And-or tree
Encyclopedia
An and–or tree is a graphical representation of the reduction of problem
s (or goals) to conjunctions
and disjunctions of subproblems (or subgoals).
represents the search space
for solving the problem P, using the goal-reduction methods:
the associated and-or tree is a set of labelled nodes such that:
A node N, labelled by a problem P, is a success node if there is a method of the form P if nothing (i.e., P is a "fact"). The node is a failure node if there is no method for solving P.
If all of the children of a node N, conjoined by the same arc, are success nodes, then the node N is also a success node. Otherwise the node is a failure node.
for searching the space are possible. These include searching the tree depth-first, breadth-first, or best-first using some measure of desirability of solutions. The search strategy can be sequential, searching or generating one node at a time, or parallel, searching or generating several nodes in parallel.
(without variables). In the case of logic programs containing variables, the solutions of conjoint sub-problems must be compatible. Subject to this complication, sequential and parallel search strategies for and-or trees provide a computational model for executing logic programs.
For each of these children nodes, there exists a set of non-conjoint children nodes, corresponding to all of the player's defending moves.
For solving game trees with proof-number search
family of algorithms, game trees are to be mapped to And/Or trees. MAX-nodes (i.e. maximizing player to move) are represented as OR nodes, MIN-nodes map to AND nodes. The mapping is possible, when the search is done with only a binary goal, which usually is "player to move wins the game".
Problem
A problem is an obstacle, impediment, difficulty or challenge, or any situation that invites resolution; the resolution of which is recognized as a solution or contribution toward a known purpose or goal...
s (or goals) to conjunctions
Logical conjunction
In logic and mathematics, a two-place logical operator and, also known as logical conjunction, results in true if both of its operands are true, otherwise the value of false....
and disjunctions of subproblems (or subgoals).
Example
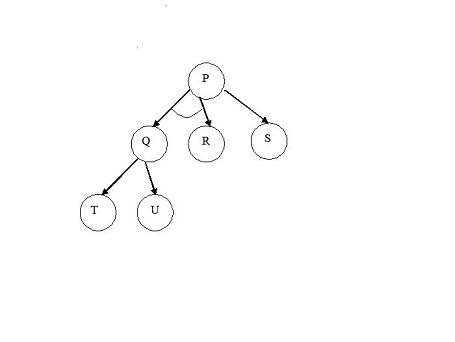
The and-or tree:
represents the search space
Search space
Search space may refer to one of the following.*In optimization, the domain of the function to be optimized*In search algorithms of computer science, the set of all possible solutions...
for solving the problem P, using the goal-reduction methods:
- P if Q and R
- P if S
- Q if T
- Q if U
Definitions
Given an initial problem P0 and set of problem solving methods of the form:- P if P1 and … and Pn
the associated and-or tree is a set of labelled nodes such that:
- The root of the tree is a node labelled by P0.
- For every node N labelled by a problem or sub-problem P and for every method of the form P if P1 and … and Pn, there exists a set of children nodes N1, …, Nn of the node N, such that each node Ni is labelled by Pi. The nodes are conjoined by an arc, to distinguish them from children of N that might be associated with other methods.
A node N, labelled by a problem P, is a success node if there is a method of the form P if nothing (i.e., P is a "fact"). The node is a failure node if there is no method for solving P.
If all of the children of a node N, conjoined by the same arc, are success nodes, then the node N is also a success node. Otherwise the node is a failure node.
Search strategies
An and-or tree specifies only the search space for solving a problem. Different search strategiesTree traversal
In computer science, tree-traversal refers to the process of visiting each node in a tree data structure, exactly once, in a systematic way. Such traversals are classified by the order in which the nodes are visited...
for searching the space are possible. These include searching the tree depth-first, breadth-first, or best-first using some measure of desirability of solutions. The search strategy can be sequential, searching or generating one node at a time, or parallel, searching or generating several nodes in parallel.
Relationship with logic programming
The methods used for generating and-or trees are propositional logic programsLogic programming
Logic programming is, in its broadest sense, the use of mathematical logic for computer programming. In this view of logic programming, which can be traced at least as far back as John McCarthy's [1958] advice-taker proposal, logic is used as a purely declarative representation language, and a...
(without variables). In the case of logic programs containing variables, the solutions of conjoint sub-problems must be compatible. Subject to this complication, sequential and parallel search strategies for and-or trees provide a computational model for executing logic programs.
Relationship with two-player games
And–or trees can also be used to represent the search spaces for two-person games. The root node of such a tree represents the problem of one of the players winning the game, starting from the initial state of the game. Given a node N, labelled by the problem P of the player winning the game from a particular state of play, there exists a single set of conjoint children nodes, corresponding to all of the opponents responding moves.For each of these children nodes, there exists a set of non-conjoint children nodes, corresponding to all of the player's defending moves.
For solving game trees with proof-number search
Proof-number search
Proof-number search is a game tree search algorithm invented by Victor Allis, with applications mostly in endgame solvers, but also for sub-goals during games....
family of algorithms, game trees are to be mapped to And/Or trees. MAX-nodes (i.e. maximizing player to move) are represented as OR nodes, MIN-nodes map to AND nodes. The mapping is possible, when the search is done with only a binary goal, which usually is "player to move wins the game".

