Evolution of complexity
Encyclopedia
The evolution of biological complexity is an important outcome of the process of evolution
. Evolution has produced some remarkably complex organisms - although the actual level of complexity is very hard to define or measure accurately in biology, with properties such as gene content, the number of cell type
s or morphology
all being used to assess an organism's complexity. This observation that complex organisms can be produced from simpler ones has led to the common misperception of evolution being progressive and having a direction that leads towards what are viewed as "higher organisms".
Nowadays, this idea of "progression" in evolution is regarded as misleading, with natural selection
having no intrinsic direction and organisms selected for either increased or decreased complexity in response to local environmental conditions. Although there has been an increase in the maximum level of complexity over the history of life, there has always been a large majority of small and simple organisms and the most common level of complexity (the mode
) appears to have remained relatively constant.
and mycoplasma
; these organisms often dispense with traits that are made unnecessary through parasitism on a host.
A lineage can also dispense with complexity when a particular complex trait merely provides no selective advantage in a particular environment. Loss of this trait need not necessarily confer a selective advantage, but may be lost due to the accumulation of mutations if its loss does not confer an immediate selective disadvantage. For example, a parasitic organism may dispense with the synthetic pathway of a metabolite where it can readily scavenge that metabolite from its host. Discarding this synthesis may not necessarily allow the parasite to conserve significant energy or resources and grow faster, but the loss may be fixed in the population through mutation accumulation if no disadvantage is incurred by loss of that pathway. Mutations causing loss of a complex trait occur more often than mutations causing gain of a complex trait.
With selection, evolution can also produce more complex organisms. Complexity often arises in the co-evolution of hosts and pathogens, with each side developing ever more sophisticated adaptations, such as the immune system
and the many techniques pathogens have developed to evade it. For example, the parasite Trypanosoma brucei
, which causes sleeping sickness, has evolved so many copies of its major surface antigen
that about 10% of its genome is devoted to different versions of this one gene. This tremendous complexity allows the parasite to constantly change its surface and thus evade the immune system through antigenic variation
.
More generally, the growth of complexity may be driven by the co-evolution
between an organism and the ecosystem
of predators, prey and parasites to which it tries to stay adapted: as any of these become more complex in order to cope better with the diversity of threats offered by the ecosystem formed by the others, the others too will have to adapt by becoming more complex, thus triggering an on-going evolutionary arms race
towards more complexity. This trend may be reinforced by the fact that ecosystems themselves tend to become more complex over time, as species diversity
increases, together with the linkages or dependencies between species.
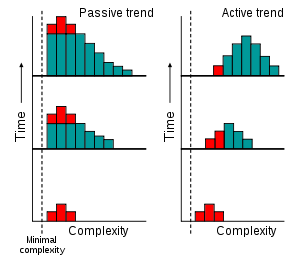 If evolution possessed an active trend toward complexity, then we would expect to see an increase over time in the most common value
If evolution possessed an active trend toward complexity, then we would expect to see an increase over time in the most common value
(the mode) of complexity among organisms, as shown to the right. Indeed, some computer models
have suggested that the generation of complex organisms is an inescapable feature of evolution. This is sometimes referred to as evolutionary self-organization
. Self-organization is the spontaneous internal organization of a system. This process is accompanied by an increase in systemic complexity, resulting in an emergent property that is distinctly different from any of the constituent parts.
However, the idea of increasing production of complexity in evolution can also be explained through a passive process. As shown on the leftt, this involves an increase in variance
but the mode does not change. The trend towards higher complexity over time exists, but also involves increasingly smaller portions of biological life.
In this hypothesis, any appearance of evolution acting with an intrinsic direction towards increasingly complex organisms is a result of people concentrating on the small number of large, complex organisms that inhabit the right-hand tail
of the complexity distribution and ignoring simpler and much more common organisms. This passive model predicts that the majority of species are microscopic
prokaryote
s, which is supported by estimates of 106 to 109 extant prokaryotes compared to diversity estimates of 106 to 3·106 for eukaryotes. Consequently, in this view, microscopic life dominates Earth, and large organisms only appear more diverse due to sampling bias.
and Ray Lankester
believed that all Nature had an innate striving to become more complex with evolution. This belief may reflect then-current ideas of Hegel
and Herbert Spencer
that all creation was gradually evolving to a higher, more perfect state.
According to this view, the evolution of parasites from an independent organism to parasite was seen as "devolution" or "degeneration", and contrary to Nature. This view has sometimes been used metaphorically by social theorists and propagandists to decry a class of people as "degenerate parasites". Today, "devolution" is regarded as nonsense; rather, lineages will become simpler or more complicated according to whatever forms have a selective advantage.
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
. Evolution has produced some remarkably complex organisms - although the actual level of complexity is very hard to define or measure accurately in biology, with properties such as gene content, the number of cell type
Cell type
A cell type is a distinct morphological or functional form of cell. When a cell switches state from one cell type to another, it undergoes cellular differentiation. A list of distinct cell types in the adult human body may include several hundred distinct types.-References:...
s or morphology
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
all being used to assess an organism's complexity. This observation that complex organisms can be produced from simpler ones has led to the common misperception of evolution being progressive and having a direction that leads towards what are viewed as "higher organisms".
Nowadays, this idea of "progression" in evolution is regarded as misleading, with natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
having no intrinsic direction and organisms selected for either increased or decreased complexity in response to local environmental conditions. Although there has been an increase in the maximum level of complexity over the history of life, there has always been a large majority of small and simple organisms and the most common level of complexity (the mode
Mode (statistics)
In statistics, the mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a data set or a probability distribution. In some fields, notably education, sample data are often called scores, and the sample mode is known as the modal score....
) appears to have remained relatively constant.
Selection for simplicity and complexity
Organisms that reproduce more quickly and plentifully than their competitors have an evolutionary advantage. Consequently, organisms can evolve to become simpler and thus multiply faster and produce more offspring, as they require fewer resources to reproduce. A good example are parasites such as malariaMalaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease of humans and other animals caused by eukaryotic protists of the genus Plasmodium. The disease results from the multiplication of Plasmodium parasites within red blood cells, causing symptoms that typically include fever and headache, in severe cases...
and mycoplasma
Mycoplasma
Mycoplasma refers to a genus of bacteria that lack a cell wall. Without a cell wall, they are unaffected by many common antibiotics such as penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis. They can be parasitic or saprotrophic. Several species are pathogenic in humans,...
; these organisms often dispense with traits that are made unnecessary through parasitism on a host.
A lineage can also dispense with complexity when a particular complex trait merely provides no selective advantage in a particular environment. Loss of this trait need not necessarily confer a selective advantage, but may be lost due to the accumulation of mutations if its loss does not confer an immediate selective disadvantage. For example, a parasitic organism may dispense with the synthetic pathway of a metabolite where it can readily scavenge that metabolite from its host. Discarding this synthesis may not necessarily allow the parasite to conserve significant energy or resources and grow faster, but the loss may be fixed in the population through mutation accumulation if no disadvantage is incurred by loss of that pathway. Mutations causing loss of a complex trait occur more often than mutations causing gain of a complex trait.
With selection, evolution can also produce more complex organisms. Complexity often arises in the co-evolution of hosts and pathogens, with each side developing ever more sophisticated adaptations, such as the immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
and the many techniques pathogens have developed to evade it. For example, the parasite Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma brucei is a parasitic protist species that causes African trypanosomiasis in humans and nagana in animals in Africa. There are 3 sub-species of T. brucei: T. b. brucei, T. b. gambiense and T. b. rhodesiense.These obligate parasites have two hosts - an insect vector and mammalian host...
, which causes sleeping sickness, has evolved so many copies of its major surface antigen
Antigen
An antigen is a foreign molecule that, when introduced into the body, triggers the production of an antibody by the immune system. The immune system will then kill or neutralize the antigen that is recognized as a foreign and potentially harmful invader. These invaders can be molecules such as...
that about 10% of its genome is devoted to different versions of this one gene. This tremendous complexity allows the parasite to constantly change its surface and thus evade the immune system through antigenic variation
Antigenic variation
Antigenic variation refers to the mechanism by which an infectious organism such as a protozoan, bacterium or virus alters its surface proteins in order to evade a host immune response. Immune evasion is particularly important for organisms that target long-lived hosts, repeatedly infect a single...
.
More generally, the growth of complexity may be driven by the co-evolution
Co-evolution
In biology, coevolution is "the change of a biological object triggered by the change of a related object." Coevolution can occur at many biological levels: it can be as microscopic as correlated mutations between amino acids in a protein, or as macroscopic as covarying traits between different...
between an organism and the ecosystem
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
of predators, prey and parasites to which it tries to stay adapted: as any of these become more complex in order to cope better with the diversity of threats offered by the ecosystem formed by the others, the others too will have to adapt by becoming more complex, thus triggering an on-going evolutionary arms race
Evolutionary arms race
In evolutionary biology, an evolutionary arms race is an evolutionary struggle between competing sets of co-evolving genes that develop adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other, resembling an arms race, which are also examples of positive feedback...
towards more complexity. This trend may be reinforced by the fact that ecosystems themselves tend to become more complex over time, as species diversity
Species diversity
Species diversity is an index that incorporates the number of species in an area and also their relative abundance. It is a more comprehensive value than species richness....
increases, together with the linkages or dependencies between species.
Types of trends in complexity

Mode (statistics)
In statistics, the mode is the value that occurs most frequently in a data set or a probability distribution. In some fields, notably education, sample data are often called scores, and the sample mode is known as the modal score....
(the mode) of complexity among organisms, as shown to the right. Indeed, some computer models
Artificial life
Artificial life is a field of study and an associated art form which examine systems related to life, its processes, and its evolution through simulations using computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American computer scientist, in 1986...
have suggested that the generation of complex organisms is an inescapable feature of evolution. This is sometimes referred to as evolutionary self-organization
Self-organization
Self-organization is the process where a structure or pattern appears in a system without a central authority or external element imposing it through planning...
. Self-organization is the spontaneous internal organization of a system. This process is accompanied by an increase in systemic complexity, resulting in an emergent property that is distinctly different from any of the constituent parts.
However, the idea of increasing production of complexity in evolution can also be explained through a passive process. As shown on the leftt, this involves an increase in variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
but the mode does not change. The trend towards higher complexity over time exists, but also involves increasingly smaller portions of biological life.
In this hypothesis, any appearance of evolution acting with an intrinsic direction towards increasingly complex organisms is a result of people concentrating on the small number of large, complex organisms that inhabit the right-hand tail
Skewness
In probability theory and statistics, skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of the probability distribution of a real-valued random variable. The skewness value can be positive or negative, or even undefined...
of the complexity distribution and ignoring simpler and much more common organisms. This passive model predicts that the majority of species are microscopic
Microorganism
A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters, or no cell at all...
prokaryote
Prokaryote
The prokaryotes are a group of organisms that lack a cell nucleus , or any other membrane-bound organelles. The organisms that have a cell nucleus are called eukaryotes. Most prokaryotes are unicellular, but a few such as myxobacteria have multicellular stages in their life cycles...
s, which is supported by estimates of 106 to 109 extant prokaryotes compared to diversity estimates of 106 to 3·106 for eukaryotes. Consequently, in this view, microscopic life dominates Earth, and large organisms only appear more diverse due to sampling bias.
History
In the 19th century, some scientists such as Jean-Baptiste LamarckJean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, Chevalier de la Marck , often known simply as Lamarck, was a French naturalist...
and Ray Lankester
Ray Lankester
Sir E. Ray Lankester KCB, FRS was a British zoologist, born in London.An invertebrate zoologist and evolutionary biologist, he held chairs at University College London and Oxford University. He was the third Director of the Natural History Museum, and was awarded the Copley Medal of the Royal...
believed that all Nature had an innate striving to become more complex with evolution. This belief may reflect then-current ideas of Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel
Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel was a German philosopher, one of the creators of German Idealism. His historicist and idealist account of reality as a whole revolutionized European philosophy and was an important precursor to Continental philosophy and Marxism.Hegel developed a comprehensive...
and Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer was an English philosopher, biologist, sociologist, and prominent classical liberal political theorist of the Victorian era....
that all creation was gradually evolving to a higher, more perfect state.
According to this view, the evolution of parasites from an independent organism to parasite was seen as "devolution" or "degeneration", and contrary to Nature. This view has sometimes been used metaphorically by social theorists and propagandists to decry a class of people as "degenerate parasites". Today, "devolution" is regarded as nonsense; rather, lineages will become simpler or more complicated according to whatever forms have a selective advantage.
See also
- BiocomplexityBiocomplexitythumb|175px|right|Biocomplexity spiralBiocomplexity is the study of complex structures and behaviors that arise from nonlinear interactions of active biological agents, which may range in scale from molecules to cells to organisms...
- BiodiversityBiodiversityBiodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
- BiosphereBiosphereThe biosphere is the global sum of all ecosystems. It can also be called the zone of life on Earth, a closed and self-regulating system...
- Complex adaptive systemComplex adaptive systemComplex adaptive systems are special cases of complex systems. They are complex in that they are dynamic networks of interactions and relationships not aggregations of static entities...
- ComplexityComplexityIn general usage, complexity tends to be used to characterize something with many parts in intricate arrangement. The study of these complex linkages is the main goal of complex systems theory. In science there are at this time a number of approaches to characterizing complexity, many of which are...
- EcosystemEcosystemAn ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
- EvolvabilityEvolvabilityEvolvability is defined as the capacity of a system for adaptive evolution. Evolvability is the ability of a population of organisms to not merely generate genetic diversity, but to generate adaptive genetic diversity, and thereby evolve through natural selection.In order for a biological organism...
- OrthogenesisOrthogenesisOrthogenesis, orthogenetic evolution, progressive evolution or autogenesis, is the hypothesis that life has an innate tendency to evolve in a unilinear fashion due to some internal or external "driving force". The hypothesis is based on essentialism and cosmic teleology and proposes an intrinsic...

