Hydraulic drive system
Encyclopedia
A hydraulic drive system is a drive or transmission
system that uses pressurized hydraulic fluid
to drive hydraulic machinery
. The term hydrostatic refers to the transfer of energy from flow and pressure, not from the kinetic energy
of the flow.
A hydraulic drive system consists of three parts: The generator (e.g. a hydraulic pump
), driven by an electric motor
, a combustion engine
or a windmill
; valves, filters, piping etc. (to guide and control the system); the motor (e.g. a hydraulic motor
or hydraulic cylinder
) to drive the machinery.
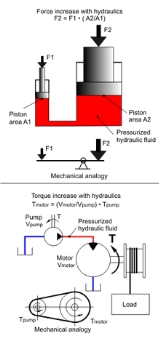
 Pascal law is the basis of hydraulic drive systems. As the pressure in the system is the same, the force that the fluid gives to the surroundings is therefore equal to pressure x area. In such a way, a small piston feels a small force and a large piston feels a large force.
Pascal law is the basis of hydraulic drive systems. As the pressure in the system is the same, the force that the fluid gives to the surroundings is therefore equal to pressure x area. In such a way, a small piston feels a small force and a large piston feels a large force.
The same principle applies for a hydraulic pump with a small swept volume that asks for a small torque
, combined with a hydraulic motor with a large swept volume that gives a large torque. In such a way a transmission with a certain ratio can be built.
Most hydraulic drive systems make use of hydraulic cylinders. Here the same principle is used- a small torque can be transmitted in to a large force.
By throttling the fluid between the generator part and the motor part, or by using hydraulic pumps and/or motors with adjustable swept volume, the ratio of the transmission can be changed easily. In case throttling is used, the efficiency of the transmission is limited. In case adjustable pumps and motors are used, the efficiency, however, is very large. In fact, up to around 1980, a hydraulic drive system had hardly any competition from other adjustable drive systems.
Nowadays, electric drive systems using electric servo-motors can be controlled in an excellent way and can easily compete with rotating hydraulic drive systems. Hydraulic cylinders are, in fact, without competition for linear forces. For these cylinders, hydraulic systems will remain of interest and if such a system is available, it is easy and logical to use this system for the rotating drives of the cooling systems, also.
s (also called linear hydraulic motors) are mechanical actuator
s that are used to give a linear force through a linear stroke. Hydraulic cylinders are able to give pushing and pulling forces of millions of metric tons with only a simple hydraulic system. Very simple hydraulic cylinders are used in presses; here, the cylinder consists of a volume in a piece of iron with a plunger pushed in it and sealed with a cover. By pumping hydraulic fluid in the volume, the plunger is pushed out with a force of plunger-area pressure.
More sophisticated cylinders have a body with end cover, a piston rod
, and a cylinder head
. At one side the bottom is, for instance, connected to a single clevis, whereas at the other side, the piston rod is also foreseen with a single clevis. The cylinder shell normally has hydraulic connections at both sides; that is, a connection at the bottom side and a connection at the cylinder head side. If oil
is pushed under the piston, the piston rod is pushed out and oil that was between the piston and the cylinder head is pushed back to the oil tank.
The pushing or pulling force of a hydraulic cylinder is as follows:
F = Ab * pb - Ah * ph
F = Pushing Force in N
Ab = (π/4) * (Bottom-diameter)^2 [in m2]
Ah = (π/4) * ((Bottom-diameter)^2-(Piston-rod-diameter)^2)) [in m2]
pb = pressure at bottom side in [N/m2]
ph = pressure at cylinder head side in [N/m2]
Apart from miniature cylinders, in general, the smallest cylinder diameter is 32 mm and the smallest piston rod diameter is 16 mm.
Simple hydraulic cylinders have a maximum working pressure of about 70 bar
. The next step is 140 bar, 210 bar, 320/350 bar and further. In general, the cylinders are custom built. The stroke of a hydraulic cylinder is limited by the manufacturing process. The majority of hydraulic cylinders have a stroke between 0, 3, and 5 meters, whereas 12-15 meter stroke is also possible, but for this length only a limited number of suppliers are on the market.
In case the retracted length of the cylinder is too long for the cylinder to be built in the structure, telescopic cylinders can be used. One has to realize that for simple pushing applications telescopic cylinders might be easily available; for higher forces and/or double acting cylinders, they must be designed especially and are very expensive. If hydraulic cylinders are only used for pushing and the piston rod is brought in again by other means, one can also use plunger cylinders. Plunger cylinders have no sealing over the piston, if the cylinder even exists. This means that only one oil connection is necessary. In general the diameter of the plunger is rather large compared with a normal piston cylinder, whereas a hydraulic motor will always leak oil. A hydraulic cylinder does not have a leakage over the piston nor over the cylinder head sealing so that there is no need for a mechanical brake.
 The hydraulic motor is the rotary counterpart of the hydraulic cylinder
The hydraulic motor is the rotary counterpart of the hydraulic cylinder
. Conceptually, a hydraulic motor should be interchangeable with the hydraulic pump
, due to the fact it performs the opposite function. However, most hydraulic pumps cannot be used as hydraulic motors because they cannot be backdriven. Also, a hydraulic motor is usually designed for the working pressure at both sides of the motor. Another difference is that a motor can be reversed by a reversing valve.
Pressure in a hydraulic system is like the voltage in an electrical system and fluid flow rate is the equivalent of current. The size and speed of the pump determines the flow rate, the load at the motor determines the pressure.
Its
Transmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
system that uses pressurized hydraulic fluid
Hydraulic fluid
Hydraulic fluids, also called hydraulic liquids, are the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water...
to drive hydraulic machinery
Hydraulic machinery
Hydraulic machines are machinery and tools that use liquid fluid power to do simple work. Heavy equipment is a common example.In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is transmitted throughout the machine to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders and which becomes pressurised according to...
. The term hydrostatic refers to the transfer of energy from flow and pressure, not from the kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
of the flow.
A hydraulic drive system consists of three parts: The generator (e.g. a hydraulic pump
Hydraulic pump
Hydraulic pumps are used in hydraulic drive systems and can be hydrostatic or hydrodynamic.Hydrostatic pumps are positive displacement pumps while hydrodynamic pumps can be fixed displacement pumps, in which the displacement cannot be adjusted, or variable displacement pumps, which have a more...
), driven by an electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
, a combustion engine
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
or a windmill
Windmill
A windmill is a machine which converts the energy of wind into rotational energy by means of vanes called sails or blades. Originally windmills were developed for milling grain for food production. In the course of history the windmill was adapted to many other industrial uses. An important...
; valves, filters, piping etc. (to guide and control the system); the motor (e.g. a hydraulic motor
Hydraulic motor
A hydraulic motor is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic pressure and flow into torque and angular displacement . The hydraulic motor is the rotary counterpart of the hydraulic cylinder....
or hydraulic cylinder
Hydraulic cylinder
A Hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in engineering vehicles.- Operation :...
) to drive the machinery.
Principle of a hydraulic drive

The same principle applies for a hydraulic pump with a small swept volume that asks for a small torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
, combined with a hydraulic motor with a large swept volume that gives a large torque. In such a way a transmission with a certain ratio can be built.
Most hydraulic drive systems make use of hydraulic cylinders. Here the same principle is used- a small torque can be transmitted in to a large force.
By throttling the fluid between the generator part and the motor part, or by using hydraulic pumps and/or motors with adjustable swept volume, the ratio of the transmission can be changed easily. In case throttling is used, the efficiency of the transmission is limited. In case adjustable pumps and motors are used, the efficiency, however, is very large. In fact, up to around 1980, a hydraulic drive system had hardly any competition from other adjustable drive systems.
Nowadays, electric drive systems using electric servo-motors can be controlled in an excellent way and can easily compete with rotating hydraulic drive systems. Hydraulic cylinders are, in fact, without competition for linear forces. For these cylinders, hydraulic systems will remain of interest and if such a system is available, it is easy and logical to use this system for the rotating drives of the cooling systems, also.
Hydraulic cylinder
Hydraulic cylinderHydraulic cylinder
A Hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in engineering vehicles.- Operation :...
s (also called linear hydraulic motors) are mechanical actuator
Actuator
An actuator is a type of motor for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. It is operated by a source of energy, usually in the form of an electric current, hydraulic fluid pressure or pneumatic pressure, and converts that energy into some kind of motion. An actuator is the mechanism by which...
s that are used to give a linear force through a linear stroke. Hydraulic cylinders are able to give pushing and pulling forces of millions of metric tons with only a simple hydraulic system. Very simple hydraulic cylinders are used in presses; here, the cylinder consists of a volume in a piece of iron with a plunger pushed in it and sealed with a cover. By pumping hydraulic fluid in the volume, the plunger is pushed out with a force of plunger-area pressure.
More sophisticated cylinders have a body with end cover, a piston rod
Piston rod
In a piston engine, a piston rod joins a piston to a connecting rod.Many internal combustion engines, and in particular all current automobile engines, do not have true piston rods, and the term piston rod is often used as a synonym for connecting rod in the context of these engines.All engines...
, and a cylinder head
Cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head sits above the cylinders on top of the cylinder block. It closes in the top of the cylinder, forming the combustion chamber. This joint is sealed by a head gasket...
. At one side the bottom is, for instance, connected to a single clevis, whereas at the other side, the piston rod is also foreseen with a single clevis. The cylinder shell normally has hydraulic connections at both sides; that is, a connection at the bottom side and a connection at the cylinder head side. If oil
Oil
An oil is any substance that is liquid at ambient temperatures and does not mix with water but may mix with other oils and organic solvents. This general definition includes vegetable oils, volatile essential oils, petrochemical oils, and synthetic oils....
is pushed under the piston, the piston rod is pushed out and oil that was between the piston and the cylinder head is pushed back to the oil tank.
The pushing or pulling force of a hydraulic cylinder is as follows:
F = Ab * pb - Ah * ph
F = Pushing Force in N
Ab = (π/4) * (Bottom-diameter)^2 [in m2]
Ah = (π/4) * ((Bottom-diameter)^2-(Piston-rod-diameter)^2)) [in m2]
pb = pressure at bottom side in [N/m2]
ph = pressure at cylinder head side in [N/m2]
Apart from miniature cylinders, in general, the smallest cylinder diameter is 32 mm and the smallest piston rod diameter is 16 mm.
Simple hydraulic cylinders have a maximum working pressure of about 70 bar
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
. The next step is 140 bar, 210 bar, 320/350 bar and further. In general, the cylinders are custom built. The stroke of a hydraulic cylinder is limited by the manufacturing process. The majority of hydraulic cylinders have a stroke between 0, 3, and 5 meters, whereas 12-15 meter stroke is also possible, but for this length only a limited number of suppliers are on the market.
In case the retracted length of the cylinder is too long for the cylinder to be built in the structure, telescopic cylinders can be used. One has to realize that for simple pushing applications telescopic cylinders might be easily available; for higher forces and/or double acting cylinders, they must be designed especially and are very expensive. If hydraulic cylinders are only used for pushing and the piston rod is brought in again by other means, one can also use plunger cylinders. Plunger cylinders have no sealing over the piston, if the cylinder even exists. This means that only one oil connection is necessary. In general the diameter of the plunger is rather large compared with a normal piston cylinder, whereas a hydraulic motor will always leak oil. A hydraulic cylinder does not have a leakage over the piston nor over the cylinder head sealing so that there is no need for a mechanical brake.
Hydraulic motor

Hydraulic cylinder
A Hydraulic cylinder is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in engineering vehicles.- Operation :...
. Conceptually, a hydraulic motor should be interchangeable with the hydraulic pump
Hydraulic pump
Hydraulic pumps are used in hydraulic drive systems and can be hydrostatic or hydrodynamic.Hydrostatic pumps are positive displacement pumps while hydrodynamic pumps can be fixed displacement pumps, in which the displacement cannot be adjusted, or variable displacement pumps, which have a more...
, due to the fact it performs the opposite function. However, most hydraulic pumps cannot be used as hydraulic motors because they cannot be backdriven. Also, a hydraulic motor is usually designed for the working pressure at both sides of the motor. Another difference is that a motor can be reversed by a reversing valve.
Pressure in a hydraulic system is like the voltage in an electrical system and fluid flow rate is the equivalent of current. The size and speed of the pump determines the flow rate, the load at the motor determines the pressure.
Hydraulic valves
These valves are usually very heavy duty to stand up to high pressures. Some special valves can control the direction of the flow of fluid and act as a control unit for a system.Classification of hydraulic valves
- Classification based on function:
- Pressure control valves
- Flow control valves
- Direction control valves (DC Valves)
- Classification based on method of activation:
- Directly operated valve
- Pilot operated valve
- Mutually operated valve
- Electrically actuated valve
- open control valve
- Servo controlled valves
Its

