
Ethylene glycol poisoning
Encyclopedia
Ethylene glycol poisoning is caused by the ingestion of ethylene glycol
(the primary ingredient in both automotive antifreeze
and hydraulic brake fluid
). It is a toxic, colorless, odorless, almost nonvolatile
liquid with a sweet taste and is occasionally consumed by children and dogs for its sweetness. Following ingestion the symptoms of poisoning follow a three step progression starting with intoxication and vomiting
, before causing metabolic acidosis
, cardiovascular dysfunction, and finally acute kidney failure. The major cause of toxicity is not the ethylene glycol itself but its metabolite
s. The major metabolites causing toxicity are glycolic acid
and oxalic acid
.
Medical diagnosis
of poisoning is most reliably done by measurement of ethylene glycol in the blood. However many hospital
s do not have the facilities to perform this test and need to rely on abnormalities in the body’s biochemistry
to diagnose poisoning. Diagnosis can also be aided by examining the urine for the presence of calcium oxalate crystals. Treatment consists of initially stabilizing the patient followed by the use of antidotes. The antidotes used are either ethanol
or fomepizole
(Antizol). The antidotes work by blocking the enzyme
responsible for metabolizing ethylene glycol and therefore halt the progression of poisoning. Hemodialysis
is also used to help remove ethylene glycol and its metabolites from the blood. As long as medical treatment is undertaken the prognosis is generally good with most patients making a full recovery. Poisoning is relatively common and due to its taste, children and animals will sometimes consume large quantities of ethylene glycol. Denatonium benzoate, a bittering agent, is added to many antifreeze products to try to prevent ingestion.
, metabolic processes, and the kidney
s. The central nervous system is affected early in the course of poisoning as the result of a direct action of ethylene glycol. Similar to ethanol
, it causes intoxication, followed by drowsiness or coma
. Seizure
s may occur due to a direct effect. The toxic mechanism of ethylene glycol poisoning is mainly due to the metabolites of ethylene glycol. Initially it is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase
to glycolaldehyde
, which is then oxidized to glycolic acid
. The increase in metabolites may cause encephalopathy
or cerebral edema
. The metabolic effects occur 12 to 36 hours post ingestion, causing primarily metabolic acidosis
which is due mainly to accumulated glycolic acid. Additionally, as a side effect of the first two steps of metabolism, an increase in the blood concentration of lactic acid
occurs contributing to lactic acidosis
. The formation of acid metabolites also causes inhibition of other metabolic pathway
s, such as oxidative phosphorylation
.
The renal toxicity of ethylene glycol occurs 24 to 72 hours post ingestion and is caused by a direct cytotoxic effect of glycolic acid. The glycolic acid is then metabolized to glyoxylic acid
and finally to oxalic acid
. Oxalic acid binds with calcium to form calcium oxalate crystals which may deposit and cause damage to many areas of the body including the brain, heart, kidneys, and lungs. The most significant effect is accumulation of calcium oxalate
crystals in the kidneys which causes kidney damage leading to oliguric or anuric
acute kidney failure. The rate-limiting
step in this cascade is the conversion of glycolic to glyoxylic acid. Accumulation of glycolic acid in the body is mainly responsible for toxicity.
(mL/kg) of pure substance
. That is roughly 16 mL of 50% ethylene glycol for an 80 kg adult and just 4 mL for a 20 kg child. Poison control center
s often use more than a lick or taste in a child or more than a mouthful in an adult as a dose requiring hospital assessment.
The orally lethal dose
in humans has been reported as approximately 1.4 mL/kg of pure ethylene glycol. That is approximately 224 mL of 50% ethylene glycol for an 80 kg adult and just 56 mL for a 20 kg child. Although survival with medical treatment has occurred with doses much higher than this, death has occurred with just 30 mL of the concentrate in an adult. In the EU classification of dangerous substances it is 'harmful' (Xn) while more toxic substances are classified as 'toxic' (T) or 'very toxic' (T+). The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency generally puts substances which are lethal at more than 30 g to adults in Toxicity Class
III.
Ethylene glycol has a low vapor pressure
; it does not evaporate readily at normal temperatures and therefore high concentrations in air or intoxication are unlikely to occur following inhalational exposures. There may be a slight risk of poisoning where mists or fogs are generated, although this rarely leads to poisoning as ethylene glycol causes irritation and coughing when breathed in, alerting victims to its presence. Ethylene glycol is not well absorbed through skin
meaning poisoning following dermal exposure is also uncommon.
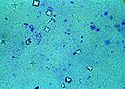 As many of the clinical signs
As many of the clinical signs
and symptoms of ethylene glycol poisoning are nonspecific and occur in many poisonings the diagnosis is often difficult. It is most reliably diagnosed by the measurement of the blood
ethylene glycol concentration. Ethylene glycol in biological fluids can be determined easily by gas chromatography. Many hospital laboratories do not have the ability to perform this blood test
and in the absence of this test the diagnosis must be made based on the clinical presentation of the patient. In this situation a helpful test to diagnose poisoning is the measurement of the osmolal gap
. The patients' serum osmolality is measured by freezing point depression and then compared with the predicted osmolality based on the patients' measured sodium
, glucose
, blood urea nitrogen
, and any ethanol
that may have been ingested. The presence of a large osmolal gap supports a diagnosis of ethylene glycol poisoning. However, a normal osmolar gap does not rule out ethylene glycol exposure because of wide individual variability.
The increased osmolal gap is caused by the ethylene glycol itself. As the metabolism of ethylene glycol progresses there will be less ethylene glycol and this will decrease the blood ethylene glycol concentration and the osmolal gap making this test less useful. Additionally, the presence of other alcohols such as ethanol
, isopropanol, or methanol
or conditions such as alcoholic
or diabetic ketoacidosis
, lactic acidosis
, or kidney failure may also produce an elevated osmolal gap leading to a false diagnosis.
Other laboratory abnormalities may suggest poisoning, especially the presence of a metabolic acidosis, particularly if it is characterized by a large anion gap
. Large anion gap acidosis is usually present during the initial stage of poisoning. However, acidosis has a large number of differential diagnosis
, including poisoning from methanol, salicylates, iron
, isoniazid
, paracetamol
, theophylline
, or from conditions such as uremia
or diabetic and alcoholic ketoacidosis. The diagnosis of ethylene glycol poisoning should be considered in any patient with a severe acidosis. Urine microscopy
can reveal needle or envelope-shaped calcium oxalate crystals in the urine which can suggest poisoning; although these crystals may not be present until the late stages of poisoning. Finally, many commercial radiator antifreeze
products have fluorescein
added to enable radiator leaks to be detected using a Wood's lamp. Following ingestion of antifreeze products containing ethylene glycol and fluorescein, a Wood's lamp may reveal fluorescence of a patient’s mouth area, clothing, vomitus, or urine
which can help to diagnose poisoning.
or nasogastric aspiration of gastric contents are the most common methods employed in ethylene glycol poisoning. The usefulness of gastric lavage has, however, been questioned, and it is now no longer used routinely in poisoning situations. Ipecac
-induced vomiting
is not recommended. As activated charcoal does not adsorb glycols, it is not recommended as it will not be effective at preventing absorption. It is only used in the presence of a toxic dose of another poison or drug. Patients with significant poisoning often present in a critical condition
. In this situation stabilization of the patient including airway management
with intubation should be performed in preference to gastrointestinal decontamination. Patients presenting with metabolic acidosis or seizures require treatment with sodium bicarbonate
and anticonvulsives such as a benzodiazepine
respectively. Sodium bicarbonate should be used cautiously as it can worsen hypocalcemia by increasing the plasma protein binding
of calcium. If hypocalcemia occurs it can be treated with calcium replacement although calcium supplementation can increase the precipitation of calcium oxalate crystals leading to tissue damage. Intubation
and respiratory support may be required in severely intoxicated patients; patients with hypotension
require treatment with intravenous fluids and possibly vasopressors.
s. The antidotes for ethylene glycol poisoning are ethanol
or fomepizole
. This antidotal treatment forms the mainstay of management of ethylene glycol poisoning. The toxicity of ethylene glycol comes from its metabolism to oxalic acid
which causes nephrotoxicity. The goal of pharmacotherapy is to prevent the formation of oxalic acid. Ethanol acts by competing with ethylene glycol for alcohol dehydrogenase, the first enzyme in the degradation pathway. Because ethanol has a much higher affinity for alcohol dehydrogenase, about a 100 times greater affinity, it successfully blocks the breakdown of ethylene glycol into glycoaldehyde which prevents the further degradation to oxalic acid. Without oxalic acid formation, the nephrotoxic effects can be avoided, but the methanol is still present in the body. It is eventually excreted in the urine, but supportive therapy for the CNS depression and metabolic acidosis will be required until the ethylene glycol levels fall below toxic limits. Pharmaceutical grade ethanol is usually given intravenously
as a 5 or 10% solution in 5% dextrose, but it is also sometimes given orally in the form of a strong spirit such as whisky
, vodka
, or gin
.
Fomepizole is a potent inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase; similar to ethanol it acts to block the formation of the toxic metabolites. Fomepizole has been shown to be highly effective as an antidote for ethylene glycol poisoning. It is the only antidote approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of ethylene glycol poisoning. Both antidotes have advantages and disadvantages. Ethanol is readily available in most hospitals, inexpensive, and can be administered orally as well as intravenously. Its adverse effects include intoxication, hypoglycemia
in children, and possible liver
toxicity. Patients receiving ethanol therapy also require frequent blood ethanol level measurements and dosage adjustments to maintain a therapeutic
ethanol concentration. Patients therefore must be monitored in an intensive care unit
. Alternatively, the adverse side effects
of fomepizole are minimal and the approved dosing regimen maintains therapeutic concentrations without the need to monitor blood levels of the drug. The disadvantage of fomepizole is that it is expensive. Costing US$1,000 per gram; an average course used in an adult poisoning would cost approximately $3,500 to $4,000. Despite the cost, fomepizole is gradually replacing ethanol as the antidote of choice in ethylene glycol poisoning. Adjunct agents including thiamine
and pyridoxine
are often given, based on the fact that they may help prevent the formation of oxalic acid. The use of these agents is based on theoretical observations and there is limited evidence to support their use in treatment; they may be of particular benefit in people who could be deficient in these vitamins such as malnourished or alcoholic patients.
. Hemodialysis is used to enhance the removal of unmetabolized ethylene glycol, as well as its metabolites from the body. It has been shown to be highly effective in the removal of ethylene glycol and its metabolites from the blood. Hemodialysis also has the added benefit of correcting other metabolic derangements or supporting deteriorating kidney function. Hemodialysis is usually indicated in patients with severe metabolic acidosis (blood pH
less than 7.3), kidney failure, severe electrolyte imbalance, or if the patients condition is deteriorating despite treatment. Often both antidotal treatment and hemodialysis are used together in the treatment of poisoning. Because hemodialysis will also remove the antidotes from the blood, doses of antidotes need to be increased to compensate. If hemodialysis is not available, then peritoneal dialysis
also removes ethylene glycol, although less efficiently.
who survive may have long term neurologic dysfunction; in some cases they may recover, although convalescence may be prolonged. The most significant long-term complication is related to the kidneys. Cases of permanent kidney damage, often requiring chronic dialysis or kidney transplantation
, have been reported after severe poisoning.
attempts. Less commonly it has been used as a means of homicide
. Children or animals may be exposed by accidental ingestion; children and animals often consume large amounts due to ethylene glycol having a sweet taste. In the United States there were 5816 cases reported to poison centers in 2002. Additionally, ethylene glycol was the most common chemical responsible for deaths reported by US poison centers in 2003. In Australia
there were 17 cases reported to the Victorian
poison center and 30 cases reported to the New South Wales
poison center in 2007. However, these numbers may underestimate actual numbers because not all cases attributable to ethylene glycol are reported to poison control centers. Most deaths from ethylene glycol are intentional suicides; deaths in children due to unintentional ingestion are extremely rare.
In an effort to prevent poisoning, often a bittering agent called denatonium benzoate, known by the trade name
Bitrex, is added to ethylene glycol preparations as an adversant to prevent accidental or intentional ingestion. The bittering agent is thought to stop ingestion as part of the human defense against ingestion of harmful substances is rejection of bitter tasting substances. In the United States, eight states (Oregon
, California
, New Mexico
, Virginia
, Arizona
, Maine
, Tennessee
, Washington) have made the addition of bittering agents to antifreeze compulsory. Three follow up studies targeting limited populations or suicidal persons to assess the efficacy of bittering agents in preventing toxicity or death have, however, shown limited benefit of bittering ethylene glycol preparations in these two populations. Specifically, Mullins finds that bittering of antifreeze does not reduce reported cases of poisoning of preschoolers in the US state of Oregon. Similarly, White found that adding bittering agents did not decrease the frequency or severity of antifreeze poisonings in children under the age of 5. Additionally, another study by White found that suicidal persons are not deterred by the bittered taste of antifreeze in their attempts to kill themselves. These studies did not focus on poisoning of domestic pets or livestock, for example, or inadvertent exposure to bittered antifreeze among a large population (of non-preschool age children).
Ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol is an organic compound widely used as an automotive antifreeze and a precursor to polymers. In its pure form, it is an odorless, colorless, syrupy, sweet-tasting liquid...
(the primary ingredient in both automotive antifreeze
Antifreeze
Antifreeze is a freeze preventive used in internal combustion engines and other heat transfer applications, such as HVAC chillers and solar water heaters....
and hydraulic brake fluid
Brake fluid
Brake fluid is a type of hydraulic fluid used in hydraulic brake and hydraulic clutch applications in automobiles, motorcycles, light trucks, and some bicycles. It is used to transfer force into pressure...
). It is a toxic, colorless, odorless, almost nonvolatile
Volatility (chemistry)
In chemistry and physics, volatility is the tendency of a substance to vaporize. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. At a given temperature, a substance with higher vapor pressure vaporizes more readily than a substance with a lower vapor pressure.The term is primarily...
liquid with a sweet taste and is occasionally consumed by children and dogs for its sweetness. Following ingestion the symptoms of poisoning follow a three step progression starting with intoxication and vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, before causing metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis
In medicine, metabolic acidosis is a condition that occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. If unchecked, metabolic acidosis leads to acidemia, i.e., blood pH is low due to increased production of hydrogen by the body or the...
, cardiovascular dysfunction, and finally acute kidney failure. The major cause of toxicity is not the ethylene glycol itself but its metabolite
Metabolite
Metabolites are the intermediates and products of metabolism. The term metabolite is usually restricted to small molecules. A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal growth, development, and reproduction. Alcohol is an example of a primary metabolite produced in large-scale by industrial...
s. The major metabolites causing toxicity are glycolic acid
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is the smallest α-hydroxy acid . This colorless, odorless, and hygroscopic crystalline solid is highly soluble in water. It is used in various skin-care products. Glycolic acid is found in some sugar-crops...
and oxalic acid
Oxalic acid
Oxalic acid is an organic compound with the formula H2C2O4. This colourless solid is a dicarboxylic acid. In terms of acid strength, it is about 3,000 times stronger than acetic acid. Oxalic acid is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate , is a chelating agent for metal cations...
.
Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis refers both to the process of attempting to determine or identify a possible disease or disorder , and to the opinion reached by this process...
of poisoning is most reliably done by measurement of ethylene glycol in the blood. However many hospital
Hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment by specialized staff and equipment. Hospitals often, but not always, provide for inpatient care or longer-term patient stays....
s do not have the facilities to perform this test and need to rely on abnormalities in the body’s biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
to diagnose poisoning. Diagnosis can also be aided by examining the urine for the presence of calcium oxalate crystals. Treatment consists of initially stabilizing the patient followed by the use of antidotes. The antidotes used are either ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
or fomepizole
Fomepizole
Fomepizole or 4-methylpyrazole is indicated for use as an antidote in confirmed or suspected methanol or ethylene glycol poisoning. It may be used alone or in combination with hemodialysis...
(Antizol). The antidotes work by blocking the enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
responsible for metabolizing ethylene glycol and therefore halt the progression of poisoning. Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis
In medicine, hemodialysis is a method for removing waste products such as creatinine and urea, as well as free water from the blood when the kidneys are in renal failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies .Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy...
is also used to help remove ethylene glycol and its metabolites from the blood. As long as medical treatment is undertaken the prognosis is generally good with most patients making a full recovery. Poisoning is relatively common and due to its taste, children and animals will sometimes consume large quantities of ethylene glycol. Denatonium benzoate, a bittering agent, is added to many antifreeze products to try to prevent ingestion.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of ethylene glycol poisoning usually follow a three-step progression, although poisoned individuals will not always develop each stage.- Stage 1 (0.5 to 12 hours) consists of neurological and gastrointestinal symptoms; people may appear to be intoxicated, exhibiting symptoms such as dizzinessDizzinessDizziness refers to an impairment in spatial perception and stability. The term is somewhat imprecise. It can be used to mean vertigo, presyncope, disequilibrium, or a non-specific feeling such as giddiness or foolishness....
, incoordination of muscle movementsAtaxiaAtaxia is a neurological sign and symptom that consists of gross lack of coordination of muscle movements. Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum...
, nystagmus, headacheHeadacheA headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
s, slurred speech, and confusionConFusionConFusion is an annual science fiction convention organized by the Stilyagi Air Corps and its parent organization, the Ann Arbor Science Fiction Association. Commonly, it is held the third weekend of January. It is the oldest science fiction convention in Michigan, a regional, general SF con...
. Irritation to the stomach may cause nauseaNauseaNausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
and vomitingVomitingVomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
. Over time, the body metabolizesMetabolismMetabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
ethylene glycol into other toxins. - Stage 2 (12 to 36 hours) is a result of accumulation of organic acidOrganic acidAn organic acid is an organic compound with acidic properties. The most common organic acids are the carboxylic acids, whose acidity is associated with their carboxyl group –COOH. Sulfonic acids, containing the group –SO2OH, are relatively stronger acids. The relative stability of the conjugate...
s formed by the metabolism of ethylene glycol and consists of increased heart rateTachycardiaTachycardia comes from the Greek words tachys and kardia . Tachycardia typically refers to a heart rate that exceeds the normal range for a resting heart rate...
, high blood pressureHypertensionHypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
, hyperventilationHyperventilationHyperventilation or overbreathing is the state of breathing faster or deeper than normal, causing excessive expulsion of circulating carbon dioxide. It can result from a psychological state such as a panic attack, from a physiological condition such as metabolic acidosis, can be brought about by...
, and metabolic acidosisMetabolic acidosisIn medicine, metabolic acidosis is a condition that occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. If unchecked, metabolic acidosis leads to acidemia, i.e., blood pH is low due to increased production of hydrogen by the body or the...
. Additionally low calcium levels in the blood, overactive muscle reflexesHyperreflexiaHyperreflexia is defined as overactive or overresponsive reflexes. Examples of this can include twitching or spastic tendencies, which are indicative of upper motor neuron disease as well as the lessening or loss of control ordinarily exerted by higher brain centers of lower neural pathways...
, muscle spasmsSpasmIn medicine a spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, or a similarly sudden contraction of an orifice. It is sometimes accompanied by a sudden burst of pain, but is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes...
, QT intervalQT intervalIn cardiology, the QT interval is a measure of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave in the heart's electrical cycle. In general, the QT interval represents electrical depolarization and repolarization of the left and right ventricles...
prolongation, and congestive heart failureCongestive heart failureHeart failure often called congestive heart failure is generally defined as the inability of the heart to supply sufficient blood flow to meet the needs of the body. Heart failure can cause a number of symptoms including shortness of breath, leg swelling, and exercise intolerance. The condition...
may occur. If untreated, death most commonly occurs during this period. - Stage 3 (24 to 72 hours) kidney failure is the result of ethylene glycol poisoning. Symptoms include acute tubular necrosisAcute tubular necrosisAcute tubular necrosis or is a medical condition involving the death of tubular cells that form the tubule that transports urine to the ureters while reabsorbing 99% of the water . Tubular cells continually replace themselves and if the cause of ATN is removed then recovery is likely...
, red blood cells in the urineHematuriaIn medicine, hematuria, or haematuria, is the presence of red blood cells in the urine. It may be idiopathic and/or benign, or it can be a sign that there is a kidney stone or a tumor in the urinary tract , ranging from trivial to lethal...
, excess proteins in the urineProteinuriaProteinuria means the presence of anexcess of serum proteins in the urine. The protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy, although foamy urine may also be caused by bilirubin in the urine , retrograde ejaculation, pneumaturia due to a fistula, or drugs such as pyridium.- Causes...
, lower back pain, decreased production of urineOliguriaOliguria is the low output of urine, It is clinically classified as an output below 300-500ml/day. The decreased output of urine may be a sign of dehydration, renal failure, hypovolemic shock, HHNS Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, urinary...
, absent production of urineAnuriaAnuria means nonpassage of urine, in practice is defined as passage of less than 50 milliliters of urine in a day. Anuria is often caused by failure in the function of kidneys. It may also occur because of some severe obstruction like kidney stones or tumours. It may occur with end stage renal...
, elevated blood level of potassiumHyperkalemiaHyperkalemia refers to the condition in which the concentration of the electrolyte potassium in the blood is elevated...
, and acute kidney failure. If kidney failure occurs it is typically reversible, although weeks or months of supportive care including hemodialysisHemodialysisIn medicine, hemodialysis is a method for removing waste products such as creatinine and urea, as well as free water from the blood when the kidneys are in renal failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies .Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy...
may be required before kidney functionRenal physiologyRenal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; regulation of fluid balance and blood pressure;...
returns.
Pathophysiology
The three main systems affected by ethylene glycol poisoning are the central nervous systemCentral nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
, metabolic processes, and the kidney
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
s. The central nervous system is affected early in the course of poisoning as the result of a direct action of ethylene glycol. Similar to ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
, it causes intoxication, followed by drowsiness or coma
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
. Seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s may occur due to a direct effect. The toxic mechanism of ethylene glycol poisoning is mainly due to the metabolites of ethylene glycol. Initially it is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenases are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide...
to glycolaldehyde
Glycolaldehyde
Glycolaldehyde is the smallest possible molecule that contains both an aldehyde group and a hydroxyl group. It is the only possible diose, a 2-carbon monosaccharide, although a diose is not strictly a saccharide...
, which is then oxidized to glycolic acid
Glycolic acid
Glycolic acid is the smallest α-hydroxy acid . This colorless, odorless, and hygroscopic crystalline solid is highly soluble in water. It is used in various skin-care products. Glycolic acid is found in some sugar-crops...
. The increase in metabolites may cause encephalopathy
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy means disorder or disease of the brain. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of global brain dysfunction; this syndrome can be caused by many different illnesses.-Terminology:...
or cerebral edema
Cerebral edema
Cerebral edema or cerebral œdema is an excess accumulation of water in the intracellular or extracellular spaces of the brain.-Vasogenic:Due to a breakdown of tight endothelial junctions which make up the blood-brain barrier...
. The metabolic effects occur 12 to 36 hours post ingestion, causing primarily metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis
In medicine, metabolic acidosis is a condition that occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. If unchecked, metabolic acidosis leads to acidemia, i.e., blood pH is low due to increased production of hydrogen by the body or the...
which is due mainly to accumulated glycolic acid. Additionally, as a side effect of the first two steps of metabolism, an increase in the blood concentration of lactic acid
Lactic acid
Lactic acid, also known as milk acid, is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. Lactic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H6O3...
occurs contributing to lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a physiological condition characterized by low pH in body tissues and blood accompanied by the buildup of lactate especially D-lactate, and is considered a distinct form of metabolic acidosis. The condition typically occurs when cells receive too little oxygen , for example...
. The formation of acid metabolites also causes inhibition of other metabolic pathway
Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
s, such as oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
.
The renal toxicity of ethylene glycol occurs 24 to 72 hours post ingestion and is caused by a direct cytotoxic effect of glycolic acid. The glycolic acid is then metabolized to glyoxylic acid
Glyoxylic acid
Glyoxylic acid or oxoacetic acid is an organic compound. Together with acetic acid, glycolic acid, and oxalic acid, glyoxylic acid is one of the C2 carboxylic acids. It is a colourless solid that occurs naturally and is useful industrially....
and finally to oxalic acid
Oxalic acid
Oxalic acid is an organic compound with the formula H2C2O4. This colourless solid is a dicarboxylic acid. In terms of acid strength, it is about 3,000 times stronger than acetic acid. Oxalic acid is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate , is a chelating agent for metal cations...
. Oxalic acid binds with calcium to form calcium oxalate crystals which may deposit and cause damage to many areas of the body including the brain, heart, kidneys, and lungs. The most significant effect is accumulation of calcium oxalate
Calcium oxalate
Calcium oxalate is a chemical compound that forms needle-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. A major constituent of human kidney stones, the chemical is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries...
crystals in the kidneys which causes kidney damage leading to oliguric or anuric
Anuria
Anuria means nonpassage of urine, in practice is defined as passage of less than 50 milliliters of urine in a day. Anuria is often caused by failure in the function of kidneys. It may also occur because of some severe obstruction like kidney stones or tumours. It may occur with end stage renal...
acute kidney failure. The rate-limiting
Rate-determining step
The rate-determining step is a chemistry term for the slowest step in a chemical reaction. The rate-determining step is often compared to the neck of a funnel; the rate at which water flows through the funnel is determined by the width of the neck, not by the speed at which water is poured in. In...
step in this cascade is the conversion of glycolic to glyoxylic acid. Accumulation of glycolic acid in the body is mainly responsible for toxicity.
Toxicity
Ethylene glycol has been shown to be toxic to humans and is also toxic to domestic pets such as cats and dogs. A toxic dose requiring medical treatment varies but is considered more than 0.1 mL per kg body weightBody weight
The term body weight is used in daily English speech as well as in the contexts of biological and medical sciences to describe the mass of an organism's body. Body weight is measured in kilograms throughout the world, although in some countries it is still measured in pounds or stones and pounds...
(mL/kg) of pure substance
Chemical substance
In chemistry, a chemical substance is a form of matter that has constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. It cannot be separated into components by physical separation methods, i.e. without breaking chemical bonds. They can be solids, liquids or gases.Chemical substances are...
. That is roughly 16 mL of 50% ethylene glycol for an 80 kg adult and just 4 mL for a 20 kg child. Poison control center
Poison control center
A poison control center is a medical facility that is able to provide immediate, free, and expert treatment advice and assistance over the telephone in case of exposure to poisonous or hazardous substances...
s often use more than a lick or taste in a child or more than a mouthful in an adult as a dose requiring hospital assessment.
The orally lethal dose
Lethal dose
A lethal dose is an indication of the lethality of a given substance or type of radiation. Because resistance varies from one individual to another, the 'lethal dose' represents a dose at which a given percentage of subjects will die...
in humans has been reported as approximately 1.4 mL/kg of pure ethylene glycol. That is approximately 224 mL of 50% ethylene glycol for an 80 kg adult and just 56 mL for a 20 kg child. Although survival with medical treatment has occurred with doses much higher than this, death has occurred with just 30 mL of the concentrate in an adult. In the EU classification of dangerous substances it is 'harmful' (Xn) while more toxic substances are classified as 'toxic' (T) or 'very toxic' (T+). The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency generally puts substances which are lethal at more than 30 g to adults in Toxicity Class
Toxicity Class
Toxicity Class refers to a classification system for pesticides that has been created by a national or international government-related or -sponsored organization...
III.
Ethylene glycol has a low vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
; it does not evaporate readily at normal temperatures and therefore high concentrations in air or intoxication are unlikely to occur following inhalational exposures. There may be a slight risk of poisoning where mists or fogs are generated, although this rarely leads to poisoning as ethylene glycol causes irritation and coughing when breathed in, alerting victims to its presence. Ethylene glycol is not well absorbed through skin
Human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body. In humans, it is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to that of most other mammals,...
meaning poisoning following dermal exposure is also uncommon.
Diagnosis

Medical sign
A medical sign is an objective indication of some medical fact or characteristic that may be detected by a physician during a physical examination of a patient....
and symptoms of ethylene glycol poisoning are nonspecific and occur in many poisonings the diagnosis is often difficult. It is most reliably diagnosed by the measurement of the blood
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
ethylene glycol concentration. Ethylene glycol in biological fluids can be determined easily by gas chromatography. Many hospital laboratories do not have the ability to perform this blood test
Blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a needle, or via fingerprick....
and in the absence of this test the diagnosis must be made based on the clinical presentation of the patient. In this situation a helpful test to diagnose poisoning is the measurement of the osmolal gap
Osmolal gap
Osmol gap in medical science is the difference between measured serum osmolality and calculated serum osmolarity.- Theory :There are a variety of ions and molecules dissolved in the serum...
. The patients' serum osmolality is measured by freezing point depression and then compared with the predicted osmolality based on the patients' measured sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
, glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
, blood urea nitrogen
Blood urea nitrogen
The blood urea nitrogen test is a measure of the amount of nitrogen in the blood in the form of urea, and a measurement of renal function. Urea is a by- product from metabolism of proteins by the liver and is removed from the blood by the kidneys.-Physiology:The liver produces urea in the urea...
, and any ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
that may have been ingested. The presence of a large osmolal gap supports a diagnosis of ethylene glycol poisoning. However, a normal osmolar gap does not rule out ethylene glycol exposure because of wide individual variability.
The increased osmolal gap is caused by the ethylene glycol itself. As the metabolism of ethylene glycol progresses there will be less ethylene glycol and this will decrease the blood ethylene glycol concentration and the osmolal gap making this test less useful. Additionally, the presence of other alcohols such as ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
, isopropanol, or methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
or conditions such as alcoholic
Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state associated with high concentrations of ketone bodies, formed by the breakdown of fatty acids and the deamination of amino acids. The two common ketones produced in humans are acetoacetic acid and β-hydroxybutyrate....
or diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a potentially life-threatening complication in patients with diabetes mellitus. It happens predominantly in those with type 1 diabetes, but it can occur in those with type 2 diabetes under certain circumstances...
, lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis is a physiological condition characterized by low pH in body tissues and blood accompanied by the buildup of lactate especially D-lactate, and is considered a distinct form of metabolic acidosis. The condition typically occurs when cells receive too little oxygen , for example...
, or kidney failure may also produce an elevated osmolal gap leading to a false diagnosis.
Other laboratory abnormalities may suggest poisoning, especially the presence of a metabolic acidosis, particularly if it is characterized by a large anion gap
Anion gap
The anion gap is the difference in the measured cations and the measured anions in serum, plasma, or urine. The magnitude of this difference in the serum is often calculated in medicine when attempting to identify the cause of metabolic acidosis...
. Large anion gap acidosis is usually present during the initial stage of poisoning. However, acidosis has a large number of differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis is a systematic diagnostic method used to identify the presence of an entity where multiple alternatives are possible , and may also refer to any of the included candidate alternatives A differential diagnosis (sometimes abbreviated DDx, ddx, DD, D/Dx, or ΔΔ) is a...
, including poisoning from methanol, salicylates, iron
Iron poisoning
Iron poisoning is an iron overload caused by a large excess of iron intake and usually refers to an acute overload rather than a gradual one. The terms has been primarily associated with young children who consumed large quantities of iron supplement pills, which resemble sweets and are widely...
, isoniazid
Isoniazid
Isoniazid , also known as isonicotinylhydrazine , is an organic compound that is the first-line antituberculosis medication in prevention and treatment. It was first discovered in 1912, and later in 1951 it was found to be effective against tuberculosis by inhibiting its mycolic acid...
, paracetamol
Paracetamol
Paracetamol INN , or acetaminophen USAN , is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic . It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies...
, theophylline
Theophylline
Theophylline, also known as dimethylxanthine, is a methylxanthine drug used in therapy for respiratory diseases such as COPD and asthma under a variety of brand names. Because of its numerous side-effects, the drug is now rarely administered for clinical use. As a member of the xanthine family, it...
, or from conditions such as uremia
Uremia
Uremia or uraemia is a term used to loosely describe the illness accompanying kidney failure , in particular the nitrogenous waste products associated with the failure of this organ....
or diabetic and alcoholic ketoacidosis. The diagnosis of ethylene glycol poisoning should be considered in any patient with a severe acidosis. Urine microscopy
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view samples and objects that cannot be seen with the unaided eye...
can reveal needle or envelope-shaped calcium oxalate crystals in the urine which can suggest poisoning; although these crystals may not be present until the late stages of poisoning. Finally, many commercial radiator antifreeze
Antifreeze
Antifreeze is a freeze preventive used in internal combustion engines and other heat transfer applications, such as HVAC chillers and solar water heaters....
products have fluorescein
Fluorescein
Fluorescein is a synthetic organic compound available as a dark orange/red powder soluble in water and alcohol. It is widely used as a fluorescent tracer for many applications....
added to enable radiator leaks to be detected using a Wood's lamp. Following ingestion of antifreeze products containing ethylene glycol and fluorescein, a Wood's lamp may reveal fluorescence of a patient’s mouth area, clothing, vomitus, or urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
which can help to diagnose poisoning.
Stabilization and decontamination
The most important initial treatment for ethylene glycol poisoning is stabilizing the patient. As ethylene glycol is rapidly absorbed, gastric decontamination is unlikely to be of benefit unless it is performed within 60 minutes of ingestion. Traditionally, gastric lavageGastric lavage
Gastric lavage, also commonly called stomach pumping or Gastric irrigation, is the process of cleaning out the contents of the stomach. It has been used for over 200 years as a means of eliminating poisons from the stomach. Such devices are normally used on a person who has ingested a poison or...
or nasogastric aspiration of gastric contents are the most common methods employed in ethylene glycol poisoning. The usefulness of gastric lavage has, however, been questioned, and it is now no longer used routinely in poisoning situations. Ipecac
Syrup of ipecac
Syrup of ipecac , commonly referred to as ipecac, is derived from the dried rhizome and roots of the ipecacuanha plant, and is a well known emetic .-Preparation:...
-induced vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
is not recommended. As activated charcoal does not adsorb glycols, it is not recommended as it will not be effective at preventing absorption. It is only used in the presence of a toxic dose of another poison or drug. Patients with significant poisoning often present in a critical condition
Medical state
Medical states or medical conditions are used to describe a patient's condition in a hospital. These terms are most commonly used by the news media and are rarely used by doctors, who in their daily business prefer to deal with medical problems in greater detail.Either or both of two aspects of...
. In this situation stabilization of the patient including airway management
Airway management
In cardiopulmonary resuscitation, anaesthesia, emergency medicine, intensive care medicine and first aid, airway management is the process of ensuring that:# there is an open pathway between a patient’s lungs and the outside world, and...
with intubation should be performed in preference to gastrointestinal decontamination. Patients presenting with metabolic acidosis or seizures require treatment with sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate is the chemical compound with the formula Na HCO3. Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda . The natural mineral form is...
and anticonvulsives such as a benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepine
A benzodiazepine is a psychoactive drug whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring...
respectively. Sodium bicarbonate should be used cautiously as it can worsen hypocalcemia by increasing the plasma protein binding
Plasma protein binding
A drug's efficiency may be affected by the degree to which it binds to the proteins within blood plasma. The less bound a drug is, the more efficiently it can traverse cell membranes or diffuse. Common blood proteins that drugs bind to are human serum albumin, lipoprotein, glycoprotein, α, β‚ and γ...
of calcium. If hypocalcemia occurs it can be treated with calcium replacement although calcium supplementation can increase the precipitation of calcium oxalate crystals leading to tissue damage. Intubation
Intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic or rubber tube into the trachea to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs...
and respiratory support may be required in severely intoxicated patients; patients with hypotension
Hypotension
In physiology and medicine, hypotension is abnormally low blood pressure, especially in the arteries of the systemic circulation. It is best understood as a physiologic state, rather than a disease. It is often associated with shock, though not necessarily indicative of it. Hypotension is the...
require treatment with intravenous fluids and possibly vasopressors.
Antidotes
Following decontamination and the institution of supportive measures, the next priority is inhibition of further ethylene glycol metabolism using antidoteAntidote
An antidote is a substance which can counteract a form of poisoning. The term ultimately derives from the Greek αντιδιδοναι antididonai, "given against"....
s. The antidotes for ethylene glycol poisoning are ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
or fomepizole
Fomepizole
Fomepizole or 4-methylpyrazole is indicated for use as an antidote in confirmed or suspected methanol or ethylene glycol poisoning. It may be used alone or in combination with hemodialysis...
. This antidotal treatment forms the mainstay of management of ethylene glycol poisoning. The toxicity of ethylene glycol comes from its metabolism to oxalic acid
Oxalic acid
Oxalic acid is an organic compound with the formula H2C2O4. This colourless solid is a dicarboxylic acid. In terms of acid strength, it is about 3,000 times stronger than acetic acid. Oxalic acid is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate , is a chelating agent for metal cations...
which causes nephrotoxicity. The goal of pharmacotherapy is to prevent the formation of oxalic acid. Ethanol acts by competing with ethylene glycol for alcohol dehydrogenase, the first enzyme in the degradation pathway. Because ethanol has a much higher affinity for alcohol dehydrogenase, about a 100 times greater affinity, it successfully blocks the breakdown of ethylene glycol into glycoaldehyde which prevents the further degradation to oxalic acid. Without oxalic acid formation, the nephrotoxic effects can be avoided, but the methanol is still present in the body. It is eventually excreted in the urine, but supportive therapy for the CNS depression and metabolic acidosis will be required until the ethylene glycol levels fall below toxic limits. Pharmaceutical grade ethanol is usually given intravenously
Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. The word intravenous simply means "within a vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals...
as a 5 or 10% solution in 5% dextrose, but it is also sometimes given orally in the form of a strong spirit such as whisky
Whisky
Whisky or whiskey is a type of distilled alcoholic beverage made from fermented grain mash. Different grains are used for different varieties, including barley, malted barley, rye, malted rye, wheat, and corn...
, vodka
Vodka
Vodka , is a distilled beverage. It is composed primarily of water and ethanol with traces of impurities and flavorings. Vodka is made by the distillation of fermented substances such as grains, potatoes, or sometimes fruits....
, or gin
Gin
Gin is a spirit which derives its predominant flavour from juniper berries . Although several different styles of gin have existed since its origins, it is broadly differentiated into two basic legal categories...
.
Fomepizole is a potent inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase; similar to ethanol it acts to block the formation of the toxic metabolites. Fomepizole has been shown to be highly effective as an antidote for ethylene glycol poisoning. It is the only antidote approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of ethylene glycol poisoning. Both antidotes have advantages and disadvantages. Ethanol is readily available in most hospitals, inexpensive, and can be administered orally as well as intravenously. Its adverse effects include intoxication, hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia or hypoglycæmia is the medical term for a state produced by a lower than normal level of blood glucose. The term literally means "under-sweet blood"...
in children, and possible liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
toxicity. Patients receiving ethanol therapy also require frequent blood ethanol level measurements and dosage adjustments to maintain a therapeutic
Therapeutic index
The therapeutic index is a comparison of the amount of a therapeutic agent that causes the therapeutic effect to the amount that causes death or toxicity ....
ethanol concentration. Patients therefore must be monitored in an intensive care unit
Intensive Care Unit
thumb|220px|ICU roomAn intensive-care unit , critical-care unit , intensive-therapy unit/intensive-treatment unit is a specialized department in a hospital that provides intensive-care medicine...
. Alternatively, the adverse side effects
Adverse effect
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
of fomepizole are minimal and the approved dosing regimen maintains therapeutic concentrations without the need to monitor blood levels of the drug. The disadvantage of fomepizole is that it is expensive. Costing US$1,000 per gram; an average course used in an adult poisoning would cost approximately $3,500 to $4,000. Despite the cost, fomepizole is gradually replacing ethanol as the antidote of choice in ethylene glycol poisoning. Adjunct agents including thiamine
Thiamine
Thiamine or thiamin or vitamin B1 , named as the "thio-vitamine" is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex. First named aneurin for the detrimental neurological effects if not present in the diet, it was eventually assigned the generic descriptor name vitamin B1. Its phosphate derivatives are...
and pyridoxine
Pyridoxine
Pyridoxine is one of the compounds that can be called vitamin B6, along with pyridoxal and pyridoxamine. It differs from pyridoxamine by the substituent at the '4' position. It is often used as 'pyridoxine hydrochloride'.-Chemistry:...
are often given, based on the fact that they may help prevent the formation of oxalic acid. The use of these agents is based on theoretical observations and there is limited evidence to support their use in treatment; they may be of particular benefit in people who could be deficient in these vitamins such as malnourished or alcoholic patients.
Hemodialysis
In addition to antidotes, an important treatment for poisoning is the use of hemodialysisHemodialysis
In medicine, hemodialysis is a method for removing waste products such as creatinine and urea, as well as free water from the blood when the kidneys are in renal failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies .Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy...
. Hemodialysis is used to enhance the removal of unmetabolized ethylene glycol, as well as its metabolites from the body. It has been shown to be highly effective in the removal of ethylene glycol and its metabolites from the blood. Hemodialysis also has the added benefit of correcting other metabolic derangements or supporting deteriorating kidney function. Hemodialysis is usually indicated in patients with severe metabolic acidosis (blood pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
less than 7.3), kidney failure, severe electrolyte imbalance, or if the patients condition is deteriorating despite treatment. Often both antidotal treatment and hemodialysis are used together in the treatment of poisoning. Because hemodialysis will also remove the antidotes from the blood, doses of antidotes need to be increased to compensate. If hemodialysis is not available, then peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis is a treatment for patients with severe chronic kidney disease. The process uses the patient's peritoneum in the abdomen as a membrane across which fluids and dissolved substances are exchanged from the blood...
also removes ethylene glycol, although less efficiently.
Prognosis
Generally if the patient is treated and survives then a full recovery is expected. Patients who present early to medical facilities and have prompt medical treatment typically will have a favorable outcome. Alternatively, patients presenting late with signs and symptoms of coma, hyperkalemia, seizures, or severe acidosis have a poor prognosis. Patients who develop severe central nervous system manifestations or strokeStroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
who survive may have long term neurologic dysfunction; in some cases they may recover, although convalescence may be prolonged. The most significant long-term complication is related to the kidneys. Cases of permanent kidney damage, often requiring chronic dialysis or kidney transplantation
Kidney transplantation
Kidney transplantation or renal transplantation is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage renal disease. Kidney transplantation is typically classified as deceased-donor or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ...
, have been reported after severe poisoning.
Epidemiology
Ethylene glycol poisoning is a relatively common occurrence worldwide. Human poisoning often occurs in isolated cases, but may also occur in epidemics. Many cases of poisoning are the result of using ethylene glycol as a cheap substitute for alcohol or intentional ingestions in suicideSuicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Suicide is often committed out of despair or attributed to some underlying mental disorder, such as depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, alcoholism, or drug abuse...
attempts. Less commonly it has been used as a means of homicide
Homicide
Homicide refers to the act of a human killing another human. Murder, for example, is a type of homicide. It can also describe a person who has committed such an act, though this use is rare in modern English...
. Children or animals may be exposed by accidental ingestion; children and animals often consume large amounts due to ethylene glycol having a sweet taste. In the United States there were 5816 cases reported to poison centers in 2002. Additionally, ethylene glycol was the most common chemical responsible for deaths reported by US poison centers in 2003. In Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
there were 17 cases reported to the Victorian
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
poison center and 30 cases reported to the New South Wales
New South Wales
New South Wales is a state of :Australia, located in the east of the country. It is bordered by Queensland, Victoria and South Australia to the north, south and west respectively. To the east, the state is bordered by the Tasman Sea, which forms part of the Pacific Ocean. New South Wales...
poison center in 2007. However, these numbers may underestimate actual numbers because not all cases attributable to ethylene glycol are reported to poison control centers. Most deaths from ethylene glycol are intentional suicides; deaths in children due to unintentional ingestion are extremely rare.
In an effort to prevent poisoning, often a bittering agent called denatonium benzoate, known by the trade name
Trade name
A trade name, also known as a trading name or a business name, is the name which a business trades under for commercial purposes, although its registered, legal name, used for contracts and other formal situations, may be another....
Bitrex, is added to ethylene glycol preparations as an adversant to prevent accidental or intentional ingestion. The bittering agent is thought to stop ingestion as part of the human defense against ingestion of harmful substances is rejection of bitter tasting substances. In the United States, eight states (Oregon
Oregon
Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern...
, California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
, Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
, Arizona
Arizona
Arizona ; is a state located in the southwestern region of the United States. It is also part of the western United States and the mountain west. The capital and largest city is Phoenix...
, Maine
Maine
Maine is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and south, New Hampshire to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the northwest and New Brunswick to the northeast. Maine is both the northernmost and easternmost...
, Tennessee
Tennessee
Tennessee is a U.S. state located in the Southeastern United States. It has a population of 6,346,105, making it the nation's 17th-largest state by population, and covers , making it the 36th-largest by total land area...
, Washington) have made the addition of bittering agents to antifreeze compulsory. Three follow up studies targeting limited populations or suicidal persons to assess the efficacy of bittering agents in preventing toxicity or death have, however, shown limited benefit of bittering ethylene glycol preparations in these two populations. Specifically, Mullins finds that bittering of antifreeze does not reduce reported cases of poisoning of preschoolers in the US state of Oregon. Similarly, White found that adding bittering agents did not decrease the frequency or severity of antifreeze poisonings in children under the age of 5. Additionally, another study by White found that suicidal persons are not deterred by the bittered taste of antifreeze in their attempts to kill themselves. These studies did not focus on poisoning of domestic pets or livestock, for example, or inadvertent exposure to bittered antifreeze among a large population (of non-preschool age children).

