
Karakalpak language
Encyclopedia
Karakalpak is a Turkic language mainly spoken by Karakalpaks
in Karakalpakstan (Uzbekistan
), as well as by Bashkirs and Nogay. Ethnic Karakalpaks who live in the viloyatlar of Uzbekistan
tend to speak local Uzbek dialects.
Turkic family of languages, which includes Tatar
, Kumyk
and Kazakh
. The Kipchak family is a subgroup of the Turkic languages
. Within the Kypchak Turkic family, Karakalpak is most closely related to Kazakh
and Nogai
. Due to its proximity to the Uzbek language
areal, much of the vocabulary and grammar has an Uzbek influence. Like Finnish, Hungarian
, and Turkish
, Karakalpak has vowel harmony
, is agglutinative
and has no grammatical gender
. Word order is usually subject–object–verb.
. Approximately 2,000 people in Afghanistan
speak Karakalpak and smaller diaspora in other parts of Russia
, Kazakhstan
, Turkey
, and other parts of the world speak Karakalpak as well. Some people hold that the Karakalpak language is in fact merely a dialect of the Kazakh language with some minor local vocabulary; this is allegedly due to Stalin's policies of mixing the ethnic groups of Central Asia to ensure they could not unite and revolt against the Russians (another example is the large Uzbek minority in the Khojend region of Tajikistan).
identifies two dialects of Karakalpak: Northeastern and Southwestern. Menges mentions a third possible dialect spoken in the Fergana Valley
. The Southwestern dialect has č for the Northeastern š.
functions in Karakalpak much as it does in other Turkic languages. Words borrowed from Russian
or other languages may not observe rules of vowel harmony, but the following rules usually apply:
and in Persian until 1928, in the Latin alphabet
(with additional characters) from 1928 to 1940, after which the Cyrillic alphabet
was introduced. Following Uzbekistan's independence in 1991, the decision was made to drop Cyrillic and to revert to the Latin alphabet. Whilst the use of Latin script is now widespread in Tashkent
, its introduction into Karakalpakstan remains gradual. The Cyrillic and Latin alphabets are shown below with their equivalent representations in the IPA. Cyrillic letters with no representation in the Latin alphabet are marked with asterisks.

Karakalpaks
The Karakalpaks are a Turkic speaking people. They mainly live in the lower reaches of the Amu Darya and in the delta of Amu Darya on the southern shore of the Aral Sea in Uzbekistan. The name "Karakalpak" comes from two words: "qara" meaning black, and "qalpaq" meaning hat...
in Karakalpakstan (Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan , officially the Republic of Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia and one of the six independent Turkic states. It shares borders with Kazakhstan to the west and to the north, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan to the east, and Afghanistan and Turkmenistan to the south....
), as well as by Bashkirs and Nogay. Ethnic Karakalpaks who live in the viloyatlar of Uzbekistan
Provinces of Uzbekistan
|Uzbekistan is divided into 12 provinces , 1 autonomous republic , and 1 independent city |Uzbekistan is divided into 12 provinces (viloyatlar, singular viloyat, viloyati in compound, e.g. Toshkent viloyati, Samarqand viloyati), 1 autonomous republic (respublika, respublikasi in compound, e.g....
tend to speak local Uzbek dialects.
Classification
Karakalpak is a member of the KypchakKypchak languages
The Kypchak languages , are a major branch of the Turkic language family spoken by more than 12 million people in an area spanning from Lithuania to China....
Turkic family of languages, which includes Tatar
Tatar language
The Tatar language , or more specifically Kazan Tatar, is a Turkic language spoken by the Tatars of historical Kazan Khanate, including modern Tatarstan and Bashkiria...
, Kumyk
Kumyk language
Kumyk is a Turkic language, spoken by about 365,000 speakers in the Dagestan republic of Russian Federation....
and Kazakh
Kazakh language
Kazakh is a Turkic language which belongs to the Kipchak branch of the Turkic languages, closely related to Nogai and Karakalpak....
. The Kipchak family is a subgroup of the Turkic languages
Turkic languages
The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
. Within the Kypchak Turkic family, Karakalpak is most closely related to Kazakh
Kazakh language
Kazakh is a Turkic language which belongs to the Kipchak branch of the Turkic languages, closely related to Nogai and Karakalpak....
and Nogai
Nogai language
Nogai , is a Turkic language spoken in southwestern Russia. Three distinct dialects are recognized: Qara-Nogay , spoken in Dagestan; Nogai Proper, in Stavropol; and Aqnogay , by the Kuban River, its tributaries in Karachay-Cherkessia, and in the Mineralnye Vody District...
. Due to its proximity to the Uzbek language
Uzbek language
Uzbek is a Turkic language and the official language of Uzbekistan. It has about 25.5 million native speakers, and it is spoken by the Uzbeks in Uzbekistan and elsewhere in Central Asia...
areal, much of the vocabulary and grammar has an Uzbek influence. Like Finnish, Hungarian
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
, and Turkish
Turkish language
Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,...
, Karakalpak has vowel harmony
Vowel harmony
Vowel harmony is a type of long-distance assimilatory phonological process involving vowels that occurs in some languages. In languages with vowel harmony, there are constraints on which vowels may be found near each other....
, is agglutinative
Agglutinative language
An agglutinative language is a language that uses agglutination extensively: most words are formed by joining morphemes together. This term was introduced by Wilhelm von Humboldt in 1836 to classify languages from a morphological point of view...
and has no grammatical gender
Grammatical gender
Grammatical gender is defined linguistically as a system of classes of nouns which trigger specific types of inflections in associated words, such as adjectives, verbs and others. For a system of noun classes to be a gender system, every noun must belong to one of the classes and there should be...
. Word order is usually subject–object–verb.
Geographic Distribution
Karakalpak is spoken mainly in the Karakalpakstan Autonomous Republic of UzbekistanUzbekistan
Uzbekistan , officially the Republic of Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia and one of the six independent Turkic states. It shares borders with Kazakhstan to the west and to the north, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan to the east, and Afghanistan and Turkmenistan to the south....
. Approximately 2,000 people in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
speak Karakalpak and smaller diaspora in other parts of Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan , officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Ranked as the ninth largest country in the world, it is also the world's largest landlocked country; its territory of is greater than Western Europe...
, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, and other parts of the world speak Karakalpak as well. Some people hold that the Karakalpak language is in fact merely a dialect of the Kazakh language with some minor local vocabulary; this is allegedly due to Stalin's policies of mixing the ethnic groups of Central Asia to ensure they could not unite and revolt against the Russians (another example is the large Uzbek minority in the Khojend region of Tajikistan).
Dialects
The EthnologueEthnologue
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is a web and print publication of SIL International , a Christian linguistic service organization, which studies lesser-known languages, to provide the speakers with Bibles in their native language and support their efforts in language development.The Ethnologue...
identifies two dialects of Karakalpak: Northeastern and Southwestern. Menges mentions a third possible dialect spoken in the Fergana Valley
Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley or Farghana Valley is a region in Central Asia spreading across eastern Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. Divided across three subdivisions of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse, and in the early 21st century was the scene of ethnic conflict...
. The Southwestern dialect has č for the Northeastern š.
Sounds
Karakalpak has 21 native consonant phonemes and regularly uses 4 non-native phonemes in loan words. Non-native sounds are shown in parentheses.
| Labial Labial consonant Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals... |
Alveolar Alveolar consonant Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth... |
Palatal Palatal consonant Palatal consonants are consonants articulated with the body of the tongue raised against the hard palate... |
Velar Velar consonant Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum).... |
Uvular Uvular consonant Uvulars are consonants articulated with the back of the tongue against or near the uvula, that is, further back in the mouth than velar consonants. Uvulars may be plosives, fricatives, nasal stops, trills, or approximants, though the IPA does not provide a separate symbol for the approximant, and... |
Glottal Glottal consonant Glottal consonants, also called laryngeal consonants, are consonants articulated with the glottis. Many phoneticians consider them, or at least the so-called fricative, to be transitional states of the glottis without a point of articulation as other consonants have; in fact, some do not consider... |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal Nasal consonant A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :... |
m | n | ŋ | |||||||||
| Plosive | p | b | t | d | k | ɡ | q | |||||
| Affricate Affricate consonant Affricates are consonants that begin as stops but release as a fricative rather than directly into the following vowel.- Samples :... |
(t͡s) | (t͡ʃ) | ||||||||||
| Fricative Fricative consonant Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate, in the case of German , the final consonant of Bach; or... |
(f) | (v) | s | z | ʃ | ʒ | x | ɣ | h | |||
| Rhotic Rhotic consonant In phonetics, rhotic consonants, also called tremulants or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho, including "R, r" from the Roman alphabet and "Р, p" from the Cyrillic alphabet... |
r | |||||||||||
| Approximant Approximant consonant Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough or with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a turbulent airstream, and vowels, which produce no... |
l | j | w | |||||||||
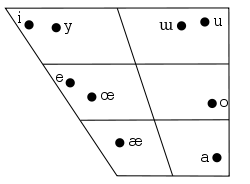
Vowel Harmony
Vowel harmonyVowel harmony
Vowel harmony is a type of long-distance assimilatory phonological process involving vowels that occurs in some languages. In languages with vowel harmony, there are constraints on which vowels may be found near each other....
functions in Karakalpak much as it does in other Turkic languages. Words borrowed from Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
or other languages may not observe rules of vowel harmony, but the following rules usually apply:
| Vowel | May be followed by: |
|---|---|
| a | a, ɯ |
| æ | e, i |
| e | e, i |
| i | e, i |
| o | a, o, u, ɯ |
| œ | e, i, œ, y |
| u | a, o, u |
| y | e, œ, y |
| ɯ | a, ɯ |
Personal Pronouns
men I, sen you (singular), ol he, she, it, that, biz we, siz you (plural), olar theyNumbers
bir 1, eki 2, u'sh 3, to'rt 4, bes 5, altı 6, jeti 7, segiz 8, tog'ıs 9, on 10, ju'z 100, mın 1000Writing system
Karakalpak was written in the Arabic alphabetArabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
and in Persian until 1928, in the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
(with additional characters) from 1928 to 1940, after which the Cyrillic alphabet
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
was introduced. Following Uzbekistan's independence in 1991, the decision was made to drop Cyrillic and to revert to the Latin alphabet. Whilst the use of Latin script is now widespread in Tashkent
Tashkent
Tashkent is the capital of Uzbekistan and of the Tashkent Province. The officially registered population of the city in 2008 was about 2.2 million. Unofficial sources estimate the actual population may be as much as 4.45 million.-Early Islamic History:...
, its introduction into Karakalpakstan remains gradual. The Cyrillic and Latin alphabets are shown below with their equivalent representations in the IPA. Cyrillic letters with no representation in the Latin alphabet are marked with asterisks.
| Cyrillic | Latin | IPA | Cyrillic | Latin | IPA | Cyrillic | Latin | IPA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Аа | Aa | /a/ | Ққ | /q/ | Фф | Ff | /f/ | |||
| Әә | A'a' | /æ/ | Лл | Ll | /l/ | Хх | Xx | /x/ | ||
| Бб | Bb | /b/ | Мм | Mm | /m/ | Ҳҳ | Hh | /h/ | ||
| Вв | Vv | /v/ | Нн | Nn | /n/ | Цц* | ts | /ts/ | ||
| Гг | Gg | /ɡ/ | Ңң | N'n' | /ŋ/ | Чч* | ch | /tʃ/ | ||
| Ғғ | G'g' | /ɣ/ | Оо | Oo | /o/ | Шш | SHsh | /ʃ/ | ||
| Дд | Dd | /d/ | Өө | O'o' | /œ/ | Щщ* | sh | /ʃ/ | ||
| Ее | Ee | /e/ | Пп | Pp | /p/ | Ъъ* | ||||
| Ёё* | yo | /jo/ | Рр | Rr | /r/ | Ыы | Iı | /ɯ/ | ||
| Жж | Jj | /ʒ/ | Сс | Ss | /s/ | Ьь* | ||||
| Зз | Zz | /z/ | Тт | Tt | /t/ | Ээ | Ee | /e/ | ||
| Ии | İi | /i/ | Уу | Uu | /u/ | Юю* | yu | /ju/ | ||
| Йй | Yy | /j/ | Үү | U'u' | /y/ | Яя | ya | /ja/ | ||
| Кк | Kk | /k/ | Ўў | Ww | /w/ |


