
History of Sikhism
Encyclopedia
The history of Sikhism
is closely associated with the history of Punjab and the socio-political situation in medieval India
. Sikh distinction was further enhanced by the establishment of the Khalsa
(ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ), by Guru Gobind Singh in 1699. Sikhism was created by Guru Nanak Dev
, a religious leader and a social reformer during the fifteenth century in the Punjab region
. The religious practice was formalized by Guru Gobind Singh
on March 30, 1699. The latter baptised five persons from different social backgrounds to form Khalsa
. The first five, Pure Ones
, then baptized Gobind Singh into the Khalsa fold. This gives the Khalsa, as an organized grouping, a religious history of around 400 years.
Generally Sikhism has had amicable relations with other religions. However, during the Mughal rule of India (1556–1707), emerging religion had strained relation with the ruling Mughals. Prominent Sikh Gurus
were martyred by Mughals for opposing some Mughal emperors' persecution of Sikhs and Hindus. Subsequently, Sikhism militarized to oppose Mughal hegemony. The emergence of the Sikh Confederacy
under the misl
s and Sikh Empire under reign of the Maharajah Ranjit Singh
was characterized by religious tolerance and pluralism
with Christians, Muslims and Hindus in positions of power. The establishment of the Sikh Empire
is commonly considered the zenith of Sikhism at political level, during this time the Sikh Empire
came to include Kashmir
, Ladakh
, and Peshawar
. Hari Singh Nalwa
, the Commander-in-chief of the Sikh army along the North West Frontier, took the boundary of the Sikh Empire to the very mouth of the Khyber Pass
. The Empire's
secular administration integrated innovative military, economic and governmental reforms.
The months leading up to the partition of India
in 1947, saw heavy conflict in the Punjab
between Sikh and Muslims, which saw the effective religious migration of Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus from West Punjab
which mirrored a similar religious migration of Punjabi Muslims in East Punjab
.

Guru Nanak Dev
(1469–1538), founder of Sikhism, was born to Kalu Mehta and Mata Tripta, wherein the Bedi Khatri
clan of a Hindu
family in the village of Talwandi
, now called Nankana Sahib, near Lahore
. His father, a Hindu
named Mehta Kalu, was a Patwari, an accountant
of land revenue in the government. Nanak's mother was Mata Tripta, and he had one older sister, Bibi Nanki.
From an early age Guru Nanak seemed to have acquired a questioning and enquiring mind and refused as a child to wear the ritualistic "sacred" thread called a Janeu and instead said that he would wear the true name of God in his heart as protection, as the thread which could be broken, be soiled, burnt or lost could not offer any security at all. From early childhood, Bibi Nanki saw in her brother the Light of God but she did not reveal this secret to anyone. She is known as the first disciple of Guru Nanak.
Even as a boy, Nanak was fascinated by hindu religion, and his desire to explore the mysteries of life eventually led him to leave home. It was during this period that Nanak was said to have met Kabir
(1440–1518), a saint revered by many. Nanak married Sulakhni, daughter of Moolchand Chona, a trader from Batala
, and they had two sons, Sri Chand and Lakshmi Das.
His brother-in-law, Jai Ram, the husband of his sister Nanki, obtained a job for him in Sultanpur
as the manager of the government granary. One morning, when he was twenty-eight, Guru Nanak Dev went as usual down to the river to bathe and meditate. It was said that he was gone for three days. When he reappeared, it is said he was "filled with the spirit of God". His first words after his re-emergence were: "there is no Hindu, there is no Muslim". With this secular principle he began his missionary
work. He made four distinct major journeys, in the four different directions, which are called Udasis, spanning many thousands of kilometres, preaching the message of God.
Guru Nanak spent the final years of his life in Kartarpur
where Langar (free blessed food) was available. The food would be partaken of by Hindus, rich, poor, high or/and so called low castes. Guru Nanak worked in the fields and earned his livelihood. After appointing Bhai Lehna as the new Sikh Guru, on 22 September 1539, aged 70, Guru Nanak met with his demise.
, on March 31, 1504. He was the son of a small trader named Pheru. His mother's name was Mata Ramo (also known as Mata Sabhirai, Mansa Devi, Daya Kaur). Baba Narayan Das Trehan was his grand father, whose ancestral house was at Matte-di-Sarai near Mukatsar.
Under the influence of his mother, Bhai Lehna began to worship Durga
(A Hindu Goddess). He used to lead a group of Hindu
worshippers to Jawalamukhi Temple every year. He married Mata Khivi
in January 1520 and had two sons, (Dasu and Datu), and two daughters (Amro and Anokhi). The whole Pheru family had to leave their ancestral village because of the ransacking by the Mughal
and Baloch military who had come with Emperor Babur
. After this the family settled at the village of Khadur Sahib by the River Beas, near Tarn Taran
Sahib, a small town about 25 km. from Amritsar
city.
One day, Bhai Lehna heard the recitation of a hymn of Guru Nanak from Bhai Jodha (a Sikh of Guru Nanak Sahib) who was in Khadur Sahib. He was thrilled and decided to proceed to Kartarpur
to have an audience (darshan
) with Guru Nanak. So while on the annual pilgrimage to Jwalamukhi Temple, Bhai Lehna left his journey to visit Kartarpur and see Baba Nanak. His very first meeting with Guru Nanak completely transformed him. He renounced the worship of the Hindu Goddess, dedicated himself to the service of Guru Nanak and so became his disciple, (his Sikh), and began to live in Kartarpur.
His devotion and service (Sewa
) to Guru Nanak and his holy mission was so great that he was instated as the Second Nanak on September 7, 1539 by Guru Nanak. Earlier Guru Nanak tested him in various ways and found an embodiment of obedience and service in him. He spent six or seven years in the service of Guru Nanak at Kartarpur.
After the death of Guru Nanak on September 22, 1539, Guru Angad left Kartarpur for the village of Khadur Sahib (near Goindwal Sahib). He carried forward the principles of Guru Nanak both in letter and spirit. Yogis and Saints of different sects visited him and held detailed discussions about Sikhism with him.
Guru Angad introduced a new alphabet known as Gurmukhi Script, modifying the old Punjabi script's characters. Soon, this script became very popular and started to be used by the people in general. He took great interest in the education of children by opening many schools for their instruction and thus increased the number of literate people. For the youth he started the tradition of Mall Akhara, where physical as well as spiritual exercises were held. He collected the facts about Guru Nanak's life from Bhai Bala
and wrote the first biography of Guru Nanak. He also wrote 63 Salok
s (stanzas), which are included in the Guru Granth Sahib
. He popularised and expanded the institution of Guru ka Langar that had been started by Guru Nanak.
Guru Angad travelled widely and visited all important religious places and centres established by Guru Nanak for the preaching of Sikhism. He also established hundreds of new Centres of Sikhism (Sikh religious Institutions) and thus strengthened the base of Sikhism. The period of his Guruship was the most crucial one. The Sikh community had moved from having a founder to a succession of Gurus and the infrastructure of Sikh society was strengthened and crystallized – from being an infant, Sikhism had moved to being a young child and ready to face the dangers that were around. During this phase, Sikhism established its own separate spiritual path.
Guru Angad, following the example set by Guru Nanak, nominated Sri Amar Das as his successor (the Third Nanak) before his death. He presented all the holy scripts, including those he received from Guru Nanak, to Guru Amar Das. He breathed his last breath on March 29, 1552 at the age of forty-eight. It is said that he started to build a new town, at Goindwal near Khadur Sahib and Guru Amar Das Sahib was appointed to supervise its construction. It is also said that Humayun
, when defeated by Sher Shah Suri
, came to obtain the blessings of Guru Angad in regaining the throne of Delhi
.
became the third Sikh guru in 1552 at the age of 73. Goindwal became an important centre for Sikhism during the Guruship of Guru Amar Das. He continued to preach the principle of equality for women, the prohibition of Sati
and the practise of Langar. In 1567, Emperor Akbar sat with the ordinary and poor people of Punjab to have Langar. Guru Amar Das also trained 140 apostles, of which 52 were women, to manage the rapid expansion of the religion. Before he died in 1574 aged 95, he appointed his son-in-law Jetha as the fourth Sikh Guru.
It is recorded that before becoming a Sikh, Bhai Amar Das, as he was known at the time, was a very religious Vaishanavite Hindu
who spent most of his life performing all of the ritual pilgrimages and fasts of a devout Hindu. One day, Bhai Amar Das heard some hymns of Guru Nanak being sung by Bibi Amro Ji, the daughter of Guru Angad, the second Sikh Guru. Bibi Amro was married to Bhai Sahib's brother, Bhai Manak Chand's son who was called Bhai Jasso. Bhai Sahib was so impressed and moved by these Shabads that he immediately decided to go to see Guru Angad at Khadur Sahib. It is recorded that this event took place when Bhai Sahib was 61 years old.
In 1635, upon meeting Guru Angad, Bhai Sahib was so touched by the Guru's message that he became a devout Sikh. Soon he became involved in Sewa
(Service) to the Guru and the Community. Under the impact of Guru Angad and the teachings of the Gurus, Bhai Amar Das became a devout Sikh. He adopted Guru as his spiritual guide (Guru). Bhai Sahib began to live at Khadur Sahib, where he used to rise early in the morning and bring water from the Beas River for the Guru's bath; he would wash the Guru's clothes and fetch wood from the jungle for 'Guru ka Langar'. He was so dedicated to Sewa
and the Guru and had completely extinguished pride and was totally lost in this commitment that he was considered an old man who had no interest in life; he was dubbed Amru, and generally forsaken.
However, as a result of Bhai Sahib's commitment to Sikhi principles, dedicated service and devotion to the Sikh cause, Guru Angad Sahib appointed Guru Amar Das Sahib as third Nanak in March 1552 at the age of 73. He established his headquarters at the newly built town of Goindwal, which Guru Angad had established.
Soon large numbers of Sikhs started flocking to Goindwal to see the new Guru. Here, Guru Amar Das propagated the Sikh faith in a vigorous, systematic and planned manner. He divided the Sikh Sangat area into 22 preaching centres or Manjis, each under the charge of a devout Sikh. He himself visited and sent Sikh missionaries to different parts of India to spread Sikhism.
Guru Amar Das was impressed with Bhai Gurdas
' thorough knowledge of Hindi
and Sanskrit
and the Hindu
scriptures. Following the tradition of sending out Masands across the country, Guru Amar Das deputed Bhai Gurdas to Agra
to spread the gospel of Sikhism
. Before leaving, Guru Amar Das prescribed the following routine for Sikhs:
Guru Ji strengthened the tradition of 'Guru ka Langar' and made it compulsory for the visitor to the Guru to eat first, saying that 'Pehle Pangat Phir Sangat' (first visit the Langar then go to the Guru). Once the emperor Akbar came to see Guru Sahib and he had to eat the coarse rice in the Langar before he could have an interview with Guru Sahib. He was so much impressed with this system that he expressed his desire to grant some royal property for 'Guru ka Langar', but Guru Sahib declined it with respect.
He introduced new birth, marriage and death ceremonies. Thus he raised the status of women and protected the rights of female infants who were killed without question as they were deemed to have no status. These teachings met with stiff resistance from the Orthodox Hindus. He fixed three Gurpurbs for Sikh celebrations: Diwali
, Vaisakhi
and Maghi
.
Guru Amar Das not only preached the equality of people irrespective of their caste but he also fostered the idea of women's equality. He preaching strongly against the practice of Sati
(a Hindu wife burning on her husband's funeral pyre). Guru Amar Das also disapproved of a young widow remaining unmarried for the rest of her life.
Guru Amar Das constructed "Baoli" at Goindwal Sahib having eighty-four steps and made it a Sikh pilgrimage centre for the first time in the history of Sikhism. He reproduced more copies of the hymns of Guru Nanak and Guru Angad. He also composed 869 (according to some chronicles these were 709) verses (stanzas) including Anand Sahib
, and then later on Guru Arjan (fifth Guru) made all the Shabads part of Guru Granth Sahib
.
When it came time for the Guru's younger daughter Bibi Bhani to marry, he selected a pious and diligent young follower of his called Jetha from Lahore
. Jetha had come to visit the Guru with a party of pilgrims from Lahore and had become so enchanted by the Guru's teachings that he had decided to settle in Goindwal. Here he earned a living selling wheat and would regularly attend the services of Guru Amar Das in his spare time.
Guru Amar Das did not consider anyone of his sons fit for Guruship and chose instead his son-in law (Guru) Ram Das to succeed him. Guru Amar Das Sahib at the age of 95 died on September 1, 1574 at Goindwal in District Amritsar
, after giving responsibility of Guruship to the Fourth Nanak, Guru Ram Das
.
As a Guru one of his main contributions to Sikhism was organizing the structure of Sikh society. Additionally, he was the author of Laava, the hymns of the Marriage Rites, the designer of the Harmandir Sahib, and the planner and creator of the township of Ramdaspur (later Amritsar
).
A hymn by Guru Ram Das from page 305 of the Guru Granth Sahib:
"One who calls himself a Sikh of the True Guru shall get up early morning and meditate on the Lord's Name. Make effort regularly to cleanse, bathe and dip in the ambrosial pool. Upon Guru's instructions, chant Har, Har singing which, all misdeeds, sins and pains shall go away."
Guru Ram Das nominated Guru Arjan Dev, his youngest son, as the next Guru of the Sikhs.

In 1581, Guru Arjan — the youngest son of the fourth guru — became the Fifth Guru of the Sikhs. In addition to being responsible for building the Golden Temple, he prepared the Sikh Sacred text and his personal addition of some 2,000 plus hymns in the Gurū Granth Sāhib
.
In 1604 he installed the Ādi Granth
for the first time as the Holy Book of the Sikhs. In 1606, for refusing to make changes to the Gurū Granth Sāhib, he was tortured and killed by the Mughal
rulers of the time.

Guru Har Rai (Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰਿ ਰਾਇ) (26 February 1630 - 6 October 1661) was the seventh of the ten Gurus of Sikhism, becoming Guru on 8 March 1644, following in the footsteps of his grandfather, Guru Har Gobind, who was the sixth guru. Before he died, he nominated Guru Har Krishan, his youngest son, as the next Guru of the Sikhs.
As a very young child he was disturbed by the suffering of a flower damaged by his robe in passing. Though such feelings are common with children, Guru Har Rai would throughout his life be noted for his compassion for life and living things. His grandfather, who was famed as an avid hunter, is said to have saved the Moghul Emperor Jahangir's life during a tiger's attack. Guru Har Rai continued the hunting tradition of his grandfather, but he would allow no animals to be killed on his grand Shikars. The Guru instead captured the animal and added it to his zoo.
He made several tours to the Malwa and Doaba regions of the Punjab.
His son, Ram Rai, seeking to assuage concerns of Aurangzeb over one line in Guru Nanak's verse (Mitti Mussalmam ki pede pai kumhar) suggested that the word Mussalmam was a mistake on the copyist's part, therefore distorting Bani. The Guru refused to meet with him again. The Guru is believed to have said, "Ram Rai, you have disobeyed my order and sinned. I will never see you again on account of your infidelity." It was also reported to the Guru that Ram Rai had also worked miracles in the Mughal's court against his father's direct instructions. Sikhs are constrained by their Gurus to not believe in magic and myth or miracles. Just before his death at age, 31, Guru Har Rai passed the Gaddi of Nanak on to his younger son, the five year old — Guru Har Krishan.
Guru Har Rai was the son of Baba Gurdita and Mata Nihal Kaur (also known as Mata Ananti Ji). Baba Gurdita was the son of the sixth Guru, Guru Hargobind. Guru Har Rai married Mata Kishan Kaur (sometimes also referred to as Sulakhni), daughter of Sri Daya Ram of Anoopshahr (Bulandshahr) in Uttar Pradesh on Har Sudi 3, Samvat 1697. Guru Har Rai had two sons: Baba Ram Rai and Sri Har Krishan.
Although, Guru Har Rai was a man of peace, he never disbanded the armed Sikh Warriors (Saint Soldiers), who earlier were maintained by his grandfather, Guru Hargobind. He always boosted the military spirit of the Sikhs, but he never himself indulged in any direct political and armed controversy with the contemporary Mughal Empire. Once, Dara Shikoh (the eldest son of emperor Shah Jahan), came to Guru Har Rai asking for help in the war of succession with his brother, the murderous Aurangzeb. The Guru had promised his grandfather to use the Sikh Cavalry only in defence. Nevertheless, he helped him to escape safely from the bloody hands of Aurangzeb's armed forces by having his Sikh warriors hide all the ferry boats at the river crossing used by Dara Shikoh in his escape.
, he nominated his granduncle, Guru Teg Bahadur, as the next Guru of the Sikhs. The following is a summary of the main highlights of his short life:
When Har Krishan stayed in Delhi there was a smallpox epidemic and many people were dying. According to Sikh history at Har Krishan's blessing, the lake at Bangla Sahib provided cure for thousands. Gurdwara Bangla Sahib was constructed in the Guru's memory. This is where he stayed during his visit to Delhi. Gurdwara Bala Sahib was built in south Delhi besides the bank of the river Yamuna, where Har Krishan was cremated at the age of about 7 years and 8 months. Guru Har Krishan was the youngest Guru at only 7 years of age. He did not make any contributions to Gurbani.
Gurus. Guru Tegh Bahadur sacrificed himself to protect Hindus. He was asked by Aurungzeb, the Mughal emperor, under coercion by Naqshbandi Islamists, to convert to Islam or to sacrifice himself. The exact place where he attained martyrdom is in front of the Red Fort in Delhi (Lal Qila) and the gurdwara is called Sisganj. This marked a turning point for Sikhism. His successor, Guru Gobind Singh
further militarised his followers.
 Guru Gobind Singh Ji was the tenth guru of Sikhs. He was born in 1666 at Patna
Guru Gobind Singh Ji was the tenth guru of Sikhs. He was born in 1666 at Patna
(Capital of Bihar, India). In 1675 Pundits from Kashmir in India came to Anandpur Sahib pleading to Guru Teg Bhadur Ji (Father of Guru Gobind Singh Ji) about Aurangzeb
forcing them to convert to Islam. Guru Teg Bahadur told them that martyrdom of a great man was needed. His son, Guru Gobind Singh Ji said "Who could be greater than you", to his father. Guru Teg Bahadur Ji told pundits to tell Aurangzeb's men that if Guru Teg Bahadur Ji will become Muslim, they all will. Guru Teg Bahadur Ji was then martyred in Delhi, but before that he assigned Guru Gobind Singh Ji as 10th Guru at age of 9. After becoming Guru he commanded Sikhs to be armed. He fought many battles with Aurangzeb and some other Kings of that time, but always winner.
In 1699 he created the Khalsa
panth
, by giving amrit
to sikhs. In 1704 he fought the great battle with collective forces of Aurangzeb, Wazir Khan (Chief of Sarhind), and other kings. He left Anandpur and went to Chamkaur with only 40 sikhs. There he fought the Battle of Chamkaur
with 40 sikhs, vastly outnumbered by the Mughal soldiers. His two elder sons (at ages 17, 15) were martyred there. Wazir Khan killed other two (ages 9, 6). Guru Ji sent Aurangzeb the Zafarnamah
(Notification of Victory). Then he went to Nanded (Maharashtra, India). From there he made Baba Gurbakhash Singh, also aliased as Baba Banda Singh Bahadur, as his general and sent him to Punjab.
On the evening of the day when Baba Gurbakhash Singh left for Punjab, Guru Gobind Singh was visited by two Muslim soldiers. One of them was commissioned by Wazir Khan
, Subedar of Sirhind, to assassinate Guru Gobind Singh. One of the assailants, Bashal Beg, kept a vigil outside the Guru's tent while Jamshed Khan, a hired assassin, stabbed the Guru twice. Khan was killed in one stroke by the Guru, while those outside, alerted by the tumult, killed Beg. Although the wound was sewn up the following day, the Guru died in Nanded
, Maharashtra
, India
in 1708.
Shortly before passing away Guru Gobind Singh Ji ordered that the Guru Granth Sahib
(the Sikh Holy Scripture), would be the ultimate spiritual authority for the Sikhs and temporal authority would be vested in the Khalsa Panth – the Sikh Nation. The first Sikh Holy Scripture was compiled and edited by the Fifth Guru, Guru Arjan in AD 1604, although some of the earlier gurus are also known to have documented their revelations. This is one of the few scriptures in the world that has been compiled by the founders of a faith during their own lifetime. The Guru Granth Sahib is particularly unique among sacred texts in that it is written in Gurmukhi script but contains many languages including Punjabi
, Hindi-Urdu, Sanskrit
, Bhojpuri, Assamese
and Persian
. Sikhs consider the Guru Granth Sahib the last, perpetual living guru.
was crowned on April 12, 1801 (to coincide with Baisakhi). Sahib Singh Bedi, a descendant of Guru Nanak Dev
, conducted the coronation. Gujranwala
served as his capital from 1799. In 1802 he shifted his capital to Lahore
& Amritsar
. Ranjit Singh rose to power in a very short period, from a leader of a single Sikh misl to finally becoming the Maharaja (Emperor) of Punjab.
There was strong collaboration in defense against foreign incursions such as those initiated by Ahmed Shah Abdali and Nadir Shah. The city of Amritsar
was attacked numerous times. Yet the time is remembered by Sikh historians as the "Heroic Century". This is mainly to describe the rise of Sikhs to political power against large odds. The circumstances were hostile religious environment against Sikhs, a tiny Sikh
population compared to other religious and political powers, which were much larger in the region than the Sikhs.
 The period from 1716 to 1799 was a highly turbulent time politically and militarily in the Punjab
The period from 1716 to 1799 was a highly turbulent time politically and militarily in the Punjab
. This was caused by the overall decline of the Mughal Empire
. This left a power vacuum that was eventually filled by the Sikhs in the late 18th century, after fighting off local Mughal remnants and allied Rajput leaders, Afghans, and occasionally hostile Punjabi Muslims who sided with other Muslim forces. Sikh warlords eventually formed their own independent Sikh administrative regions (misls), which were united in large part by Ranjit Singh.
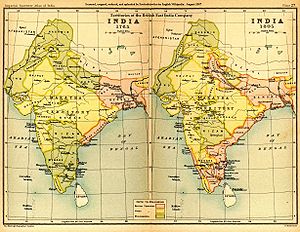
 The Sikh Empire (from 1801–1849) was formed on the foundations of the Punjabi Army by Maharaja Ranjit Singh
The Sikh Empire (from 1801–1849) was formed on the foundations of the Punjabi Army by Maharaja Ranjit Singh
. The Empire extended from Khyber Pass
in the west, to Kashmir in the north, to Sindh
in the south, and Tibet
in the east. The main geographical footprint of the empire was the Punjab
. The religious demography
of the Sikh Empire was Muslim
(80%), Sikh
(10%), Hindu
(10%),.
The foundations of the Sikh Empire, during the Punjab Army, could be defined as early as 1707, starting from the death of Aurangzeb
and the downfall of the Mughal Empire
. The fall of the Mughal Empire provided opportunities for the army, known as the Dal Khalsa
, to lead expeditions against the Mughals and Afghans
. This led to a growth of the army, which was split into different Punjabi Armies and then semi-independent misls. Each of these component armies were known as a misl
, each controlling different areas and cities. However, in the period from 1762-1799 Sikh
rulers of their misls appeared to be coming into their own. The formal start of the Sikh Empire began with the disbandment of the Punjab Army by the time of Coronation of Maharaja Ranjit Singh
in 1801, creating the one unified political Empire. All the misldars who were affiliated with the Army were nobility with usually long and prestigious family histories in Punjab's history.
 After Maharaja Ranjit Singh
After Maharaja Ranjit Singh
's death in 1839, the empire was severely weakened by internal divisions and political mismanagement. This opportunity was used by the British Empire
to launch the First Anglo-Sikh War
. The Battle of Ferozeshah
in 1845 marked many turning points, the British encountered the Punjabi Army, opening with a gun-duel in which the Sikhs "had the better of the British artillery". But as the British made advancements, Europeans in their army were especially targeted, as the Sikhs believed if the army "became demoralised, the backbone of the enemy's position would be broken". The fighting continued throughout the night earning the nickname "night of terrors". The British position "grew graver as the night wore on", and "suffered terrible casualties with every single member of the Governor General's staff either killed or wounded".
British General Sire James Hope Grant
recorded: "Truly the night was one of gloom and forbidding and perhaps never in the annals of warfare has a British Army on such a large scale been nearer to a defeat which would have involved annihilation" The Punjabi ended up recovering their camp, and the British were exhausted. Lord Hardinge sent his son to Mudki with a sword from his Napoleonic campaigns. A note in Robert Needham Cust
's diary revealed that the "British generals decided to lay down arms: News came from the Governor General that our attack of yesterday had failed, that affairs were disparate, all state papers were to be destroyed, and that if the morning attack failed all would be over, this was kept secret by Mr.Currie and we were considering measures to make an unconditional surrender to save the wounded...".
However, a series of events of the Sikhs being betrayed by some prominent leaders in the army led to its downfall. Maharaja
Gulab Singh and Dhian Singh, were Hindu
Dogra
s from Jammu
, and top Generals of the army. Tej Singh and Lal Singh were secretly allied to the British. They supplied important war plans of the Army, and provided the British with updated vital intelligence on the Army dealings, which ended up changing the scope of the war and benefiting the British positions.
The Punjab Empire was finally dissolved after a series of wars with the British at the end of the Second Anglo-Sikh War
in 1849 into separate princely states, and the British province of Punjab
that where granted a statehood, and eventually a lieutenant governorship stationed in Lahore as a direct representative of the Royal Crown in London.
in 1947, saw heavy conflict in the Punjab
between Sikh and Muslims, which saw the effective religious migration of Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus from West Punjab
which mirrored a similar religious migration of Punjabi Muslims in East Punjab
. The 1960s saw growing animosity and rioting between Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus in India, as the Punjabi Sikhs agitated for the creation of a Punjabi Sikh majority state, an undertaking which was promised to the Sikh leader Master Tara Singh
by Nehru in return for Sikh political support during the negotiations for Indian Independence. Sikhs obtained the Sikh majority state of Punjab
on November 1, 1966.
 Communal tensions arose again in the late 1970s, fueled by Sikh claims of discrimination and marginalization by the secularist dominated Indian National Congress
Communal tensions arose again in the late 1970s, fueled by Sikh claims of discrimination and marginalization by the secularist dominated Indian National Congress
ruling party and the "dictatorial" tactics adopted the then Indian Prime Minister, Indira Gandhi
. Frank argues that Gandhi
's assumption of emergency powers in 1975 resulted in the weakening of the "legitimate and impartial machinery of government" and her increasing "paranoia" of opposing political groups led her to instigate a "despotic policy of playing castes, religions and political groups against each other for political advantage". As a reaction against these actions came the emergence of the Sikh leader Sant Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale who vocalized Sikh sentiment for justice and advocated the creation of a Sikh homeland, Khalistan
. This accelerated Punjab into a state of communal violence. Gandhi
's 1984 action to defeat Sant Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale led to desecration of the Golden Temple
in Operation Bluestar and ultimately led to Gandhi's assassination by her Sikh bodyguards. This resulted in an explosion of violence against the Sikh community in the Anti Sikh Riots which resulted in the massacre of thousands of Sikhs throughout India; Khushwant Singh
described the actions as being a Sikh pogrom
in which he "felt like a refugee in my country. In fact, I felt like a Jew in Nazi Germany". Since 1984, relations between Sikhs and Hindus have reached a rapprochement helped by growing economic prosperity; however in 2002 the claims of the popular right-wing Hindu organization the RSS
, that "Sikhs are Hindus" angered Sikh sensibilities. Many Sikhs still are campaigning for justice for victims of the violence and the political and economic needs of the Punjab espoused in the Khalistan movement
. In 1996 the Special Rapporteur
for the Commission on Human Rights on freedom of religion or belief, Abdelfattah Amor (Tunisia, 1993–2004), visited India in order to compose a report on religious discrimination. In 1997, Amor concluded, "it appears that the situation of the Sikhs in the religious field is satisfactory, but that difficulties are arising in the political (foreign interference, terrorism, etc.), economic (in particular with regard to sharing of water supplies) and even occupational fields. Information received from nongovernment (sic) sources indicates that discrimination does exist in certain sectors of the public administration; examples include the decline in the number of Sikhs in the police force and the absence of Sikhs in personal bodyguard units since the murder of Indira Gandhi". In May 22, 2004 Manmohan Singh
became the first Sikh
to become the Prime Minister of India
.
Guru Angad
Sikh Guru's
Audio
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
is closely associated with the history of Punjab and the socio-political situation in medieval India
Medieval India
Medieval India refers to the Middle Ages i.e. 5th to 15th century AD in the Indian subcontinent, it includes:*Early Middle Ages: Middle kingdoms of India*Hoysala Empire*Kakatiya Kingdom*Delhi Sultanate*Ahom Kingdom*Reddy Kingdom...
. Sikh distinction was further enhanced by the establishment of the Khalsa
Khalsa
+YouWebImagesVideosMapsNewsMailMoreTranslateFrom: ArabicTo: EnglishEnglishHindiEnglishAllow phonetic typingHindiEnglishArabicAssumptionGoogle Translate for Business:Translator ToolkitWebsite TranslatorGlobal Market Finder...
(ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ), by Guru Gobind Singh in 1699. Sikhism was created by Guru Nanak Dev
Guru Nanak Dev
Guru Nanak was the founder of the religion of Sikhism and the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. The Sikhs believe that all subsequent Gurus possessed Guru Nanak’s divinity and religious authority, and were named "Nanak" in the line of succession.-Early life:Guru Nanak was born on 15 April 1469, now...
, a religious leader and a social reformer during the fifteenth century in the Punjab region
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
. The religious practice was formalized by Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh is the tenth and last Sikh guru in a sacred lineage of ten Sikh gurus. Born in Patna, Bihar in India, he was also a warrior, poet and philosopher. He succeeded his father Guru Tegh Bahadur as the leader of Sikhs at a young age of nine...
on March 30, 1699. The latter baptised five persons from different social backgrounds to form Khalsa
Khalsa
+YouWebImagesVideosMapsNewsMailMoreTranslateFrom: ArabicTo: EnglishEnglishHindiEnglishAllow phonetic typingHindiEnglishArabicAssumptionGoogle Translate for Business:Translator ToolkitWebsite TranslatorGlobal Market Finder...
. The first five, Pure Ones
Panj Piare
The Panj Piare , name given to the five Sikhs, Bhai Daya Singh, Bhai Dharam Singh, Bhai Himmat Singh, Bhai Mohkam Singh and Bhai Sahib Singh, who were so designated by Guru Gobind Singh at the historic divan at Anandpur Sahib on 30 March 1699 and who formed the nucleus of the Khalsa as the first...
, then baptized Gobind Singh into the Khalsa fold. This gives the Khalsa, as an organized grouping, a religious history of around 400 years.
Generally Sikhism has had amicable relations with other religions. However, during the Mughal rule of India (1556–1707), emerging religion had strained relation with the ruling Mughals. Prominent Sikh Gurus
Sikh Gurus
The Sikh Gurus established Sikhism from over the centuries beginning in the year 1469. Sikhism was founded by the first guru, Guru Nanak, and subsequently, all in order were referred to as "Nanak", and as "Lights", making their teachings in the holy scriptures, equivalent...
were martyred by Mughals for opposing some Mughal emperors' persecution of Sikhs and Hindus. Subsequently, Sikhism militarized to oppose Mughal hegemony. The emergence of the Sikh Confederacy
Sikh Confederacy
The Sikh Empire was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The empire, based around the Punjab region, existed from 1799 to 1849. It was forged, on the foundations of the Khalsa, under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh from a collection of autonomous Punjabi Misls...
under the misl
Misl
Misl generally refers to the twelve sovereign states in the Sikh Confederacy. The states formed a commonwealth that was described by Antoine Polier as an "aristocratic republic"...
s and Sikh Empire under reign of the Maharajah Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh
Maharaja Ranjit Singh Ji was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.-Early life:...
was characterized by religious tolerance and pluralism
Religious pluralism
Religious pluralism is a loosely defined expression concerning acceptance of various religions, and is used in a number of related ways:* As the name of the worldview according to which one's religion is not the sole and exclusive source of truth, and thus that at least some truths and true values...
with Christians, Muslims and Hindus in positions of power. The establishment of the Sikh Empire
Sikh Confederacy
The Sikh Empire was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The empire, based around the Punjab region, existed from 1799 to 1849. It was forged, on the foundations of the Khalsa, under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh from a collection of autonomous Punjabi Misls...
is commonly considered the zenith of Sikhism at political level, during this time the Sikh Empire
Sikh Confederacy
The Sikh Empire was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The empire, based around the Punjab region, existed from 1799 to 1849. It was forged, on the foundations of the Khalsa, under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh from a collection of autonomous Punjabi Misls...
came to include Kashmir
Kashmir
Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range...
, Ladakh
Ladakh
Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
, and Peshawar
Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa and the administrative center and central economic hub for the Federally Administered Tribal Areas of Pakistan....
. Hari Singh Nalwa
Hari Singh Nalwa
Hari Singh Nalwa was Commander-in-chief of the Khalsa, the army of the Sikh Empire. He is known for his role in the conquests of Kasur, Sialkot, Multan, Kashmir, Attock, and Peshawar. He led the Sikh Army in freeing Shah Shuja from Kashmir and secured the Koh-i-Nor diamond for Maharaja Ranjit Singh...
, the Commander-in-chief of the Sikh army along the North West Frontier, took the boundary of the Sikh Empire to the very mouth of the Khyber Pass
Khyber Pass
The Khyber Pass, is a mountain pass linking Pakistan and Afghanistan.The Pass was an integral part of the ancient Silk Road. It is mentioned in the Bible as the "Pesh Habor," and it is one of the oldest known passes in the world....
. The Empire's
Sikh Confederacy
The Sikh Empire was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The empire, based around the Punjab region, existed from 1799 to 1849. It was forged, on the foundations of the Khalsa, under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh from a collection of autonomous Punjabi Misls...
secular administration integrated innovative military, economic and governmental reforms.
The months leading up to the partition of India
Partition of India
The Partition of India was the partition of British India on the basis of religious demographics that led to the creation of the sovereign states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India on 14 and 15...
in 1947, saw heavy conflict in the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
between Sikh and Muslims, which saw the effective religious migration of Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus from West Punjab
Punjab (Pakistan)
Punjab is the most populous province of Pakistan, with approximately 45% of the country's total population. Forming most of the Punjab region, the province is bordered by Kashmir to the north-east, the Indian states of Punjab and Rajasthan to the east, the Pakistani province of Sindh to the...
which mirrored a similar religious migration of Punjabi Muslims in East Punjab
Punjab (India)
Punjab ) is a state in the northwest of the Republic of India, forming part of the larger Punjab region. The state is bordered by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south and southeast and Rajasthan to the southwest as well as the Pakistani province of Punjab to the...
.
Guru Nanak

Guru Nanak Dev
Guru Nanak Dev
Guru Nanak was the founder of the religion of Sikhism and the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. The Sikhs believe that all subsequent Gurus possessed Guru Nanak’s divinity and religious authority, and were named "Nanak" in the line of succession.-Early life:Guru Nanak was born on 15 April 1469, now...
(1469–1538), founder of Sikhism, was born to Kalu Mehta and Mata Tripta, wherein the Bedi Khatri
Khatri
Khatri is a caste from the northern Indian subcontinent. Khatris in India are mostly from Punjab, region but later they migrated to regions like Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Jammu, Uttarkhand, Himachal Pradesh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, Balochistan, Sindh and Khyber...
clan of a Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
family in the village of Talwandi
Nankana Sahib
Nankana Sahib , earlier known as Rai-Bhoi-Di-Talwandi, is a city in the Pakistani province of Punjab. It is named after the first Guru of the Sikhs, Guru Nanak Dev, the central figure in Sikhism who was born here, so it is a city of high historic and religious value and is a popular pilgrimage site...
, now called Nankana Sahib, near Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
. His father, a Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
named Mehta Kalu, was a Patwari, an accountant
Accountant
An accountant is a practitioner of accountancy or accounting , which is the measurement, disclosure or provision of assurance about financial information that helps managers, investors, tax authorities and others make decisions about allocating resources.The Big Four auditors are the largest...
of land revenue in the government. Nanak's mother was Mata Tripta, and he had one older sister, Bibi Nanki.
From an early age Guru Nanak seemed to have acquired a questioning and enquiring mind and refused as a child to wear the ritualistic "sacred" thread called a Janeu and instead said that he would wear the true name of God in his heart as protection, as the thread which could be broken, be soiled, burnt or lost could not offer any security at all. From early childhood, Bibi Nanki saw in her brother the Light of God but she did not reveal this secret to anyone. She is known as the first disciple of Guru Nanak.
Even as a boy, Nanak was fascinated by hindu religion, and his desire to explore the mysteries of life eventually led him to leave home. It was during this period that Nanak was said to have met Kabir
Kabir
Kabīr was a mystic poet and saint of India, whose writings have greatly influenced the Bhakti movement...
(1440–1518), a saint revered by many. Nanak married Sulakhni, daughter of Moolchand Chona, a trader from Batala
Batala
Batala is a municipal council in Gurdaspur district in the state of Punjab, India. It is located about 30 km from Gurdaspur, the headquarters of the district....
, and they had two sons, Sri Chand and Lakshmi Das.
His brother-in-law, Jai Ram, the husband of his sister Nanki, obtained a job for him in Sultanpur
Sultanpur Lodhi
Sultanpur Lodhi is a city and a municipal council in Kapurthala district in the Indian state of Punjab. The town is named after its founder, Sultan Khan Lodhi who was a general of Mahmud of Ghazni in AD 1103, which has been also mentioned in Ain-e-Akbari...
as the manager of the government granary. One morning, when he was twenty-eight, Guru Nanak Dev went as usual down to the river to bathe and meditate. It was said that he was gone for three days. When he reappeared, it is said he was "filled with the spirit of God". His first words after his re-emergence were: "there is no Hindu, there is no Muslim". With this secular principle he began his missionary
Missionary
A missionary is a member of a religious group sent into an area to do evangelism or ministries of service, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care and economic development. The word "mission" originates from 1598 when the Jesuits sent members abroad, derived from the Latin...
work. He made four distinct major journeys, in the four different directions, which are called Udasis, spanning many thousands of kilometres, preaching the message of God.
Guru Nanak spent the final years of his life in Kartarpur
Kartarpur
Kartarpur , was established by Guru Nanak in 1522. When Guru Nanak died, Hindus and Muslims disagreed on how to perform his last rites. A samadh lies in the Gurudwara and a grave lies on the premises as a reminder of this discord...
where Langar (free blessed food) was available. The food would be partaken of by Hindus, rich, poor, high or/and so called low castes. Guru Nanak worked in the fields and earned his livelihood. After appointing Bhai Lehna as the new Sikh Guru, on 22 September 1539, aged 70, Guru Nanak met with his demise.
Guru Angad
In 1538, Guru Nanak chose Lehna, his disciple, as a successor to the Guruship rather than one of his sons. Bhai Lehna was named Guru Angad and became the successor of Guru Nanak. Bhai Lehna was born in the village of Harike in Ferozepur district in PunjabPunjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
, on March 31, 1504. He was the son of a small trader named Pheru. His mother's name was Mata Ramo (also known as Mata Sabhirai, Mansa Devi, Daya Kaur). Baba Narayan Das Trehan was his grand father, whose ancestral house was at Matte-di-Sarai near Mukatsar.
Under the influence of his mother, Bhai Lehna began to worship Durga
Durga
For the 1985 Hindi Film of Rajesh Khanna see DurgaaIn Hinduism, Durga ; ; meaning "the inaccessible" or "the invincible"; , durga) or Maa Durga "one who can redeem in situations of utmost distress" is a form of Devi, the supremely radiant goddess, depicted as having eighteen arms, riding a lion...
(A Hindu Goddess). He used to lead a group of Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
worshippers to Jawalamukhi Temple every year. He married Mata Khivi
Mata Khivi
Mata Khivi came from the small town of Sanghar which is now located in the province of Sindh in Pakistan. She was married in 1519 at the age of 13. She was married to Lehna for 20 years before he became the second Guru of the Sikhs.She had 4 children,two boys and two girls. Their names were Bhai...
in January 1520 and had two sons, (Dasu and Datu), and two daughters (Amro and Anokhi). The whole Pheru family had to leave their ancestral village because of the ransacking by the Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
and Baloch military who had come with Emperor Babur
Babur
Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
. After this the family settled at the village of Khadur Sahib by the River Beas, near Tarn Taran
Tarn Taran
Tarn Taran may refer to:*Tarn Taran Sahib, a city in Tarn Taran district, Punjab, India*Tarn Taran district, a district in Punjab, India*Tarn Taran...
Sahib, a small town about 25 km. from Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
city.
One day, Bhai Lehna heard the recitation of a hymn of Guru Nanak from Bhai Jodha (a Sikh of Guru Nanak Sahib) who was in Khadur Sahib. He was thrilled and decided to proceed to Kartarpur
Kartarpur
Kartarpur , was established by Guru Nanak in 1522. When Guru Nanak died, Hindus and Muslims disagreed on how to perform his last rites. A samadh lies in the Gurudwara and a grave lies on the premises as a reminder of this discord...
to have an audience (darshan
Darshan
or Darshan is a Sanskrit term meaning "sight" , vision, apparition, or glimpse. It is most commonly used for "visions of the divine" in Hindu worship, e.g. of a deity , or a very holy person or artifact...
) with Guru Nanak. So while on the annual pilgrimage to Jwalamukhi Temple, Bhai Lehna left his journey to visit Kartarpur and see Baba Nanak. His very first meeting with Guru Nanak completely transformed him. He renounced the worship of the Hindu Goddess, dedicated himself to the service of Guru Nanak and so became his disciple, (his Sikh), and began to live in Kartarpur.
His devotion and service (Sewa
SEWA
The Self-Employed Women's Association of India is a trade union for poor, self-employed women workers in India. SEWA was founded in 1972 by the noted Gandhian and civil rights leader Dr Ela Bhatt. SEWA's main office is located in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, and it works in several states of India. SEWA...
) to Guru Nanak and his holy mission was so great that he was instated as the Second Nanak on September 7, 1539 by Guru Nanak. Earlier Guru Nanak tested him in various ways and found an embodiment of obedience and service in him. He spent six or seven years in the service of Guru Nanak at Kartarpur.
After the death of Guru Nanak on September 22, 1539, Guru Angad left Kartarpur for the village of Khadur Sahib (near Goindwal Sahib). He carried forward the principles of Guru Nanak both in letter and spirit. Yogis and Saints of different sects visited him and held detailed discussions about Sikhism with him.
Guru Angad introduced a new alphabet known as Gurmukhi Script, modifying the old Punjabi script's characters. Soon, this script became very popular and started to be used by the people in general. He took great interest in the education of children by opening many schools for their instruction and thus increased the number of literate people. For the youth he started the tradition of Mall Akhara, where physical as well as spiritual exercises were held. He collected the facts about Guru Nanak's life from Bhai Bala
Bhai Bala
Bhai Bala , born in Talvandi Rai Bhoi in a Jatt family. He was a supposed childhood friend and all his life a constant companion of Bhai Mardana and Guru Nanak. According to the Bhai Bala Janam Sakhi's. he travelled with Guru Nanak and Bhai Mardana on all their great journeys around the world...
and wrote the first biography of Guru Nanak. He also wrote 63 Salok
Salok
Salok is normally the final verse in a Bani. The final verse in the Japji Sahib is a Salok and the English translation is given below:Salok is normally the final verse in a Bani. The final verse in the Japji Sahib is a Salok and the English translation is given below:Salok is normally the final...
s (stanzas), which are included in the Guru Granth Sahib
Guru Granth Sahib
Sri Guru Granth Sahib , or Adi Granth, is the religious text of Sikhism. It is the final and eternal guru of the Sikhs. It is a voluminous text of 1430 angs, compiled and composed during the period of Sikh gurus, from 1469 to 1708...
. He popularised and expanded the institution of Guru ka Langar that had been started by Guru Nanak.
Guru Angad travelled widely and visited all important religious places and centres established by Guru Nanak for the preaching of Sikhism. He also established hundreds of new Centres of Sikhism (Sikh religious Institutions) and thus strengthened the base of Sikhism. The period of his Guruship was the most crucial one. The Sikh community had moved from having a founder to a succession of Gurus and the infrastructure of Sikh society was strengthened and crystallized – from being an infant, Sikhism had moved to being a young child and ready to face the dangers that were around. During this phase, Sikhism established its own separate spiritual path.
Guru Angad, following the example set by Guru Nanak, nominated Sri Amar Das as his successor (the Third Nanak) before his death. He presented all the holy scripts, including those he received from Guru Nanak, to Guru Amar Das. He breathed his last breath on March 29, 1552 at the age of forty-eight. It is said that he started to build a new town, at Goindwal near Khadur Sahib and Guru Amar Das Sahib was appointed to supervise its construction. It is also said that Humayun
Humayun
Nasir ud-din Muhammad Humayun was the second Mughal Emperor who ruled present day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of northern India from 1530–1540 and again from 1555–1556. Like his father, Babur, he lost his kingdom early, but with Persian aid, he eventually regained an even larger one...
, when defeated by Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri , birth name Farid Khan, also known as Sher Khan , was the founder of the short-lived Sur Empire in northern India, with its capital at Delhi, before its demise in the hands of the resurgent Mughal Empire...
, came to obtain the blessings of Guru Angad in regaining the throne of Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
.
Guru Amar Das
Guru Amar DasGuru Amar Das
Guru Amar Das was the third of the Ten Gurus of Sikhism and was given the title of Sikh Guru on 26 March 1552.-His life:...
became the third Sikh guru in 1552 at the age of 73. Goindwal became an important centre for Sikhism during the Guruship of Guru Amar Das. He continued to preach the principle of equality for women, the prohibition of Sati
Sati (practice)
For other uses, see Sati .Satī was a religious funeral practice among some Indian communities in which a recently widowed woman either voluntarily or by use of force and coercion would have immolated herself on her husband’s funeral pyre...
and the practise of Langar. In 1567, Emperor Akbar sat with the ordinary and poor people of Punjab to have Langar. Guru Amar Das also trained 140 apostles, of which 52 were women, to manage the rapid expansion of the religion. Before he died in 1574 aged 95, he appointed his son-in-law Jetha as the fourth Sikh Guru.
It is recorded that before becoming a Sikh, Bhai Amar Das, as he was known at the time, was a very religious Vaishanavite Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
who spent most of his life performing all of the ritual pilgrimages and fasts of a devout Hindu. One day, Bhai Amar Das heard some hymns of Guru Nanak being sung by Bibi Amro Ji, the daughter of Guru Angad, the second Sikh Guru. Bibi Amro was married to Bhai Sahib's brother, Bhai Manak Chand's son who was called Bhai Jasso. Bhai Sahib was so impressed and moved by these Shabads that he immediately decided to go to see Guru Angad at Khadur Sahib. It is recorded that this event took place when Bhai Sahib was 61 years old.
In 1635, upon meeting Guru Angad, Bhai Sahib was so touched by the Guru's message that he became a devout Sikh. Soon he became involved in Sewa
SEWA
The Self-Employed Women's Association of India is a trade union for poor, self-employed women workers in India. SEWA was founded in 1972 by the noted Gandhian and civil rights leader Dr Ela Bhatt. SEWA's main office is located in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, and it works in several states of India. SEWA...
(Service) to the Guru and the Community. Under the impact of Guru Angad and the teachings of the Gurus, Bhai Amar Das became a devout Sikh. He adopted Guru as his spiritual guide (Guru). Bhai Sahib began to live at Khadur Sahib, where he used to rise early in the morning and bring water from the Beas River for the Guru's bath; he would wash the Guru's clothes and fetch wood from the jungle for 'Guru ka Langar'. He was so dedicated to Sewa
SEWA
The Self-Employed Women's Association of India is a trade union for poor, self-employed women workers in India. SEWA was founded in 1972 by the noted Gandhian and civil rights leader Dr Ela Bhatt. SEWA's main office is located in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, and it works in several states of India. SEWA...
and the Guru and had completely extinguished pride and was totally lost in this commitment that he was considered an old man who had no interest in life; he was dubbed Amru, and generally forsaken.
However, as a result of Bhai Sahib's commitment to Sikhi principles, dedicated service and devotion to the Sikh cause, Guru Angad Sahib appointed Guru Amar Das Sahib as third Nanak in March 1552 at the age of 73. He established his headquarters at the newly built town of Goindwal, which Guru Angad had established.
Soon large numbers of Sikhs started flocking to Goindwal to see the new Guru. Here, Guru Amar Das propagated the Sikh faith in a vigorous, systematic and planned manner. He divided the Sikh Sangat area into 22 preaching centres or Manjis, each under the charge of a devout Sikh. He himself visited and sent Sikh missionaries to different parts of India to spread Sikhism.
Guru Amar Das was impressed with Bhai Gurdas
Bhai Gurdas
Bhai Gurdas was a Punjabi Sikh writer, historian, preacher and religious figure. He was the original scribe of the Guru Granth Sahib and a companion of four of the Sikh Gurus.-Early life:...
' thorough knowledge of Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
and Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
and the Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
scriptures. Following the tradition of sending out Masands across the country, Guru Amar Das deputed Bhai Gurdas to Agra
Agra
Agra a.k.a. Akbarabad is a city on the banks of the river Yamuna in the northern state of Uttar Pradesh, India, west of state capital, Lucknow and south from national capital New Delhi. With a population of 1,686,976 , it is one of the most populous cities in Uttar Pradesh and the 19th most...
to spread the gospel of Sikhism
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
. Before leaving, Guru Amar Das prescribed the following routine for Sikhs:
Guru Ji strengthened the tradition of 'Guru ka Langar' and made it compulsory for the visitor to the Guru to eat first, saying that 'Pehle Pangat Phir Sangat' (first visit the Langar then go to the Guru). Once the emperor Akbar came to see Guru Sahib and he had to eat the coarse rice in the Langar before he could have an interview with Guru Sahib. He was so much impressed with this system that he expressed his desire to grant some royal property for 'Guru ka Langar', but Guru Sahib declined it with respect.
He introduced new birth, marriage and death ceremonies. Thus he raised the status of women and protected the rights of female infants who were killed without question as they were deemed to have no status. These teachings met with stiff resistance from the Orthodox Hindus. He fixed three Gurpurbs for Sikh celebrations: Diwali
Diwali
Diwali or DeepavaliThe name of the festival in various regional languages include:, , , , , , , , , , , , , popularly known as the "festival of lights," is a festival celebrated between mid-October and mid-December for different reasons...
, Vaisakhi
Vaisakhi
Vaisakhi is an ancient harvest festival celebrated across North Indian states, especially Punjab by all Punjabis regardless of religion. In Sikhism the Khalsa was founded on same day as the Vaisakhi festival, so Sikhs celebrate twice as much....
and Maghi
Maghi
Maghi is the Punjabi festival of Makar Sankranti. It is celebrated in Punjab, Himachal Pradesh and Haryana. It is traditional for all Punjabis to eat rice made in boiled milk .-Celebration by Hindus:...
.
Guru Amar Das not only preached the equality of people irrespective of their caste but he also fostered the idea of women's equality. He preaching strongly against the practice of Sati
Sati (practice)
For other uses, see Sati .Satī was a religious funeral practice among some Indian communities in which a recently widowed woman either voluntarily or by use of force and coercion would have immolated herself on her husband’s funeral pyre...
(a Hindu wife burning on her husband's funeral pyre). Guru Amar Das also disapproved of a young widow remaining unmarried for the rest of her life.
Guru Amar Das constructed "Baoli" at Goindwal Sahib having eighty-four steps and made it a Sikh pilgrimage centre for the first time in the history of Sikhism. He reproduced more copies of the hymns of Guru Nanak and Guru Angad. He also composed 869 (according to some chronicles these were 709) verses (stanzas) including Anand Sahib
Anand Sahib
Anand Sahib: This Bani is part of the Nitnem or prayer which are read by Amritdhari Sikhs in the morning. The Bani was written by Guru Amar Das, the third Guru of the Sikhs and form part of the 5 Banis that are recited daily by baptised Sikhs. The Bani appears on pages 917 to 922 of Guru Granth...
, and then later on Guru Arjan (fifth Guru) made all the Shabads part of Guru Granth Sahib
Guru Granth Sahib
Sri Guru Granth Sahib , or Adi Granth, is the religious text of Sikhism. It is the final and eternal guru of the Sikhs. It is a voluminous text of 1430 angs, compiled and composed during the period of Sikh gurus, from 1469 to 1708...
.
When it came time for the Guru's younger daughter Bibi Bhani to marry, he selected a pious and diligent young follower of his called Jetha from Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
. Jetha had come to visit the Guru with a party of pilgrims from Lahore and had become so enchanted by the Guru's teachings that he had decided to settle in Goindwal. Here he earned a living selling wheat and would regularly attend the services of Guru Amar Das in his spare time.
Guru Amar Das did not consider anyone of his sons fit for Guruship and chose instead his son-in law (Guru) Ram Das to succeed him. Guru Amar Das Sahib at the age of 95 died on September 1, 1574 at Goindwal in District Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
, after giving responsibility of Guruship to the Fourth Nanak, Guru Ram Das
Guru Ram Das
Guru Ram Das was the fourth of the Ten Gurus of Sikhism and was given the title of Sikh Guru on 30 August 1574.-Early life:Ram Das was born in Lahore, Punjab on 24 September 1534[1] to a Sodhi family of the Khatri clan. His father was Hari Das and his mother Anup Devi. His wife was Bibi Bhani,...
.
Guru Ram Das
Guru Ram Das (Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ ਰਾਮ ਦਾਸ) (Born in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan on 24 September 1534 – 1 September 1581, Amritsar, Punjab, India) was the fourth of the Ten Gurus of Sikhism, and he became Guru on 30 August 1574, following in the footsteps of Guru Amar Das. He was born in Lahore to a Sodhi family of the Khatri clan. His father was Hari Das and mother Anup Devi, and his name was Jetha, meaning 'first born'. His wife was Bibi Bhani, the younger daughter of Guru Amar Das, the third guru of the Sikhs. They had three sons: Prithi Chand, Mahadev and Arjan Dev.As a Guru one of his main contributions to Sikhism was organizing the structure of Sikh society. Additionally, he was the author of Laava, the hymns of the Marriage Rites, the designer of the Harmandir Sahib, and the planner and creator of the township of Ramdaspur (later Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
).
A hymn by Guru Ram Das from page 305 of the Guru Granth Sahib:
"One who calls himself a Sikh of the True Guru shall get up early morning and meditate on the Lord's Name. Make effort regularly to cleanse, bathe and dip in the ambrosial pool. Upon Guru's instructions, chant Har, Har singing which, all misdeeds, sins and pains shall go away."
Guru Ram Das nominated Guru Arjan Dev, his youngest son, as the next Guru of the Sikhs.
Guru Arjan

In 1581, Guru Arjan — the youngest son of the fourth guru — became the Fifth Guru of the Sikhs. In addition to being responsible for building the Golden Temple, he prepared the Sikh Sacred text and his personal addition of some 2,000 plus hymns in the Gurū Granth Sāhib
Guru Granth Sahib
Sri Guru Granth Sahib , or Adi Granth, is the religious text of Sikhism. It is the final and eternal guru of the Sikhs. It is a voluminous text of 1430 angs, compiled and composed during the period of Sikh gurus, from 1469 to 1708...
.
In 1604 he installed the Ādi Granth
Adi Granth
Adi Granth is the early compilation of the Sikh Scriptures by Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji, the fifth Sikh Guru, in 1604. This Granth is the Holy Scripture of the Sikhs. The tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh added further holy Shabads to this Granth during the period 1704 to 1706...
for the first time as the Holy Book of the Sikhs. In 1606, for refusing to make changes to the Gurū Granth Sāhib, he was tortured and killed by the Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
rulers of the time.
Guru Har Gobind
Guru Har Gobind became the sixth guru of the Sikhs. He carried two swords — one for Spiritual reasons and one for temporal (worldly) reasons. From this point onward, the Sikhs became a military force and always had a trained fighting force to defend their independence.Guru Har Rai

Guru Har Rai (Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰਿ ਰਾਇ) (26 February 1630 - 6 October 1661) was the seventh of the ten Gurus of Sikhism, becoming Guru on 8 March 1644, following in the footsteps of his grandfather, Guru Har Gobind, who was the sixth guru. Before he died, he nominated Guru Har Krishan, his youngest son, as the next Guru of the Sikhs.
As a very young child he was disturbed by the suffering of a flower damaged by his robe in passing. Though such feelings are common with children, Guru Har Rai would throughout his life be noted for his compassion for life and living things. His grandfather, who was famed as an avid hunter, is said to have saved the Moghul Emperor Jahangir's life during a tiger's attack. Guru Har Rai continued the hunting tradition of his grandfather, but he would allow no animals to be killed on his grand Shikars. The Guru instead captured the animal and added it to his zoo.
He made several tours to the Malwa and Doaba regions of the Punjab.
His son, Ram Rai, seeking to assuage concerns of Aurangzeb over one line in Guru Nanak's verse (Mitti Mussalmam ki pede pai kumhar) suggested that the word Mussalmam was a mistake on the copyist's part, therefore distorting Bani. The Guru refused to meet with him again. The Guru is believed to have said, "Ram Rai, you have disobeyed my order and sinned. I will never see you again on account of your infidelity." It was also reported to the Guru that Ram Rai had also worked miracles in the Mughal's court against his father's direct instructions. Sikhs are constrained by their Gurus to not believe in magic and myth or miracles. Just before his death at age, 31, Guru Har Rai passed the Gaddi of Nanak on to his younger son, the five year old — Guru Har Krishan.
Guru Har Rai was the son of Baba Gurdita and Mata Nihal Kaur (also known as Mata Ananti Ji). Baba Gurdita was the son of the sixth Guru, Guru Hargobind. Guru Har Rai married Mata Kishan Kaur (sometimes also referred to as Sulakhni), daughter of Sri Daya Ram of Anoopshahr (Bulandshahr) in Uttar Pradesh on Har Sudi 3, Samvat 1697. Guru Har Rai had two sons: Baba Ram Rai and Sri Har Krishan.
Although, Guru Har Rai was a man of peace, he never disbanded the armed Sikh Warriors (Saint Soldiers), who earlier were maintained by his grandfather, Guru Hargobind. He always boosted the military spirit of the Sikhs, but he never himself indulged in any direct political and armed controversy with the contemporary Mughal Empire. Once, Dara Shikoh (the eldest son of emperor Shah Jahan), came to Guru Har Rai asking for help in the war of succession with his brother, the murderous Aurangzeb. The Guru had promised his grandfather to use the Sikh Cavalry only in defence. Nevertheless, he helped him to escape safely from the bloody hands of Aurangzeb's armed forces by having his Sikh warriors hide all the ferry boats at the river crossing used by Dara Shikoh in his escape.
Guru Har Krishan
Guru Har Krishan born in Kirat Pur, Ropar (Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰਿ ਕ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਨ) (7 July 1656 - 30 March 1664) was the eighth of the Ten Gurus of Sikhism, becoming the Guru on 7 October 1661, following in the footsteps of his father, Guru Har Rai. Before Har Krishan died of complications of SmallpoxSmallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease unique to humans, caused by either of two virus variants, Variola major and Variola minor. The disease is also known by the Latin names Variola or Variola vera, which is a derivative of the Latin varius, meaning "spotted", or varus, meaning "pimple"...
, he nominated his granduncle, Guru Teg Bahadur, as the next Guru of the Sikhs. The following is a summary of the main highlights of his short life:
When Har Krishan stayed in Delhi there was a smallpox epidemic and many people were dying. According to Sikh history at Har Krishan's blessing, the lake at Bangla Sahib provided cure for thousands. Gurdwara Bangla Sahib was constructed in the Guru's memory. This is where he stayed during his visit to Delhi. Gurdwara Bala Sahib was built in south Delhi besides the bank of the river Yamuna, where Har Krishan was cremated at the age of about 7 years and 8 months. Guru Har Krishan was the youngest Guru at only 7 years of age. He did not make any contributions to Gurbani.
Guru Tegh Bahadur
Guru Tegh Bahadur is the ninth of the SikhSikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
Gurus. Guru Tegh Bahadur sacrificed himself to protect Hindus. He was asked by Aurungzeb, the Mughal emperor, under coercion by Naqshbandi Islamists, to convert to Islam or to sacrifice himself. The exact place where he attained martyrdom is in front of the Red Fort in Delhi (Lal Qila) and the gurdwara is called Sisganj. This marked a turning point for Sikhism. His successor, Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh is the tenth and last Sikh guru in a sacred lineage of ten Sikh gurus. Born in Patna, Bihar in India, he was also a warrior, poet and philosopher. He succeeded his father Guru Tegh Bahadur as the leader of Sikhs at a young age of nine...
further militarised his followers.
Guru Gobind Singh Ji

Patna
Paṭnā , is the capital of the Indian state of Bihar and the second largest city in Eastern India . Patna is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world...
(Capital of Bihar, India). In 1675 Pundits from Kashmir in India came to Anandpur Sahib pleading to Guru Teg Bhadur Ji (Father of Guru Gobind Singh Ji) about Aurangzeb
Aurangzeb
Abul Muzaffar Muhy-ud-Din Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir , more commonly known as Aurangzeb or by his chosen imperial title Alamgir , was the sixth Mughal Emperor of India, whose reign lasted from 1658 until his death in 1707.Badshah Aurangzeb, having ruled most of the Indian subcontinent for nearly...
forcing them to convert to Islam. Guru Teg Bahadur told them that martyrdom of a great man was needed. His son, Guru Gobind Singh Ji said "Who could be greater than you", to his father. Guru Teg Bahadur Ji told pundits to tell Aurangzeb's men that if Guru Teg Bahadur Ji will become Muslim, they all will. Guru Teg Bahadur Ji was then martyred in Delhi, but before that he assigned Guru Gobind Singh Ji as 10th Guru at age of 9. After becoming Guru he commanded Sikhs to be armed. He fought many battles with Aurangzeb and some other Kings of that time, but always winner.
In 1699 he created the Khalsa
Khalsa
+YouWebImagesVideosMapsNewsMailMoreTranslateFrom: ArabicTo: EnglishEnglishHindiEnglishAllow phonetic typingHindiEnglishArabicAssumptionGoogle Translate for Business:Translator ToolkitWebsite TranslatorGlobal Market Finder...
panth
Panth
Panthan is the term used for several religious traditions in India.A panth is founded by a guru or an acharya, and is often led by scholars or senior practitioners of the tradition.Some of the major panthas in India are:...
, by giving amrit
Amrit Sanskar
Amrit Sanchar or the Amrit ceremony is the Sikh ceremony of initiation or baptism. This practice has been in existence since the times of Guru Nanak Dev . During that time-period, this ceremony was known as Charan Amrit or Charan Pahul or the Pag Pahul, the words Charan and Pag both signifying the...
to sikhs. In 1704 he fought the great battle with collective forces of Aurangzeb, Wazir Khan (Chief of Sarhind), and other kings. He left Anandpur and went to Chamkaur with only 40 sikhs. There he fought the Battle of Chamkaur
Battle of Chamkaur
The Battle Of Chamkaur or also known as Battle Of Chamkaur Sahib was a battle fought between the Khalsa led by Guru Gobind Singh against the Mughal forces led by Wazir Khan. Guru Gobind Singh makes a reference to this battle in Zafarnamah...
with 40 sikhs, vastly outnumbered by the Mughal soldiers. His two elder sons (at ages 17, 15) were martyred there. Wazir Khan killed other two (ages 9, 6). Guru Ji sent Aurangzeb the Zafarnamah
Zafarnamah
Zafarnāmah means the Epistle of Victory and is the name given to the letter sent by the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh Sahib in 1705 to the Mughal Emperor of India, Aurangzeb. The letter is written in Persian verse....
(Notification of Victory). Then he went to Nanded (Maharashtra, India). From there he made Baba Gurbakhash Singh, also aliased as Baba Banda Singh Bahadur, as his general and sent him to Punjab.
On the evening of the day when Baba Gurbakhash Singh left for Punjab, Guru Gobind Singh was visited by two Muslim soldiers. One of them was commissioned by Wazir Khan
Wazir Khan
Wazir Khan,Shaikh Ilam-ud-din Ansari , a native of Chiniot, who rose to be a minor court physician to Shah Jahan in Lahore, was a Mughal noble, who was the Subedar of Sirhind, he personally commanded an army of over 30,000 men consisting mainly of Muslim Rajputs.Wazir Khan is noted for his...
, Subedar of Sirhind, to assassinate Guru Gobind Singh. One of the assailants, Bashal Beg, kept a vigil outside the Guru's tent while Jamshed Khan, a hired assassin, stabbed the Guru twice. Khan was killed in one stroke by the Guru, while those outside, alerted by the tumult, killed Beg. Although the wound was sewn up the following day, the Guru died in Nanded
Nanded
Nanded is the second largest city in the Marathwada region of Maharashtra, India. It is also headquarters of Nanded district in the Marathwada Division of the state. It is an important holy place for the Sikh faith and is famous for the Hazur Sahib Gurudwara. It is the district headquarters once...
, Maharashtra
Maharashtra
Maharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
in 1708.
Shortly before passing away Guru Gobind Singh Ji ordered that the Guru Granth Sahib
Guru Granth Sahib
Sri Guru Granth Sahib , or Adi Granth, is the religious text of Sikhism. It is the final and eternal guru of the Sikhs. It is a voluminous text of 1430 angs, compiled and composed during the period of Sikh gurus, from 1469 to 1708...
(the Sikh Holy Scripture), would be the ultimate spiritual authority for the Sikhs and temporal authority would be vested in the Khalsa Panth – the Sikh Nation. The first Sikh Holy Scripture was compiled and edited by the Fifth Guru, Guru Arjan in AD 1604, although some of the earlier gurus are also known to have documented their revelations. This is one of the few scriptures in the world that has been compiled by the founders of a faith during their own lifetime. The Guru Granth Sahib is particularly unique among sacred texts in that it is written in Gurmukhi script but contains many languages including Punjabi
Punjabi language
Punjabi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by inhabitants of the historical Punjab region . For Sikhs, the Punjabi language stands as the official language in which all ceremonies take place. In Pakistan, Punjabi is the most widely spoken language...
, Hindi-Urdu, Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
, Bhojpuri, Assamese
Assamese language
Assamese is the easternmost Indo-Aryan language. It is used mainly in the state of Assam in North-East India. It is also the official language of Assam. It is also spoken in parts of Arunachal Pradesh and other northeast Indian states. Nagamese, an Assamese-based Creole language is widely used in...
and Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
. Sikhs consider the Guru Granth Sahib the last, perpetual living guru.
History
Ranjit SinghRanjit Singh
Maharaja Ranjit Singh Ji was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.-Early life:...
was crowned on April 12, 1801 (to coincide with Baisakhi). Sahib Singh Bedi, a descendant of Guru Nanak Dev
Guru Nanak Dev
Guru Nanak was the founder of the religion of Sikhism and the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. The Sikhs believe that all subsequent Gurus possessed Guru Nanak’s divinity and religious authority, and were named "Nanak" in the line of succession.-Early life:Guru Nanak was born on 15 April 1469, now...
, conducted the coronation. Gujranwala
Gujranwala
Gujranwala is a industrial city in the north-east of the Punjab province. It is the sixth largest city in Pakistan with a population of approximately 2,661,360 as on 24 June 2011...
served as his capital from 1799. In 1802 he shifted his capital to Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
& Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
. Ranjit Singh rose to power in a very short period, from a leader of a single Sikh misl to finally becoming the Maharaja (Emperor) of Punjab.
There was strong collaboration in defense against foreign incursions such as those initiated by Ahmed Shah Abdali and Nadir Shah. The city of Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
was attacked numerous times. Yet the time is remembered by Sikh historians as the "Heroic Century". This is mainly to describe the rise of Sikhs to political power against large odds. The circumstances were hostile religious environment against Sikhs, a tiny Sikh
Sikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
population compared to other religious and political powers, which were much larger in the region than the Sikhs.
Before the Empire

Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
. This was caused by the overall decline of the Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
. This left a power vacuum that was eventually filled by the Sikhs in the late 18th century, after fighting off local Mughal remnants and allied Rajput leaders, Afghans, and occasionally hostile Punjabi Muslims who sided with other Muslim forces. Sikh warlords eventually formed their own independent Sikh administrative regions (misls), which were united in large part by Ranjit Singh.
Formation

Maharaja Ranjit Singh (Punjab)
Maharaja Ranjit Singh Ji was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.-Early life:...
. The Empire extended from Khyber Pass
Khyber Pass
The Khyber Pass, is a mountain pass linking Pakistan and Afghanistan.The Pass was an integral part of the ancient Silk Road. It is mentioned in the Bible as the "Pesh Habor," and it is one of the oldest known passes in the world....
in the west, to Kashmir in the north, to Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
in the south, and Tibet
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region , Tibet or Xizang for short, also called the Xizang Autonomous Region is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China , created in 1965....
in the east. The main geographical footprint of the empire was the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
. The religious demography
Demography
Demography is the statistical study of human population. It can be a very general science that can be applied to any kind of dynamic human population, that is, one that changes over time or space...
of the Sikh Empire was Muslim
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
(80%), Sikh
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
(10%), Hindu
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
(10%),.
The foundations of the Sikh Empire, during the Punjab Army, could be defined as early as 1707, starting from the death of Aurangzeb
Aurangzeb
Abul Muzaffar Muhy-ud-Din Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir , more commonly known as Aurangzeb or by his chosen imperial title Alamgir , was the sixth Mughal Emperor of India, whose reign lasted from 1658 until his death in 1707.Badshah Aurangzeb, having ruled most of the Indian subcontinent for nearly...
and the downfall of the Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
. The fall of the Mughal Empire provided opportunities for the army, known as the Dal Khalsa
Dal Khalsa (Sikh Empire)
The Dal Khalsa was an army that operated in the 18th and 17th century Punjab region.-Mughal Rule of Punjab:The religion of Sikhism began at the time of the Conquest of Northern India by Babur. His grandson, Akbar supported religious freedom and after visiting the langar of Guru Amar Das had a...
, to lead expeditions against the Mughals and Afghans
Demographics of Afghanistan
The population of Afghanistan is around 29,835,392 as of the year 2011, which is unclear if the refugees living outside the country are included or not. The nation is composed of a multi-ethnic and multi-lingual society, reflecting its location astride historic trade and invasion routes between...
. This led to a growth of the army, which was split into different Punjabi Armies and then semi-independent misls. Each of these component armies were known as a misl
Misl
Misl generally refers to the twelve sovereign states in the Sikh Confederacy. The states formed a commonwealth that was described by Antoine Polier as an "aristocratic republic"...
, each controlling different areas and cities. However, in the period from 1762-1799 Sikh
Sikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
rulers of their misls appeared to be coming into their own. The formal start of the Sikh Empire began with the disbandment of the Punjab Army by the time of Coronation of Maharaja Ranjit Singh
Maharaja Ranjit Singh (Punjab)
Maharaja Ranjit Singh Ji was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.-Early life:...
in 1801, creating the one unified political Empire. All the misldars who were affiliated with the Army were nobility with usually long and prestigious family histories in Punjab's history.
End of Empire

Ranjit Singh
Maharaja Ranjit Singh Ji was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.-Early life:...
's death in 1839, the empire was severely weakened by internal divisions and political mismanagement. This opportunity was used by the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
to launch the First Anglo-Sikh War
First Anglo-Sikh War
The First Anglo-Sikh War was fought between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company between 1845 and 1846. It resulted in partial subjugation of the Sikh kingdom.-Background and causes of the war:...
. The Battle of Ferozeshah
Battle of Ferozeshah
The Battle of Ferozeshah was fought on 21 December and 22 December 1845 between the British and the Sikhs, at the village of Ferozeshah in Punjab. The British were led by Sir Hugh Gough and Governor-General Sir Henry Hardinge, while the Sikhs were led by Lal Singh.The British emerged victorious,...
in 1845 marked many turning points, the British encountered the Punjabi Army, opening with a gun-duel in which the Sikhs "had the better of the British artillery". But as the British made advancements, Europeans in their army were especially targeted, as the Sikhs believed if the army "became demoralised, the backbone of the enemy's position would be broken". The fighting continued throughout the night earning the nickname "night of terrors". The British position "grew graver as the night wore on", and "suffered terrible casualties with every single member of the Governor General's staff either killed or wounded".
British General Sire James Hope Grant
James Hope Grant
General Sir James Hope Grant GCB , British general, was the fifth and youngest son of Francis Grant of Kilgraston, Perthshire, and brother of Sir Francis Grant, President of the Royal Academy.-Military career:...
recorded: "Truly the night was one of gloom and forbidding and perhaps never in the annals of warfare has a British Army on such a large scale been nearer to a defeat which would have involved annihilation" The Punjabi ended up recovering their camp, and the British were exhausted. Lord Hardinge sent his son to Mudki with a sword from his Napoleonic campaigns. A note in Robert Needham Cust
Robert Needham Cust
Robert Needham Cust was a British colonial administrator and linguist.He was educated at Eton College, Trinity College, Cambridge, Haileybury and the College of Fort William, Calcutta, graduating from the last-named institution in 1844. He then worked for the East India Company, in Hoshiarpur and...
's diary revealed that the "British generals decided to lay down arms: News came from the Governor General that our attack of yesterday had failed, that affairs were disparate, all state papers were to be destroyed, and that if the morning attack failed all would be over, this was kept secret by Mr.Currie and we were considering measures to make an unconditional surrender to save the wounded...".
However, a series of events of the Sikhs being betrayed by some prominent leaders in the army led to its downfall. Maharaja
Maharaja
Mahārāja is a Sanskrit title for a "great king" or "high king". The female equivalent title Maharani denotes either the wife of a Maharaja or, in states where that was customary, a woman ruling in her own right. The widow of a Maharaja is known as a Rajamata...
Gulab Singh and Dhian Singh, were Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
Dogra
Dogra
The Dogras are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group in South Asia. Being a diversified group, the Dogras include both Savarnas such as Brahmins, Rajputs and Non-savarnas. The Dogras also incluide merchant castes such as Mahajans...
s from Jammu
Jammu
Jammu , also known as Duggar, is one of the three administrative divisions within Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state in India.Jammu city is the largest city in Jammu and the winter capital of Jammu and Kashmir...
, and top Generals of the army. Tej Singh and Lal Singh were secretly allied to the British. They supplied important war plans of the Army, and provided the British with updated vital intelligence on the Army dealings, which ended up changing the scope of the war and benefiting the British positions.
The Punjab Empire was finally dissolved after a series of wars with the British at the end of the Second Anglo-Sikh War
Second Anglo-Sikh War
The Second Anglo-Sikh War took place in 1848 and 1849, between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company. It resulted in the subjugation of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab and what subsequently became the North-West Frontier Province by the East India Company.-Background...
in 1849 into separate princely states, and the British province of Punjab
Punjab (British India)
Punjab was a province of British India, it was one of the last areas of the Indian subcontinent to fall under British rule. With the end of British rule in 1947 the province was split between West Punjab, which went to Pakistan, and East Punjab, which went to India...
that where granted a statehood, and eventually a lieutenant governorship stationed in Lahore as a direct representative of the Royal Crown in London.
Modern
The months leading up to the partition of IndiaPartition of India
The Partition of India was the partition of British India on the basis of religious demographics that led to the creation of the sovereign states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India on 14 and 15...
in 1947, saw heavy conflict in the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
between Sikh and Muslims, which saw the effective religious migration of Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus from West Punjab
Punjab (Pakistan)
Punjab is the most populous province of Pakistan, with approximately 45% of the country's total population. Forming most of the Punjab region, the province is bordered by Kashmir to the north-east, the Indian states of Punjab and Rajasthan to the east, the Pakistani province of Sindh to the...
which mirrored a similar religious migration of Punjabi Muslims in East Punjab
Punjab (India)
Punjab ) is a state in the northwest of the Republic of India, forming part of the larger Punjab region. The state is bordered by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south and southeast and Rajasthan to the southwest as well as the Pakistani province of Punjab to the...
. The 1960s saw growing animosity and rioting between Punjabi Sikhs and Hindus in India, as the Punjabi Sikhs agitated for the creation of a Punjabi Sikh majority state, an undertaking which was promised to the Sikh leader Master Tara Singh
Master Tara Singh
Master Tara Singh Malhotra was a prominent Sikh political and religious leader in the first half of the 20th century...
by Nehru in return for Sikh political support during the negotiations for Indian Independence. Sikhs obtained the Sikh majority state of Punjab
Punjab (India)
Punjab ) is a state in the northwest of the Republic of India, forming part of the larger Punjab region. The state is bordered by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south and southeast and Rajasthan to the southwest as well as the Pakistani province of Punjab to the...
on November 1, 1966.

Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is the largest and one of the oldest democratic political parties in the world. The party's modern liberal platform is largely considered center-left in the Indian...
ruling party and the "dictatorial" tactics adopted the then Indian Prime Minister, Indira Gandhi
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhara was an Indian politician who served as the third Prime Minister of India for three consecutive terms and a fourth term . She was assassinated by Sikh extremists...
. Frank argues that Gandhi
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhara was an Indian politician who served as the third Prime Minister of India for three consecutive terms and a fourth term . She was assassinated by Sikh extremists...
's assumption of emergency powers in 1975 resulted in the weakening of the "legitimate and impartial machinery of government" and her increasing "paranoia" of opposing political groups led her to instigate a "despotic policy of playing castes, religions and political groups against each other for political advantage". As a reaction against these actions came the emergence of the Sikh leader Sant Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale who vocalized Sikh sentiment for justice and advocated the creation of a Sikh homeland, Khalistan
Khalistan
Khalistan refers to a global political secessionist movement to create a separate Sikh state, called Khālistān , carved out of parts mostly consisting of the Punjab region of India, depending on definition....
. This accelerated Punjab into a state of communal violence. Gandhi
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhara was an Indian politician who served as the third Prime Minister of India for three consecutive terms and a fourth term . She was assassinated by Sikh extremists...
's 1984 action to defeat Sant Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale led to desecration of the Golden Temple
Harmandir Sahib
The Harmandir Sahib also Darbar Sahib , also referred to as the Golden Temple, is a prominent Sikh gurdwara located in the city of Amritsar, Punjab . Construction of the gurdwara was begun by Guru Ram Das, the fourth Sikh Guru, and completed by his successor, Guru Arjan Dev...
in Operation Bluestar and ultimately led to Gandhi's assassination by her Sikh bodyguards. This resulted in an explosion of violence against the Sikh community in the Anti Sikh Riots which resulted in the massacre of thousands of Sikhs throughout India; Khushwant Singh
Khushwant Singh
Khushwant Singh is a prominent Indian novelist and journalist. Singh's weekly column, "With Malice towards One and All", carried by several Indian newspapers, is among the most widely-read columns in the country....
described the actions as being a Sikh pogrom
Pogrom
A pogrom is a form of violent riot, a mob attack directed against a minority group, and characterized by killings and destruction of their homes and properties, businesses, and religious centres...
in which he "felt like a refugee in my country. In fact, I felt like a Jew in Nazi Germany". Since 1984, relations between Sikhs and Hindus have reached a rapprochement helped by growing economic prosperity; however in 2002 the claims of the popular right-wing Hindu organization the RSS
Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh
Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh or National Patriotic Organization), also known the Sangh, is a right-wing Hindu nationalist, paramilitary, volunteer, and allegedly militant organization for Hindu males in India...
, that "Sikhs are Hindus" angered Sikh sensibilities. Many Sikhs still are campaigning for justice for victims of the violence and the political and economic needs of the Punjab espoused in the Khalistan movement
Khalistan movement
Khalistan refers to a global political secessionist movement to create a separate Sikh state, called Khālistān , carved out of parts mostly consisting of the Punjab region of India, depending on definition....
. In 1996 the Special Rapporteur
Special Rapporteur
Special Rapporteur is a title given to individuals working on behalf of the United Nations within the scope of "Special Procedures" mechanisms who bear a specific mandate from the United Nations Human Rights Council....
for the Commission on Human Rights on freedom of religion or belief, Abdelfattah Amor (Tunisia, 1993–2004), visited India in order to compose a report on religious discrimination. In 1997, Amor concluded, "it appears that the situation of the Sikhs in the religious field is satisfactory, but that difficulties are arising in the political (foreign interference, terrorism, etc.), economic (in particular with regard to sharing of water supplies) and even occupational fields. Information received from nongovernment (sic) sources indicates that discrimination does exist in certain sectors of the public administration; examples include the decline in the number of Sikhs in the police force and the absence of Sikhs in personal bodyguard units since the murder of Indira Gandhi". In May 22, 2004 Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh is the 13th and current Prime Minister of India. He is the only Prime Minister since Jawaharlal Nehru to return to power after completing a full five-year term. A Sikh, he is the first non-Hindu to occupy the office. Singh is also the 7th Prime Minister belonging to the Indian...
became the first Sikh
Sikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
to become the Prime Minister of India
Prime Minister of India
The Prime Minister of India , as addressed to in the Constitution of India — Prime Minister for the Union, is the chief of government, head of the Council of Ministers and the leader of the majority party in parliament...
.
See also
- SikhSikhA Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
- Sikhism and Hinduism
- Sikhism and Jainism
- Islam and Sikhism
- Indian religions
External links
Guru Nanak- Max Arthur MacAuliff, The Sikh Religion, Vol 1, (The Life of Guru Nanak), Oxford University Press, 1909.
- Eternal Glory of Sri Guru Nanak Dev Ji
- Video on Guru Nanak Dev Ji
- Allaboutsikhs.com
- Sikhs.org
- Sikh-History.com
- JargSahib.com
- G5SikhMedia.co.uk
Guru Angad
- Detailed Account
- www.sgpc.net
- Gateway to Sikhism
- Sikh Missionary Center
- www.sikhpoint.com/
- www.ikonkar.com
- G5SikhMedia.co.uk
Sikh Guru's
Audio

