Korean name
Encyclopedia
A Korean name consists of a family name
followed by a given name
, as used by the Korean people
in both North Korea
and South Korea
. In the Korean language
, 'ireum' or 'seong-myeong' usually refers to the family name (seong) and given name (ireum in a narrow sense) together. There are only about 250 Korean family names currently in use, and the three most common (Kim
, Lee
, and Park
) account for nearly half of the population. While the small number of surnames at first suggests that a long history of the use of family names has led to surname extinction, the history is much more complicated – as recently as 1910, over half the population had no family name.
Traditional Korean names typically consist of only one syllable, due in part to the Korean Naming Laws of 1812. There is no middle name
in the Western sense. Many Koreans have their given names made of a generational name
syllable and an individually distinct syllable, while this practice is declining in the younger generations. The generational name syllable is shared by siblings in North Korea
, and by all members of the same generation of an extended family in South Korea
. Married men and women usually keep their full personal names, and children inherit the father's family name.
The family names are subdivided into bon-gwan
(clans), i.e. extended families which originate in the lineage system used in previous historical periods. Each clan is identified by a specific place, and traces its origin to a common patrilineal ancestor.
Early names based on the Korean language
were recorded in the Three Kingdoms
period (57 BCE – 668 CE), but with the growing adoption of Chinese writing system, these were gradually replaced by names based on Chinese characters. During periods of Mongol influence, the ruling class supplemented their Korean names with Mongolian names. In addition, during the later period of Japanese rule
in the early 20th century, Koreans were forced to adopt Japanese names. In recent decades, there has been a trend towards using native Korean words as names, although still a small minority.
Because of the many changes in Korean romanization practices
over the years, modern Koreans, when using European languages, romanize their names in various ways, most often approximating the pronunciation in English orthography
. Some keep the original order of names, while others reverse the names to match the usual Western
pattern.
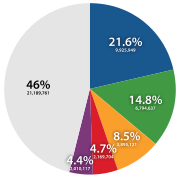
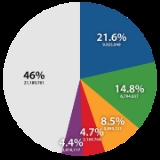
 There are approximately 250 family names in use today. Each family name is divided into one or more clans (bon-gwan
There are approximately 250 family names in use today. Each family name is divided into one or more clans (bon-gwan
), identifying the clan's city of origin. For example, the most populous clan is Gimhae Kim
; that is, the Kim
clan from the city of Gimhae
. Clans are further subdivided into various pa, or branches stemming from a more recent common ancestor, so that a full identification of a person's family name would be clan-surname-branch. For example, "Kyoungjoo Yi(Lee)ssi"(Kyoung-Joo Lee Clan, or Lee Clan of Kyoung-Joo) and "Yeonan-Yissi"(Lee Clan of Yeonan) are, technically speaking, completely different surnames, even though both are - in the most areas of life - simply referred to as "Yi(Lee)". This also means that people from the same clan are considered to be of same blood, such that marriage of a man and a woman of same surname and "bon-gwan" is considered a strong taboo, regardless of how distant the actual lineages may be, even to the present day.
Korean women traditionally keep their family names after their marriage, but their children take the father's surname. In the pre-modern, patriarchal Korean society people were extremely conscious of familial values and their own family identities. Korean women keep their surnames after marriage based on traditional reasoning that it is what they inherited from their parents and ancestors, and cannot be changed. According to traditions, each clan publishes a comprehensive genealogy (jokbo
) every 30 years. However, it is not uncommon for women to be addressed with their husband's surnames after marriage.
There are around a dozen two-syllable surnames, all of which rank after the 100 most common surnames. The five most common family names, which together make up over half of the Korean population, are used by over 20 million people in South Korea.
s, a custom originating in China. One of the two characters in a given name is unique to the individual, while the other is shared by all people in a family generation. Therefore, it is common for cousins to have the same character (dollimja) in their given names in the same fixed position. In North Korea
, generational names are no longer shared across families, but are still commonly shared by brothers and sisters.
Given names are typically composed of hanja
, or Chinese characters. In North Korea, the hanja are no longer used to write the names, but the meanings are still understood; thus, for example, the syllable cheol (철, 鐵) is used in boys' names and means "iron". In South Korea, section 37 of the Family Registry Law requires that the hanja in personal names be taken from a restricted list. Unapproved hanja must be represented by hangul, or Korean characters, in the family registry. In March 1991, the Supreme Court of South Korea
published the Table of Hanja for Personal Name Use which allowed a total of 2,854 hanja in new South Korean given names (as well as 61 alternate forms). The list was expanded in 1994, 1997, 2001, and 2005. Thus there are now 5,038 hanja permitted in South Korean names, in addition to a small number of alternate forms.
While the traditional practice is still largely followed, since the late 1970s, some parents have given their children names that are native Korean
words, usually of two syllables. This has been largely restricted to girl's names. Popular native Korean given names of this sort include Haneul (하늘; "Heaven" or "Sky"), Areum (아름; "Beauty"), Gippeum (기쁨; "Joy") and Iseul (이슬; "Dew"). Despite this trend away from traditional practice, people's names are still recorded in both hangul
and hanja
(if available) on official documents, in family genealogies, and so on.
difficulty for learners of Korean as a foreign language, and for Korean learners of Western languages.
A variety of replacements are used for the actual name of the person. It is acceptable among adults of similar status to address the other by their full name, with the suffix ssi (氏, 씨) added. However, it is inappropriate to address someone by their surname alone, even with such a suffix. Whenever the person has an official rank, it is typical to address him or her by the name of that rank (such as "Manager"), often with the honorific nim (님) added. In such cases, the full name of the person may be appended, although this can also imply that the speaker is of higher status.
Among children and close friends, it is common to use a person's birth name.
s are used sparingly for children today.
Upon marriage, women usually lost their amyeong, and were called by a taekho, referring to their town of origin.
In addition, teknonymy
, or referring to parents by their children's names, is a common practice. It is most commonly used in referring to a mother by the name of her eldest son, as in "Cheolsu's mom" (철수 엄마). However, it can be extended to either parent and any child, depending upon the context.
Confucianism
is characterized by extreme sexual segregation and a double standard of sexual morality. Examples of this can be observed in the clear hierarchical order of sexes. For example, women who are married are often referred to as ansaram (inside person) or jibsaram (home person), indicating that a wife’s realm is strictly restricted to domesticity.
In traditional Korean name acquisition, it is very common for the wife to keep her family name after marriage; however, the children must take their father’s name.
Honorifics suggest the more complicated relationships of roles and power to be the prime system of address in Korean society. Kinship ties are very important and these ties will go beyond the nuclear family unit. In Korean names however, the singular pronoun used to identify individuals has no gender. This means that, while most English first names (Jennifer, Mark, Candice, and Nicholas) attach a gender specific context, Korean names do not. Commonly, English-to-Korean translating programs cannot identify the proper Korean pronouns as being male or female and will therefore skew the original sentence structure.
through the gradual adoption of Chinese forms of naming as centralized kingdoms came to dominate Korean life. A complex system, including courtesy names and pen name
s as well as posthumous name
s and childhood names, arose out of Confucian
tradition. The courtesy name system in particular arose from the Classic of Rites
, a core text of the Confucian canon.
, native given names were sometimes composed of three syllables like Misaheun (미사흔) and Sadaham (사다함), which were later transcribed into hanja
(未斯欣, 斯多含). The use of family names was limited to kings in the beginning, but gradually spread to aristocrats and eventually to most of the population.
Some recorded family names are apparently native Korean words, such as toponyms. At that time, some characters of Korean names might have been read not by their Sino-Korean pronunciation but by their native reading (see hanja
). For example, the native Korean name of Yeon Gaesomun
(연개소문; 淵蓋蘇文), the first Grand Prime Minister of Goguryeo
, can linguistically be reconstructed as "Eol Kasum" (/*älkasum/). Early Silla
names are also believed to represent Old Korean
vocabulary; for example, Bak Hyeokgeose, the name of the founder of Silla, was pronounced something like "Bulgeonuri" (弗矩內), which can be translated as "bright world".
, family names were bestowed by kings upon their supporters. For example, in 33 CE, King Yuri
gave the six headmen of Saro (later Silla
) the names Lee (이), Bae (배), Choi (최), Jeong (정), Son (손) and Seol (설). However, this account is not generally credited by modern historians, who hold that Confucian-style surnames as above were more likely to have come into general use in the 5th and subsequent centuries, as the Three Kingdoms increasingly adopted the Chinese model.
Only a handful of figures from the Three Kingdoms period are recorded as having borne a courtesy name, such as Seol Chong
. The custom only became widespread in the Goryeo
period, as Confucianism took hold among the literati. In 1055, Goryeo established a new law limiting access to the civil service exam to those with family names.
For men of yangban
rank, a complex system of alternate names had been developed by the Joseon Dynasty
. Peasants sometimes had only amyong throughout their lives. According to a census taken in 1910, at the end of the Joseon Dynasty and the beginning of Japanese rule, a little more than half of the population did not have family names.
and Sino-Korean names. The scions of the ruling class were sent to the Yuan
court for schooling. For example, King Gongmin
had both the Mongolian name Bayan Temür (伯顏帖木兒) and the Sino-Korean name Wang Gi (王祺) (later renamed Wang Jeon (王顓)).
of Korea (1910–1945), Koreans were forced to adopt Japanese
-language names.
In 1939, as part of Governor-General
Jiro Minami
's policy of cultural assimilation (同化政策; dōka seisaku), Ordinance No. 20 (commonly called the "Name Order", or Sōshi-kaimei (創氏改名) in Japanese
) was issued, and became law in April 1940. Although the Japanese Governor-General officially prohibited compulsion, low-level officials effectively forced Koreans to adopt Japanese-style family and given names. By 1944, approximately 84 percent of the population had registered Japanese family names.
Sōshi (Japanese) means the creation of a Japanese family name (shi, Korean ssi), distinct from a Korean family name or seong (Japanese sei). Japanese family names represent the families they belong to and can be changed by marriage and other procedures, while Korean family names represent paternal linkages and are unchangeable. Japanese policy dictated that Koreans either could register a completely new Japanese family name unrelated to their Korean surname, or have their Korean family name, in Japanese form, automatically become their Japanese name if no surname was submitted before the deadline.
After the liberation of Korea from Japanese rule, the Name Restoration Order (조선 성명 복구령; 朝鮮姓名復舊令) was issued on October 23, 1946 by the United States military administration
south of the 38th parallel north
, enabling Koreans to restore their original Korean names if they wished to.
Japanese conventions of creating given names, such as using "子" (Japanese ko and Korean ja) in feminine names, is seldom seen in present-day Korea, both North and South. In the North, a campaign to eradicate such Japanese-based names was launched in the 1970s. In the South, and presumably in the North as well, these names are regarded as old and unsophisticated.
systems used for geographic and other names in North and South Korea, personal names are generally romanized according to personal preference. Thus a family name such as "Lee" may also be found spelled "I", "Yi", "Rhee", and "Rhie".
The initial sound in "Kim" shares features with both the English 'k' (in initial position, an aspirated voiceless velar stop) and "hard g" (an unaspirated voiced velar stop). When pronounced initially, Kim starts with an unaspirated voiceless velar stop
sound; it is voiceless like /k/, but also unaspirated like /ɡ/. As aspiration is a distinctive feature in Korean but voicing is not, "Gim" is more likely to be understood correctly. "Kim" is used nearly universally in both North and South Korea.
The family name "Lee" is pronounced as 리 (ri) in North Korea and as 이 (i) in South Korea. In the former case, the initial sound is an alveolar liquid. There is no distinction between the alveolar liquids /l/ and /r/, which is why "Lee" and "Rhee" are both common spellings. In South Korea, the pronunciation of the name is simply the English vowel sound for a "long e", as in see. This pronunciation is also often spelled as "Yi"; the Northern pronunciation is commonly romanized "Ri".
In Korean pronunciation, the name usually romanized as "Park" actually has no 'r' sound at all. Its initial sound is an unaspirated voiceless bilabial stop, like a cross between English 'p' and 'b'. The vowel is a, similar to the 'a' in father. For this reason, the name is also often transcribed "Pak" or "Bak".
Family name
A family name is a type of surname and part of a person's name indicating the family to which the person belongs. The use of family names is widespread in cultures around the world...
followed by a given name
Given name
A given name, in Western contexts often referred to as a first name, is a personal name that specifies and differentiates between members of a group of individuals, especially in a family, all of whose members usually share the same family name...
, as used by the Korean people
Korean people
The Korean people are an ethnic group originating in the Korean peninsula and Manchuria. Koreans are one of the most ethnically and linguistically homogeneous groups in the world.-Names:...
in both North Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
and South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
. In the Korean language
Korean language
Korean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
, 'ireum' or 'seong-myeong' usually refers to the family name (seong) and given name (ireum in a narrow sense) together. There are only about 250 Korean family names currently in use, and the three most common (Kim
Kim (Korean name)
Kim, sometimes spelled Gim, is the most common family name in Korea. The name is common in both modern-day North Korea and South Korea. The hanja used for the name means "gold," and although the character is usually pronounced 금 geum, it is pronounced 김 gim when used for the family name and...
, Lee
Lee (Korean name)
Lee is the common English spelling of 이 , a common Korean family name. The proper pronunciation in South Korea is like the English letter "E", although in North Korea the name is still written as "리" and pronounced "Lee". Many times South Koreans will knowingly introduce themselves as "Lee" to...
, and Park
Park (Korean name)
Park is a common and time-honoured Korean surname, founded by King Hyeokgeose. All Parks are descendants of him in principle except naturalized people...
) account for nearly half of the population. While the small number of surnames at first suggests that a long history of the use of family names has led to surname extinction, the history is much more complicated – as recently as 1910, over half the population had no family name.
Traditional Korean names typically consist of only one syllable, due in part to the Korean Naming Laws of 1812. There is no middle name
Middle name
People's names in several cultures include one or more additional names placed between the first given name and the surname. In Canada and the United States all such names are specifically referred to as middle name; in most European countries they would simply be regarded as second, third, etc....
in the Western sense. Many Koreans have their given names made of a generational name
Generation name
Generation name, variously zibei or banci, is one of the characters in a traditional Chinese name, and is so called because each member of a generation share that character, unlike surnames or given names...
syllable and an individually distinct syllable, while this practice is declining in the younger generations. The generational name syllable is shared by siblings in North Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
, and by all members of the same generation of an extended family in South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
. Married men and women usually keep their full personal names, and children inherit the father's family name.
The family names are subdivided into bon-gwan
Bon-gwan
Bon-gwan is the concept of clan in Korea, which is used to distinguish clans that happen to share a same family name . Since Korea has been traditionally a Buddhist country this clan system is cognate with Gotra in Sanskrit texts and shares most features...
(clans), i.e. extended families which originate in the lineage system used in previous historical periods. Each clan is identified by a specific place, and traces its origin to a common patrilineal ancestor.
Early names based on the Korean language
Korean language
Korean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
were recorded in the Three Kingdoms
Three Kingdoms of Korea
The Three Kingdoms of Korea refer to the ancient Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla, which dominated the Korean peninsula and parts of Manchuria for much of the 1st millennium...
period (57 BCE – 668 CE), but with the growing adoption of Chinese writing system, these were gradually replaced by names based on Chinese characters. During periods of Mongol influence, the ruling class supplemented their Korean names with Mongolian names. In addition, during the later period of Japanese rule
Korea under Japanese rule
Korea was under Japanese rule as part of Japan's 35-year imperialist expansion . Japanese rule ended in 1945 shortly after the Japanese defeat in World War II....
in the early 20th century, Koreans were forced to adopt Japanese names. In recent decades, there has been a trend towards using native Korean words as names, although still a small minority.
Because of the many changes in Korean romanization practices
Korean romanization
Korean romanization is a system for representing the Korean language using the Roman alphabet. In Korea, the Korean language is written using hangul, and sometimes hanja....
over the years, modern Koreans, when using European languages, romanize their names in various ways, most often approximating the pronunciation in English orthography
English orthography
English orthography is the alphabetic spelling system used by the English language. English orthography, like other alphabetic orthographies, uses a set of habits to represent speech sounds in writing. In most other languages, these habits are regular enough so that they may be called rules...
. Some keep the original order of names, while others reverse the names to match the usual Western
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West and the Occident , is a term referring to the countries of Western Europe , the countries of the Americas, as well all countries of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand...
pattern.

Family names
| Hangul | Hanja | Revised Revised Romanization of Korean The Revised Romanization of Korean is the official Korean language romanization system in South Korea proclaimed by Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism, replacing the older McCune–Reischauer system... |
MR McCune-Reischauer McCune–Reischauer romanization is one of the two most widely used Korean language romanization systems, along with the Revised Romanization of Korean, which replaced McCune–Reischauer as the official romanization system in South Korea in 2000... |
Common spellings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 김 | 金 | Gim | Kim Kim (Korean name) Kim, sometimes spelled Gim, is the most common family name in Korea. The name is common in both modern-day North Korea and South Korea. The hanja used for the name means "gold," and although the character is usually pronounced 금 geum, it is pronounced 김 gim when used for the family name and... |
Kim |
| 리 (N North Korea The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea... ) 이 (S South Korea The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south... ) |
李 | Ri (N) I (S) |
Ri (N) Yi (S) |
Lee Lee (Korean name) Lee is the common English spelling of 이 , a common Korean family name. The proper pronunciation in South Korea is like the English letter "E", although in North Korea the name is still written as "리" and pronounced "Lee". Many times South Koreans will knowingly introduce themselves as "Lee" to... , Yi, Rhee, Rhie, Reeh, Yie, Ee |
| 박 | 朴 | Bak | Pak | Park Park (Korean name) Park is a common and time-honoured Korean surname, founded by King Hyeokgeose. All Parks are descendants of him in principle except naturalized people... , Pak |
| 최 | 崔 | Choe | Ch'oe | Choi |
| 정 | 鄭 丁 |
Jeong | Chŏng | Chung, Jung |

Bon-gwan
Bon-gwan is the concept of clan in Korea, which is used to distinguish clans that happen to share a same family name . Since Korea has been traditionally a Buddhist country this clan system is cognate with Gotra in Sanskrit texts and shares most features...
), identifying the clan's city of origin. For example, the most populous clan is Gimhae Kim
Kim (Korean name)
Kim, sometimes spelled Gim, is the most common family name in Korea. The name is common in both modern-day North Korea and South Korea. The hanja used for the name means "gold," and although the character is usually pronounced 금 geum, it is pronounced 김 gim when used for the family name and...
; that is, the Kim
Kim (Korean name)
Kim, sometimes spelled Gim, is the most common family name in Korea. The name is common in both modern-day North Korea and South Korea. The hanja used for the name means "gold," and although the character is usually pronounced 금 geum, it is pronounced 김 gim when used for the family name and...
clan from the city of Gimhae
Gimhae
Gimhae, also commonly spelled Kimhae, is a city in South Gyeongsang Province, South Korea. Gimhae is known to locals as "The Paris of Gyeongsangnamdo." It is the seat of the large Gimhae Kim clan, one of the largest Kim clans in Korea...
. Clans are further subdivided into various pa, or branches stemming from a more recent common ancestor, so that a full identification of a person's family name would be clan-surname-branch. For example, "Kyoungjoo Yi(Lee)ssi"(Kyoung-Joo Lee Clan, or Lee Clan of Kyoung-Joo) and "Yeonan-Yissi"(Lee Clan of Yeonan) are, technically speaking, completely different surnames, even though both are - in the most areas of life - simply referred to as "Yi(Lee)". This also means that people from the same clan are considered to be of same blood, such that marriage of a man and a woman of same surname and "bon-gwan" is considered a strong taboo, regardless of how distant the actual lineages may be, even to the present day.
Korean women traditionally keep their family names after their marriage, but their children take the father's surname. In the pre-modern, patriarchal Korean society people were extremely conscious of familial values and their own family identities. Korean women keep their surnames after marriage based on traditional reasoning that it is what they inherited from their parents and ancestors, and cannot be changed. According to traditions, each clan publishes a comprehensive genealogy (jokbo
Jokbo
The jokbo or chokbo is a Korean genealogical record equivalent to the family tree. Each family has one jokbo which has been passed down through numerous generations, though copies are often printed and distributed among family members as necessary...
) every 30 years. However, it is not uncommon for women to be addressed with their husband's surnames after marriage.
There are around a dozen two-syllable surnames, all of which rank after the 100 most common surnames. The five most common family names, which together make up over half of the Korean population, are used by over 20 million people in South Korea.
Given names
Traditionally, given names for males are partly determined by generation nameGeneration name
Generation name, variously zibei or banci, is one of the characters in a traditional Chinese name, and is so called because each member of a generation share that character, unlike surnames or given names...
s, a custom originating in China. One of the two characters in a given name is unique to the individual, while the other is shared by all people in a family generation. Therefore, it is common for cousins to have the same character (dollimja) in their given names in the same fixed position. In North Korea
North Korea
The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea , , is a country in East Asia, occupying the northern half of the Korean Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. The Korean Demilitarized Zone serves as the buffer zone between North Korea and South Korea...
, generational names are no longer shared across families, but are still commonly shared by brothers and sisters.
Given names are typically composed of hanja
Hanja
Hanja is the Korean name for the Chinese characters hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese and incorporated into the Korean language with Korean pronunciation...
, or Chinese characters. In North Korea, the hanja are no longer used to write the names, but the meanings are still understood; thus, for example, the syllable cheol (철, 鐵) is used in boys' names and means "iron". In South Korea, section 37 of the Family Registry Law requires that the hanja in personal names be taken from a restricted list. Unapproved hanja must be represented by hangul, or Korean characters, in the family registry. In March 1991, the Supreme Court of South Korea
Supreme Court of South Korea
The Supreme Court of Korea is the highest court in South Korea. It is located in Seoul.Articles 101-110 of the Constitution of the Republic of Korea establish the Supreme Court and enumerates its powers and responsibilities.-Composition:...
published the Table of Hanja for Personal Name Use which allowed a total of 2,854 hanja in new South Korean given names (as well as 61 alternate forms). The list was expanded in 1994, 1997, 2001, and 2005. Thus there are now 5,038 hanja permitted in South Korean names, in addition to a small number of alternate forms.
While the traditional practice is still largely followed, since the late 1970s, some parents have given their children names that are native Korean
Korean language
Korean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
words, usually of two syllables. This has been largely restricted to girl's names. Popular native Korean given names of this sort include Haneul (하늘; "Heaven" or "Sky"), Areum (아름; "Beauty"), Gippeum (기쁨; "Joy") and Iseul (이슬; "Dew"). Despite this trend away from traditional practice, people's names are still recorded in both hangul
Hangul
Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean...
and hanja
Hanja
Hanja is the Korean name for the Chinese characters hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese and incorporated into the Korean language with Korean pronunciation...
(if available) on official documents, in family genealogies, and so on.
Forms of address
The usage of names is governed by strict norms in traditional Korean society. It is generally considered rude to address anyone by their given name in Korean culture. This is particularly the case when dealing with adults or one's elders. This is often a source of pragmaticPragmatics
Pragmatics is a subfield of linguistics which studies the ways in which context contributes to meaning. Pragmatics encompasses speech act theory, conversational implicature, talk in interaction and other approaches to language behavior in philosophy, sociology, and linguistics. It studies how the...
difficulty for learners of Korean as a foreign language, and for Korean learners of Western languages.
A variety of replacements are used for the actual name of the person. It is acceptable among adults of similar status to address the other by their full name, with the suffix ssi (氏, 씨) added. However, it is inappropriate to address someone by their surname alone, even with such a suffix. Whenever the person has an official rank, it is typical to address him or her by the name of that rank (such as "Manager"), often with the honorific nim (님) added. In such cases, the full name of the person may be appended, although this can also imply that the speaker is of higher status.
Among children and close friends, it is common to use a person's birth name.
Traditional nicknames
Among the common people, who have suffered from high child mortality, children were often given amyeong (childhood name), to wish them long lives by avoiding notice from the messenger of death. These sometimes-insulting nicknameNickname
A nickname is "a usually familiar or humorous but sometimes pointed or cruel name given to a person or place, as a supposedly appropriate replacement for or addition to the proper name.", or a name similar in origin and pronunciation from the original name....
s are used sparingly for children today.
Upon marriage, women usually lost their amyeong, and were called by a taekho, referring to their town of origin.
In addition, teknonymy
Teknonymy
Teknonymy is the practice of referring to parents by the names of their children. This practice can be found in many different cultures around the world....
, or referring to parents by their children's names, is a common practice. It is most commonly used in referring to a mother by the name of her eldest son, as in "Cheolsu's mom" (철수 엄마). However, it can be extended to either parent and any child, depending upon the context.
Korean names and gender
Korean history has a strong foundation of Confucian Principles, acquired mostly during the Chosŏn Dynasty, 1392. These principles determine the family as the fundamental unit of society. This emphasis on family is placed within a patriarchal family structure with the male as the superior. Traditionally, males dominate females and the elders dominate the young. Males are depicted as ambitious, have aspirations, are strong, practical, and independent. Women are [ideally] seen as not ambitious, have no aspirations, are emotional and romantic.Confucianism
Confucianism
Confucianism is a Chinese ethical and philosophical system developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius . Confucianism originated as an "ethical-sociopolitical teaching" during the Spring and Autumn Period, but later developed metaphysical and cosmological elements in the Han...
is characterized by extreme sexual segregation and a double standard of sexual morality. Examples of this can be observed in the clear hierarchical order of sexes. For example, women who are married are often referred to as ansaram (inside person) or jibsaram (home person), indicating that a wife’s realm is strictly restricted to domesticity.
In traditional Korean name acquisition, it is very common for the wife to keep her family name after marriage; however, the children must take their father’s name.
Honorifics suggest the more complicated relationships of roles and power to be the prime system of address in Korean society. Kinship ties are very important and these ties will go beyond the nuclear family unit. In Korean names however, the singular pronoun used to identify individuals has no gender. This means that, while most English first names (Jennifer, Mark, Candice, and Nicholas) attach a gender specific context, Korean names do not. Commonly, English-to-Korean translating programs cannot identify the proper Korean pronouns as being male or female and will therefore skew the original sentence structure.
History
The use of names has evolved over time, from the first recording of Korean names in the early Three Kingdoms periodThree Kingdoms of Korea
The Three Kingdoms of Korea refer to the ancient Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla, which dominated the Korean peninsula and parts of Manchuria for much of the 1st millennium...
through the gradual adoption of Chinese forms of naming as centralized kingdoms came to dominate Korean life. A complex system, including courtesy names and pen name
Pen name
A pen name, nom de plume, or literary double, is a pseudonym adopted by an author. A pen name may be used to make the author's name more distinctive, to disguise his or her gender, to distance an author from some or all of his or her works, to protect the author from retribution for his or her...
s as well as posthumous name
Posthumous name
A posthumous name is an honorary name given to royalty, nobles, and sometimes others, in East Asia after the person's death, and is used almost exclusively instead of one's personal name or other official titles during his life...
s and childhood names, arose out of Confucian
Confucianism
Confucianism is a Chinese ethical and philosophical system developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius . Confucianism originated as an "ethical-sociopolitical teaching" during the Spring and Autumn Period, but later developed metaphysical and cosmological elements in the Han...
tradition. The courtesy name system in particular arose from the Classic of Rites
Classic of Rites
The Classic of Rites , also known as the Book of Rites, Book of Customs, the Record of Rites, was one of the Chinese Five Classics of the Confucian canon. It described the social forms, governmental system, and ancient/ceremonial rites of the Zhou Dynasty...
, a core text of the Confucian canon.
Native names
During the Three Kingdoms periodThree Kingdoms of Korea
The Three Kingdoms of Korea refer to the ancient Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla, which dominated the Korean peninsula and parts of Manchuria for much of the 1st millennium...
, native given names were sometimes composed of three syllables like Misaheun (미사흔) and Sadaham (사다함), which were later transcribed into hanja
Hanja
Hanja is the Korean name for the Chinese characters hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese and incorporated into the Korean language with Korean pronunciation...
(未斯欣, 斯多含). The use of family names was limited to kings in the beginning, but gradually spread to aristocrats and eventually to most of the population.
Some recorded family names are apparently native Korean words, such as toponyms. At that time, some characters of Korean names might have been read not by their Sino-Korean pronunciation but by their native reading (see hanja
Hanja
Hanja is the Korean name for the Chinese characters hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese and incorporated into the Korean language with Korean pronunciation...
). For example, the native Korean name of Yeon Gaesomun
Yeon Gaesomun
Yeon Gaesomun was a powerful and controversial military dictator and Generalissimo in the waning days of Goguryeo, which was one of the Three Kingdoms of ancient Korea. Yeon is also remembered for a number of successful resistance in military conflicts with Tang Dynasty under Emperor Li Shimin and...
(연개소문; 淵蓋蘇文), the first Grand Prime Minister of Goguryeo
Goguryeo
Goguryeo or Koguryŏ was an ancient Korean kingdom located in present day northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula, southern Manchuria, and southern Russian Maritime province....
, can linguistically be reconstructed as "Eol Kasum" (/*älkasum/). Early Silla
Silla
Silla was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, and one of the longest sustained dynasties in...
names are also believed to represent Old Korean
Old Korean
Old Korean corresponds to the Korean language from the beginning of Three Kingdoms of Korea to the latter part of the Unified Silla, of which period is roughly from 1 AD to 1000 AD. There are many theories to differentiate the Korean language histories. It is distinct from Proto-Korean , which is...
vocabulary; for example, Bak Hyeokgeose, the name of the founder of Silla, was pronounced something like "Bulgeonuri" (弗矩內), which can be translated as "bright world".
Confucian naming system
According to the chronicle Samguk SagiSamguk Sagi
Samguk Sagi is a historical record of the Three Kingdoms of Korea: Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla. The Samguk Sagi is written in Classical Chinese and its compilation was ordered by Goryeo's King Injong Samguk Sagi (History of the Three Kingdoms) is a historical record of the Three Kingdoms of...
, family names were bestowed by kings upon their supporters. For example, in 33 CE, King Yuri
Yuri of Silla
Yuri of Silla was the third king of Silla, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. He is commonly called Yuri Isageum.- Name :As a descendent of Silla's founder Hyeokgeose, his surname was Park....
gave the six headmen of Saro (later Silla
Silla
Silla was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, and one of the longest sustained dynasties in...
) the names Lee (이), Bae (배), Choi (최), Jeong (정), Son (손) and Seol (설). However, this account is not generally credited by modern historians, who hold that Confucian-style surnames as above were more likely to have come into general use in the 5th and subsequent centuries, as the Three Kingdoms increasingly adopted the Chinese model.
Only a handful of figures from the Three Kingdoms period are recorded as having borne a courtesy name, such as Seol Chong
Seol Chong
Seol Chong was a leading scholar of the Unified Silla period. He studied Confucian writings and the related Chinese classics. He is also known by the courtesy name Chongji and the pen name Bingwoldang....
. The custom only became widespread in the Goryeo
Goryeo
The Goryeo Dynasty or Koryŏ was a Korean dynasty established in 918 by Emperor Taejo. Korea gets its name from this kingdom which came to be pronounced Korea. It united the Later Three Kingdoms in 936 and ruled most of the Korean peninsula until it was removed by the Joseon dynasty in 1392...
period, as Confucianism took hold among the literati. In 1055, Goryeo established a new law limiting access to the civil service exam to those with family names.
For men of yangban
Yangban
The yangban were part of the traditional ruling class or nobles of dynastic Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. The yangban were either landed or unlanded aristocracy who comprised the Korean Confucian idea of a "scholarly official." In reality, they were basically administrators and bureaucrats who...
rank, a complex system of alternate names had been developed by the Joseon Dynasty
Joseon Dynasty
Joseon , was a Korean state founded by Taejo Yi Seong-gye that lasted for approximately five centuries. It was founded in the aftermath of the overthrow of the Goryeo at what is today the city of Kaesong. Early on, Korea was retitled and the capital was relocated to modern-day Seoul...
. Peasants sometimes had only amyong throughout their lives. According to a census taken in 1910, at the end of the Joseon Dynasty and the beginning of Japanese rule, a little more than half of the population did not have family names.
Mongolian names
For a brief period after the Mongol invasion of Korea during the Goryeo Dynasty, Korean kings and aristocrats had both MongolianMongolian names
Mongolian names have gone through certain revolutions in the history of Mongolia. In the first, traditional Mongolian names were replaced by Tibetan names, while in the second, Tibetan names were replaced by new Mongolian names rather different from those before the first naming revolution...
and Sino-Korean names. The scions of the ruling class were sent to the Yuan
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan Dynasty , or Great Yuan Empire was a ruling dynasty founded by the Mongol leader Kublai Khan, who ruled most of present-day China, all of modern Mongolia and its surrounding areas, lasting officially from 1271 to 1368. It is considered both as a division of the Mongol Empire and as an...
court for schooling. For example, King Gongmin
Gongmin of Goryeo
King Gongmin ruled Goryeo Dynasty Korea from 1351 until 1374.he was the second son of King Chungsuk. In addition to his various Korean names , he bore the Mongolian name Bayàn Temür .-Early life:...
had both the Mongolian name Bayan Temür (伯顏帖木兒) and the Sino-Korean name Wang Gi (王祺) (later renamed Wang Jeon (王顓)).
Japanese names
During the period of Japanese colonial ruleKorea under Japanese rule
Korea was under Japanese rule as part of Japan's 35-year imperialist expansion . Japanese rule ended in 1945 shortly after the Japanese defeat in World War II....
of Korea (1910–1945), Koreans were forced to adopt Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
-language names.
In 1939, as part of Governor-General
Governor-General of Korea
The post of Japanese Governor-General of Korea served as the chief administrator of the Japanese government in Korea while it was held as the Japanese colony of Chōsen from 1910 to 1945...
Jiro Minami
Jiro Minami
- Notes :...
's policy of cultural assimilation (同化政策; dōka seisaku), Ordinance No. 20 (commonly called the "Name Order", or Sōshi-kaimei (創氏改名) in Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
) was issued, and became law in April 1940. Although the Japanese Governor-General officially prohibited compulsion, low-level officials effectively forced Koreans to adopt Japanese-style family and given names. By 1944, approximately 84 percent of the population had registered Japanese family names.
Sōshi (Japanese) means the creation of a Japanese family name (shi, Korean ssi), distinct from a Korean family name or seong (Japanese sei). Japanese family names represent the families they belong to and can be changed by marriage and other procedures, while Korean family names represent paternal linkages and are unchangeable. Japanese policy dictated that Koreans either could register a completely new Japanese family name unrelated to their Korean surname, or have their Korean family name, in Japanese form, automatically become their Japanese name if no surname was submitted before the deadline.
After the liberation of Korea from Japanese rule, the Name Restoration Order (조선 성명 복구령; 朝鮮姓名復舊令) was issued on October 23, 1946 by the United States military administration
United States Army Military Government in Korea
The United States Army Military Government in Korea, also known as USAMGIK, was the official ruling body of the southern half of the Korean Peninsula from September 8, 1945 to August 15, 1948...
south of the 38th parallel north
38th parallel north
The 38th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 38 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean...
, enabling Koreans to restore their original Korean names if they wished to.
Japanese conventions of creating given names, such as using "子" (Japanese ko and Korean ja) in feminine names, is seldom seen in present-day Korea, both North and South. In the North, a campaign to eradicate such Japanese-based names was launched in the 1970s. In the South, and presumably in the North as well, these names are regarded as old and unsophisticated.
Romanization and pronunciation
In English speaking nations, the three most common family names are often written and pronounced as "Kim" (김), "Lee" or "Rhee" (이, 리), and "Park" (박). Despite official Korean romanizationKorean romanization
Korean romanization is a system for representing the Korean language using the Roman alphabet. In Korea, the Korean language is written using hangul, and sometimes hanja....
systems used for geographic and other names in North and South Korea, personal names are generally romanized according to personal preference. Thus a family name such as "Lee" may also be found spelled "I", "Yi", "Rhee", and "Rhie".
The initial sound in "Kim" shares features with both the English 'k' (in initial position, an aspirated voiceless velar stop) and "hard g" (an unaspirated voiced velar stop). When pronounced initially, Kim starts with an unaspirated voiceless velar stop
Velar stop
In phonetics and phonology, a velar stop is a type of consonantal sound, made with the back of the tongue in contact with the soft palate , held tightly enough to block the passage of air . The most common sounds are the plosives and , as in English cut and gut...
sound; it is voiceless like /k/, but also unaspirated like /ɡ/. As aspiration is a distinctive feature in Korean but voicing is not, "Gim" is more likely to be understood correctly. "Kim" is used nearly universally in both North and South Korea.
The family name "Lee" is pronounced as 리 (ri) in North Korea and as 이 (i) in South Korea. In the former case, the initial sound is an alveolar liquid. There is no distinction between the alveolar liquids /l/ and /r/, which is why "Lee" and "Rhee" are both common spellings. In South Korea, the pronunciation of the name is simply the English vowel sound for a "long e", as in see. This pronunciation is also often spelled as "Yi"; the Northern pronunciation is commonly romanized "Ri".
In Korean pronunciation, the name usually romanized as "Park" actually has no 'r' sound at all. Its initial sound is an unaspirated voiceless bilabial stop, like a cross between English 'p' and 'b'. The vowel is a, similar to the 'a' in father. For this reason, the name is also often transcribed "Pak" or "Bak".
See also
- List of Korean family names
- List of most common surnames
- Most popular given namesMost popular given namesThe most popular given names vary nationally, regionally, and culturally. Lists of widely used given names can consist of those most often bestowed upon infants born within the last year, thus reflecting the current naming trends, or else be composed of the personal names occurring most within the...
- Article 809 of the Korean Civil CodeArticle 809 of the Korean Civil CodeArticle 809 of the Korean Civil Code was the codification of a traditional rule prohibiting marriage between men and women who have the same surname and ancestral home. On 16 July 1997, the Constitutional Court of Korea ruled the article unconstitutional...
Further reading
External links
- Translate your name into Korean
- Korean surnames at Wiktionary
- Table of in 2001 added Hanja for Personal Name Use
- Choosing between Korean Hanja and Hangul Names
- Family Register Law, Act 6438, 호적법, 법률6438호, partially revised October 24, 2005.
- Examples of Koreans who used Japanese names: by Saga Women's Junior College

