German public banks
Encyclopedia
The German banking system is structured in three different pillars, totally separated from each other.Was Banken leistenhttps://www.bankenverband.de/publikationen/ods/was-banken-leisten/was-banken-leisten/download publisher: Bundesverband deutscher Banken, Berlin 2010, P.15.; accessed: 13.06.2011 They typically differ in their legal form and the ownership
Private Banks
, represented by banks like Deutsche Bank
or Commerzbank
as listed companies or Hauck & Aufhäuser
or Bankhaus Lampe as less known private companies, are part of the first tier. The second tier is composed of co-operative banks
like the numerous Volksbanken
or RaiffeisenbankenWas Banken leistenhttps://www.bankenverband.de/publikationen/ods/was-banken-leisten/was-banken-leisten/download publisher: Bundesverband deutscher Banken, Berlin 2010, P.15.; accessed: 13.06.2011. They are based on a member-structure where each member, independently from its capital share, has one vote. The third tier consists of public banks, that are a legally defined arm of the banking industry in Germany and separate into two main groups.
The German Savings Banks Finance Group (Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe) is the most numerous sub-sector with 431 savings banks using the Sparkasse brand, 8 Landesbank
en including the DekaBank
using separate brands and 10 real estate financing banks using the LBS brand
The Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband (German Savings Banks Association, DSGV) represents the interests of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe on a national and international level concerning law and the financial services industry. It also coordinates, promotes and harmonises the interests of Sparkassen.
Based on OECD studies, the German public banking system had a share of 40% of total banking assets in Germany
. This shows the important and significant role of this group of banks in Germany.
, the states, administrative districts or cities. Not all companies are fully publicly owned. They can also be defined as public by providing services out of a public interest.
The public banks are represented through the Association of German Public Sector Banks
as one of the leading associations in the German banking industry. The association counts 34 ordinary members, but to distinguish the different groups of public banks it is important to know, that the Landesbank
en as part of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe described below, are also members of this association.
The typical public bank acts as business development bank (Förderbank, Aufbaubank or Investitionsbank) or international project, infrastructure and export financing institution. Most known representatives of this group are the KfW-Group, the NRW.Bank in NorthRhine-Westphalia, the LfA Förderbank Bayern in Bavaria and the L-Bank, Staatsbank für Baden-Wuerttemberg in Baden-Wuerttemberg.
The Group of public development banks manage assets of EUR 880,9 billion. In total, 13.000 people work for the various institutions. (December 2010)
s in German-speaking countries are called Sparkasse (pl: Sparkassen). They work as commercial banks in a decentralized structure. Each savings bank is independent, locally managed and concentrates its business activities on customers in the region it is situated in. In general, savings banks are not profit oriented. Shareholder
s of the savings bank
s are usually single cities or numerous cities in an administrative district. Some 6 savings banks (Bordesholmer Sparkasse AG,Spar- und Leihkasse zu Bredstedt AG, Die Sparkasse Bremen AG, Hamburger Sparkasse AG, Sparkasse zu Lübeck AG, Sparkasse Mittelholstein AG) are independent from municipalities.
The first savings banks in Germany were founded at the dusk of the 18th century in its major trading cities. One of the first institutions with the business model of modern savings banks was the Ersparungsclasse der Hamburgischen Allgemeinen Versorgungsanstalt in Hamburg in 1778. Founders were rich merchants, clerks and academics. They intended to develop solutions for people with low income to save small sums of money and to support business start-ups. In 1801 the first savings bank with a municipal guarantor was founded in Göttingen to fight poverty. Between 1850 and 1903 the idea of the municipal savings banks spread and the number of savings banks in Germany increased from 630 to 2.834. Fulfilling public interests is still one of the most significant characteristics of public banks in general and the savings banks in particular. Although public interest is very unspecific, objects of those companies are usually
The total assets of the Sparkassen amount to about EUR1 trillion. The 431 savings banks operate a network of over 15.600 branches and offices and employ over 250.000 people.
Savings bank
s are universal banks and provide the whole spectrum of banking services for private and commercial medium-sized customers. 50 million customers maintain business activities with savings banks. Although independent and regionally spread, the savings banks act as one unit under the brand Sparkasse with the famous logo and the well known red colour.
Depending on the strength of the economy in their region, the sizes of savings banks differ extremely. While the Hamburger Sparkasse as biggest savings bank had total assets of EUR 37,7 billion and 5.500 employees in 2009, the smallest one (Stadtsparkasse Bad Sachsa) had only EUR 129,6 million assets and 45 employees.
The German Savings Banks Association (Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband) was founded in 1924 as umbrella organization to organize decision-making processes, coordinate the strategy of the savings banks and represent its members political and regulatory interests on national and international level.
The regional associations are statutory bodies, savings banks and their municipal holders (Gewährträger) are statutory members of. They are responsible for the coordination between savings banks in a region. They also act as auditors and operate regional savings banks academies for educational and training purposes.
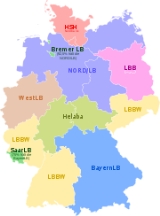
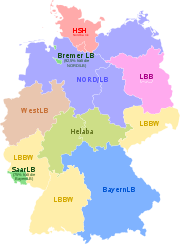 The Landesbank
The Landesbank
en are mostly owned by the regional Savings banks through its regional association and the respective federal state. After several mergers and acquisitions
, there are seven Landesbank
en-Groups left: BayernLB
, Norddeutsche Landesbank (Nord/LB), HSH Nordbank
, Landesbank Baden-Württemberg
(LBBW), Landesbank Berlin (LBB), Landesbank Hessen-Thuringen
- Girozentrale (Helaba), WestLB
. Bremer Landesbank Kreditanstalt Oldenburg - Girozentrale belongs with a share of 92,5% to the Nord/LB-Group. The rest is owned by the federal state of Bremen
.The Sachsen LB and the Landesbank Rheinland-Pfalz (LRP) since April 2008 are subsidiaries of the Landesbank Baden-Württemberg
(LBBW). Until 21.06.2010, the BayernLB
was majority shareholder of the Landesbank Saar (SaarLB) with a share of 75,1%. Since June 2010, the Saarland
has become shareholder with a stake of 35,2% and the BayernLB reduced its share to 49,9%. The remaining 14,9% are held by the Sparkassen through its regional confederation.
The regional banks / clearing houses are the central banks of a savings bank association and act as the "main bank" of the states. They are also local banks, mortgage banks and general commercial banks. Their duties and power is codified in the individual country banking laws of the Länder (Landesbankengesetze). The specific tasks for the savings bank
s include the central clearing for cashless payments and liquidity funding for the regional savings bank
s. They also provide many services for the savings banks in the region in securities and cross-country businesses. In contrast to savings banks, they are doing "wholesale-banking" instead of retail-banking. With combined total assets of EUR 1,620 trillion as of December 2010, the 7 Landesbanken-Groups employ some 44.000 people.
DekaBank
with its subsidiaries is the central asset manager of the German Savings Bank Finance Group. Based in Frankfurt
and Berlin
it provides asset management services for the Sparkassen
and the Landesbanken
and their customers. With managed fund assets of about € 155 billion, approximately five million customer deposits and group locations in Luxembourg
and Switzerland
, the DekaBank Group is one of the largest asset managers in Germany.
DekaBank's roots date back to the year 1918, when Deutsche Girozentrale (DGZ) was founded.. Deka as an investment company was founded in 1956 (17.08.1956) by DGZ with a share of 23% an 11 other regional Landesbank
en. Todays DekaBank
was created in 1999 by a merger of DGZ and Deka..
Until the 8. June 2011, DekaBank
has been owned by the German Savings Banks and Giro Association Landesbanken itselfves grouped their shares in the GLB GmbH & Co.OHG, who has hold the DekaBank shares. On 7. April 2011, the Savings Banks bought the 50% stake from the landesbanken for a price of EUR 2.3 billion to become sole owner of the DekaBank. The acquisition was closed on the 8. June 2011 and DekaBank
became fully, directly owned by the savings banks.
3,700 people throughout the group work in one of the 3 business divisions AMK (Asset Management Capital Markets), AMI (Asset Management Real Estate Business), C&M (Corporates and Markets), the sales division or one of the corporate centers.
Core business of the Landesbausparkassen is the offering of collective real estate saving products (Bausparen) and providing of low-interest residential mortgage loans.
Private Banks
Private banking
Private banking is banking, investment and other financial services provided by banks to private individuals investing sizable assets. The term "private" refers to the customer service being rendered on a more personal basis than in mass-market retail banking, usually via dedicated bank advisers...
, represented by banks like Deutsche Bank
Deutsche Bank
Deutsche Bank AG is a global financial service company with its headquarters in Frankfurt, Germany. It employs more than 100,000 people in over 70 countries, and has a large presence in Europe, the Americas, Asia Pacific and the emerging markets...
or Commerzbank
Commerzbank
Commerzbank AG is the second-largest bank in Germany, after Deutsche Bank, headquartered in Frankfurt am Main.-Activities:Commerzbank is mainly active in commercial bank, retail banking and mortgaging. It suffered reversals in investment banking in early 2000s and scaled back its Securities unit...
as listed companies or Hauck & Aufhäuser
Hauck & Aufhäuser
Hauck & Aufhäuser is a private bank with offices in Frankfurt am Main and Munich. Established in 1796, Hauck & Aufhäuser is one of the few private banks operated as limited partnership with personally liable partners....
or Bankhaus Lampe as less known private companies, are part of the first tier. The second tier is composed of co-operative banks
Cooperative banking
Cooperative banking is retail and commercial banking organized on a cooperative basis. Cooperative banking institutions take deposits and lend money in most parts of the world....
like the numerous Volksbanken
Volksbank
Volksbank was founded in 1850 and is a retail bank in Central Europe based in Vienna, Austria. It currently operates in Austria, Germany, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Malta, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia and Ukraine.There are also 1,156 independent local...
or RaiffeisenbankenWas Banken leistenhttps://www.bankenverband.de/publikationen/ods/was-banken-leisten/was-banken-leisten/download publisher: Bundesverband deutscher Banken, Berlin 2010, P.15.; accessed: 13.06.2011. They are based on a member-structure where each member, independently from its capital share, has one vote. The third tier consists of public banks, that are a legally defined arm of the banking industry in Germany and separate into two main groups.
The German Savings Banks Finance Group (Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe) is the most numerous sub-sector with 431 savings banks using the Sparkasse brand, 8 Landesbank
Landesbank
The Landesbanken in Germany are a group of state owned banks of a type unique to Germany. They are regionally organised and their business is predominantly wholesale banking...
en including the DekaBank
DekaBank
The DekaBank is the central asset manager of the German Sparkassen. Deka as an investment company was founded in 1956. In 1999 it merged with Deutsche Girozentrale , which was founded in 1918...
using separate brands and 10 real estate financing banks using the LBS brand
The Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband (German Savings Banks Association, DSGV) represents the interests of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe on a national and international level concerning law and the financial services industry. It also coordinates, promotes and harmonises the interests of Sparkassen.
Based on OECD studies, the German public banking system had a share of 40% of total banking assets in Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. This shows the important and significant role of this group of banks in Germany.
German public banks
Public banks in Germany are financial institutes, typically held directly or indirectly by the public sector, e.g. the federal governmentFederal government
The federal government is the common government of a federation. The structure of federal governments varies from institution to institution. Based on a broad definition of a basic federal political system, there are two or more levels of government that exist within an established territory and...
, the states, administrative districts or cities. Not all companies are fully publicly owned. They can also be defined as public by providing services out of a public interest.
The public banks are represented through the Association of German Public Sector Banks
Bundesverband Öffentlicher Banken Deutschlands
The Bundesverband Öffentlicher Banken Deutschlands is the association of national and regional state banks. It assembles 62 financial institutes representing the German public bank branch of the banking industry...
as one of the leading associations in the German banking industry. The association counts 34 ordinary members, but to distinguish the different groups of public banks it is important to know, that the Landesbank
Landesbank
The Landesbanken in Germany are a group of state owned banks of a type unique to Germany. They are regionally organised and their business is predominantly wholesale banking...
en as part of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe described below, are also members of this association.
The typical public bank acts as business development bank (Förderbank, Aufbaubank or Investitionsbank) or international project, infrastructure and export financing institution. Most known representatives of this group are the KfW-Group, the NRW.Bank in NorthRhine-Westphalia, the LfA Förderbank Bayern in Bavaria and the L-Bank, Staatsbank für Baden-Wuerttemberg in Baden-Wuerttemberg.
The Group of public development banks manage assets of EUR 880,9 billion. In total, 13.000 people work for the various institutions. (December 2010)
Sparkassen
Savings bankSavings bank
A savings bank is a financial institution whose primary purpose is accepting savings deposits. It may also perform some other functions.In Europe, savings banks originated in the 19th or sometimes even the 18th century. Their original objective was to provide easily accessible savings products to...
s in German-speaking countries are called Sparkasse (pl: Sparkassen). They work as commercial banks in a decentralized structure. Each savings bank is independent, locally managed and concentrates its business activities on customers in the region it is situated in. In general, savings banks are not profit oriented. Shareholder
Shareholder
A shareholder or stockholder is an individual or institution that legally owns one or more shares of stock in a public or private corporation. Shareholders own the stock, but not the corporation itself ....
s of the savings bank
Savings bank
A savings bank is a financial institution whose primary purpose is accepting savings deposits. It may also perform some other functions.In Europe, savings banks originated in the 19th or sometimes even the 18th century. Their original objective was to provide easily accessible savings products to...
s are usually single cities or numerous cities in an administrative district. Some 6 savings banks (Bordesholmer Sparkasse AG,Spar- und Leihkasse zu Bredstedt AG, Die Sparkasse Bremen AG, Hamburger Sparkasse AG, Sparkasse zu Lübeck AG, Sparkasse Mittelholstein AG) are independent from municipalities.
The first savings banks in Germany were founded at the dusk of the 18th century in its major trading cities. One of the first institutions with the business model of modern savings banks was the Ersparungsclasse der Hamburgischen Allgemeinen Versorgungsanstalt in Hamburg in 1778. Founders were rich merchants, clerks and academics. They intended to develop solutions for people with low income to save small sums of money and to support business start-ups. In 1801 the first savings bank with a municipal guarantor was founded in Göttingen to fight poverty. Between 1850 and 1903 the idea of the municipal savings banks spread and the number of savings banks in Germany increased from 630 to 2.834. Fulfilling public interests is still one of the most significant characteristics of public banks in general and the savings banks in particular. Although public interest is very unspecific, objects of those companies are usually

- providing financial and monetary services in economically underdeveloped regions
- supporting saving processes and accumulation of capital
- strengthening competition in the banking industry
The total assets of the Sparkassen amount to about EUR1 trillion. The 431 savings banks operate a network of over 15.600 branches and offices and employ over 250.000 people.
Savings bank
Savings bank
A savings bank is a financial institution whose primary purpose is accepting savings deposits. It may also perform some other functions.In Europe, savings banks originated in the 19th or sometimes even the 18th century. Their original objective was to provide easily accessible savings products to...
s are universal banks and provide the whole spectrum of banking services for private and commercial medium-sized customers. 50 million customers maintain business activities with savings banks. Although independent and regionally spread, the savings banks act as one unit under the brand Sparkasse with the famous logo and the well known red colour.
Depending on the strength of the economy in their region, the sizes of savings banks differ extremely. While the Hamburger Sparkasse as biggest savings bank had total assets of EUR 37,7 billion and 5.500 employees in 2009, the smallest one (Stadtsparkasse Bad Sachsa) had only EUR 129,6 million assets and 45 employees.
The German Savings Banks Association (Deutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband) was founded in 1924 as umbrella organization to organize decision-making processes, coordinate the strategy of the savings banks and represent its members political and regulatory interests on national and international level.
The regional associations are statutory bodies, savings banks and their municipal holders (Gewährträger) are statutory members of. They are responsible for the coordination between savings banks in a region. They also act as auditors and operate regional savings banks academies for educational and training purposes.
Landesbanken

Landesbank
The Landesbanken in Germany are a group of state owned banks of a type unique to Germany. They are regionally organised and their business is predominantly wholesale banking...
en are mostly owned by the regional Savings banks through its regional association and the respective federal state. After several mergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions refers to the aspect of corporate strategy, corporate finance and management dealing with the buying, selling, dividing and combining of different companies and similar entities that can help an enterprise grow rapidly in its sector or location of origin, or a new field or...
, there are seven Landesbank
Landesbank
The Landesbanken in Germany are a group of state owned banks of a type unique to Germany. They are regionally organised and their business is predominantly wholesale banking...
en-Groups left: BayernLB
BayernLB
BayernLB or Bayerische Landesbank is a publicly regulated bank based in Munich, Germany and one of the eight Landesbanken. It is 94% owned by the free state of Bavaria and 6% owned by the Sparkassenverband Bayern, the umbrella organization of Bavarian Sparkassen...
, Norddeutsche Landesbank (Nord/LB), HSH Nordbank
HSH Nordbank
HSH Nordbank is a commercial bank in northern Europe with headquarters in Hamburg as well as Kiel, Germany. It is active in corporate and private banking. HSHs main focus is on shipping, transportation, real estate and renewable energy....
, Landesbank Baden-Württemberg
Landesbank Baden-Württemberg
Landesbank Baden-Württemberg is a parent company of three commercial bank and the Landesbank for some Federal States of Germany.-History:...
(LBBW), Landesbank Berlin (LBB), Landesbank Hessen-Thuringen
Helaba
Helaba short for Hessische Landesbank Landesbank Hessen-Thüringen is a commercial bank with core regions in Hesse and Thuringia, Germany...
- Girozentrale (Helaba), WestLB
WestLB
WestLB AG is a European commercial bank based in Düsseldorf in Germany which is partly owned by the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The letters LB in the name stand for Landesbank. The Landesbanken are a group of state owned banks unique to Germany...
. Bremer Landesbank Kreditanstalt Oldenburg - Girozentrale belongs with a share of 92,5% to the Nord/LB-Group. The rest is owned by the federal state of Bremen
Bremen
The City Municipality of Bremen is a Hanseatic city in northwestern Germany. A commercial and industrial city with a major port on the river Weser, Bremen is part of the Bremen-Oldenburg metropolitan area . Bremen is the second most populous city in North Germany and tenth in Germany.Bremen is...
.The Sachsen LB and the Landesbank Rheinland-Pfalz (LRP) since April 2008 are subsidiaries of the Landesbank Baden-Württemberg
Landesbank Baden-Württemberg
Landesbank Baden-Württemberg is a parent company of three commercial bank and the Landesbank for some Federal States of Germany.-History:...
(LBBW). Until 21.06.2010, the BayernLB
BayernLB
BayernLB or Bayerische Landesbank is a publicly regulated bank based in Munich, Germany and one of the eight Landesbanken. It is 94% owned by the free state of Bavaria and 6% owned by the Sparkassenverband Bayern, the umbrella organization of Bavarian Sparkassen...
was majority shareholder of the Landesbank Saar (SaarLB) with a share of 75,1%. Since June 2010, the Saarland
Saarland
Saarland is one of the sixteen states of Germany. The capital is Saarbrücken. It has an area of 2570 km² and 1,045,000 inhabitants. In both area and population, it is the smallest state in Germany other than the city-states...
has become shareholder with a stake of 35,2% and the BayernLB reduced its share to 49,9%. The remaining 14,9% are held by the Sparkassen through its regional confederation.
The regional banks / clearing houses are the central banks of a savings bank association and act as the "main bank" of the states. They are also local banks, mortgage banks and general commercial banks. Their duties and power is codified in the individual country banking laws of the Länder (Landesbankengesetze). The specific tasks for the savings bank
Savings bank
A savings bank is a financial institution whose primary purpose is accepting savings deposits. It may also perform some other functions.In Europe, savings banks originated in the 19th or sometimes even the 18th century. Their original objective was to provide easily accessible savings products to...
s include the central clearing for cashless payments and liquidity funding for the regional savings bank
Savings bank
A savings bank is a financial institution whose primary purpose is accepting savings deposits. It may also perform some other functions.In Europe, savings banks originated in the 19th or sometimes even the 18th century. Their original objective was to provide easily accessible savings products to...
s. They also provide many services for the savings banks in the region in securities and cross-country businesses. In contrast to savings banks, they are doing "wholesale-banking" instead of retail-banking. With combined total assets of EUR 1,620 trillion as of December 2010, the 7 Landesbanken-Groups employ some 44.000 people.
DekaBank
DekaBank
The DekaBank is the central asset manager of the German Sparkassen. Deka as an investment company was founded in 1956. In 1999 it merged with Deutsche Girozentrale , which was founded in 1918...
with its subsidiaries is the central asset manager of the German Savings Bank Finance Group. Based in Frankfurt
Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main , commonly known simply as Frankfurt, is the largest city in the German state of Hesse and the fifth-largest city in Germany, with a 2010 population of 688,249. The urban area had an estimated population of 2,300,000 in 2010...
and Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
it provides asset management services for the Sparkassen
Savings bank
A savings bank is a financial institution whose primary purpose is accepting savings deposits. It may also perform some other functions.In Europe, savings banks originated in the 19th or sometimes even the 18th century. Their original objective was to provide easily accessible savings products to...
and the Landesbanken
Landesbank
The Landesbanken in Germany are a group of state owned banks of a type unique to Germany. They are regionally organised and their business is predominantly wholesale banking...
and their customers. With managed fund assets of about € 155 billion, approximately five million customer deposits and group locations in Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
and Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
, the DekaBank Group is one of the largest asset managers in Germany.
DekaBank's roots date back to the year 1918, when Deutsche Girozentrale (DGZ) was founded.. Deka as an investment company was founded in 1956 (17.08.1956) by DGZ with a share of 23% an 11 other regional Landesbank
Landesbank
The Landesbanken in Germany are a group of state owned banks of a type unique to Germany. They are regionally organised and their business is predominantly wholesale banking...
en. Todays DekaBank
DekaBank
The DekaBank is the central asset manager of the German Sparkassen. Deka as an investment company was founded in 1956. In 1999 it merged with Deutsche Girozentrale , which was founded in 1918...
was created in 1999 by a merger of DGZ and Deka..
Until the 8. June 2011, DekaBank
DekaBank
The DekaBank is the central asset manager of the German Sparkassen. Deka as an investment company was founded in 1956. In 1999 it merged with Deutsche Girozentrale , which was founded in 1918...
has been owned by the German Savings Banks and Giro Association Landesbanken itselfves grouped their shares in the GLB GmbH & Co.OHG, who has hold the DekaBank shares. On 7. April 2011, the Savings Banks bought the 50% stake from the landesbanken for a price of EUR 2.3 billion to become sole owner of the DekaBank. The acquisition was closed on the 8. June 2011 and DekaBank
DekaBank
The DekaBank is the central asset manager of the German Sparkassen. Deka as an investment company was founded in 1956. In 1999 it merged with Deutsche Girozentrale , which was founded in 1918...
became fully, directly owned by the savings banks.
3,700 people throughout the group work in one of the 3 business divisions AMK (Asset Management Capital Markets), AMI (Asset Management Real Estate Business), C&M (Corporates and Markets), the sales division or one of the corporate centers.
Landesbausparkassen
The Landesbausparkassen are as subsidiaries of the Sparkasseen and its associations regionally organized and focused on real estate banking. There are 10 Landesbausparkassen in Germany which employ around 8.900 people. Their combined balance would show summarized assets of EUR 52 billion per December 2009.Core business of the Landesbausparkassen is the offering of collective real estate saving products (Bausparen) and providing of low-interest residential mortgage loans.
Other members
In addition to several banking units, the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe also consists of 11 regional, public insurance groups, leasing and factoring companies, i.e. the Deutsche Leasing-Group, and numerous venture capital companies.See also
- Savings bankSavings bankA savings bank is a financial institution whose primary purpose is accepting savings deposits. It may also perform some other functions.In Europe, savings banks originated in the 19th or sometimes even the 18th century. Their original objective was to provide easily accessible savings products to...
- DekaBankDekaBankThe DekaBank is the central asset manager of the German Sparkassen. Deka as an investment company was founded in 1956. In 1999 it merged with Deutsche Girozentrale , which was founded in 1918...
- savings and loan associationSavings and loan associationA savings and loan association , also known as a thrift, is a financial institution that specializes in accepting savings deposits and making mortgage and other loans...
- Deutscher Sparkassen- und GiroverbandDeutscher Sparkassen- und GiroverbandDeutscher Sparkassen- und Giroverband is the German association of saving banks. It was founded in 1924 by the merger of Deutscher Sparkassenverband and Deutscher Zentral-Giroverband. The headquarter is located in Berlin since 1999, having previously been located in Bonn.-Presidents:*Ernst...

