
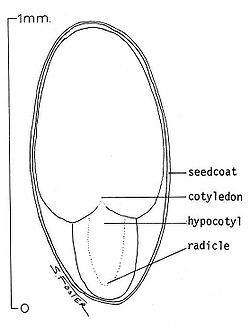
Hypocotyl
Encyclopedia
Seedling
thumb|Monocot and dicot seedlingsA seedling is a young plant sporophyte developing out of a plant embryo from a seed. Seedling development starts with germination of the seed. A typical young seedling consists of three main parts: the radicle , the hypocotyl , and the cotyledons...
, found below the cotyledon
Cotyledon
A cotyledon , is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Upon germination, the cotyledon may become the embryonic first leaves of a seedling. The number of cotyledons present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants...
s (seed leaves) and above the radicle
Radicle
In botany, the radicle is the first part of a seedling to emerge from the seed during the process of germination. The radicle is the embryonic root of the plant, and grows downward in the soil...
(root
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
).
Dicots
As the plant embryoEmbryo
An embryo is a multicellular diploid eukaryote in its earliest stage of development, from the time of first cell division until birth, hatching, or germination...
grows at germination, it sends out a shoot called a radicle
Radicle
In botany, the radicle is the first part of a seedling to emerge from the seed during the process of germination. The radicle is the embryonic root of the plant, and grows downward in the soil...
that becomes the primary root and penetrates down into the soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
. After emergence of the radicle, the hypocotyl emerges and lifts the growing tip (usually including the seed coat) above the ground, bearing the embryonic leaves (called cotyledon
Cotyledon
A cotyledon , is a significant part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Upon germination, the cotyledon may become the embryonic first leaves of a seedling. The number of cotyledons present is one characteristic used by botanists to classify the flowering plants...
s) and the plumule that gives rise to the first true leaves. The hypocotyl is the primary organ of extension of the young plant and develops into the stem
Plant stem
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes, the nodes hold buds which grow into one or more leaves, inflorescence , conifer cones, roots, other stems etc. The internodes distance one node from another...
.
Monocots
The early development of a monocotMonocotyledon
Monocotyledons, also known as monocots, are one of two major groups of flowering plants that are traditionally recognized, the other being dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocot seedlings typically have one cotyledon , in contrast to the two cotyledons typical of dicots...
seedling like cereal
Cereal
Cereals are grasses cultivated for the edible components of their grain , composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran...
s and other grasses
Poaceae
The Poaceae is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called grasses, although the term "grass" is also applied to plants that are not in the Poaceae lineage, including the rushes and sedges...
is somewhat different. A structure called the coleoptile
Coleoptile
Coleoptile is the pointed protective sheath covering the emerging shoot in monocotyledons such as oats and grasses. Coleoptiles have two vascular bundles, one on either side. Unlike the flag leaves rolled up within, the pre-emergent coleoptile does not accumulate significant protochlorophyll or...
, essentially a part of the cotyledon, protects the young stem and plumule as growth pushes them up through the soil. A mesocotyl—that part of the young plant that lies between the seed (which remains buried) and the plumule—extends the shoot up to the soil surface, where secondary roots develop from just beneath the plumule. The primary root from the radicle may then fail to develop further. The mesocotyl is considered to be partly hypocotyl and partly cotyledon (see seed
Seed
A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a covering called the seed coat, usually with some stored food. It is the product of the ripened ovule of gymnosperm and angiosperm plants which occurs after fertilization and some growth within the mother plant...
).
Not all monocots develop like the grasses. The onion
Onion
The onion , also known as the bulb onion, common onion and garden onion, is the most widely cultivated species of the genus Allium. The genus Allium also contains a number of other species variously referred to as onions and cultivated for food, such as the Japanese bunching onion The onion...
develops in a manner similar to the first sequence described above, the seed coat and endosperm
Endosperm
Endosperm is the tissue produced inside the seeds of most flowering plants around the time of fertilization. It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and protein. This makes endosperm an important source of nutrition in human diet...
(stored food reserve) pulled upwards as the cotyledon extends. Later, the first true leaf grows from the node between the radicle and the sheath-like cotyledon, breaking through the cotyledon to grow past it.
Storage organ
In some plants, the hypocotyl becomes enlarged as a storage organStorage organ
A storage organ is a part of a plant specifically modified for storage of energy or water. Storage organs often grow underground, where they are better protected from attack by herbivores. Plants that have an underground storage organ are called geophytes in the Raunkiær plant life-form...
. Examples include cyclamen
Cyclamen
Cyclamen is a genus of 23 species of perennials growing from tubers, valued for their flowers with upswept petals and variably patterned leaves...
, gloxinia
Gloxinia (genus)
Gloxinia is a genus of three species of tropical rhizomatous herbs in the flowering plant family Gesneriaceae. The species are primarily found in the Andes of South America but Gloxinia perennis is also found in Central America and the West Indies, where it has probably escaped from...
and celeriac
Celeriac
Celeriac is also known as celery root, turnip-rooted celery or knob celery. It is a kind of celery, grown as a root vegetable primarily for its large and bulbous hypocotyl rather than for its stem and leaves. The swollen hypocotyl is typically used when it is about 10–12 cm in...
. In cyclamen
Cyclamen
Cyclamen is a genus of 23 species of perennials growing from tubers, valued for their flowers with upswept petals and variably patterned leaves...
, this storage organ is called a tuber
Tuber
Tubers are various types of modified plant structures that are enlarged to store nutrients. They are used by plants to survive the winter or dry months and provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growing season and they are a means of asexual reproduction...
.

