
Four sons of Horus
Encyclopedia
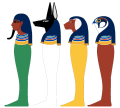
The four sons of Horus were a group of four gods
God (male deity)
A god, as a male deity, contrasts with female deities, or "goddesses". While the term 'goddess' specifically refers to a female deity, the plural 'gods' can be applied to all gods collectively, regardless of gender....
in Egyptian religion, who were essentially the personifications of the four canopic jar
Canopic jar
Canopic jars were used by the Ancient Egyptians during the mummification process to store and preserve the viscera of their owner for the afterlife. They were commonly either carved from limestone or were made of pottery...
s, which accompanied mummified
Mummy
A mummy is a body, human or animal, whose skin and organs have been preserved by either intentional or incidental exposure to chemicals, extreme coldness , very low humidity, or lack of air when bodies are submerged in bogs, so that the recovered body will not decay further if kept in cool and dry...
bodies. Since the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
was thought to embody the soul
Egyptian soul
The ancient Egyptians believed that a human soul was made up of five parts: the Ren, the Ba, the Ka, the Sheut, and the Ib. In addition to these components of the soul there was the human body...
, it was left inside the body. The brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
was thought only to be the origin of mucus
Mucus
In vertebrates, mucus is a slippery secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. Mucous fluid is typically produced from mucous cells found in mucous glands. Mucous cells secrete products that are rich in glycoproteins and water. Mucous fluid may also originate from mixed glands, which...
, so it was reduced to liquid, syphoned off, and discarded. This left the stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
(and small intestines), liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, large intestine
Intestine
In human anatomy, the intestine is the segment of the alimentary canal extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to the anus and, in humans and other mammals, consists of two segments, the small intestine and the large intestine...
s, and lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s, which were removed, embalmed and stored, each organ in its own jar. There were times when embalmers deviated from this scheme: during the 21st Dynasty they embalmed and wrapped the viscera and returned them to the body, while the Canopic jars remained empty symbols.
The earliest reference to the sons of Horus is found in the Pyramid Texts
Pyramid Texts
The Pyramid Texts are a collection of ancient Egyptian religious texts from the time of the Old Kingdom. The pyramid texts are possibly the oldest known religious texts in the world. Written in Old Egyptian, the pyramid texts were carved on the walls and sarcophagi of the pyramids at Saqqara during...
where they are described as friends of the king, as they assist the king in his ascension to heaven in the eastern sky by means of ladders. Their association with Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
specifically goes back to the Old Kingdom
Old Kingdom
Old Kingdom is the name given to the period in the 3rd millennium BC when Egypt attained its first continuous peak of civilization in complexity and achievement – the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley .The term itself was...
when they were said not only to be his children but also his souls. As the king, or Pharaoh
Pharaoh
Pharaoh is a title used in many modern discussions of the ancient Egyptian rulers of all periods. The title originates in the term "pr-aa" which means "great house" and describes the royal palace...
was seen as a manifestation of, or especially protected by, Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
, these parts of the deceased pharaoh, referred to as the Osiris, were seen as parts of Horus, or rather, his children, an association which did not diminish with each successive pharaoh. Since Horus was their father, so Isis
Isis
Isis or in original more likely Aset is a goddess in Ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. She was worshipped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic...
, Horus' original wife in the early mythological phase, was usually seen as their mother, though in the details of the funerary ritual each son, and therefore each canopic jar, was protected by a particular goddess. Just as the sons of Horus protected the contents of a canopic jar, the king's organs, so they in turn were protected. As they were male in accordance with the principles of male/female duality their protectors were female.
Imsety in human form, protected the liver and was protected by Isis
Isis
Isis or in original more likely Aset is a goddess in Ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. She was worshipped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic...
.
Hapi
Hapi
Hapi, sometimes transliterated as Hapy, is one of the Four sons of Horus in ancient Egyptian religion, depicted in funerary literature as protecting the throne of Osiris in the Underworld. He is not to be confused with another god of the same name...
in baboon form, protected the lungs and was protected by Nephthys
Nephthys
In Egyptian mythology, Nephthys is a member of the Great Ennead of Heliopolis, a daughter of Nut and Geb. Nephthys was typically paired with her sister Isis in funerary rites because of their role as protectors of the mummy and the god Osiris and as the sister-wife of Seth.Nephthys is regarded as...
.
Duamutef
Duamutef
Duamutef was one of the Four Sons of Horus and a protectiongod of the Canopic jars. Commonly he is said to be the son of the god Horus the Elder and the goddess Isis. There is another myth that describes...
in jackal form, protected the stomach and was protected by Neith
Neith
In Egyptian mythology, Neith was an early goddess in the Egyptian pantheon. She was the patron deity of Sais, where her cult was centered in the Western Nile Delta of Egypt and attested as early as the First Dynasty...
.
Qebehsenuef
Qebehsenuef
Qebehsenuef was one of the sons of Horus in Egyptian mythology, the god of protection and of the West. In the preparation of mummies, his canopic jar was used for the intestines. He is seen as a mummy with a falcon head...
in hawk form, protected the large intestines and was protected by Serket
Serket
In Egyptian mythology, Serket is the goddess of healing stings and bites who originally was the deification of the scorpion....
.
The classic depiction of the four sons of Horus on Middle Kingdom
Middle Kingdom of Egypt
The Middle Kingdom of Egypt is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the establishment of the Eleventh Dynasty to the end of the Fourteenth Dynasty, between 2055 BC and 1650 BC, although some writers include the Thirteenth and Fourteenth dynasties in the Second Intermediate...
coffins show Imsety and Duamutef on the eastern side of the coffin and Hapi and Qebehsenuef on the western side. The eastern side is decorated with a pair of eyes and the mummy was turned on its side to face the east and the rising sun, therefore, this side is sometimes referred to as the front. The sons of Horus also became associated with the cardinal compass points, so that Hapi was the North, Imsety the south, Duamutef the east and Qebehsenuef the west.
Up until the end of the 18th Dynasty the canopic jars had the head of the king but later they were shown with animal heads. Inscriptions on coffins and sarcophagi from earliest times showed them usually in animal form.
Hapi
Hapi (xapi) the baboon headed son of Horus protected the lungs of the deceased and was in turn protected by the goddess NephthysNephthys
In Egyptian mythology, Nephthys is a member of the Great Ennead of Heliopolis, a daughter of Nut and Geb. Nephthys was typically paired with her sister Isis in funerary rites because of their role as protectors of the mummy and the god Osiris and as the sister-wife of Seth.Nephthys is regarded as...
. The spelling of his name includes a hieroglyph which is thought to be connected with steering a boat, although its exact nature is not known. For this reason he was sometimes connected with navigation, although early references call him the great runner.
In Spell 151 of the Book of the Dead
Book of the Dead
The Book of the Dead is the modern name of an ancient Egyptian funerary text, used from the beginning of the New Kingdom to around 50 BC. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated rw nw prt m hrw is translated as "Book of Coming Forth by Day". Another translation would be "Book of...
he is given the following words to say:
As one of the four pillars of Shu and one of the four rudders of heaven he was associated with the North, and is specifically referenced as such in Spell 148 in the Book of the Dead
Book of the Dead
The Book of the Dead is the modern name of an ancient Egyptian funerary text, used from the beginning of the New Kingdom to around 50 BC. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated rw nw prt m hrw is translated as "Book of Coming Forth by Day". Another translation would be "Book of...
.
Imsety
Imsety the human headed son of Horus, protected the liver of the deceased and was in turn protected by the goddess IsisIsis
Isis or in original more likely Aset is a goddess in Ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. She was worshipped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic...
. It seems that his role was to help revivify the corpse of the dead person, as he is asked to 'lift them up' by Horus.
To stand up meant to be active and thus alive while to be prone signified death.
In Spell 151 of the Book of the Dead he is given the following words to say:
Again the theme of making alive and revivifying is alluded to through the metaphor of making his house flourish. He does this with the authority of two creator gods Ptah
Ptah
In Ancient Egyptian Religion, Ptah was the deification of the primordial mound in the Ennead cosmogony, which was more literally referred to as Ta-tenen , meaning risen land, or as Tanen, meaning submerged land, though Tatenen was a god in his...
and Re
Ra
Ra is the ancient Egyptian sun god. By the Fifth Dynasty he had become a major deity in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the mid-day sun...
.
Spell 148 in the Book of the Dead directly associates all four of Horus' sons to the four cardinal points
Cardinal Points
Cardinal Points is a student newspaper published in Plattsburgh, New York which serves the SUNY Plattsburgh community. The newspaper publishes 3,000 copies every Friday morning throughout the semester, from February until May 12...
. Imsety was associated with the South.
Duamutef

Neith
In Egyptian mythology, Neith was an early goddess in the Egyptian pantheon. She was the patron deity of Sais, where her cult was centered in the Western Nile Delta of Egypt and attested as early as the First Dynasty...
. It seems that his role was to worship the dead person, and his name means literally 'he who worships his mother'. In the Coffin Texts Horus calls upon him to:
Rather confusingly, as is borne out here, Isis had a dual role. Not only was she the wife of Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
and the mother of Horus
Horus
Horus is one of the oldest and most significant deities in the Ancient Egyptian religion, who was worshipped from at least the late Predynastic period through to Greco-Roman times. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists...
, but she was also the consort of Horus the Elder and thus the mother of the sons of Horus. This ambiguity is added to when Duamutef calls Osiris his father, rather than Horus.
In Spell 151 of the Book of the Dead he is given the following words to say:
The text does not make it clear who is going to harm Osiris, although there are two major candidates. The obvious one is Set, the murderer of Osiris. Somehow the son who worships his mother Isis is able to assist in overcoming Set
Set (mythology)
Set was in Ancient Egyptian religion, a god of the desert, storms, and foreigners. In later myths he was also the god of darkness, and chaos...
. the other possibility is Apophis
Apophis
Apophis may refer to:* Apep, an Ancient Egyptian mythological demon, in Greek known as Apophis* Apepi , a Hyksos pharaoh of Lower Egypt* 99942 Apophis, a near-Earth asteroid...
, the serpent demon who prevents the Sun's passage and thus the resurrection of Osiris. Either way, Duamutef through his worship of Isis has the power to protect the deceased from harm.
He was also considered one of the four pillars of Shu, a rudder of heaven, and was associated with the East.
Qebehsenuef
Qebehsenuef was the falcon-headed son of Horus, and protected the intestines of the deceased. He was in turn protected by the goddess SerketSerket
In Egyptian mythology, Serket is the goddess of healing stings and bites who originally was the deification of the scorpion....
. It appears that his role was to refresh the dead person, and his name means literally 'he who libates his siblings'. Horus tells him to:
Libation or showering with cool water was a traditional form of worship in Ancient Egypt. There are many images of the pharaoh presenting libation to the gods. There is a sense of a dual function of cleansing and refreshing them.
In Spell 151 of the Book of the Dead Qebehsenuef was given the following words to say:
After Set
Set (mythology)
Set was in Ancient Egyptian religion, a god of the desert, storms, and foreigners. In later myths he was also the god of darkness, and chaos...
murdered the king Osiris
Osiris
Osiris is an Egyptian god, usually identified as the god of the afterlife, the underworld and the dead. He is classically depicted as a green-skinned man with a pharaoh's beard, partially mummy-wrapped at the legs, wearing a distinctive crown with two large ostrich feathers at either side, and...
in order to hide his body he cut it into pieces and scattered them around the Delta. This was an anathema to the Egyptians and the service that Qebehsenuef gives to the dead is to reassemble their parts so they can be properly preserved.
He was the god associated with the West.

Jackal, baboon, falcon and human
The reasons for attributing these four animals to the sons of Horus is not known, although we may point to other associations which these animals have in Egyptian mythology. The baboon with the moon and Thoth, the god of wisdom and knowledge, and also the baboons which chatter when the sun rises raising their hands as if in worship. The jackal (or possibly dog) linked to AnubisAnubis
Anubis is the Greek name for a jackal-headed god associated with mummification and the afterlife in ancient Egyptian religion. In the ancient Egyptian language, Anubis is known as Inpu . According to the Akkadian transcription in the Amarna letters, Anubis' name was vocalized as Anapa...
and the act of embalming and also Wepwawet
Wepwawet
In late Egyptian mythology, Wepwawet was originally a war deity, whose cult centre was Asyut in Upper Egypt . His name means, opener of the ways...
the 'opener of the ways' who seeks out the paths of the dead. The hawk with Horus himself and also Seker the mummified necropolis god. And the man who may be linked to Osiris himself or Onuris the hunter.
However what is known is that the Egyptians themselves linked them with the ancient kings of Lower and Upper Egypt, the Souls of Pe and Nekhen
Souls of Pe and Nekhen
The Souls of Pe and Nekhen, mentioned first in the Pyramid Texts, refer to the ancestors of the ancient Egyptian kings. Nekhen was the Upper Egyptian centre of Horus worship, whose successors the Egyptian pharaohs were thought to be...
. In Spells 112 and 113 of the Book of the Dead
Book of the Dead
The Book of the Dead is the modern name of an ancient Egyptian funerary text, used from the beginning of the New Kingdom to around 50 BC. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated rw nw prt m hrw is translated as "Book of Coming Forth by Day". Another translation would be "Book of...
which have their origins in the earlier Coffin Texts
Coffin Texts
The Coffin Texts are a collection of ancient Egyptian funerary spells written on coffins beginning in the First Intermediate Period. The texts are derived in part from the earlier pyramid texts, reserved for royal use only, but they contain substantial new material related to everyday desires that...
Spells 157 and 158, it is described how Horus has his eye injured, and because of this is given the sons of Horus:
"Imsety, Hapi, Duamutef, Qebehsenuef whose father was the elder Horus and whose mother is Isis. - and he [Horus] said to Re: 'Give me two in Pe and two in Nekhen from this second company. May I be in my own right an alloter of eternity, an opener of everlasting, a queller of strife in this my name of Horus-who-is-on-his-pillar'. (Coffin Texts 157 , R.O. Faulkner).
The injury of Horus' eye is part of the myth cycle known as the Contending of Horus and Set recounting how they fought over the crown of Egypt.
In a unique illustration in the tomb of Ay the sons of Horus are shown wearing the red and white crowns as the Souls of Pe and Nekhen, the souls of the royal ancestors.
The attributes of the sons of Horus are not limited to their role as the protectors of canopic jars. they appear as the four rudders of heaven in Spell 148 of the Book of the Dead, as four of the seven celestial spirits summoned by Anubis in Spell 17 of the Book of the Dead and through this are linked to the circumpolar stars of the Great Bear
Ursa Major
Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April...
.
In fiction
Referenced in the fantasy series The Order of the Four Sons by Coyote Kishpaugh and Lauren Scharhag.Included as collectibles in the Egyptian-themed world in Hexen II
Hexen II
Hexen II is a first-person shooter developed by Raven Software from 1996 to 1997, published by id Software and distributed by Activision. It was the third game in the Hexen/Heretic series, and the last in the Serpent Riders trilogy. It was made available on Steam on August 3, 2007...
.

