
Hydraulic pump
Encyclopedia
Hydraulic drive system
A hydraulic drive system is a drive or transmission system that uses pressurized hydraulic fluid to drive hydraulic machinery. The term hydrostatic refers to the transfer of energy from flow and pressure, not from the kinetic energy of the flow....
s and can be hydrostatic or hydrodynamic.
Hydrostatic pumps are positive displacement pumps while hydrodynamic pumps can be fixed displacement pumps, in which the displacement (flow through the pump per rotation of the pump) cannot be adjusted, or variable displacement pump
Variable displacement pump
A variable displacement pump is a device that converts mechanical energy to hydraulic energy. The displacement, or amount of fluid pumped per revolution of the pump's input shaft can be varied while the pump is running....
s, which have a more complicated construction that allows the displacement to be adjusted.
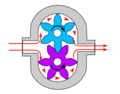
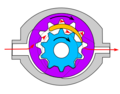
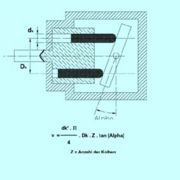
Gear pumps
Gear pumpGear pump
A gear pump uses the meshing of gears to pump fluid by displacement. They are one of the most common types of pumps for hydraulic fluid power applications. Gear pumps are also widely used in chemical installations to pump fluid with a certain viscosity...
s (with external teeth) (fixed displacement) are simple and economical pumps. The swept volume or displacement
Engine displacement
Engine displacement is the volume swept by all the pistons inside the cylinders of an internal combustion engine in a single movement from top dead centre to bottom dead centre . It is commonly specified in cubic centimeters , litres , or cubic inches...
of gear pumps for hydraulics will be between about 1 cm3 (0.001 litre) and 200 cm3 (0.2 litre). These pumps create pressure through the meshing of the gear teeth, which forces fluid around the gears to pressurize the outlet side. For lubrication, the gear pump uses a small amount of oil from the pressurized side of the gears, bleeds this through the (typically) hydrodynamic bearings, and vents the same oil either to the low pressure side of the gears, or through a dedicated drain port on the pump housing. Some gear pumps can be quite noisy, compared to other types, but modern gear pumps are highly reliable and much quieter than older models. This is in part due to designs incorporating split gears, helical gear teeth and higher precision/quality tooth profiles that mesh and unmesh more smoothly, reducing pressure ripple and related detrimental problems. Another positive attribute of the gear pump, is that catastrophic breakdown is a lot less common than in most other types of hydraulic pumps. This is because the gears gradually wear down the housing and/or main bushings, reducing the volumetric efficiency of the pump gradually until it is all but useless. This often happens long before wear causes the unit to seize or break down.
Rotary vane pumps
Rotary vane pumpRotary vane pump
A rotary vane pump is a positive-displacement pump that consists of vanes mounted to a rotor that rotates inside of a cavity. In some cases these vanes can be variable length and/or tensioned to maintain contact with the walls as the pump rotates. It was invented by Charles C...
s (fixed and simple adjustable displacement) have higher efficiencies than gear pumps, but are also used for mid pressures up to 180 bars in general. Modern units can exceed 300 bars in continuous operation, although vane pumps are not regarded as "high pressure" components. Some types of vane pumps can change the centre of the vane body, so that a simple adjustable pump is obtained. These adjustable vane pumps are in general constant pressure or constant power pumps: the displacement is increased until the required pressure or power is reached and subsequently the displacement or swept volume is decreased until an equilibrium is reached. A critical element in vane pump design is how the vanes are pushed into contact with the pump housing, and how the vane tips are machined at this very point. Several type of "lip" designs are used, and the main objective is to provide a tight seal between the inside of the housing and the vane, and at the same time to minimize wear and metal-to-metal contact. Forcing the vane out of the rotating center and towards the pump housing is accomplished using spring-loaded vanes, or more traditionally, vanes loaded hydrodynamically (via the pressurized system fluid).
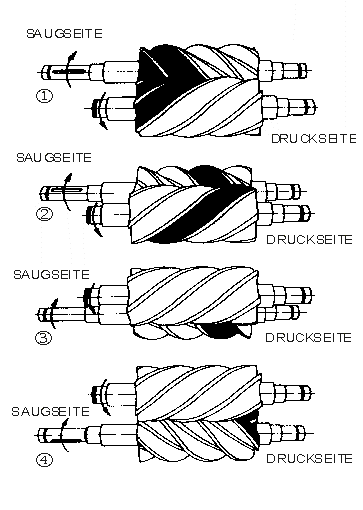
Screw pumps
Screw pumpScrew pump
A screw pump is a positive displacement pump that use one or several screws to move fluids or solids along the screw axis. In its simplest form , a single screw rotates in a cylindrical cavity, thereby moving the material along the screw's spindle...
s (fixed displacement) are a double Archimedes' screw
Archimedes' screw
The Archimedes' screw, also called the Archimedean screw or screwpump, is a machine historically used for transferring water from a low-lying body of water into irrigation ditches...
, but closed. This means that two screws are used in one body. The pumps are used for high flows and relatively low pressure (max 100 bar). They were used on board ships where the constant pressure hydraulic system was going through the whole ship, especially for the control of ball valve
Ball valve
A ball valve is a valve with a spherical disc, the part of the valve which controls the flow through it. The sphere has a hole, or port, through the middle so that when the port is in line with both ends of the valve, flow will occur. When the valve is closed, the hole is perpendicular to the ends...
s, but also for the steering gear and help drive systems. The advantage of the screw pumps is the low sound level of these pumps; the efficiency is not that high.
The major problem of screw pumps is the hydraulic reaction forces which is transmitted axially opposed to the flow direction,
there are two ways to overcome this problem:
1- put a thrust bearing beneath each rotor.
2- make a hydraulic balance with directing a hydraulic force to a piston under the rotor.
Types of screw pumps:
1-single end.
2-double end.
3-single rotor.
4-multi rotor timed.
5-multi rotor untimed.
Bent axis pumps
Bent axis pumps, axial piston pumps and motors using the bent axis principle, fixed or adjustable displacement, exists in two different basic designs. The Thoma-principle (engineer Hans Thoma, Germany, patent 1935) with max 25 degrees angle and the Wahlmark-principle (Gunnar Axel Wahlmark, patent 1960) with spherical-shaped pistons in one piece with the piston rod, piston rings, and maximum 40 degrees between the driveshaft centerline and pistons (Volvo Hydraulics Co.). These have the best efficiency of all pumps. Although in general the largest displacements are approximately one litre per revolution, if necessary a two-liter swept volume pump can be built. Often variable-displacement pumps are used, so that the oil flow can be adjusted carefully. These pumps can in general work with a working pressure of up to 350–420 bars in continuous work.Axial piston pumps swashplate principle
Axial piston pumpAxial piston pump
An axial piston pump is a positive displacement pump that has a number of pistons in a circular array within a cylinder block. It can be used as a stand-alone pump, a hydraulic motor or an automotive air conditioning compressor.-Description:...
s using the swashplate
Swashplate
A swashplate is a device used in mechanical engineering to translate the motion of a rotating shaft into reciprocating motion, or to translate a reciprocating motion into a rotating one to replace the crankshaft in engine designs.- Construction :...
principle (fixed and adjustable displacement) have a quality that is almost the same as the bent axis model. They have the advantage of being more compact in design. The pumps are easier and more economical to manufacture; the disadvantage is that they are more sensitive to oil contamination.
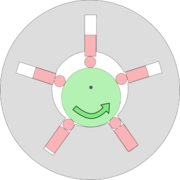
Radial piston pumps
Radial piston pumpRadial piston pump
A radial piston pump is a form of hydraulic pump. The working pistons extend in a radial direction symmetrically around the drive shaft, in contrast to the axial piston pump.-Construction:...
s (fixed displacement) are used especially for high pressure and relatively small flows. Pressures of up to 650 bar are normal. In fact variable displacement is not possible, but sometimes the pump is designed in such a way that the plungers can be switched off one by one, so that a sort of variable displacement pump is obtained.
Pumps for open and closed systems
Most pumps are working in open systems. The pump draws oil from a reservoir at atmospheric pressureAtmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
. It is very important that there is no cavitation
Cavitation
Cavitation is the formation and then immediate implosion of cavities in a liquidi.e. small liquid-free zones that are the consequence of forces acting upon the liquid...
at the suction side of the pump. For this reason the connection of the suction side of the pump is larger in diameter than the connection of the pressure side. In case of the use of multi-pump assemblies, the suction connection of the pump is often combined. It is preferred to have free flow to the pump (pressure at inlet of pump at least 0.8 bars). The body of the pump is often in open connection with the suction side of the pump.
In case of a closed system, both sides of the pump can be at high pressure. The reservoir is often pressurized with 6-20 bars boost pressure. For closed loop systems, normally axial piston pumps are used. Because both sides are pressurized, the body of the pump needs a separate leakage connection.
Multi pump assembly
In a hydraulic installation, one pump can serve several cylinders and motors. However, in that case a constant pressure system is required and the system always needs full power. It is more economic to give each cylinder and motor its own pump. In that case, multi-pump assemblies can be used. Gear pumps are often supplied as multi-pumps. The different chambers (sometimes of different sizes) are mounted in one body or built together. Vane pumps and gerotor pumps too are often available as multi-pumps. Screw pumps can be combined with gear or vane pumps. Axial piston swashplate pumps can be combined with a second pump, or with one or more gear pumps or vane pumps (the gear or vane pumps often serving as flush pumps for cooling larger units). Axial plunger pumps of the bent-axis design cannot be combined with other pumps.Flow
Q = n * Vstroke *η volQ = Flow in m3/s
n = revs per second
Vstroke = swept volume in m3
η volume is volumetric efficiency
Power
P = n * Vstroke * Δp / ηmech,hydrP = Power in Watt (Nm/s)
n = revs per second.
Vstroke = swept volume in m3
Δp = pressure difference over pump in N/m2
ηmech,hydr = mechanical/hydraulic efficiency

