
Lambert conformal conic projection
Encyclopedia
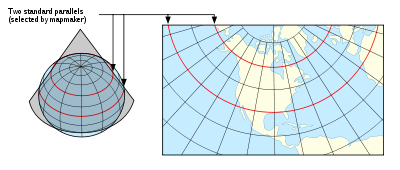
Conic section
In mathematics, a conic section is a curve obtained by intersecting a cone with a plane. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of degree 2...
map projection
Map projection
A map projection is any method of representing the surface of a sphere or other three-dimensional body on a plane. Map projections are necessary for creating maps. All map projections distort the surface in some fashion...
, which is often used for aeronautical chart
Aeronautical chart
An aeronautical chart is a map designed to assist in navigation of aircraft, much as nautical charts do for watercraft, or a roadmap for drivers...
s. In essence, the projection superimposes a cone
Cone (geometry)
A cone is an n-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a base to a point called the apex or vertex. Formally, it is the solid figure formed by the locus of all straight line segments that join the apex to the base...
over the sphere of the Earth, with two reference parallel
Circle of latitude
A circle of latitude, on the Earth, is an imaginary east-west circle connecting all locations that share a given latitude...
s secant
Secant line
A secant line of a curve is a line that intersects two points on the curve. The word secant comes from the Latin secare, to cut.It can be used to approximate the tangent to a curve, at some point P...
to the globe and intersecting it. This minimizes distortion from projecting a three dimensional surface to a two-dimensional surface. There is no distortion along the standard parallels, but distortion increases further from the chosen parallels. As the name indicates, maps using this projection are conformal
Conformal map
In mathematics, a conformal map is a function which preserves angles. In the most common case the function is between domains in the complex plane.More formally, a map,...
.
Pilot
Aviator
An aviator is a person who flies an aircraft. The first recorded use of the term was in 1887, as a variation of 'aviation', from the Latin avis , coined in 1863 by G. de la Landelle in Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne...
s favor these charts because a straight line drawn on a Lambert conformal conic projection approximates a great-circle
Great circle
A great circle, also known as a Riemannian circle, of a sphere is the intersection of the sphere and a plane which passes through the center point of the sphere, as opposed to a general circle of a sphere where the plane is not required to pass through the center...
route between endpoints. The European Environment Agency
European Environment Agency
European Environment Agency is an agency of the European Union. Its task is to provide sound, independent information on the environment. It is a major information source for those involved in developing, adopting, implementing and evaluating environmental policy, and also the general public...
recommends its usage for conformal pan-European mapping at scales smaller or equal to 1:500,000.
In the United States, the National Geodetic Survey's "State Plane Coordinate System
State Plane Coordinate System
The State Plane Coordinate System is a set of 124 geographic zones or coordinate systems designed for specific regions of the United States. Each state contains one or more state plane zones, the boundaries of which usually follow county lines...
of 1983" uses Lambert Conformal Conic Projection to define the grid-coordinate systems used in several States (primarily those that are elongated west to east, like Tennessee). The Lambert projection is relatively easy to use: conversions from Geodetic (latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
/longitude
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
) to State Plane Grid coordinates involve trigonometric equations that are fairly straightforward and which can be solved on most scientific calculators, especially programmable models
. Lambert projection as used in CCS83 produces maps in which scale errors produced by the inherent distortion are limited to 1 part in 10,000.
History
The Lambert conformal conic is one of several map projection systems developed by Johann Heinrich LambertJohann Heinrich Lambert
Johann Heinrich Lambert was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, philosopher and astronomer.Asteroid 187 Lamberta was named in his honour.-Biography:...
, an 18th century Swiss mathematician, physicist, philosopher, and astronomer.
Transformation
Coordinates from a spherical datum can be transformed into Lambert conformal conic projection coordinates with the following formulas, where λ is the longitude, λ0 the reference longitude, φ the latitude, φ0 the reference latitude, and φ1 and φ2 the standard parallels: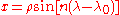
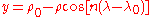
where
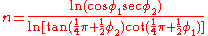
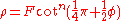
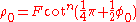

Formulæ for ellipsoidal datums are more involved.
See also
- Albers projectionAlbers projectionThe Albers equal-area conic projection, or Albers projection , is a conic, equal areamap projection that uses two standard parallels. Although scale and shape are not preserved, distortion is minimal between the standard parallels.The Albers projection is the standard projection for British Columbia...
- Lambert cylindrical equal-area projectionLambert cylindrical equal-area projectionIn cartography, the Lambert cylindrical equal-area projection, or Lambert cylindrical projection, is acylindrical, equal area map projection...
- Lambert azimuthal equal-area projectionLambert azimuthal equal-area projectionThe Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection is a particular mapping from a sphere to a disk . It accurately represents area in all regions of the sphere, but it does not accurately represent angles...
- Johann Heinrich LambertJohann Heinrich LambertJohann Heinrich Lambert was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, philosopher and astronomer.Asteroid 187 Lamberta was named in his honour.-Biography:...
External links
- Table of examples and properties of all common projections, from radicalcartography.net
- An interactive Java Applet to study the metric deformations of the Lambert Conformal Conic Projection
- This document from the U.S. National Geodetic Survey describes the State Plane Coordinate System of 1983, including details on the equations used to perform the Lambert Conformal Conic and Mercator map projections of CCS83
- Lambert Conformal Conic to Geographic Transformation Formulae from Land Information New Zealand

