History of rail transport in Great Britain
Encyclopedia
Rail transport in Great Britain
The railway system in Great Britain is the oldest in the world, with the world's first locomotive-hauled public railway opening in 1825. As of 2010, it consists of of standard gauge lines , of which are electrified. These lines range from single to double, triple, quadruple track and up to twelve...
Great Britain, the principal territory of the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, is the oldest in the world. The system was originally built as a patchwork of local rail links operated by small private railway companies. These isolated links developed during the railway boom of the 1840s into a national network, although still run by dozens of competing companies. Over the course of the 19th and early 20th centuries, these amalgamated or were bought by competitors until only a handful of larger companies remained (see railway mania
Railway Mania
The Railway Mania was an instance of speculative frenzy in Britain in the 1840s. It followed a common pattern: as the price of railway shares increased, more and more money was poured in by speculators, until the inevitable collapse...
). The entire network was brought under government control during the First World War
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
and a number of advantages of amalgamation and planning were revealed. However, the government resisted calls for the nationalisation
Nationalization
Nationalisation, also spelled nationalization, is the process of taking an industry or assets into government ownership by a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to private assets, but may also mean assets owned by lower levels of government, such as municipalities, being...
of the network. In 1923, almost all the remaining companies were grouped
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921, also known as the Grouping Act, was an enactment by the British government of David Lloyd George intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, move the railways away from internal competition, and to retain some of the benefits which...
into the "big four", the Great Western Railway
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway was a British railway company that linked London with the south-west and west of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament in 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838...
, the London and North Eastern Railway
London and North Eastern Railway
The London and North Eastern Railway was the second-largest of the "Big Four" railway companies created by the Railways Act 1921 in Britain...
, the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
London, Midland and Scottish Railway
The London Midland and Scottish Railway was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railway companies into just four...
and the Southern Railway. The "Big Four" were joint-stock public companies and they continued to run the railway system until 31 December 1947.
From the start of 1948, the "big four" were nationalised
Nationalization
Nationalisation, also spelled nationalization, is the process of taking an industry or assets into government ownership by a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to private assets, but may also mean assets owned by lower levels of government, such as municipalities, being...
to form British Railways. Though there were few initial changes to the service, usage increased and the network became profitable. Declining passenger numbers and financial losses in the late 1950s and early 1960s prompted the closure of many branch and main lines, and small stations, under the Beeching Axe
Beeching Axe
The Beeching Axe or the Beeching Cuts are informal names for the British Government's attempt in the 1960s to reduce the cost of running British Railways, the nationalised railway system in the United Kingdom. The name is that of the main author of The Reshaping of British Railways, Dr Richard...
. Passenger services experienced a renaissance with the introduction of high-speed inter-city trains in the 1970s. The 1980s saw severe cuts in government funding and above-inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
increases in fares and the service became more cost-effective . Railway operations were privatised
Privatisation of British Rail
The privatisation of British Rail was set in motion when the Conservative government enacted, on 19 January 1993, the British Coal and British Rail Act 1993 . This enabled the relevant Secretary of State to issue directions to the relevant Board...
during 1994-1997. Ownership of the track and infrastructure passed to Railtrack
Railtrack
Railtrack was a group of companies that owned the track, signalling, tunnels, bridges, level crossings and all but a handful of the stations of the British railway system from its formation in April 1994 until 2002...
, whilst passenger operations were franchised to individual private sector operators (originally there were 25 franchises) and the freight services sold outright. Passenger levels have since increased to above the level they had been at in the late-1940s. The Hatfield accident
Hatfield rail crash
The Hatfield rail crash was a railway accident on 17 October 2000, at Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK. Although the accident killed fewer than other accidents, Hatfield exposed the major stewardship shortcomings of the privatised national railway infrastructure company Railtrack and the failings of...
set in motion the series of events that resulted in the ultimate collapse of Railtrack and its replacement with Network Rail
Network Rail
Network Rail is the government-created owner and operator of most of the rail infrastructure in Great Britain .; it is not responsible for railway infrastructure in Northern Ireland...
, a state-owned, not-for-dividend company.
Before 1830: The pioneers

Benjamin Outram
Benjamin Outram was an English civil engineer, surveyor and industrialist. He was a pioneer in the building of canals and tramways.-Personal life:...
constructed a mile-long tramway with L-shaped cast iron
Cast iron
Cast iron is derived from pig iron, and while it usually refers to gray iron, it also identifies a large group of ferrous alloys which solidify with a eutectic. The color of a fractured surface can be used to identify an alloy. White cast iron is named after its white surface when fractured, due...
rails. These rails became obsolete when William Jessop
William Jessop
William Jessop was an English civil engineer, best known for his work on canals, harbours and early railways in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.-Early life:...
began to manufacture cast iron rails without guiding ledges - the wheels of the carts had flange
Flange
A flange is an external or internal ridge, or rim , for strength, as the flange of an iron beam such as an I-beam or a T-beam; or for attachment to another object, as the flange on the end of a pipe, steam cylinder, etc., or on the lens mount of a camera; or for a flange of a rail car or tram wheel...
s instead. Cast iron is brittle and so the rails tended to break easily. Consequently, in 1820, John Birkenshaw introduced a method of rolling wrought iron
Wrought iron
thumb|The [[Eiffel tower]] is constructed from [[puddle iron]], a form of wrought ironWrought iron is an iron alloy with a very low carbon...
rails, which were used from then onwards.
The first passenger-carrying public railway was opened by the Oystermouth Railway in 1807, using horse drawn carriages
Horsecar
A horsecar or horse-drawn tram is an animal-powered streetcar or tram.These early forms of public transport developed out of industrial haulage routes that had long been in existence, and from the omnibus routes that first ran on public streets in the 1820s, using the newly improved iron or steel...
on an existing tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
line.
In 1804, Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick was a British inventor and mining engineer from Cornwall. His most significant success was the high pressure steam engine and he also built the first full-scale working railway steam locomotive...
designed and built the first (unnamed) steam locomotive
Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine...
to run on smooth rails.
.jpg)
The Salamanca
Salamanca was the first commercially successful steam locomotive, built in 1812 by Matthew Murray of Holbeck, for the edge railed Middleton Railway between Middleton and Leeds. It was the first to have two cylinders...
, built in 1812 by John Blenkinsop
John Blenkinsop
John Blenkinsop was an English mining engineer and an inventor of steam locomotives, who designed the first practical railway locomotive....
and Matthew Murray
Matthew Murray
Matthew Murray was an English steam engine and machine tool manufacturer, who designed and built the first commercially viable steam locomotive, the twin cylinder Salamanca in 1812...
for the gauge Middleton Railway
Middleton Railway
The Middleton Railway is the world's oldest continuously working railway. It was founded in 1758 and is now a heritage railway run by volunteers from The Middleton Railway Trust Ltd...
. Salamanca was a rack and pinion
Rack and pinion
A rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a pair of gears which convert rotational motion into linear motion. A circular gear called "the pinion" engages teeth on a linear "gear" bar called "the rack"; rotational motion applied to the pinion causes the rack to move, thereby...
locomotive, with cog wheels driven by two cylinders embedded into the top of the centre-flue boiler.
In 1813, William Hedley
William Hedley
William Hedley was one of the leading industrial engineers of the early 19th century, and was very instrumental in several major innovations in early railway development...
and Timothy Hackworth
Timothy Hackworth
Timothy Hackworth was a steam locomotive engineer who lived in Shildon, County Durham, England and was the first locomotive superintendent of the Stockton and Darlington Railway.- Youth and early work :...
designed a locomotive (Puffing Billy
Puffing Billy (locomotive)
Puffing Billy is an early railway steam locomotive, constructed in 1813-1814 by engineer William Hedley, enginewright Jonathan Forster and blacksmith Timothy Hackworth for Christopher Blackett, the owner of Wylam Colliery near Newcastle upon Tyne, in the United Kingdom. It is the world's oldest...
) for use on the tramway between Stockton
Stockton-on-Tees
Stockton-on-Tees is a market town in north east England. It is the major settlement in the unitary authority and borough of Stockton-on-Tees. For ceremonial purposes, the borough is split between County Durham and North Yorkshire as it also incorporates a number of smaller towns including...
and Darlington
Darlington
Darlington is a market town in the Borough of Darlington, part of the ceremonial county of County Durham, England. It lies on the small River Skerne, a tributary of the River Tees, not far from the main river. It is the main population centre in the borough, with a population of 97,838 as of 2001...
. Puffing Billy featured piston rods extending upwards to pivoting beams, connected in turn by rods to a crankshaft beneath the frames which, in turn, drove the gears attached to the wheels. This meant that the wheels were coupled, allowing better traction. A year later, George Stephenson
George Stephenson
George Stephenson was an English civil engineer and mechanical engineer who built the first public railway line in the world to use steam locomotives...
improved on that design with his first locomotive Blücher
Blücher (locomotive)
Blücher was an early railway locomotive built in 1814 by George Stephenson for Killingworth Colliery. It was the first of a series of locomotives that he designed in the period 1814-16 which established his reputation as an engine designer and laid the foundations for his subsequent pivotal role in...
, which was the first locomotive to use single-flanged wheels.
That design convinced the backers of the proposed Stockton and Darlington Railway
Stockton and Darlington Railway
The Stockton and Darlington Railway , which opened in 1825, was the world's first publicly subscribed passenger railway. It was 26 miles long, and was built in north-eastern England between Witton Park and Stockton-on-Tees via Darlington, and connected to several collieries near Shildon...
to appoint Stephenson as Engineer
Engineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
for the line in 1821. While traffic was originally intended to be horse-drawn, Stephenson carried out a fresh survey of the route to allow steam haulage. The Act was subsequently amended to allow the usage of steam locomotives and also to allow passengers to be carried on the railway. The 25-mile (40 km) long route opened on 27 September 1825 and, with the aid of Stephenson's Locomotion No 1
Locomotion No 1
Locomotion No. 1 is an early British steam locomotive. Built by George and Robert Stephenson's company Robert Stephenson and Company in 1825, it hauled the first train on the Stockton and Darlington Railway on 27 September 1825....
, was the first locomotive-hauled public railway in the world.
1830 – 1922: Early development
The first public railways were built as local rail links operated by small private railway companies. With increasing rapidity, more and more lines were built, often with scant regard for their potential for traffic. The 1840s were by far the biggest decade for railway growth. In 1840, when the decade began, railway lines in Britain were few and scattered but, within ten years, a virtually complete network had been laid down and the vast majority of towns and villages had a rail connection and sometimes two or three. Over the course of the 19th and early 20th centuries, most of the pioneering independent railway companies amalgamated or were bought by competitors, until only a handful of larger companies remained (see Railway ManiaRailway Mania
The Railway Mania was an instance of speculative frenzy in Britain in the 1840s. It followed a common pattern: as the price of railway shares increased, more and more money was poured in by speculators, until the inevitable collapse...
).
The period also saw a steady increase in government involvement, especially in safety matters. The 1840 "Act for Regulating Railways
Railway Regulation Act 1840
The Railway Regulation Act of 1840 brought regulation to the rapidly emerging railway industry in the UK. It was enacted on 10th August 1840 and originally titled An Act for regulating Railways....
" empowered the Board of Trade
Board of Trade
The Board of Trade is a committee of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom, originating as a committee of inquiry in the 17th century and evolving gradually into a government department with a diverse range of functions...
to appoint railway inspectors. The Railway Inspectorate was established in 1840, to enquire into the causes of accidents and recommend ways of avoiding them. As early as 1844, a bill had been put before Parliament suggesting the state purchase of the railways; this was not adopted. It did, however, lead to the introduction of minimum standards for the construction of carriages and the compulsory provision of 3rd class accommodation for passengers - so-called "Parliamentary train
Parliamentary train
A Parliamentary train or Parly is, nowadays, a British English term for a train that operates a Parliamentary service - that is to say a token service to a given station, thus maintaining a legal fiction that either the station or, in some cases, the whole line is open, although in reality the...
s".
The entire network was brought under government control during the First World War
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
and a number of advantages of amalgamation and planning were revealed. However, the Conservative members of the wartime coalition government resisted calls for the formal nationalisation
Nationalization
Nationalisation, also spelled nationalization, is the process of taking an industry or assets into government ownership by a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to private assets, but may also mean assets owned by lower levels of government, such as municipalities, being...
of the railways (first proposed by William Ewart Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone FRS FSS was a British Liberal statesman. In a career lasting over sixty years, he served as Prime Minister four separate times , more than any other person. Gladstone was also Britain's oldest Prime Minister, 84 years old when he resigned for the last time...
as early as the 1830s) in 1921.
1923 – 1947: The Big Four
On 1 January 1923, almost all the railway companies were groupedRailways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921, also known as the Grouping Act, was an enactment by the British government of David Lloyd George intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, move the railways away from internal competition, and to retain some of the benefits which...
into the Big Four
Big Four British railway companies
The Big Four was a name used to describe the four largest railway companies in the United Kingdom in the period 1923-1947. The name was coined by the Railway Magazine in its issue of February 1923: "The Big Four of the New Railway Era".The Big Four were:...
: the Great Western Railway
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway was a British railway company that linked London with the south-west and west of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament in 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838...
, the London and North Eastern Railway
London and North Eastern Railway
The London and North Eastern Railway was the second-largest of the "Big Four" railway companies created by the Railways Act 1921 in Britain...
, the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
London, Midland and Scottish Railway
The London Midland and Scottish Railway was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railway companies into just four...
and the Southern Railway companies. A number of other lines, already operating as joint railway
Joint railway
A joint railway is a railway operating under the control of more than one railway company: those companies very often supplying the traction over the railway.-United Kingdom:There are many examples of joint railway working in the United Kingdom...
s, remained separate from the Big Four; these included the Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway
Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway
The Somerset & Dorset Joint Railway – almost always referred to as "the S&D" – was an English railway line connecting Bath in north east Somerset and Bournemouth now in south east Dorset but then in Hampshire...
and the Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway
Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway
The Midland and Great Northern Joint Railway, was a joint railway owned by the Midland Railway and the Great Northern Railway in eastern England, affectionately known as the 'Muddle and Get Nowhere' to generations of passengers, enthusiasts, and other users.The main line ran from Peterborough to...
. The "Big Four" were joint-stock public companies and they continued to run the railway system until 31 December 1947.

Salter Report
The Salter Report was named after Arthur Salter, who chaired an influential conference of road and rail experts in 1932. The report directed British government policy for transport funding for decades to follow.- Railways :...
of 1933 finally recommended that road transport should be taxed directly to fund the roads and increased Vehicle Excise Duty
Vehicle excise duty
Vehicle Excise Duty is a vehicle road use tax levied as an excise duty which must be paid for most types of vehicle which are to be used on the public roads in the United Kingdom...
and fuel duties were introduced. It also noted that many small lines would never be likely to compete with road haulage. Although these road pricing changes helped their survival, the railways entered a period of slow decline, owing to a lack of investment and changes in transport policy and lifestyles.
During the Second World War, the companies' managements joined together, effectively operating as one company. Assisting the country's 'war effort' put a severe strain on the railways' resources and a substantial maintenance backlog developed. After 1945, for both practical and ideological reasons, the government decided to bring the rail service into the public sector
Public sector
The public sector, sometimes referred to as the state sector, is a part of the state that deals with either the production, delivery and allocation of goods and services by and for the government or its citizens, whether national, regional or local/municipal.Examples of public sector activity range...
.
1948 – 1994: British Rail

From the start of 1948, the railways were nationalised
Nationalization
Nationalisation, also spelled nationalization, is the process of taking an industry or assets into government ownership by a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to private assets, but may also mean assets owned by lower levels of government, such as municipalities, being...
to form British Railways (latterly "British Rail") under the control of the British Transport Commission
British Transport Commission
The British Transport Commission was created by Clement Attlee's post-war Labour government as a part of its nationalisation programme, to oversee railways, canals and road freight transport in Great Britain...
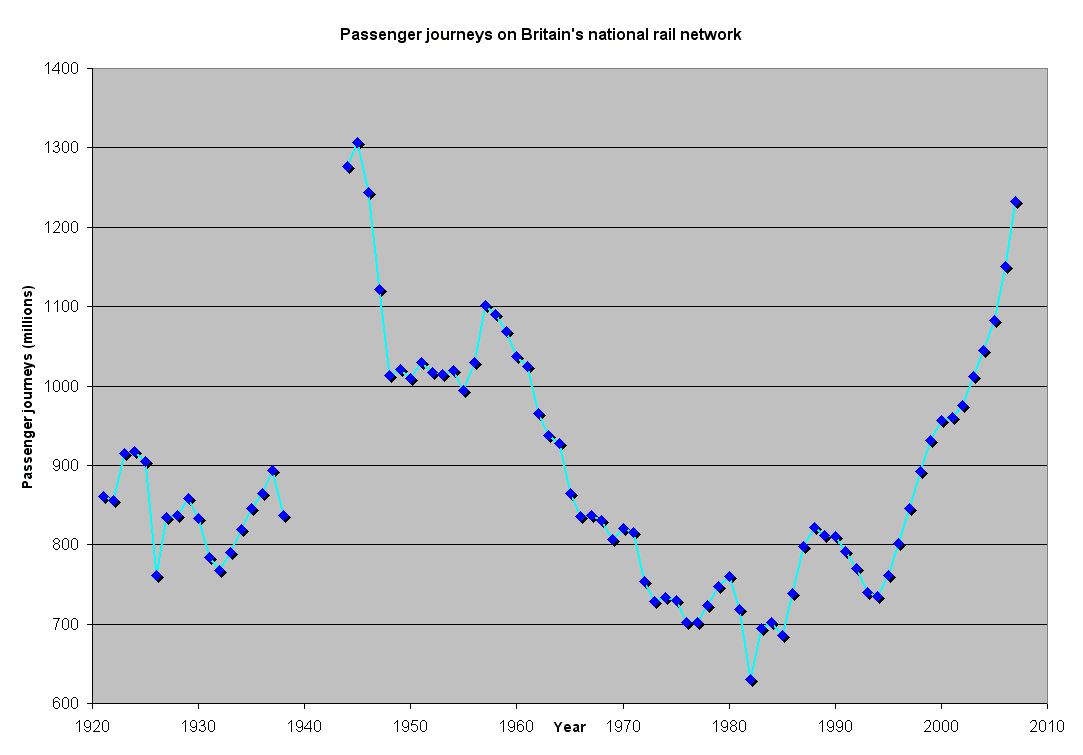
. Though there were few initial changes to the service, usage increased and the network became profitable. Regeneration of track and stations was completed by 1954. In the same year, changes to the British Transport Commission, including the privatisation of road haulage, ended the coordination of transport in the UK. Rail revenue fell and, in 1955, the network again ceased to be profitable. The mid-1950s saw the hasty introduction of diesel and electric rolling stock to replace steam in a modernisation plan costing many millions of pounds but the expected transfer back from road to rail did not occur and losses began to mount. This failure to make the railways more profitable through investment led governments of all political persuasions to restrict rail investment to a drip feed and seek economies through cutbacks.
The desire for profitability led to a major reduction in the network during the mid-1960s. Dr. Richard Beeching
Richard Beeching
Richard Beeching, Baron Beeching , commonly known as Doctor Beeching, was chairman of British Railways and a physicist and engineer...
was given the task by the government of re-organising the railways ("the Beeching Axe
Beeching Axe
The Beeching Axe or the Beeching Cuts are informal names for the British Government's attempt in the 1960s to reduce the cost of running British Railways, the nationalised railway system in the United Kingdom. The name is that of the main author of The Reshaping of British Railways, Dr Richard...
"). This policy resulted in many branch lines and secondary routes being closed because they were deemed uneconomic. The closure of stations serving rural communities removed much feeder traffic from main line passenger services. The closure of many freight depots that had been used by larger industries such as coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
and iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
led to much freight transferring to road haulage. The closures were extremely unpopular with the general public at that time and remain so today.
Passenger levels decreased steadily from the late fifties to late seventies. Passenger services then experienced a renaissance with the introduction of the high-speed Intercity 125
InterCity 125
The InterCity 125 was the brand name of British Rail's High Speed Train fleet. The InterCity 125 train is made up of two power cars, one at each end of a fixed formation of Mark 3 carriages, and is capable of , making the train the fastest diesel-powered locomotive in regular service in the...
trains in the late 1970s and early 1980s. The 1980s saw severe cuts in government funding and above-inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
increases in fares, and the service became more cost-effective.
Between 1994 and 1997, British Rail was privatised
Privatisation of British Rail
The privatisation of British Rail was set in motion when the Conservative government enacted, on 19 January 1993, the British Coal and British Rail Act 1993 . This enabled the relevant Secretary of State to issue directions to the relevant Board...
. Ownership of the track and infrastructure passed to Railtrack
Railtrack
Railtrack was a group of companies that owned the track, signalling, tunnels, bridges, level crossings and all but a handful of the stations of the British railway system from its formation in April 1994 until 2002...
, passenger operations were franchised to individual private sector operators (originally there were 25 franchises) and the freight services sold outright (six companies were set up, but five of these were sold to the same buyer). The Conservative government under John Major
John Major
Sir John Major, is a British Conservative politician, who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1990–1997...
said that privatisation would see an improvement in passenger services. Passenger levels have since increased to above the level they had been at in the late 1950s, though whether this is as a result of any actual improvement in passenger services is moot.
1995 onwards: Post-privatisation

The railways have become significantly safer since privatisation. However, the public image of rail travel was severely damaged following some significant accidents after privatisation. These included the Southall rail crash
Southall rail crash
The Southall rail crash was an accident on the British railway system that occurred on 19 September 1997, on the Great Western Main Line at Southall, west London. Seven people were killed and 139 injured...
(where a train with faulty automatic train protection
Automatic Train Protection
Automatic Train Protection in Great Britain refers to either of two implementations of a train protection system installed in some trains in order to help prevent collisions through a driver's failure to observe a signal or speed restriction...
equipment went through a red light), the Ladbroke Grove rail crash
Ladbroke Grove rail crash
The Ladbroke Grove Rail Crash was a rail accident which occurred on 5 October 1999 at Ladbroke Grove, London, England. Thirty-one people were killed and more than 520 injured...
(also caused by a train going through a red light) and the Hatfield accident
Hatfield rail crash
The Hatfield rail crash was a railway accident on 17 October 2000, at Hatfield, Hertfordshire, UK. Although the accident killed fewer than other accidents, Hatfield exposed the major stewardship shortcomings of the privatised national railway infrastructure company Railtrack and the failings of...
(caused by a rail fragmenting due to the development of microscopic cracks).
Following the Hatfield accident, the rail infrastructure company Railtrack imposed over 1,200 emergency speed restrictions across its network and instigated an extremely costly nationwide track replacement programme. The consequential severe operational disruption to the national network and the company's spiralling costs set in motion the series of events which resulted in the ultimate collapse of the company and its replacement with Network Rail
Network Rail
Network Rail is the government-created owner and operator of most of the rail infrastructure in Great Britain .; it is not responsible for railway infrastructure in Northern Ireland...
, a state-owned, not-for-dividend company.
As franchisees (most notably GNER) have over-bid to renew their franchises, it is believed that some will have wiped out their profitability in the light of rising subsidy repayments back to the Exchequer. If the franchise holders withdraw, responsibility for operating trains will go back to the Department of Transport, further fuelling calls for a full-scale re-nationalisation. However, the recently terminated Connex South Eastern
Connex South Eastern
Connex South Eastern was a train operating company in the United Kingdom. It was owned by the Connex Group and operated between 14 October 1996 and 9 November 2003. The company operated passenger services in South London and Kent...
franchise, while "nationalised" as South Eastern Trains
South Eastern Trains
South Eastern Trains was a British train operating company, in public ownership, that provided train services in south east London and South East England from 9 November 2003 to 31 March 2006....
until the end of the franchise period, was subsequently re-franchised as Southeastern
Southeastern (train operating company)
London & South Eastern Railway Limited, trading as Southeastern is a train operating company in south-east England. On 1 April 2006 it became the franchisee for the new Integrated Kent Franchise , replacing the publicly owned South Eastern Trains on the former South East Franchise...
.
See also
- History of rail transportHistory of rail transportThe history of rail transport dates back nearly 500 years and includes systems with man or horse power and rails of wood or stone. Modern rail transport systems first appeared in England in the 1820s...
- Rail transport in Great BritainRail transport in Great BritainThe railway system in Great Britain is the oldest in the world, with the world's first locomotive-hauled public railway opening in 1825. As of 2010, it consists of of standard gauge lines , of which are electrified. These lines range from single to double, triple, quadruple track and up to twelve...
- List of early British railway companies
- History of rail transport in IrelandHistory of rail transport in IrelandThe history of rail transport in Ireland began only a decade later than that of Great Britain. By its peak in 1920, Ireland counted 5,500 route kilometers...
- British postal system
- List of railway lines in Great Britain
- List of closed railway lines in Great Britain
- British narrow gauge railwaysBritish narrow gauge railwaysThere were more than a thousand British narrow gauge railways ranging from large, historically significant common carriers to small, short-lived industrial railways...
- British industrial narrow gauge railwaysBritish industrial narrow gauge railwaysBritish industrial narrow gauge railways are narrow gauge railways in the United Kingdom and the Isle of Man that were primarily built to serve one or more industries. Some offered passenger services for employees or workmen, but they did not run public passenger trains...
- Railway electrification in Great BritainRailway electrification in Great BritainRailway electrification in Great Britain started towards of the 19th century. A great range of voltages have been used in the intervening period using both overhead lines and third rails, however the most common standard for mainline services is now 25 kV AC using overhead lines and the...
- British diesel and electric multiple unitsBritish diesel and electric multiple units'Multiple Unit' is a term used to describe a train which does not have a separate locomotive. Typically these are passenger trains with accommodation in every vehicle and motors or engines distributed under the floor along the length of the train...
1830 - 1922
- McKenna, Frank. "Victorian Railway Workers," History Workshop (spring 1975) #1 pp. 26-73 in JSTOR

