
Hanja
Encyclopedia
Hanja is the Korean
name for the Chinese character
s hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese
and incorporated into the Korean language
with Korean pronunciation
. Hanja-mal or hanja-eo refers to words which can be written with hanja, and hanmun refers to Classical Chinese
writing, although "hanja" is sometimes used loosely to encompass these other concepts. Because hanja never underwent major reform, they are almost entirely identical to traditional Chinese and kyūjitai
characters. Only a small number of hanja characters are modified or unique to Korean. By contrast, many of the Chinese characters currently in use in Japan (kanji
) and Mainland China have been simplified, and contain fewer strokes than the corresponding hanja characters.
Although a phonetic Korean alphabet, now known as hangul
, had been created by a team of scholars commissioned in the 1440s by King Sejong the Great, it did not come into widespread use until the late 19th and early 20th century. Thus, until that time it was necessary to be fluent in reading and writing hanja in order to be literate in Korean, as the vast majority of Korean literature and most other Korean documents were written in hanja. Today, hanja plays a different role. Scholars who wish to study Korean history must study hanja in order to read historical documents. For the general public, learning a certain number of hanja is very helpful in understanding words that are formed with them. Hanja are not used to write native Korean words, which are always rendered in hangul, and even words of Chinese origin — hanja-eo (한자어, 漢字語) — are written with the hangul alphabet most of the time.
s into Korea
was the spread of Buddhism
. The major Chinese text that introduced hanja to Koreans, however, was not a religious text but the Chinese text, Cheonjamun
(Thousand Character Classic).
Koreans had to learn Classical Chinese
to be properly literate for the most part, but there were some systems developed to use simplified forms of Chinese characters that phonetically transcribe Korean, namely, hyangchal
(향찰; 鄕札), gugyeol
(구결; 口訣), and idu (이두; 吏讀).
One way of adapting hanja to write Korean in such systems (such as Gugyeol) was to represent native Korean grammatical particle
s and other words solely according to their pronunciation. For example, Gugyeol uses the characters 爲尼 to transcribe the Korean word "hăni", in modern Korean, that means "does, and so". However, in Chinese, the same characters are read as the expression "wéi ní," meaning "becoming a nun." This is a typical example of Gugyeol words where the radical (爲) is read in Korean for its meaning (hă — "to do") and the suffix 尼, ni (meaning 'nun'), used phonetically.
Hanja was the sole means of writing Korean until King Sejong the Great
promoted the invention of hangul
in the 15th century. However, even after the invention of hangul, most Korean scholars continued to write in hanmun.
It was not until the 20th century that hangul truly replaced hanja. Officially, hanja has not been used in North Korea
since June 1949 (additionally, all texts are now written horizontally instead of vertically). Additionally, many words borrowed from Chinese have been replaced in the North with native Korean words. However, there are a large number of Chinese-borrowed words in widespread usage in the North (although written in hangul), and hanja characters still appear in special contexts, such as recent North Korean dictionaries.
s plus in most cases one or more additional elements. The vast majority of hanja use the additional elements to indicate the sound of the character, but a few hanja are purely pictographic, and some were formed in other ways.
The word or words used to denote the meaning are often—though hardly always—words of native Korean (i.e., non-Chinese) origin, and are sometimes archaic words no longer commonly used.
, apart from the normal Korean language curriculum. Formal hanja education begins in grade 7 (junior high school) and continues until graduation from senior high school in grade 12. A total of 1,800 hanja are taught: 900 for junior high, and 900 for senior high (starting in grade 10). Post-secondary hanja education continues in some liberal arts
universities. The 1972 promulgation of basic hanja for educational purposes was altered on December 31, 2000, to replace 44 hanja with 44 others. The choice of characters to eliminate and exclude caused heated debates prior to and after the 2000 promulgation.
Though North Korea rapidly abandoned the general use of hanja soon after independence, the number of hanja actually taught in primary and secondary schools is greater than the 1,800 taught in South Korea. Kim Il-sung
had earlier called for a gradual elimination of the use of hanja, but by the 1960s, he had reversed his stance; he was quoted as saying in 1966, "While we should use as few Sinitic terms as possible, students must be exposed to the necessary Chinese characters and taught how to write them." As a result, a Chinese-character textbook was designed for North Korean schools for use in grades 5-9, teaching 1,500 characters, with another 500 for high school students. College students are exposed to another 1,000, bringing the total to 3,000.
In Korean language and Korean studies programs at universities around the world, a sample of hanja is typically a requirement for students. Becoming a graduate student in these fields usually requires students to learn at least the 1,800 basic hanja.
, two distinct hanja words (hanjaeo) may be spelled identically in the phonetic hangul alphabet
. Thus, hanja are often used to clarify meaning, either on their own without the equivalent hangul spelling, or in parentheses after the hangul spelling as a kind of gloss. Hanja are often also used as a form of shorthand in newspaper headlines, advertisements, and on signs, for example the banner at the funeral for the sailors
lost in the sinking of ROKS Cheonan (PCC-772)
.
es. For example, the hanja 辛 (sin or shin, meaning sour or hot) appears prominently on packages of Shin Ramyun
noodles.
This practice helps to eliminate ambiguity, and it also serves as a sort of shorthand etymology, since the meaning of the hanja and the fact that the word is composed of hanja often help to illustrate the word's origin.
As an example of how hanja can help to clear up ambiguity, many homophones are written in hangul as 수도 (sudo), including:
Hanja dictionaries (Jajeon (자전, 字典) or Okpyeon (옥편, 玉篇)) are organized by radical
s, and kanji (Japanese, 漢字).
are generally based on hanja, although some exceptions exist. On business cards, the use of hanja is slowly fading away, with most older people displaying their names in hanja while most of the younger generation utilizes Hangul
. Korean personal names usually consist of a one-character family name (seong, 성, 姓) followed by a two-character given name (ireum, 이름). There are a few 2-character family names (e.g. 남궁, 南宮, Namgung), and the holders of such names — but not only them — tend to have one-syllable given names. Traditionally, the given name in turn consists of one character unique to the individual and one character shared by all people in a family of the same sex and generation (see Generation name
). Things have changed, however, and while these rules are still largely followed, some people have given names that are native Korean words (popular ones include "Haneul" — meaning "sky" — and "Iseul" — meaning "morning dew"). Nevertheless, on official documents, people's names are still recorded in both hangul and in hanja (if the name is composed of hanja).
and Joseon
eras, native Korean placenames were converted to hanja, and most names used today are hanja-based. The most notable exception is the name of the capital, Seoul
– although Seoul is the English pronunciation of 서울 (Seo-Ul) which literally means 'Capital'. Disyllabic names of railway lines, freeways, and provinces are often formed by taking one character from each of the two locales' names. For Seoul, the abbreviation is the hanja gyeong (경, 京, "capital"). Thus,
Most atlases of Korea today are published in two versions: one in hangul (sometimes with some English as well), and one in hanja. Subway and railway station signs give the station's name in hangul, hanja, and English, both to assist visitors and to disambiguate the name.
, the standard script in the Korean language. Some studies suggest that hanja use appears to be in decline. In 1956, one study found mixed-script Korean text (in which Sino-Korean nouns are written using hanja, and other words using hangul) were read faster than texts written purely in hangul; however, by 1977, the situation had reversed. In 1988, 80% of one sample of people without a college education "evinced no reading comprehension of any but the simplest, most common hanja" when reading mixed-script passages.
).
Further examples include 媤 시 /si/, 曺 조 /jo/, 㕦/夻 화 /hwa/, 巭 부 /bu/, 娚 남 /nam/, 頉 탈 /tal/, 囍 희 /hui/, 䭏 편 /pyeon/, and 哛 뿐 /ppun/.
Compare to the parallel development in Japan of , of which there are hundreds, many rarely used – these were often developed for native Japanese plants and animals.
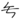 Some hanja characters have simplified forms (약자, 略字, yakja) that can be seen in casual use. An example is
Some hanja characters have simplified forms (약자, 略字, yakja) that can be seen in casual use. An example is 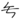 , which is a cursive form of 無 (meaning "nothing").
, which is a cursive form of 無 (meaning "nothing").
of hanja in Korean is not identical to the way they are pronounced in modern Chinese, particularly Mandarin, although some Chinese dialects and Korean share similar pronunciations for some characters. For example, 印刷 "print" is yìnshuā in Mandarin Chinese and inswae (인쇄) in Korean, but it is pronounced insue in Shanghainese
(a Wu Chinese dialect). One obvious difference is the complete loss of tone
from Korean while all Chinese dialects retain tone. In other aspects, the pronunciation of hanja is more conservative than most northern and central Chinese dialects, for example in the retention of labial consonant
coda
s in characters with labial consonant
onsets, such as the characters 法 (법 beop) and 凡 (범 beom); the labial codas existed in Middle Chinese
but do not survive intact in most northern and central Chinese varieties today.
Due to divergence in pronunciation since the time of borrowing, sometimes the pronunciation of a hanja and its corresponding hanzi may differ considerably. For example, 女 ("woman") is nǚ in Mandarin Chinese and nyeo (녀) in Korean. However, in most modern Korean dialects (especially South Korea
n ones), 女 is pronounced as yeo (여) when used in an initial position, due to a systematic elision
of initial ns when followed by y or i.
Additionally, sometimes a hanja-derived word will have altered pronunciation of a character to reflect Korean pronunciation shifts, for example mogwa 모과 木瓜 "quince" from mokgwa 목과.
Korean language
Korean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
name for the Chinese character
Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
and incorporated into the Korean language
Korean language
Korean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
with Korean pronunciation
Pronunciation
Pronunciation refers to the way a word or a language is spoken, or the manner in which someone utters a word. If one is said to have "correct pronunciation", then it refers to both within a particular dialect....
. Hanja-mal or hanja-eo refers to words which can be written with hanja, and hanmun refers to Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese or Literary Chinese is a traditional style of written Chinese based on the grammar and vocabulary of ancient Chinese, making it different from any modern spoken form of Chinese...
writing, although "hanja" is sometimes used loosely to encompass these other concepts. Because hanja never underwent major reform, they are almost entirely identical to traditional Chinese and kyūjitai
Kyujitai
Kyūjitai, literally "old character forms" , are the traditional forms of kanji, Chinese written characters used in Japanese. Their simplified counterparts are shinjitai, "new character forms". Some of the simplified characters arose centuries ago and were in everyday use in both China and Japan,...
characters. Only a small number of hanja characters are modified or unique to Korean. By contrast, many of the Chinese characters currently in use in Japan (kanji
Kanji
Kanji are the adopted logographic Chinese characters hanzi that are used in the modern Japanese writing system along with hiragana , katakana , Indo Arabic numerals, and the occasional use of the Latin alphabet...
) and Mainland China have been simplified, and contain fewer strokes than the corresponding hanja characters.
Although a phonetic Korean alphabet, now known as hangul
Hangul
Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean...
, had been created by a team of scholars commissioned in the 1440s by King Sejong the Great, it did not come into widespread use until the late 19th and early 20th century. Thus, until that time it was necessary to be fluent in reading and writing hanja in order to be literate in Korean, as the vast majority of Korean literature and most other Korean documents were written in hanja. Today, hanja plays a different role. Scholars who wish to study Korean history must study hanja in order to read historical documents. For the general public, learning a certain number of hanja is very helpful in understanding words that are formed with them. Hanja are not used to write native Korean words, which are always rendered in hangul, and even words of Chinese origin — hanja-eo (한자어, 漢字語) — are written with the hangul alphabet most of the time.
History
A major impetus for the introduction of Chinese characterChinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s into Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
was the spread of Buddhism
Korean Buddhism
Korean Buddhism is distinguished from other forms of Buddhism by its attempt to resolve what it sees as inconsistencies in Mahayana Buddhism. Early Korean monks believed that the traditions they received from foreign countries were internally inconsistent. To address this, they developed a new...
. The major Chinese text that introduced hanja to Koreans, however, was not a religious text but the Chinese text, Cheonjamun
Thousand Character Classic
The Thousand Character Classic is a Chinese poem used as a primer for teaching Chinese characters to children. It contains exactly one thousand unique characters. It is said that Emperor Wu of the Liang Dynasty commissioned 周興嗣 to compose this poem for his prince to practice calligraphy...
(Thousand Character Classic).
Koreans had to learn Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese or Literary Chinese is a traditional style of written Chinese based on the grammar and vocabulary of ancient Chinese, making it different from any modern spoken form of Chinese...
to be properly literate for the most part, but there were some systems developed to use simplified forms of Chinese characters that phonetically transcribe Korean, namely, hyangchal
Hyangchal
Hyangchal is an archaic writing system of Korea and was used to transcribe the Korean language in hanja. Under the hyangchal system, Chinese characters were given a Korean reading based on the syllable associated with the character. The hyangchal writing system is often classified as a...
(향찰; 鄕札), gugyeol
Gugyeol
Gugyeol is a system for rendering texts written in Classical Chinese into understandable Korean. It was chiefly used during the Joseon Dynasty, when readings of the Chinese classics were of paramount social importance...
(구결; 口訣), and idu (이두; 吏讀).
One way of adapting hanja to write Korean in such systems (such as Gugyeol) was to represent native Korean grammatical particle
Grammatical particle
In grammar, a particle is a function word that does not belong to any of the inflected grammatical word classes . It is a catch-all term for a heterogeneous set of words and terms that lack a precise lexical definition...
s and other words solely according to their pronunciation. For example, Gugyeol uses the characters 爲尼 to transcribe the Korean word "hăni", in modern Korean, that means "does, and so". However, in Chinese, the same characters are read as the expression "wéi ní," meaning "becoming a nun." This is a typical example of Gugyeol words where the radical (爲) is read in Korean for its meaning (hă — "to do") and the suffix 尼, ni (meaning 'nun'), used phonetically.
Hanja was the sole means of writing Korean until King Sejong the Great
Sejong the Great of Joseon
Sejong the Great was the fourth king of the Joseon Dynasty of Korea. During his regency, he reinforced Korean Confucian policies and executed major legal amendments . He also used the creation of Hangul and the advancement of technology to expand his territory...
promoted the invention of hangul
Hangul
Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean...
in the 15th century. However, even after the invention of hangul, most Korean scholars continued to write in hanmun.
It was not until the 20th century that hangul truly replaced hanja. Officially, hanja has not been used in North Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
since June 1949 (additionally, all texts are now written horizontally instead of vertically). Additionally, many words borrowed from Chinese have been replaced in the North with native Korean words. However, there are a large number of Chinese-borrowed words in widespread usage in the North (although written in hangul), and hanja characters still appear in special contexts, such as recent North Korean dictionaries.
Character formation
Each hanja is composed of one of 214 radicalRadical (Chinese character)
A Chinese radical is a component of a Chinese character. The term may variously refer to the original semantic element of a character, or to any semantic element, or, loosely, to any element whatever its origin or purpose...
s plus in most cases one or more additional elements. The vast majority of hanja use the additional elements to indicate the sound of the character, but a few hanja are purely pictographic, and some were formed in other ways.
Eumhun (sound and meaning)
To aid in understanding the meaning of a character, or to describe it orally to distinguish it from other characters with the same pronunciation, character dictionaries and school textbooks refer to each character with a combination of its sound and a word indicating its meaning. This dual meaning-sound reading of a character is called eumhun (음훈; 音訓; from 音 "sound" + 訓 "meaning," "teaching").The word or words used to denote the meaning are often—though hardly always—words of native Korean (i.e., non-Chinese) origin, and are sometimes archaic words no longer commonly used.
Education
Hanja are still taught in separate courses in South Korean high schoolsEducation in South Korea
Education in South Korea is viewed as being crucial for success and competition is consequently very heated and fierce. A centralized administration oversees the process for the education of children from kindergarten to the third and final year of high school. Mathematics, science, Korean, social...
, apart from the normal Korean language curriculum. Formal hanja education begins in grade 7 (junior high school) and continues until graduation from senior high school in grade 12. A total of 1,800 hanja are taught: 900 for junior high, and 900 for senior high (starting in grade 10). Post-secondary hanja education continues in some liberal arts
Liberal arts
The term liberal arts refers to those subjects which in classical antiquity were considered essential for a free citizen to study. Grammar, Rhetoric and Logic were the core liberal arts. In medieval times these subjects were extended to include mathematics, geometry, music and astronomy...
universities. The 1972 promulgation of basic hanja for educational purposes was altered on December 31, 2000, to replace 44 hanja with 44 others. The choice of characters to eliminate and exclude caused heated debates prior to and after the 2000 promulgation.
Though North Korea rapidly abandoned the general use of hanja soon after independence, the number of hanja actually taught in primary and secondary schools is greater than the 1,800 taught in South Korea. Kim Il-sung
Kim Il-sung
Kim Il-sung was a Korean communist politician who led the Democratic People's Republic of Korea from its founding in 1948 until his death in 1994. He held the posts of Prime Minister from 1948 to 1972 and President from 1972 to his death...
had earlier called for a gradual elimination of the use of hanja, but by the 1960s, he had reversed his stance; he was quoted as saying in 1966, "While we should use as few Sinitic terms as possible, students must be exposed to the necessary Chinese characters and taught how to write them." As a result, a Chinese-character textbook was designed for North Korean schools for use in grades 5-9, teaching 1,500 characters, with another 500 for high school students. College students are exposed to another 1,000, bringing the total to 3,000.
In Korean language and Korean studies programs at universities around the world, a sample of hanja is typically a requirement for students. Becoming a graduate student in these fields usually requires students to learn at least the 1,800 basic hanja.
Current uses of hanja
Because many different hanja—and thus, many different words written using hanja—often share the same soundsHomophone
A homophone is a word that is pronounced the same as another word but differs in meaning. The words may be spelled the same, such as rose and rose , or differently, such as carat, caret, and carrot, or to, two, and too. Homophones that are spelled the same are also both homographs and homonyms...
, two distinct hanja words (hanjaeo) may be spelled identically in the phonetic hangul alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
. Thus, hanja are often used to clarify meaning, either on their own without the equivalent hangul spelling, or in parentheses after the hangul spelling as a kind of gloss. Hanja are often also used as a form of shorthand in newspaper headlines, advertisements, and on signs, for example the banner at the funeral for the sailors
Republic of Korea Navy
The Republic of Korea Navy or the ROK Navy is the branch of the South Korean armed forces responsible for conducting naval operations and amphibious landing operations. The ROK Navy includes the Republic of Korea Marine Corps, which is a quasi-autonomous organization...
lost in the sinking of ROKS Cheonan (PCC-772)
ROKS Cheonan (PCC-772)
ROKS Cheonan was a South Korean Pohang-class corvette of the Republic of Korea Navy , commissioned in 1989. On 26 March 2010, it broke in two and sank near the sea border with North Korea...
.
Hanja in print media
In South Korea, hanja are used most frequently in academic literature, where they often appear without the equivalent hangul spelling. Usually, only those words with a specialized or ambiguous meaning are printed in hanja. In mass-circulation books and magazines, hanja are generally used rarely, and only to gloss words already spelled in hangul when the meaning is ambiguous. Hanja are also often used in newspaper headlines as abbreviations or to eliminate the ambiguity typical of newspaper headlines in any language. In formal publications, personal names are also usually glossed in hanja in parentheses next to the hangul. In contrast, North Korea eliminated the use of hanja even in academic publications by 1949, a situation which has since remained unchanged. Hanja are often used for advertising or decorative purposes, and appear frequently in athletic events and cultural parades, dictionaries and atlasAtlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a map of Earth or a region of Earth, but there are atlases of the other planets in the Solar System. Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats...
es. For example, the hanja 辛 (sin or shin, meaning sour or hot) appears prominently on packages of Shin Ramyun
Shin ramyun
Shin Ramyun is a spicy brand of Korean instant noodles produced by Nong Shim Ltd. since 1986. It is exported to over 80 different countries, and is the highest selling brand of noodles in Korea.-Packaging:...
noodles.
Hanja in dictionaries
In modern Korean dictionaries, all entry words of Sino-Korean origin are printed in hangul and listed in hangul order, with the hanja given in parentheses immediately following the entry word.This practice helps to eliminate ambiguity, and it also serves as a sort of shorthand etymology, since the meaning of the hanja and the fact that the word is composed of hanja often help to illustrate the word's origin.
As an example of how hanja can help to clear up ambiguity, many homophones are written in hangul as 수도 (sudo), including:
- 修道 — spiritual discipline
- 受渡 — receipt and delivery
- 囚徒 — prisoner
- 水都 — 'city of water' (e.g. Venice or Hong Kong)
- 水稻 — riceRiceRice is the seed of the monocot plants Oryza sativa or Oryza glaberrima . As a cereal grain, it is the most important staple food for a large part of the world's human population, especially in East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and the West Indies...
- 水道 — drain
- 隧道 — tunnelTunnelA tunnel is an underground passageway, completely enclosed except for openings for egress, commonly at each end.A tunnel may be for foot or vehicular road traffic, for rail traffic, or for a canal. Some tunnels are aqueducts to supply water for consumption or for hydroelectric stations or are sewers...
- 水道 — rivers, path of surface water
- 首都 — capital (city)
- 手刀 — hand-knife
Hanja dictionaries (Jajeon (자전, 字典) or Okpyeon (옥편, 玉篇)) are organized by radical
Radical (Chinese character)
A Chinese radical is a component of a Chinese character. The term may variously refer to the original semantic element of a character, or to any semantic element, or, loosely, to any element whatever its origin or purpose...
s, and kanji (Japanese, 漢字).
Hanja in personal names
Korean personal namesKorean name
A Korean name consists of a family name followed by a given name, as used by the Korean people in both North Korea and South Korea. In the Korean language, 'ireum' or 'seong-myeong' usually refers to the family name and given name together...
are generally based on hanja, although some exceptions exist. On business cards, the use of hanja is slowly fading away, with most older people displaying their names in hanja while most of the younger generation utilizes Hangul
Hangul
Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean...
. Korean personal names usually consist of a one-character family name (seong, 성, 姓) followed by a two-character given name (ireum, 이름). There are a few 2-character family names (e.g. 남궁, 南宮, Namgung), and the holders of such names — but not only them — tend to have one-syllable given names. Traditionally, the given name in turn consists of one character unique to the individual and one character shared by all people in a family of the same sex and generation (see Generation name
Generation name
Generation name, variously zibei or banci, is one of the characters in a traditional Chinese name, and is so called because each member of a generation share that character, unlike surnames or given names...
). Things have changed, however, and while these rules are still largely followed, some people have given names that are native Korean words (popular ones include "Haneul" — meaning "sky" — and "Iseul" — meaning "morning dew"). Nevertheless, on official documents, people's names are still recorded in both hangul and in hanja (if the name is composed of hanja).
Hanja in place names
Due to standardization efforts during GoryeoGoryeo
The Goryeo Dynasty or Koryŏ was a Korean dynasty established in 918 by Emperor Taejo. Korea gets its name from this kingdom which came to be pronounced Korea. It united the Later Three Kingdoms in 936 and ruled most of the Korean peninsula until it was removed by the Joseon dynasty in 1392...
and Joseon
Joseon Dynasty
Joseon , was a Korean state founded by Taejo Yi Seong-gye that lasted for approximately five centuries. It was founded in the aftermath of the overthrow of the Goryeo at what is today the city of Kaesong. Early on, Korea was retitled and the capital was relocated to modern-day Seoul...
eras, native Korean placenames were converted to hanja, and most names used today are hanja-based. The most notable exception is the name of the capital, Seoul
Seoul
Seoul , officially the Seoul Special City, is the capital and largest metropolis of South Korea. A megacity with a population of over 10 million, it is the largest city proper in the OECD developed world...
– although Seoul is the English pronunciation of 서울 (Seo-Ul) which literally means 'Capital'. Disyllabic names of railway lines, freeways, and provinces are often formed by taking one character from each of the two locales' names. For Seoul, the abbreviation is the hanja gyeong (경, 京, "capital"). Thus,
- The GyeongbuGyeongbuThe name Gyeongbu refers to the Seoul-Busan corridor in South Korea. It is used as the name of the Gyeongbu railway line and Gyeongbu Expressway, both of which connect Seoul—the South Korean capital and largest city—to Busan—the largest port and second-largest city...
(경부, 京釜) corridor connects Seoul (gyeong) with BusanBusanBusan , formerly spelled Pusan is South Korea's second largest metropolis after Seoul, with a population of around 3.6 million. The Metropolitan area population is 4,399,515 as of 2010. It is the largest port city in South Korea and the fifth largest port in the world...
(bu); - The GyeonginGyeonginThe name Gyeongin refers to the Seoul-Incheon corridor in South Korea, and is used as a name for the Gyeongin railway line, the Gyeongin Expressway, and the Gyeongin Canal , all of which link Seoul—the South Korean capital and largest city—to nearby Incheon—the second-largest port and...
(경인, 京仁) corridor connects Seoul with IncheonIncheonThe Incheon Metropolitan City is located in northwestern South Korea. The city was home to just 4,700 people when Jemulpo port was built in 1883. Today 2.76 million people live in the city, making it Korea’s third most populous city after Seoul and Busan Metropolitan City...
(in); - The former JeollaJeollaJeolla was a province in southwestern Korea, one of the historical Eight Provinces of Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. It consisted of the modern South Korean provinces of North Jeolla, South Jeolla and the Special City of Gwangju as well as Jeju Island...
(전라, 全羅) Province took its name from the first characters in the city names JeonjuJeonjuJeonju is a city in South Korea, and the capital of Jeollabuk-do, or North Jeolla Province. It is an important tourist center famous for Korean food, historic buildings, sports activities and innovative festivals.- History :...
(전주, 全州) and NajuNajuNaju is a city in South Jeolla Province, South Korea.The capital of South Jeolla was located at Naju until it was moved to Gwangju in 1895. The name Jeolla actually originates from the first character of Jeonju and the first character of Naju . Dongshin University is situated in Naju...
(나주, 羅州) ("Naju" is originally "Raju," but the initial "r/l" sound in South Korean is simplified to "n").
Most atlases of Korea today are published in two versions: one in hangul (sometimes with some English as well), and one in hanja. Subway and railway station signs give the station's name in hangul, hanja, and English, both to assist visitors and to disambiguate the name.
Hanja usage
Opinion surveys show that the South Korean public do not consider hanja literacy essential, a situation attributed to the fact that formal hanja education in South Korea does not begin until the seventh year of schooling. Hanja terms are also expressed through hangulHangul
Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean...
, the standard script in the Korean language. Some studies suggest that hanja use appears to be in decline. In 1956, one study found mixed-script Korean text (in which Sino-Korean nouns are written using hanja, and other words using hangul) were read faster than texts written purely in hangul; however, by 1977, the situation had reversed. In 1988, 80% of one sample of people without a college education "evinced no reading comprehension of any but the simplest, most common hanja" when reading mixed-script passages.
Korean hanja
A small number of characters were invented by Koreans themselves. Most of them are for proper names (place-names and people's names) but some refer to Korean-specific concepts and materials. They include 畓 (논 답; non dap; "paddyfield"), 乭 (Dol, a character only used in given names), 㸴 (So, a rare surname from Seongju), and 怾 (Gi, an old name of the KumgangsanKumgangsan
Kŭmgangsan , Geumgangsan, or Mount Geumgang is a -high mountain in Kangwon-do, North Korea. Its name means "a firm heart in the face of truth". It is about 50 km away from South Korea's Sokcho in Gangwon-do. It is one of the best-known mountains in North Korea...
).
Further examples include 媤 시 /si/, 曺 조 /jo/, 㕦/夻 화 /hwa/, 巭 부 /bu/, 娚 남 /nam/, 頉 탈 /tal/, 囍 희 /hui/, 䭏 편 /pyeon/, and 哛 뿐 /ppun/.
Compare to the parallel development in Japan of , of which there are hundreds, many rarely used – these were often developed for native Japanese plants and animals.
Yakja
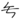
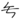 , which is a cursive form of 無 (meaning "nothing").
, which is a cursive form of 無 (meaning "nothing").Pronunciation
Each hanja character is pronounced as a single syllable, corresponding to a single composite character in hangul. The pronunciationPronunciation
Pronunciation refers to the way a word or a language is spoken, or the manner in which someone utters a word. If one is said to have "correct pronunciation", then it refers to both within a particular dialect....
of hanja in Korean is not identical to the way they are pronounced in modern Chinese, particularly Mandarin, although some Chinese dialects and Korean share similar pronunciations for some characters. For example, 印刷 "print" is yìnshuā in Mandarin Chinese and inswae (인쇄) in Korean, but it is pronounced insue in Shanghainese
Shanghainese
Shanghainese , or the Shanghai language , is a dialect of Wu Chinese spoken in the city of Shanghai and the surrounding region. It is classified as part of the Sino-Tibetan family of languages. Shanghainese, like other Wu dialects, is largely not mutually intelligible with other Chinese varieties...
(a Wu Chinese dialect). One obvious difference is the complete loss of tone
Tone (linguistics)
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or inflect words. All verbal languages use pitch to express emotional and other paralinguistic information, and to convey emphasis, contrast, and other such features in what is called...
from Korean while all Chinese dialects retain tone. In other aspects, the pronunciation of hanja is more conservative than most northern and central Chinese dialects, for example in the retention of labial consonant
Labial consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals...
coda
Syllable coda
In phonology, a syllable coda comprises the consonant sounds of a syllable that follow the nucleus, which is usually a vowel. The combination of a nucleus and a coda is called a rime. Some syllables consist only of a nucleus with no coda...
s in characters with labial consonant
Labial consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals...
onsets, such as the characters 法 (법 beop) and 凡 (범 beom); the labial codas existed in Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese , also called Ancient Chinese by the linguist Bernhard Karlgren, refers to the Chinese language spoken during Southern and Northern Dynasties and the Sui, Tang, and Song dynasties...
but do not survive intact in most northern and central Chinese varieties today.
Due to divergence in pronunciation since the time of borrowing, sometimes the pronunciation of a hanja and its corresponding hanzi may differ considerably. For example, 女 ("woman") is nǚ in Mandarin Chinese and nyeo (녀) in Korean. However, in most modern Korean dialects (especially South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
n ones), 女 is pronounced as yeo (여) when used in an initial position, due to a systematic elision
Elision
Elision is the omission of one or more sounds in a word or phrase, producing a result that is easier for the speaker to pronounce...
of initial ns when followed by y or i.
Additionally, sometimes a hanja-derived word will have altered pronunciation of a character to reflect Korean pronunciation shifts, for example mogwa 모과 木瓜 "quince" from mokgwa 목과.
See also
- Basic hanja for educational use
- List of Korea-related topics
- Sino-Korean vocabulary
- Chinese characterChinese characterChinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
- Korean mixed scriptKorean mixed scriptKorean mixed script is a form of writing that uses both Hangul and hanja .The script has never been used for languages other than Korean. In North Korea, writing in mixed script was replaced by writing only in Hangul in the middle of the 20th century and has not been used since...
- KanjiKanjiKanji are the adopted logographic Chinese characters hanzi that are used in the modern Japanese writing system along with hiragana , katakana , Indo Arabic numerals, and the occasional use of the Latin alphabet...
(Japanese equivalent) - Hantu (Vietnamese equivalent)

