
Junior Certificate
Encyclopedia
The Junior Certificate is an educational qualification awarded in Ireland
by the Department of Education to students who have successfully completed the junior cycle of secondary education, and achieved a minimum standard in their Junior Cert. examinations. These exams, like those for the Leaving Certificate
, are supervised by the State Examinations Commission
.
A "recognised pupil"Definitions, Rules and Programme for Secondary Education, Department of Education, Ireland, 2004 who commences the Junior Cycle must reach at least 12 years of age on January 1 of the school year of admission and must have completed primary education; the examination is normally taken after three years' study in a secondary school
. Typically a student takes 9 to 12 subjects – including English, Irish and Mathematics – as part of the Junior Cycle. The examination does not reach the standards for college
or university
entrance; instead a school leaver in Ireland will typically take the Leaving Certificate Examination two or three years after completion of the Junior Certificate in order to reach that standard.
The objective of the Junior Cycle is:
The 2011 Junior Certificate started on 8 June and finished on 24 June 2011.
The 2012 Junior Cerificate will begin on 6 June.
 Near the end of the decade, in 1999, the Department of Education and Science began to replace many subject curricula, particularly those that were dated, such as History
Near the end of the decade, in 1999, the Department of Education and Science began to replace many subject curricula, particularly those that were dated, such as History
and Geography
. In 1999, Civic, Social, and Political Education
was introduced as a subject, and made mandatory from 2000, when Religious Education was also brought in. Religion was phased in with just a few schools adopting it in its first year, many but not all still do the exam for Junior Cert, whilst CSPE was implemented nationwide. In 2002 a new Science course was introduced. The new course emphasised greater class participation and introduced the awarding of a percentage of marks for class practicals throughout the three years. However, many teachers complained about a lack of information from the Department about this change. Sample papers were not released until early 2006, the year when the new exam would be sat for the first time. Also, some schools complained that they did not have the laboratory facilities to do the new course but were forced to teach it anyway.
In 2004, results were made available on the Internet for the first time, thus allowing students who, for instance, had moved school or left school to get their results without having to return to their old school.
 The Junior Cycle is the first three years of second-level education. In the final year of the course, teachers allocate a substantial amount of time for revision of key topics. Candidates also practice answering questions which appeared on previous examination papers. Courses are quite broad - for example the Business Studies
The Junior Cycle is the first three years of second-level education. In the final year of the course, teachers allocate a substantial amount of time for revision of key topics. Candidates also practice answering questions which appeared on previous examination papers. Courses are quite broad - for example the Business Studies
course covers business organisation
, marketing
, economics
, accounting and several other areas. The same is also true for the Science course, which covers basic physics
, chemistry
and biology
. The Leaving Cert exam by comparison is much more specific.
A "recognised junior pupil" must undertake all the mandatory subjects and at least two of the optional subjects, except insofar as exemptions or exclusions apply. In certain types of schools, subjects in the optional grouping (or a selection from combinations of them) may in fact be mandatory, for instance History and Geography are mandatory in certain types of schools. Most schools do not offer all the optional subjects, but must offer all the mandatory and certain optional subjects.
†An exemption from taking Irish may be awarded in some cases, for students with dyslexia and who moved to the Republic Of Ireland after the age 10.
‡Classical Studies can not be taken by a student who is also taking Greek or Latin.
, then the other main subjects and finish with the subjects that have the fewest candidates. The exams can take the form of written papers, aurals, orals, practicals and marks from course work assignments (such as in CSPE, where 60% of the exam rests on an action project). Exams are usually 2 to 3 hours long; most subjects are one paper only (i.e. they are taken in a single session), however 4 subjects have two papers at higher level - Irish, English, Mathematics and Business Studies. Candidates are permitted to leave the exam hall after 30 minutes have passed, up until the last 10 minutes of the examination.
The level taken at Junior Certificate has bearing on the level taken in the Leaving Certificate; thus for instance a student could take an Ordinary level in the Junior Certificate and then could not take a Higher level in the corresponding Leaving Certificate subject, later.
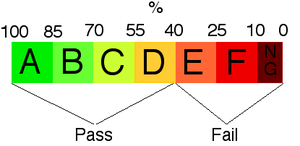 A mark below 10% receives no grade. Above this, there are six ranges of 15%, from F up to A. Grades A, B, C and D are passing grades, E and F are failing grades; therefore, the pass mark for the Junior Cert is 40%.
A mark below 10% receives no grade. Above this, there are six ranges of 15%, from F up to A. Grades A, B, C and D are passing grades, E and F are failing grades; therefore, the pass mark for the Junior Cert is 40%.
) results take centre place in the Irish media during the week surrounding their release. The newspapers publish various statistics about the exam and cover high achievers (some receive ten or more "A" grades). Schools generally give students (who have received their results) the day off and disco
s especially for the teenagers are organised in most cities and towns.
32 per exam) and the principal of the school writes a letter of appeal application to the State Examinations Commission, stating the candidate's name, exam number and the exam they would like to appeal. There is a deadline to appeal, usually 14–21 days after the results are published, in which the student's application must be made. The appeal results are usually handed out mid-November. The grade that is received this time is final, and no more appeals can be made. If the candidate's grade did not change, no further action will be taken. However, if a change did occur, then the candidate will be refunded the appeal fee via a Cheque
made out to the principal of the school. These refunds take time to be issued, but in an appeal made in September 2005 the refund was issued as late as March 2006.
- the requirement for college entry in Ireland. A new type of Leaving Certificate, the Leaving Certificate Applied has been designed to discourage people from dropping out. This is all practical work and students may work after school or do an apprenticeship, respectively.
The vast majority of students continue from lower level to senior level, with only 12.3% leaving after the Junior Certificate. This is lower than the EU average of 15.2%.
and is intended to make the senior cycle a three year programme encompassing both Transition Year and Leaving Certificate
. The idea of such a year is strange in other countries, as they don't have the same year. Transition Year was created as a result of the Programme for Economic and Social Progress which called for a six-year cycle of post-primary education.
Republic of Ireland
Ireland , described as the Republic of Ireland , is a sovereign state in Europe occupying approximately five-sixths of the island of the same name. Its capital is Dublin. Ireland, which had a population of 4.58 million in 2011, is a constitutional republic governed as a parliamentary democracy,...
by the Department of Education to students who have successfully completed the junior cycle of secondary education, and achieved a minimum standard in their Junior Cert. examinations. These exams, like those for the Leaving Certificate
Leaving Certificate
The Leaving Certificate Examinations , commonly referred to as the Leaving Cert is the final examination in the Irish secondary school system. It takes a minimum of two years preparation, but an optional Transition Year means that for those students it takes place three years after the Junior...
, are supervised by the State Examinations Commission
State Examinations Commission
The State Examinations Commission is the organisation that replaced the Department of Education and Science, Examinations Branch of the Minister for Education and Science in the Republic of Ireland...
.
A "recognised pupil"Definitions, Rules and Programme for Secondary Education, Department of Education, Ireland, 2004 who commences the Junior Cycle must reach at least 12 years of age on January 1 of the school year of admission and must have completed primary education; the examination is normally taken after three years' study in a secondary school
Secondary school
Secondary school is a term used to describe an educational institution where the final stage of schooling, known as secondary education and usually compulsory up to a specified age, takes place...
. Typically a student takes 9 to 12 subjects – including English, Irish and Mathematics – as part of the Junior Cycle. The examination does not reach the standards for college
College
A college is an educational institution or a constituent part of an educational institution. Usage varies in English-speaking nations...
or university
University
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees in a variety of subjects. A university is an organisation that provides both undergraduate education and postgraduate education...
entrance; instead a school leaver in Ireland will typically take the Leaving Certificate Examination two or three years after completion of the Junior Certificate in order to reach that standard.
The objective of the Junior Cycle is:
- ...to provide a well-balanced, general education suitable for pupils who leave full-time education at the end of compulsory schooling or, alternatively, who wish to enter on more advanced courses of study.
The 2011 Junior Certificate started on 8 June and finished on 24 June 2011.
The 2012 Junior Cerificate will begin on 6 June.
History
The Junior Certificate officially replaced the Day Vocational (Group) Certificate ("Day Cert" or "Group Cert") and the Intermediate Certificate ("Inter Cert") in 1992 when the first Junior Cert examinations were held; instruction in the new course had commenced in September 1989. The new, modern course was acclaimed as it was much more flexible than its predecessors. The Junior Certificate quickly became the minimum requirement for getting a job in Ireland.
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
and Geography
Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
. In 1999, Civic, Social, and Political Education
Civic, Social and Political Education
Civic, Social and Political Education is one of the compulsory subjects in the Junior Certificate course in the Ireland.-Further Details:*CSPE is a common level subject unlike other subjects in the curriculum...
was introduced as a subject, and made mandatory from 2000, when Religious Education was also brought in. Religion was phased in with just a few schools adopting it in its first year, many but not all still do the exam for Junior Cert, whilst CSPE was implemented nationwide. In 2002 a new Science course was introduced. The new course emphasised greater class participation and introduced the awarding of a percentage of marks for class practicals throughout the three years. However, many teachers complained about a lack of information from the Department about this change. Sample papers were not released until early 2006, the year when the new exam would be sat for the first time. Also, some schools complained that they did not have the laboratory facilities to do the new course but were forced to teach it anyway.
In 2004, results were made available on the Internet for the first time, thus allowing students who, for instance, had moved school or left school to get their results without having to return to their old school.
The Junior Cycle

Business studies
Business studies is an academic subject taught at higher level in Australia, Canada, Hong Kong, India, Ireland, New Zealand, Pakistan, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Zimbabwe and the United Kingdom, as well as at university level in many countries...
course covers business organisation
Management
Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively...
, marketing
Marketing
Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
, economics
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, accounting and several other areas. The same is also true for the Science course, which covers basic physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
and biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
. The Leaving Cert exam by comparison is much more specific.
A "recognised junior pupil" must undertake all the mandatory subjects and at least two of the optional subjects, except insofar as exemptions or exclusions apply. In certain types of schools, subjects in the optional grouping (or a selection from combinations of them) may in fact be mandatory, for instance History and Geography are mandatory in certain types of schools. Most schools do not offer all the optional subjects, but must offer all the mandatory and certain optional subjects.
Mandatory subjects
- IrishIrish languageIrish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
† (Higher, Ordinary and Foundation) - EnglishEnglish languageEnglish is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
(Higher, Ordinary and Foundation) - MathematicsMathematicsMathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
(Higher, Ordinary and Foundation) - Civic, Social and Political EducationCivic, Social and Political EducationCivic, Social and Political Education is one of the compulsory subjects in the Junior Certificate course in the Ireland.-Further Details:*CSPE is a common level subject unlike other subjects in the curriculum...
(CSPE) (Common Level only) - Social, Personal and Health EducationPersonal, Social and Health EducationPersonal, social, health and economic education has in various forms been part of the national curriculum for schools in England since 2000. Some aspects, but not all, have been compulsory...
(SPHE) (not examined) - Physical EducationPhysical educationPhysical education or gymnastics is a course taken during primary and secondary education that encourages psychomotor learning in a play or movement exploration setting....
(PE) (not examined) - Students must also take a minimum of one modern language such as: French, German, Spanish or Italian
†An exemption from taking Irish may be awarded in some cases, for students with dyslexia and who moved to the Republic Of Ireland after the age 10.
Optional subjects
All subjects are offered at Ordinary and Higher Level.(excluding CSPE which is examined at a common level)Arts and Humanities
- Ancient GreekAncient GreekAncient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
‡ - Art, Craft & DesignArtArt is the product or process of deliberately arranging items in a way that influences and affects one or more of the senses, emotions, and intellect....
- Classical Studies‡
- HistoryHistoryHistory is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
- LatinLatinLatin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
‡ - Music (Listening, Composing & General Study)MusicMusic is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
- Religious EducationReligious educationIn secular usage, religious education is the teaching of a particular religion and its varied aspects —its beliefs, doctrines, rituals, customs, rites, and personal roles...
‡Classical Studies can not be taken by a student who is also taking Greek or Latin.
Modern languages
- FrenchFrench languageFrench is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
- GermanGerman languageGerman is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
- ItalianItalian languageItalian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
- SpanishSpanish languageSpanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
Sciences
- Environmental and Social StudiesEnvironmental and Social StudiesEnvironmental and Social Studies is a subject area in the Junior Certificate examination, an Irish secondary school test. Introduced with the "new" Junior Certificate examination, ESS is an integrated subject comprising history, geography, and elements of civics, town planning, cartography and...
- GeographyGeographyGeography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
- Home EconomicsHome Economics (Junior Cert)Home Economics is a subject taught in the Junior Certificate course in the Republic of Ireland, Northern Ireland and Libya. The course is similar to other Home Economics courses but with some differences. The subject is generally optional and many of its participants are female...
- ScienceScienceScience is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
Applied Sciences
- Materials Technology (Wood)WoodworkingWoodworking is the process of building, making or carving something using wood.-History:Along with stone, mud, and animal parts, wood was one of the first materials worked by early humans. Microwear analysis of the Mousterian stone tools used by the Neanderthals show that many were used to work wood...
- Metalwork (Materials & Technology)MetalworkingMetalworking is the process of working with metals to create individual parts, assemblies, or large scale structures. The term covers a wide range of work from large ships and bridges to precise engine parts and delicate jewelry. It therefore includes a correspondingly wide range of skills,...
- Technical GraphicsTechnical drawingTechnical drawing, also known as drafting or draughting, is the act and discipline of composing plans that visually communicate how something functions or has to be constructed.Drafting is the language of industry....
- TechnologyTechnologyTechnology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
The examination
The final examination takes place after 3 years of the course, in early June. The exams always start with EnglishEnglish studies
English studies is an academic discipline that includes the study of literatures written in the English language , English linguistics English studies is an academic discipline that includes the study of literatures written in the English language (including literatures from the U.K., U.S.,...
, then the other main subjects and finish with the subjects that have the fewest candidates. The exams can take the form of written papers, aurals, orals, practicals and marks from course work assignments (such as in CSPE, where 60% of the exam rests on an action project). Exams are usually 2 to 3 hours long; most subjects are one paper only (i.e. they are taken in a single session), however 4 subjects have two papers at higher level - Irish, English, Mathematics and Business Studies. Candidates are permitted to leave the exam hall after 30 minutes have passed, up until the last 10 minutes of the examination.
Levels
At the Junior Certificate, students can take an examination subject at one of four levels. These are:- Higher Level (IrishIrish languageIrish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
: Ardleibhéal; sometimes called "Honours") – available in all subjects except CSPE. - Ordinary Level (IrishIrish languageIrish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
: Gnáthleibhéal; sometimes called "Pass") – an easier course than Higher Level; available in all subjects except CSPE. - Foundation Level (IrishIrish languageIrish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
: Bonnleibhéal) – an easier course than Ordinary Level; available only in EnglishEnglish languageEnglish is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, IrishIrish languageIrish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
and MathematicsMathematicsMathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
). - Common Level (IrishIrish languageIrish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
: Leibhéal Comónta) – available only in CSPECivic, Social and Political EducationCivic, Social and Political Education is one of the compulsory subjects in the Junior Certificate course in the Ireland.-Further Details:*CSPE is a common level subject unlike other subjects in the curriculum...
.
The level taken at Junior Certificate has bearing on the level taken in the Leaving Certificate; thus for instance a student could take an Ordinary level in the Junior Certificate and then could not take a Higher level in the corresponding Leaving Certificate subject, later.
Grading

Irish
In the Junior Certificate candidates have the option of answering either in Irish or in English, except in the case of the subjects Irish and English and questions in other language subjects. Certain subjects and components are not available for bonus marks, marks awarded also vary depending on the written nature of the subject.Exemptions
Students who face disadvantages (i.e. suffer spelling problems caused by dyslexia can not be penalised for bad spellings in exams such as English and Irish. These candidates will then be marked harder on all topics. (e.g. if a student has a spelling problem in English he/she will be marked out of 50 for their mechanics).Results
It's not possible to fail the Junior Cert overall: all students continue to their next year of education no matter what their results, but most schools will not permit a student to take a Leaving Cert subject at Higher Level if they did not receive at least a Higher Level "C" grade at Junior Cert. The Junior Certificate (and more so, the Leaving CertificateLeaving Certificate
The Leaving Certificate Examinations , commonly referred to as the Leaving Cert is the final examination in the Irish secondary school system. It takes a minimum of two years preparation, but an optional Transition Year means that for those students it takes place three years after the Junior...
) results take centre place in the Irish media during the week surrounding their release. The newspapers publish various statistics about the exam and cover high achievers (some receive ten or more "A" grades). Schools generally give students (who have received their results) the day off and disco
Disco
Disco is a genre of dance music. Disco acts charted high during the mid-1970s, and the genre's popularity peaked during the late 1970s. It had its roots in clubs that catered to African American, gay, psychedelic, and other communities in New York City and Philadelphia during the late 1960s and...
s especially for the teenagers are organised in most cities and towns.
Appealing grades
If a student is unhappy with a grade they received on any of the exam results, they may appeal the decision made by the SEC. They need to pay a fee (in 2010 the fee was €Euro
The euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
32 per exam) and the principal of the school writes a letter of appeal application to the State Examinations Commission, stating the candidate's name, exam number and the exam they would like to appeal. There is a deadline to appeal, usually 14–21 days after the results are published, in which the student's application must be made. The appeal results are usually handed out mid-November. The grade that is received this time is final, and no more appeals can be made. If the candidate's grade did not change, no further action will be taken. However, if a change did occur, then the candidate will be refunded the appeal fee via a Cheque
Cheque
A cheque is a document/instrument See the negotiable cow—itself a fictional story—for discussions of cheques written on unusual surfaces. that orders a payment of money from a bank account...
made out to the principal of the school. These refunds take time to be issued, but in an appeal made in September 2005 the refund was issued as late as March 2006.
Drop-outs
Although school attendance in Ireland is very high, some students drop out of the education system after completion of the Junior Certificate. Those who stay in the education system sit the Leaving CertificateLeaving Certificate
The Leaving Certificate Examinations , commonly referred to as the Leaving Cert is the final examination in the Irish secondary school system. It takes a minimum of two years preparation, but an optional Transition Year means that for those students it takes place three years after the Junior...
- the requirement for college entry in Ireland. A new type of Leaving Certificate, the Leaving Certificate Applied has been designed to discourage people from dropping out. This is all practical work and students may work after school or do an apprenticeship, respectively.
The vast majority of students continue from lower level to senior level, with only 12.3% leaving after the Junior Certificate. This is lower than the EU average of 15.2%.
Transition year
Transition Year (TY) is an optional one-year programme that can be taken in the year after the Junior Certificate in the Republic of IrelandRepublic of Ireland
Ireland , described as the Republic of Ireland , is a sovereign state in Europe occupying approximately five-sixths of the island of the same name. Its capital is Dublin. Ireland, which had a population of 4.58 million in 2011, is a constitutional republic governed as a parliamentary democracy,...
and is intended to make the senior cycle a three year programme encompassing both Transition Year and Leaving Certificate
Leaving Certificate
The Leaving Certificate Examinations , commonly referred to as the Leaving Cert is the final examination in the Irish secondary school system. It takes a minimum of two years preparation, but an optional Transition Year means that for those students it takes place three years after the Junior...
. The idea of such a year is strange in other countries, as they don't have the same year. Transition Year was created as a result of the Programme for Economic and Social Progress which called for a six-year cycle of post-primary education.

