
Game tree
Encyclopedia
In game theory
, a game tree is a directed graph
whose nodes are positions in a game
and whose edges are moves. The complete game tree for a game is the game tree starting at the initial position and containing all possible moves from each position; the complete tree is the same tree as that obtained from the extensive-form game representation.
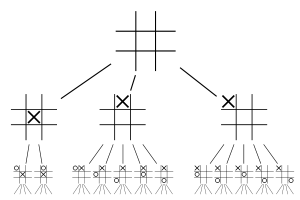 The diagram shows the first two levels, or plies
The diagram shows the first two levels, or plies
, in the game tree for tic-tac-toe
. We consider all the rotations and reflections of positions as being equivalent, so the first player has three choices of move: in the center, at the edge, or in the corner. The second player has two choices for the reply if the first player played in the center, otherwise five choices. And so on.
The number of leaf nodes in the complete game tree is the number of possible different ways the game can be played. For example, the game tree for tic-tac-toe has 26,830 leaf nodes.
Game trees are important in artificial intelligence
because one way to pick the best move in a game is to search the game tree using the minimax
algorithm or its variants. The game tree for tic-tac-toe is easily searchable, but the complete game trees for larger games like chess
are much too large to search. Instead, a chess-playing program searches a partial game tree: typically as many plies from the current position as it can search in the time available. Except for the case of "pathological" game trees (which seem to be quite rare in practice), increasing the search depth (i.e., the number of plies searched) generally improves the chance of picking the best move.
Two-person games can also be represented as and-or tree
s. For the first player to win a game, there must exist a winning move for all moves of the second player. This is represented in the and-or tree by using disjunction to represent the first player's alternative moves and using conjunction to represent all of the second player's moves.
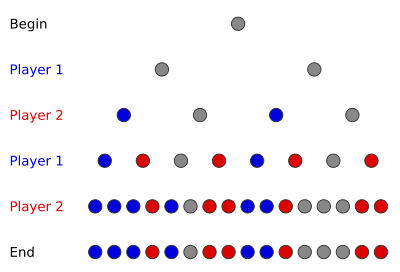 With a complete game tree, it is possible to "solve" the game – that is to say, find a sequence of moves that either the first or second player can follow that will guarantee either a win or tie. The algorithm (which is generally called backward induction
With a complete game tree, it is possible to "solve" the game – that is to say, find a sequence of moves that either the first or second player can follow that will guarantee either a win or tie. The algorithm (which is generally called backward induction
or retrograde analysis
) can be described recursively as follows.
The diagram shows a game tree for an arbitrary game, colored using the above algorithm.
It is usually possible to solve a game (in this technical sense of "solve") using only a subset of the game tree, since in many games a move need not be analyzed if there is another move that is better for the same player (for example alpha-beta pruning
can be used in many deterministic games).
Any subtree that can be used to solve the game is known as a decision tree, and the sizes of decision trees of various shapes are used as measures of game complexity
.
Game theory
Game theory is a mathematical method for analyzing calculated circumstances, such as in games, where a person’s success is based upon the choices of others...
, a game tree is a directed graph
Directed graph
A directed graph or digraph is a pair G= of:* a set V, whose elements are called vertices or nodes,...
whose nodes are positions in a game
Game
A game is structured playing, usually undertaken for enjoyment and sometimes used as an educational tool. Games are distinct from work, which is usually carried out for remuneration, and from art, which is more often an expression of aesthetic or ideological elements...
and whose edges are moves. The complete game tree for a game is the game tree starting at the initial position and containing all possible moves from each position; the complete tree is the same tree as that obtained from the extensive-form game representation.

Ply (game theory)
In two-player sequential games, a ply refers to one turn taken by one of the players. The word is used to clarify what is meant when one might otherwise say "turn"....
, in the game tree for tic-tac-toe
Tic-tac-toe
Tic-tac-toe, also called wick wack woe and noughts and crosses , is a pencil-and-paper game for two players, X and O, who take turns marking the spaces in a 3×3 grid. The X player usually goes first...
. We consider all the rotations and reflections of positions as being equivalent, so the first player has three choices of move: in the center, at the edge, or in the corner. The second player has two choices for the reply if the first player played in the center, otherwise five choices. And so on.
The number of leaf nodes in the complete game tree is the number of possible different ways the game can be played. For example, the game tree for tic-tac-toe has 26,830 leaf nodes.
Game trees are important in artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science that aims to create it. AI textbooks define the field as "the study and design of intelligent agents" where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its...
because one way to pick the best move in a game is to search the game tree using the minimax
Minimax
Minimax is a decision rule used in decision theory, game theory, statistics and philosophy for minimizing the possible loss for a worst case scenario. Alternatively, it can be thought of as maximizing the minimum gain...
algorithm or its variants. The game tree for tic-tac-toe is easily searchable, but the complete game trees for larger games like chess
Chess
Chess is a two-player board game played on a chessboard, a square-checkered board with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. It is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide at home, in clubs, online, by correspondence, and in tournaments.Each player...
are much too large to search. Instead, a chess-playing program searches a partial game tree: typically as many plies from the current position as it can search in the time available. Except for the case of "pathological" game trees (which seem to be quite rare in practice), increasing the search depth (i.e., the number of plies searched) generally improves the chance of picking the best move.
Two-person games can also be represented as and-or tree
And-or tree
An and–or tree is a graphical representation of the reduction of problems to conjunctions and disjunctions of subproblems .-Example:The and-or tree:...
s. For the first player to win a game, there must exist a winning move for all moves of the second player. This is represented in the and-or tree by using disjunction to represent the first player's alternative moves and using conjunction to represent all of the second player's moves.
Solving Game Trees

Backward induction
Backward induction is the process of reasoning backwards in time, from the end of a problem or situation, to determine a sequence of optimal actions. It proceeds by first considering the last time a decision might be made and choosing what to do in any situation at that time. Using this...
or retrograde analysis
Retrograde analysis
In chess, retrograde analysis is a computational method used to solve game positions for optimal play by working backward from known outcomes , such as the construction of endgame tablebases. In game theory at large, this method is called backward induction...
) can be described recursively as follows.
-
- Color the final ply of the game tree so that all wins for player 1 are colored one way, all wins for player 2 are colored another way, and all ties are colored a third way.
- Look at the next ply up. If there exists a node colored opposite as the current player, color this node for that player as well. If all immediately lower nodes are colored for the same player, color this node for the same player as well. Otherwise, color this node a tie.
- Repeat for each ply, moving upwards, until all nodes are colored. The color of the root node will determine the nature of the game.
The diagram shows a game tree for an arbitrary game, colored using the above algorithm.
It is usually possible to solve a game (in this technical sense of "solve") using only a subset of the game tree, since in many games a move need not be analyzed if there is another move that is better for the same player (for example alpha-beta pruning
Alpha-beta pruning
Alpha-beta pruning is a search algorithm which seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree. It is an adversarial search algorithm used commonly for machine playing of two-player games...
can be used in many deterministic games).
Any subtree that can be used to solve the game is known as a decision tree, and the sizes of decision trees of various shapes are used as measures of game complexity
Game complexity
Combinatorial game theory has several ways of measuring game complexity. This article describes five of them: state-space complexity, game tree size, decision complexity, game-tree complexity, and computational complexity.-Measures of game complexity:...
.
See also
- Alpha-beta pruningAlpha-beta pruningAlpha-beta pruning is a search algorithm which seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree. It is an adversarial search algorithm used commonly for machine playing of two-player games...
- Extensive form gameExtensive form gameAn extensive-form game is a specification of a game in game theory, allowing explicit representation of a number of important aspects, like the sequencing of players' possible moves, their choices at every decision point, the information each player has about the other player's moves when he...
- Shannon numberShannon numberThe Shannon number, named after Claude Shannon, is an estimated lower bound on the game-tree complexity of chess. Shannon calculated it as an aside in his 1950 paper "Programming a Computer for Playing Chess"...
- Game complexityGame complexityCombinatorial game theory has several ways of measuring game complexity. This article describes five of them: state-space complexity, game tree size, decision complexity, game-tree complexity, and computational complexity.-Measures of game complexity:...

