
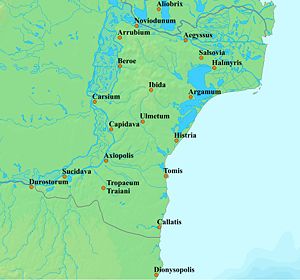
Halmyris
Encyclopedia
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
legionary
Legionary
The Roman legionary was a professional soldier of the Roman army after the Marian reforms of 107 BC. Legionaries had to be Roman citizens under the age of 45. They enlisted in a legion for twenty-five years of service, a change from the early practice of enlisting only for a campaign...
base and naval port for 600 years, located at the mouth of the Danube Delta
Danube Delta
The Danube Delta is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. The greater part of the Danube Delta lies in Romania , while its northern part, on the left bank of the Chilia arm, is situated in Ukraine . The approximate surface is...
in Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
.
History
The city (better known by its Greek name) is situated, in ancient times on the shore of the Halmyris gulf. It was named Salmorus/Thalamonium in the Roman period, the Latin for Halmyris—salt water.The region was inhabited during the Second Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
; nearby two Getic
Getae
The Getae was the name given by the Greeks to several Thracian tribes that occupied the regions south of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria, and north of the Lower Danube, in Romania...
incineration necropoli
Necropolis
A necropolis is a large cemetery or burial ground, usually including structural tombs. The word comes from the Greek νεκρόπολις - nekropolis, literally meaning "city of the dead"...
were discovered, dating from 4th-2nd centuries BC. In the Roman period, on a 3rd-2nd century BC Getic settlement, the first stone castrum
Castra
The Latin word castra, with its singular castrum, was used by the ancient Romans to mean buildings or plots of land reserved to or constructed for use as a military defensive position. The word appears in both Oscan and Umbrian as well as in Latin. It may have descended from Indo-European to Italic...
was built during Trajan
Trajan
Trajan , was Roman Emperor from 98 to 117 AD. Born into a non-patrician family in the province of Hispania Baetica, in Spain Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor Domitian. Serving as a legatus legionis in Hispania Tarraconensis, in Spain, in 89 Trajan supported the emperor against...
's reign. The fortification was destroyed several times and had four phases of reconstruction. It was abandoned in the 7th century AD.
The Late Roman fortification had a trapezoid
Trapezoid
In Euclidean geometry, a convex quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides is referred to as a trapezoid in American English and as a trapezium in English outside North America. A trapezoid with vertices ABCD is denoted...
shape, two gates, 15 towers and a defensive system of three vallae and ditches. Inside thermae
Thermae
In ancient Rome, thermae and balnea were facilities for bathing...
, a basilica
Basilica
The Latin word basilica , was originally used to describe a Roman public building, usually located in the forum of a Roman town. Public basilicas began to appear in Hellenistic cities in the 2nd century BC.The term was also applied to buildings used for religious purposes...
, administrative buildings and dwelling places were discovered.
Halmyris was the most easterly point of the Danubian border in Roman times and probably served as a supply centre for the fleet; early Roman inscriptions inform us of the existence of a "mariner's village"—vicus classicorum. During the late Roman period two units of the military fleet—Classis in Plateypegiis and Musculi Schytici (which had little ships, suited for the Danube Delta) may have been hosted by this city.
As for religious life, we know that in 290 AD, during the persecutions ordered by Diocletian
Diocletian
Diocletian |latinized]] upon his accession to Diocletian . c. 22 December 244 – 3 December 311), was a Roman Emperor from 284 to 305....
, Saint Epictetus
July 7 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics)
July 6 - Eastern Orthodox Church calendar - July 8All fixed commemorations below celebrated on July 20 by Old Calendarists-Saints:*Venerable Thomas of Mt...
and Astion suffered martyrdom at Halmyris.
- Halmyris served as a depot for supplies, colonization and cultural exchange in the region for 1,100 years. It was occupied from the Iron Age to the Byzantine periodByzantine EmpireThe Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
.
- The original settlers of the region were called GetaeGetaeThe Getae was the name given by the Greeks to several Thracian tribes that occupied the regions south of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria, and north of the Lower Danube, in Romania...
or Dacians and after the Romans conquered the region in AD 106 and made it a province, it was given the name of DaciaDaciaIn ancient geography, especially in Roman sources, Dacia was the land inhabited by the Dacians or Getae as they were known by the Greeks—the branch of the Thracians north of the Haemus range...
.
- The original fort was made of timber and turf, but as the fort gained importance and a regular garrison was established along the Danube, the fort was rebuilt in stone.
- Early in the fort's history, the Goths and Huns from the North crossed the Danube and conquered the fort. It was later re-captured by the Romans.
- In the early 4th century, the Emperor ConstantineConstantine IConstantine the Great , also known as Constantine I or Saint Constantine, was Roman Emperor from 306 to 337. Well known for being the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity, Constantine and co-Emperor Licinius issued the Edict of Milan in 313, which proclaimed religious tolerance of all...
added a basilica.
- A series of earthquakes altered the course of the Danube and the fort became more removed from the river. Halmyris gradually lost its importance and was abandoned.
Current activities
- The fort is being excavated by Dr. Mihail Zahariade and Dr. John Karavas.
- Current areas of excavation include the military barracks, northwestern towers and harbor installations.
See also
- STRATEG. Defensive strategies and cross border policies. Integration of the Lower Danube area in the Roman civilization
- HistriaHistria (Sinoe)Ancient Histria or Istros , was a Greek colony or polis on the Black Sea coast, established by Milesian settlers to trade with the native Getae. It became the first Greek town on the present day Romanian territory. Scymnus of Chios , the Greek geographer and poet, dated it to 630 BC...
- List of ancient towns in Scythia Minor
- List of castra
- Peuce IslandPeuce IslandPeuce in ancient geography was an island located in the Danube Delta, in Scythia Minor . Its name came from the ancient Greek word peuke, 'pine tree'. It was about the size of the island of Rhodes...

