
Fundamental unit
Encyclopedia
A set of fundamental units is a set of units
for physical quantities
from which every other unit can be generated.
In the language of measurement
, quantities are quantifiable aspects of the world, such as time
, distance
, velocity
, mass
, momentum
, energy
, and weight
, and units are used to describe their measure. Many of these quantities are related to each other by various physical laws, and as a result the units of some of the quantities can be expressed as products (or ratios) of powers of other units (e.g., momentum is mass times velocity and velocity is measured in distance divided by time). These relationships are discussed in dimensional analysis
. Those that cannot be so expressed can be regarded as "fundamental" in this sense.
There are other relationships between physical quantities which can be expressed by means of fundamental constants, and to some extent it is an arbitrary decision whether to retain the fundamental constant as a quantity with dimensions or simply to define it as unity or a fixed dimensionless number, and reduce the number of fundamental constants by one.
For instance, time and distance are related to each other by the speed of light
, c, which is a fundamental constant. It is possible to use this relationship to eliminate either the fundamental unit of time or that of distance. Similar considerations apply to Planck's constant, h, which relates energy (with dimensions of mass, length and time) to frequency (dimensions of time). In theoretical physics it is customary to use such units (natural units
) in which c = 1 and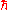 = 1.
= 1.
Slightly different considerations apply to the so-called permittivity of free space, which historically has been regarded as a separate physical constant in some systems of measurement but not in others.
In the SI
system, there are seven fundamental units: kilogram
, meter, candela
, second
, ampere
, kelvin
, and mole
.
In theory, a system of fundamental quantities (or sometimes fundamental dimensions) would be such that every other physical quantity (or dimension of physical quantity) can be generated from them.
A widely used choice is the so-called Planck units
, which are defined by setting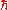 = c = G = 1.
= c = G = 1.
That leaves every physical quantity expressed simply as a dimensionless number, so it is not surprising that there are also physicists who have cast doubt on the very existence of incompatible fundamental quantities.
Units of measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention and/or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same physical quantity. Any other value of the physical quantity can be expressed as a simple multiple of the unit of...
for physical quantities
Physical quantity
A physical quantity is a physical property of a phenomenon, body, or substance, that can be quantified by measurement.-Definition of a physical quantity:Formally, the International Vocabulary of Metrology, 3rd edition defines quantity as:...
from which every other unit can be generated.
In the language of measurement
Measurement
Measurement is the process or the result of determining the ratio of a physical quantity, such as a length, time, temperature etc., to a unit of measurement, such as the metre, second or degree Celsius...
, quantities are quantifiable aspects of the world, such as time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
, distance
Distance
Distance is a numerical description of how far apart objects are. In physics or everyday discussion, distance may refer to a physical length, or an estimation based on other criteria . In mathematics, a distance function or metric is a generalization of the concept of physical distance...
, velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
, mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
, momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
, energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
, and weight
Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force on the object due to gravity. Its magnitude , often denoted by an italic letter W, is the product of the mass m of the object and the magnitude of the local gravitational acceleration g; thus:...
, and units are used to describe their measure. Many of these quantities are related to each other by various physical laws, and as a result the units of some of the quantities can be expressed as products (or ratios) of powers of other units (e.g., momentum is mass times velocity and velocity is measured in distance divided by time). These relationships are discussed in dimensional analysis
Dimensional analysis
In physics and all science, dimensional analysis is a tool to find or check relations among physical quantities by using their dimensions. The dimension of a physical quantity is the combination of the basic physical dimensions which describe it; for example, speed has the dimension length per...
. Those that cannot be so expressed can be regarded as "fundamental" in this sense.
There are other relationships between physical quantities which can be expressed by means of fundamental constants, and to some extent it is an arbitrary decision whether to retain the fundamental constant as a quantity with dimensions or simply to define it as unity or a fixed dimensionless number, and reduce the number of fundamental constants by one.
For instance, time and distance are related to each other by the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, c, which is a fundamental constant. It is possible to use this relationship to eliminate either the fundamental unit of time or that of distance. Similar considerations apply to Planck's constant, h, which relates energy (with dimensions of mass, length and time) to frequency (dimensions of time). In theoretical physics it is customary to use such units (natural units
Natural units
In physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed...
) in which c = 1 and
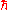 = 1.
= 1.Slightly different considerations apply to the so-called permittivity of free space, which historically has been regarded as a separate physical constant in some systems of measurement but not in others.
In the SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
system, there are seven fundamental units: kilogram
Kilogram
The kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water...
, meter, candela
Candela
The candela is the SI base unit of luminous intensity; that is, power emitted by a light source in a particular direction, weighted by the luminosity function . A common candle emits light with a luminous intensity of roughly one candela...
, second
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
, ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
, kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
, and mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
.
In theory, a system of fundamental quantities (or sometimes fundamental dimensions) would be such that every other physical quantity (or dimension of physical quantity) can be generated from them.
- One could eliminate any two of the metre, kilogram and second by setting c and h to unity or to a fixed dimensionless number.
- One could then eliminate the ampere either by setting the permittivity of free space to a fixed dimensionless number or by setting the electronic charge to such a number.
- One could similarly eliminate the mole as a fundamental unit by reference to Avogadro's numberAvogadro's numberIn chemistry and physics, the Avogadro constant is defined as the ratio of the number of constituent particles N in a sample to the amount of substance n through the relationship NA = N/n. Thus, it is the proportionality factor that relates the molar mass of an entity, i.e...
. - One could eliminate the kelvin as it can be argued that temperature simply expresses the energy per particle per degree of freedom which can be expressed in terms of energy (or mass, length, and time). Another way of saying this is that Boltzmann's constant could be expressed as a fixed dimensionless number.
- Similarly, one could eliminate the candela as that is defined in terms of other physical quantities.
- That just leaves one fundamental dimension and one fundamental unit, but we still have plenty of fundamental constants left to eliminate that too - for instance one could use G, the gravitational constantGravitational constantThe gravitational constant, denoted G, is an empirical physical constant involved in the calculation of the gravitational attraction between objects with mass. It appears in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Einstein's theory of general relativity. It is also known as the universal...
, or m(e), the electronElectronThe electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
rest mass.
A widely used choice is the so-called Planck units
Planck units
In physics, Planck units are physical units of measurement defined exclusively in terms of five universal physical constants listed below, in such a manner that these five physical constants take on the numerical value of 1 when expressed in terms of these units. Planck units elegantly simplify...
, which are defined by setting
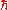 = c = G = 1.
= c = G = 1.That leaves every physical quantity expressed simply as a dimensionless number, so it is not surprising that there are also physicists who have cast doubt on the very existence of incompatible fundamental quantities.
See also
- Characteristic units
- Dimensional analysisDimensional analysisIn physics and all science, dimensional analysis is a tool to find or check relations among physical quantities by using their dimensions. The dimension of a physical quantity is the combination of the basic physical dimensions which describe it; for example, speed has the dimension length per...
- Natural unitsNatural unitsIn physics, natural units are physical units of measurement based only on universal physical constants. For example the elementary charge e is a natural unit of electric charge, or the speed of light c is a natural unit of speed...
- SI base unitSI base unitThe International System of Units defines seven units of measure as a basic set from which all other SI units are derived. These SI base units and their physical quantities are:* metre for length...
- SI system of unitsSiSi, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
- Units of measurementUnits of measurementA unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention and/or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same physical quantity. Any other value of the physical quantity can be expressed as a simple multiple of the unit of...

