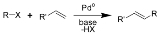
Heck reaction
Overview
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
of an unsaturated halide
Halide
A halide is a binary compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, or astatide compound. Many salts are halides...
(or triflate
Triflate
Trifluoromethanesulfonate, also known by the trivial name triflate, is a functional group with the formula CF3SO3-. The triflate group is often represented by -OTf, as opposed to -Tf...
) with an alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
and a base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
and palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. Together with the other palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions, this reaction is of great importance, as it allows one to do substitution reactions on planar centers. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck
Richard F. Heck
Richard Fred Heck is an American chemist noted for the discovery and development of the Heck reaction, which uses palladium to catalyze organic chemical reactions that couple aryl halides with alkenes....
. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outstanding contributions in chemistry, physics, literature,...
for the discovery and development of this reaction.
The reaction is performed in the presence of an organopalladium
Organopalladium
Organopalladium chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic palladium compounds and their reactions. Palladium is often used as a catalyst in the reduction of alkenes and alkynes with hydrogen. This process involves the formation of a palladium-carbon covalent bond...
catalyst.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

