community
and the Flemish Region
(merged to Flanders
) and, along with French, an official language of the Brussels-Capital Region. The main Dutch dialects spoken in Belgium are Brabantian
, West Flemish
, East Flemish
, and Limburgish
. All these are spoken across the border in the Netherlands as well, and West Flemish is also spoken in French Flanders
(see French Flemish). Some sub-dialects may be quite distant from standard Dutch and not be readily intelligible for other Dutch-speakers. Words which are unique to Belgian Dutch are called belgicism
s (as are words used primarily in Belgian French
). The original Brabantian dialect of Brussels
has been very much influenced by French. It is now spoken by a minority in the city since the language of most inhabitants shifted during the Frenchification of Brussels
.
(which, like the Flemish Community, is a political entity), the dominant language in Wallonia (having also a small German-speaking Community
) as well as the Brussels-Capital Region. Almost all of the inhabitants of the Capital region speak French as either their primary language (50%) or as a lingua franca
(45%). There are also many Flemish people who speak French as a second language. Belgian French
is in most respects identical to standard, Parisian French, but differs in some points of vocabulary, pronunciation, and semantics.
in Belgium, spoken natively by less than 1% of the population. The German-speaking Community of Belgium
numbers 71,000, residing in an area of Belgium that was ceded by the former German Empire
as part of the Treaty of Versailles
, which concluded World War I
. In 1940, Nazi Germany
re-annexed the region following its invasion of Belgium during World War II
; after the war it was returned to Belgium.
In national politics, politicians can choose which of the three official languages they want to speak. In Belgian parliament simultaneous translation is available for those who require it.
Education is provided by the communities, Dutch in the Flemish Community
(Flanders and Brussels), French in the French Community
(Wallonia and Brussels), German in the German-speaking community
. Education in other languages is prohibited (except for foreign language subjects of course, and in higher education where English is increasingly used).
Also all official communication with the government (Tax papers, local politics, id/passport requests, building permits, ...) must be in the official language of the region or community. A few municipalities are granted an exception on these rules; see the municipalities with language facilities.
, the country's largest French-speaking university, published a report with the introduction (here translated): Within the report, professors in economics Ginsburgh
and Weber
further show that of the Brussels' residents, 95% declared they can speak French, 59% Dutch, and 41% know the non-local English. Of those under the age of forty, 59% in Flanders declared that they could speak all three, along with 10% in Wallonia and 28% in Brussels. In each region, Belgium's third official language, German, is notably less known than those.
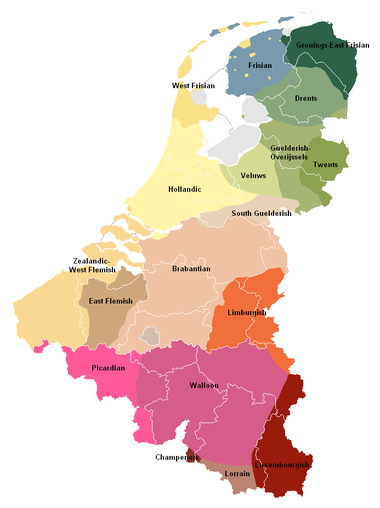
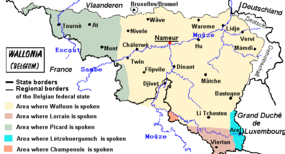 In addition to the three official languages, others are spoken in Belgium, like in Wallonia, where French became dominant only relatively recently. Sometimes seen as dialects, the varieties related to French are now recognised as separate languages by the French Community, however without taking any further measures to support those varieties.
In addition to the three official languages, others are spoken in Belgium, like in Wallonia, where French became dominant only relatively recently. Sometimes seen as dialects, the varieties related to French are now recognised as separate languages by the French Community, however without taking any further measures to support those varieties.
rather than a separate Flemish language. The main Dutch dialects in Belgium are Brabantian
, Limburgish, East Flemish
, and West Flemish
. Standard Dutch, as spoken in Belgium, is mostly influenced by Brabantian. There are literary traditions in both the East Flemish and West Flemish dialects.
, a dialect of French, is the historical language of southern Belgium, and most of the areas where French is now spoken were Walloon-speaking. It is also the traditional national language
of the Walloons
. Though it has been recognized, like other vernaculars in Belgium, since 1990, it is mainly spoken by older people, though younger Walloons may claim some knowledge. It is mainly used in rural regions, and is used in theaters and literature, though not in schools.
, was recognized by the government of the French Community in 1990. Picard has its core area in France, stretching into the western part of Wallonia.
, France, and a small part of Wallonia.
was recognized in 1990. It is mainly spoken in Gaume
, a part of Belgian Lorraine
.
is a Germanic
language or dialect in the north-east of the Belgian province of Liege, in the kernel area of the historical (and linguistically mixed) Duchy of Limburg
. It is spoken in towns and villages such as Plombières (Bleiberg)
, Gemmenich, Homburg
, Montzen and Welkenraedt
. By linguists, the variety is classified as a transition between Limburgish and Ripuarian. It has been defined as either varieties of Dutch or of German. Low Dietsch is acknowledged as an internal regional language by the Walloon authority since 1992. Low Dietsch is practically identical to the German dialect in the northern part of the neighbouring official German-speaking region of Belgium
. The different definition is due to the fact that the German-speaking region was annexed by Belgium in 1919, whereas the "Low Dietsch" area has been part of Belgium since 1830.
language formerly regarded as a variety of German, is native to Arelerland
, the eastern part of the Belgian province of Luxembourg
, including the city of Arlon (Arel). Here it has largely been replaced by Belgian French in recent decades, contrarily to its flourishing on the other side of the border, in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
. The language has since 1990 been recognised by the Walloon authorities as Francique (Franconian
).
, and similar Orthodox neighborhoods in the United States, London
, Paris
, Montreal
and Israel
).
(Riff language), Arabic (Maghrebi Arabic), Spanish
, Turkish
, Portuguese
, Italian
and Polish
.
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
, French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, and German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
. A number of non-official, minority languages and dialects are spoken as well.
Dutch

Flemish
Flemish can refer to anything related to Flanders, and may refer directly to the following articles:*Flemish, an informal, though linguistically incorrect, name of any kind of the Dutch language as spoken in Belgium....
".
Dutch is the official language of the Flemish Community
Flemish Community
The term Flemish Community has two distinct, though related, meanings:...
and the Flemish Region
Flemish Region
The Flemish Region is one of the three official regions of the Kingdom of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Colloquially, it is usually simply referred to as Flanders, of which it is the institutional iteration within the context of the Belgian political system...
(merged to Flanders
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
) and, along with French, an official language of the Brussels-Capital Region. The main Dutch dialects spoken in Belgium are Brabantian
Brabantian
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic , is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant which corresponded mainly to the Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgian provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant, as well as the institutional Region of...
, West Flemish
West Flemish
West Flemish , , , Fransch vlaemsch in French Flemish) is a group of dialects or regional language related to Dutch spoken in parts of the Netherlands, Belgium, and France....
, East Flemish
East Flemish
East Flemish is a group of dialects of the Dutch language, which is a Low Franconian language. It is spoken in the province of East Flanders in Belgium, but also spoken in Zeeuws-Vlaanderen in the Netherlands.-Brabantic Expansion:...
, and Limburgish
Limburgish language
Limburgish, also called Limburgian or Limburgic is a group of East Low Franconian language varieties spoken in the Limburg and Rhineland regions, near the common Dutch / Belgian / German border...
. All these are spoken across the border in the Netherlands as well, and West Flemish is also spoken in French Flanders
French Flanders
French Flanders is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France. The region today lies in the modern-day region of Nord-Pas de Calais, the department of Nord, and roughly corresponds to the arrondissements of Lille, Douai and Dunkirk on the Belgian border.-Geography:French...
(see French Flemish). Some sub-dialects may be quite distant from standard Dutch and not be readily intelligible for other Dutch-speakers. Words which are unique to Belgian Dutch are called belgicism
Belgicism
The word belgicism refers to a word, expression, or turn of phrase that is uniquely Belgian French, or Belgian Dutch...
s (as are words used primarily in Belgian French
Belgian French
Belgian French is the variety of French spoken mainly in the French Community of Belgium, alongside related minority regional languages such as Walloon, Picard, Champenois and Gaumais. The French spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, and Burundi, which were formerly Belgian...
). The original Brabantian dialect of Brussels
Brussels
Brussels , officially the Brussels Region or Brussels-Capital Region , is the capital of Belgium and the de facto capital of the European Union...
has been very much influenced by French. It is now spoken by a minority in the city since the language of most inhabitants shifted during the Frenchification of Brussels
Frenchification of Brussels
The Frenchification of Brussels is the transformation of Brussels, Belgium, from a Dutch-speaking city to one that is bilingual or even multilingual, with French as both the majority language and lingua franca...
.
French
The second-most spoken primary (Belgian) language, used natively by almost 40% of the population, is French. It is the official language of the French CommunityFrench Community of Belgium
The French Community of Belgium is one of the three official communities in Belgium along with the Flemish Community and the German speaking Community. Although its name could suggest that it is a community of French citizens in Belgium, it is not...
(which, like the Flemish Community, is a political entity), the dominant language in Wallonia (having also a small German-speaking Community
German-speaking Community of Belgium
The German-speaking Community of Belgium is one of the three federal communities of Belgium. Covering an area of 854 km² within the province of Liège in Wallonia, it includes nine of the eleven municipalities of the so-called East Cantons...
) as well as the Brussels-Capital Region. Almost all of the inhabitants of the Capital region speak French as either their primary language (50%) or as a lingua franca
Lingua franca
A lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
(45%). There are also many Flemish people who speak French as a second language. Belgian French
Belgian French
Belgian French is the variety of French spoken mainly in the French Community of Belgium, alongside related minority regional languages such as Walloon, Picard, Champenois and Gaumais. The French spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, and Burundi, which were formerly Belgian...
is in most respects identical to standard, Parisian French, but differs in some points of vocabulary, pronunciation, and semantics.
German
German is the least prevalent official languageOfficial language
An official language is a language that is given a special legal status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically a nation's official language will be the one used in that nation's courts, parliament and administration. However, official status can also be used to give a...
in Belgium, spoken natively by less than 1% of the population. The German-speaking Community of Belgium
German-speaking Community of Belgium
The German-speaking Community of Belgium is one of the three federal communities of Belgium. Covering an area of 854 km² within the province of Liège in Wallonia, it includes nine of the eleven municipalities of the so-called East Cantons...
numbers 71,000, residing in an area of Belgium that was ceded by the former German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
as part of the Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
, which concluded World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
. In 1940, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
re-annexed the region following its invasion of Belgium during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
; after the war it was returned to Belgium.
Official use of languages
In national politics, politicians can choose which of the three official languages they want to speak. In Belgian parliament simultaneous translation is available for those who require it.
Education is provided by the communities, Dutch in the Flemish Community
Flemish Community
The term Flemish Community has two distinct, though related, meanings:...
(Flanders and Brussels), French in the French Community
French Community of Belgium
The French Community of Belgium is one of the three official communities in Belgium along with the Flemish Community and the German speaking Community. Although its name could suggest that it is a community of French citizens in Belgium, it is not...
(Wallonia and Brussels), German in the German-speaking community
German-speaking Community of Belgium
The German-speaking Community of Belgium is one of the three federal communities of Belgium. Covering an area of 854 km² within the province of Liège in Wallonia, it includes nine of the eleven municipalities of the so-called East Cantons...
. Education in other languages is prohibited (except for foreign language subjects of course, and in higher education where English is increasingly used).
Also all official communication with the government (Tax papers, local politics, id/passport requests, building permits, ...) must be in the official language of the region or community. A few municipalities are granted an exception on these rules; see the municipalities with language facilities.
Multilingualism
In 2006, the Université Catholique de LouvainUniversité catholique de Louvain
The Université catholique de Louvain, sometimes known, especially in Belgium, as UCL, is Belgium's largest French-speaking university. It is located in Louvain-la-Neuve and in Brussels...
, the country's largest French-speaking university, published a report with the introduction (here translated): Within the report, professors in economics Ginsburgh
Victor Ginsburgh
Victor Alexandre Ginsburgh is a Belgian economist of Austrian origin.Ginsburgh studied at the Solvay Business School at the Free University of Brussels and mastered in econometrics. He holds a Ph.D. in economics, 1972. He is professor at Université Libre de Bruxelles since 1975...
and Weber
Shlomo Weber
Shlomo Weber is an Russian professor and economist.Weber earned a degree of Master of Science in mathematics from the Moscow State University in 1971. Eight years later at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem, Israel, he became a Doctor of Philosophy in mathematical economics...
further show that of the Brussels' residents, 95% declared they can speak French, 59% Dutch, and 41% know the non-local English. Of those under the age of forty, 59% in Flanders declared that they could speak all three, along with 10% in Wallonia and 28% in Brussels. In each region, Belgium's third official language, German, is notably less known than those.
Non-official languages


Flemish
Flanders too has a number of dialects, but linguists regard these as varieties of DutchDutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
rather than a separate Flemish language. The main Dutch dialects in Belgium are Brabantian
Brabantian
Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic , is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant which corresponded mainly to the Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgian provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant, as well as the institutional Region of...
, Limburgish, East Flemish
East Flemish
East Flemish is a group of dialects of the Dutch language, which is a Low Franconian language. It is spoken in the province of East Flanders in Belgium, but also spoken in Zeeuws-Vlaanderen in the Netherlands.-Brabantic Expansion:...
, and West Flemish
West Flemish
West Flemish , , , Fransch vlaemsch in French Flemish) is a group of dialects or regional language related to Dutch spoken in parts of the Netherlands, Belgium, and France....
. Standard Dutch, as spoken in Belgium, is mostly influenced by Brabantian. There are literary traditions in both the East Flemish and West Flemish dialects.
Walloon
WalloonWalloon language
Walloon is a Romance language which was spoken as a primary language in large portions of the Walloon Region of Belgium and some villages of Northern France until the middle of the 20th century. It belongs to the langue d'oïl language family, whose most prominent member is the French language...
, a dialect of French, is the historical language of southern Belgium, and most of the areas where French is now spoken were Walloon-speaking. It is also the traditional national language
National language
A national language is a language which has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a people and perhaps by extension the territory they occupy. The term is used variously. A national language may for instance represent the national identity of a nation or country...
of the Walloons
Walloons
Walloons are a French-speaking people who live in Belgium, principally in Wallonia. Walloons are a distinctive community within Belgium, important historical and anthropological criteria bind Walloons to the French people. More generally, the term also refers to the inhabitants of the Walloon...
. Though it has been recognized, like other vernaculars in Belgium, since 1990, it is mainly spoken by older people, though younger Walloons may claim some knowledge. It is mainly used in rural regions, and is used in theaters and literature, though not in schools.
Picard
Another dialect of French that is a traditional language of the region, PicardPicard language
Picard is a language closely related to French, and as such is one of the larger group of Romance languages. It is spoken in two regions in the far north of France – Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardy – and in parts of the Belgian region of Wallonia, the district of Tournai and a part of...
, was recognized by the government of the French Community in 1990. Picard has its core area in France, stretching into the western part of Wallonia.
Champenois
Champenois was also legally recognized in 1990. It is mainly spoken in ChampagneChampagne (province)
The Champagne wine region is a historic province within the Champagne administrative province in the northeast of France. The area is best known for the production of the sparkling white wine that bears the region's name...
, France, and a small part of Wallonia.
Lorrain
Like the other indigenous dialects of French, LorrainLorrain language
Lorrain is a language spoken by a minority of people in Lorraine in France and in Gaume in Belgium. It is one of the Langues d'oïl. It is classified as a regional language of France, and has the recognised status of a regional language of Wallonia...
was recognized in 1990. It is mainly spoken in Gaume
Gaume
Gaume is a region in the far south of Belgium. Situated at a lower altitude than the Ardennes, it is delineated by borders with France, Luxembourg and the Belgian Ardennes. Gaume is the roman part of the Belgian Lorraine region...
, a part of Belgian Lorraine
Belgian Lorraine
Belgian Lorraine is the part of Lorraine that lies in the south of the Belgian province of Luxembourg, part of Wallonia.The term is used in a geological context, bordering the Ardennes in the north...
.
Low Dietsch
Low DietschLow Dietsch
Low Dietsch is a term mainly used within the Flemish terminology for the transitional Limburgish–Ripuarian dialects of a number of towns and villages in the north-east of the Belgian province of Liege, such as Gemmenich, Homburg, Montzen and Welkenraedt....
is a Germanic
Germanic languages
The Germanic languages constitute a sub-branch of the Indo-European language family. The common ancestor of all of the languages in this branch is called Proto-Germanic , which was spoken in approximately the mid-1st millennium BC in Iron Age northern Europe...
language or dialect in the north-east of the Belgian province of Liege, in the kernel area of the historical (and linguistically mixed) Duchy of Limburg
Duchy of Limburg
The Duchy of Limburg, situated in the Low Countries between the river Meuse and the city of Aachen, was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. Its territory is now divided between the Belgian provinces of Liège and Limburg , the Dutch province of Limburg , and a small part of North Rhine-Westphalia in...
. It is spoken in towns and villages such as Plombières (Bleiberg)
Plombières
Plombières is a Walloon municipality located in the Belgian province of Liège. On January 1, 2006, Plombières had a total population of 9,672. The total area is 53.17 km² which gives a population density of 182 inhabitants per km². The municipality Plombières consists of the villages...
, Gemmenich, Homburg
Homburg
-In Germany:* Homburg, Saarland, capital of the Saarpfalz district of Saarland* Bad Homburg, town and spa in Hesse* Homburg Forest, a hill range in Lower Saxony* Homburg, a quarter of Triefenstein, Bavaria...
, Montzen and Welkenraedt
Welkenraedt
Welkenraedt is a Walloon municipality located in the province of Liège, Belgium. On January 1, 2006, Welkenraedt had a total population of 9,163. The total area is 24.47 km² which gives a population density of 374 inhabitants per km²....
. By linguists, the variety is classified as a transition between Limburgish and Ripuarian. It has been defined as either varieties of Dutch or of German. Low Dietsch is acknowledged as an internal regional language by the Walloon authority since 1992. Low Dietsch is practically identical to the German dialect in the northern part of the neighbouring official German-speaking region of Belgium
German-speaking Community of Belgium
The German-speaking Community of Belgium is one of the three federal communities of Belgium. Covering an area of 854 km² within the province of Liège in Wallonia, it includes nine of the eleven municipalities of the so-called East Cantons...
. The different definition is due to the fact that the German-speaking region was annexed by Belgium in 1919, whereas the "Low Dietsch" area has been part of Belgium since 1830.
Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish, a Moselle FranconianMoselle Franconian
Moselle Franconian is a group of West Central German dialects, part of the Central Franconian language area.It is spoken in the southern Rhineland and along the course of the Moselle River, from the Siegerland in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia throughout western Rhineland-Palatinate and...
language formerly regarded as a variety of German, is native to Arelerland
Arelerland
The Land of Arlon is the traditionally Luxembourgish-speaking part of Belgian Lorraine, but now predominantly French-speaking. Arlon is the main city of this region....
, the eastern part of the Belgian province of Luxembourg
Luxembourg (Belgium)
Luxembourg is the southernmost province of Wallonia and of Belgium. It borders on the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, France, and the Belgian provinces of Namur and Liège. Its capital is Arlon, in the south-east of the province.It has an area of 4,443 km², making it the largest Belgian province...
, including the city of Arlon (Arel). Here it has largely been replaced by Belgian French in recent decades, contrarily to its flourishing on the other side of the border, in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
. The language has since 1990 been recognised by the Walloon authorities as Francique (Franconian
Franconian
Franconian may refer to:*anything related to Franconia , a historic region in Germany, now part of Bavaria, Thuringia and Baden-Württemberg*Franconian languages*Franconian , a stage in North American stratigraphy...
).
Yiddish
Yiddish is spoken by the 20,000 Orthodox Jews living in Antwerp. The community there is among the strongest in Europe, and one of the few Jewish communities worldwide in which Yiddish remains the dominant language (others include Kiryas Joel, New YorkKiryas Joel, New York
Kiryas Joel is a village within the town of Monroe in Orange County, New York, United States...
, and similar Orthodox neighborhoods in the United States, London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
, Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
, Montreal
Montreal
Montreal is a city in Canada. It is the largest city in the province of Quebec, the second-largest city in Canada and the seventh largest in North America...
and Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
).
Other minority and foreign languages
Languages spoken by immigrants from recent decades and their descendants include BerberBerber languages
The Berber languages are a family of languages indigenous to North Africa, spoken from Siwa Oasis in Egypt to Morocco , and south to the countries of the Sahara Desert...
(Riff language), Arabic (Maghrebi Arabic), Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, Turkish
Turkish language
Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,...
, Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
, Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
and Polish
Polish language
Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries...
.

