
Grace note
Encyclopedia
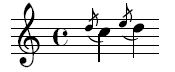
A grace note is a kind of music notation used to denote several kinds of musical ornaments
Ornament (music)
In music, ornaments or embellishments are musical flourishes that are not necessary to carry the overall line of the melody , but serve instead to decorate or "ornament" that line. Many ornaments are performed as "fast notes" around a central note...
. When occurring by itself, a single grace note normally indicates the intention of either an appoggiatura or an acciaccatura. When they occur in groups, grace notes can be interpreted to indicate any of several different classes of ornamentation, depending on interpretation.
Notation
In notation a grace noteNote
In music, the term note has two primary meanings:#A sign used in musical notation to represent the relative duration and pitch of a sound;#A pitched sound itself....
is distinguished from a regular note by print size. A grace note is indicated by printing a note that is much smaller than a regular note, sometimes with a slash through the note stem (if two or more grace notes, there might be a slash through the note stem of the first note but not the subsequent grace note). The presence or absence of a slash through a note stem is often interpreted to indicate the intention of an acciaccatura or an appoggiatura, respectively.
The works of some composers, especially Frédéric Chopin
Frédéric Chopin
Frédéric François Chopin was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist. He is considered one of the great masters of Romantic music and has been called "the poet of the piano"....
, may contain long series of notes printed in the small type reserved for grace notes simply to show that the amount of time to be taken up by those notes as a whole unit is a subjective matter to be decided by the performer. Such a group of small-printed notes may or may not have an accompanying principal note, and so may or may not be considered as grace notes in analysis.
Function
A grace note represents an ornamentOrnament (music)
In music, ornaments or embellishments are musical flourishes that are not necessary to carry the overall line of the melody , but serve instead to decorate or "ornament" that line. Many ornaments are performed as "fast notes" around a central note...
, and distinguishing whether a given singular grace note is to be played as an appoggiatura or acciaccatura in the performance practice of a given historical period (or in the practice of a given composer
Composer
A composer is a person who creates music, either by musical notation or oral tradition, for interpretation and performance, or through direct manipulation of sonic material through electronic media...
) is usually the subject of lively debate. This is because we must rely on literary, interpretative accounts of performance practice in those days before such time as audio recording was implemented, since only a composer's personal or sanctioned recording could directly document usage.
As either an appoggiatura or an acciaccatura, grace notes occur as notes of short duration before the sounding of the relatively longer-lasting note which immediately follows them. This longer note, to which any grace notes can be considered harmonically and melodically subservient (except in the cases of certain appoggiaturas, in which the ornament may be held for a longer duration than the note it ornaments), is called the principal in relation to the grace notes. Please see the article on ornamentation
Ornament (music)
In music, ornaments or embellishments are musical flourishes that are not necessary to carry the overall line of the melody , but serve instead to decorate or "ornament" that line. Many ornaments are performed as "fast notes" around a central note...
for a discussion of the rhythmic differences between the interpretations and usages of grace notes outlined herein.
Use in music
In bagpipe music there is extensive use of grace notes. Indeed, because the chanterChanter
The chanter is the part of the bagpipe upon which the player creates the melody. It consists of a number of finger-holes, and in its simpler forms looks similar to a recorder...
is not tongued but supplied by a continuous air source from the bag, grace notes are sometimes the only way to differentiate between notes. For example, inserting a grace note between two crotchet
Quarter note
A quarter note or crotchet is a note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note . Often people will say that a crotchet is one beat, however, this is not always correct, as the beat is indicated by the time signature of the music; a quarter note may or may not be the beat...
s (quarter notes) played at the same pitch is the only way to indicate them as opposed to them sounding like a single minim
Half note
In music, a half note or minim is a note played for half the duration of a whole note and twice the duration of a quarter note...
(half note). Various multiple grace note ornaments are formalised into distinct types, such as doublings, throws, and birls. A single grace notes is played on the beat as is the first grace note of a complex ornament such as a doubling. The ornament taorluath is an exception: its last grace note is played on the beat. Gracenotes are typically played as short as possible by lifting the fingers quickly and a short distance of the chanter
Chanter
The chanter is the part of the bagpipe upon which the player creates the melody. It consists of a number of finger-holes, and in its simpler forms looks similar to a recorder...
.
In modern editions of Western classical works, editors often seek to eliminate the potential for different interpretations of ornamental symbology, of which grace notes are a prime example, by converting a composer's original ornamental notation into literal notation, the interpretation of which is far less subject to variation. Most modern composers, although by no means all of them, have followed this trend in the prima facie notation of their works.
In the context of Indian classical music
Indian classical music
The origins of Indian classical music can be found in the Vedas, which are the oldest scriptures in the Hindu tradition. Indian classical music has also been significantly influenced by, or syncretised with, Indian folk music and Persian music. The Samaveda, one of the four Vedas, describes music...
(Hindustani
Hindustani classical music
Hindustani classical music is the Hindustani or North Indian style of Indian classical music found throughout the northern Indian subcontinent. The style is sometimes called North Indian Classical Music or Shāstriya Sangeet...
(North Indian), Carnatic
Carnatic music
Carnatic music is a system of music commonly associated with the southern part of the Indian subcontinent, with its area roughly confined to four modern states of India: Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu...
(South Indian)) some specific forms of notes (swara-s
Swara
The seven notes of the scale , in Indian music are named shadja, rishabh, gandhar, madhyam, pancham, dhaivat and nishad, and are shortened to Sa, Ri or Re , Ga, Ma, Pa, Dha, and Ni and written S, R, G, M, P, D, N. Collectively these notes are known as the sargam...
) fulfill the technique of playing a note (swara
Swara
The seven notes of the scale , in Indian music are named shadja, rishabh, gandhar, madhyam, pancham, dhaivat and nishad, and are shortened to Sa, Ri or Re , Ga, Ma, Pa, Dha, and Ni and written S, R, G, M, P, D, N. Collectively these notes are known as the sargam...
). Such ornamentic
Ornament (music)
In music, ornaments or embellishments are musical flourishes that are not necessary to carry the overall line of the melody , but serve instead to decorate or "ornament" that line. Many ornaments are performed as "fast notes" around a central note...
(Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
: Alankar or Alankara) in Indian Classical Music is important for the proper rendition and essential to create the beauty of a raga
Raga
A raga is one of the melodic modes used in Indian classical music.It is a series of five or more musical notes upon which a melody is made...
. Some notes are linked with its preceding and succeeding note; these linked notes are called Kan-swars (= grace notes). Kan-swars deal with so called touch notes. sparsh means "touch" in Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
(Devangari). These grace notes (acciaccatura) are often referred to as sparsh-swars. Kan-swars or sparsh-swars can be executed vocally and on instruments in three ways:
- using a swift short glide (meendMeendIn Hindustani music, meend refers to a glide from one note to another. It is an essential performance practice, and is used often in vocal and instrumental music. On the veena, sitar, and other plucked stringed instruments, it is usually done by pushing the strings across the frets to vary their...
or ghaseet), - as a Sparsh (technique of playing a note on a plucked stringed instrument, the movement of notes is ascending) and
- as a Krintan (the opposite of a Sparsh, movement of notes is descending).
In a book on Sitar compositions, Kan has been defined as 'fast deflection which can be approached while descending or ascending'. The act of Kaṇ being repeated twice, thrice or four times in a single stroke of mizrāb is called Krintan.

