
Energy production in Japan
Encyclopedia
Japan
lacks significant domestic sources of fossil energy except coal
and must import substantial amounts of crude oil, natural gas
, and other energy resources, including uranium
. In 1990 Japan's dependence on import
s for primary energy
stood at more than 85%, and the country had a total energy requirement of 428.2 million tons of petroleum equivalent.
doubled the nation's energy consumption every five years into the 1990s. During the 1960–72 period of accelerated growth, energy consumption grew much faster than GNP, doubling Japan's consumption of world energy. By 1976, with only 3% of the world's population, Japan was consuming 6% of global energy supplies.
In 1990, consumption totaled 298 million tons: 46.7% of which was used by industry; 23.3% by the transportation sector; 26.6% for agricultural, residential, services, and other uses; and 3.3% for non-energy uses, such as lubricating oil or asphalt
. (source?)
Compared with other nations, electricity in Japan is relatively expensive.
ranked third in the world in electricity production, after the United States
and China
, with 1.025×1012 kWh produced during that year.
In terms of per capita electricity consumption, the average person in Japan consumed 8,459 Kilowatt-Hours in 2004 compared to 14,240 for the average American. In that respect it ranked 18th among the countries of the world. Its per capita electricity consumption increased by 21.8% between 1990 and 2004.
With 53 active nuclear power generating reactor units in 2009, Japan ranked third in the world in that respect, after the United States (104 reactors) and France (59). Almost one quarter (24.93%) of its electricity production was from nuclear plants, compared to 76.18% for France
and 19.66% for the United States.
In 1989 Japan was the world's third largest producer of electricity. About 75% of the available power was controlled by the ten major regional power utilities, of which Tokyo Electric Power Company was the world's largest. Electricity rates in Japan were among the world's highest.
like most other industrial countries have, but has separate eastern and western grids. The standard voltage at power outlets is 100 V, but the grids operate at different frequencies: 50 Hz in Eastern Japan and 60 Hz in Western Japan. The grids are connected together by 3 frequency converter stations
(Higashi-Shimizu, Shin Shinano and Sakuma), but these can only handle 1 GW. The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
resulted in 11 reactors being taken offline with a loss of 9.7GW. The 3 converter stations did not have the capacity to transfer enough power from Japan's western power grid to significantly help the eastern grid.
The two grids were originally developed by separate companies. Tokyo Electric Light Co was established in 1883 which also established electric power in Japan
. In 1885 demand had grown enough that TELCO bought generation equipment from AEG
of Germany
. The same happened in the western parts of Japan with General Electric
being the supplier to Osaka Electric Lamp. GE's equipment used the US standard 60Hz while AEG's equipment used the European standard of 50Hz.
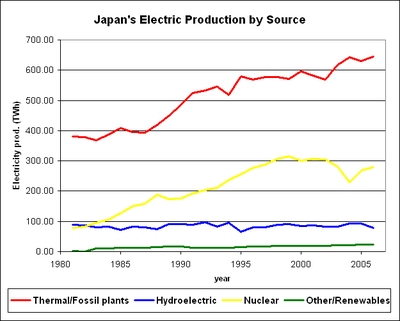
In 1950 coal supplied half of Japan's energy needs, hydroelectricity
one-third, and oil the rest. In 1988 oil provided Japan with 57.3% of energy needs, coal 18.1%, natural gas 10.1%, nuclear power
9.0%, hydroelectic power 4.6%, geothermal power
0.1%, and 1.3% came from other sources. By 2001 the contribution of oil had declined to 50.2% of the total, with rises in the use of nuclear power and natural gas.
and 1979
), Japan made efforts to diversify to other forms of energy resources in order to increase energy security
. Japan's domestic oil consumption dropped slightly, from around 5.1 Moilbbl of oil per day in the late 1970s to 4.9 Moilbbl per day in 1990. While the country's use of oil declined, its consumption of nuclear power and LNG rose substantially. Several Japanese industries, including electric power companies and steelmakers
, switched from petroleum
to coal, most of which is imported.
The state stockpile equals about 92 days of consumption and the privately held stockpiles equal another 77 days of consumption for a total of 169 days or 579 Moilbbl. The Japanese SPR is run by the Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corporation.
(51.3%), Malaysia (20.4%), Brunei
(17.8%), United Arab Emirates
(7.3%), and the United States
(3.2%).
, France
, South Africa
, and Australia
. By 1991 the country had 42 nuclear reactor
s in operation, with a total generating capacity of approximately 33 gigawatts. The ratio of nuclear power generation to total electricity production increased from 2% in 1973 to 23.6% in 1990.
During the 1980s, Japan's nuclear power program was strongly opposed by environmental groups, particularly after the Three Mile Island accident
in the United States. Other problems for the program were the rising costs of nuclear reactors and fuel, the huge investments necessary for fuel enrichment
and reprocessing plants, reactor failures
, and nuclear waste disposal
. Nevertheless, Japan continued to build nuclear power plants. After the 2011 earthquake and tsunami some nuclear reactors were damaged, causing much uncertainty and fear about the release of radioactive material, as well as highlighting the ongoing concerns over Japanese nuclear seismic design standards.
. The country had six geothermal power stations with a combined capacity of 133 megawatts in 1989. By 2011, the country had 18 geothermal plants.
In addition, although it only makes a minor contribution to the total, Japan was the world's second largest producer of photovoltaic electricity
until overtaken by Germany in 2005, a year in which it had 38% of the world supply compared to Germany's 39%.
As of September 2011, Japan had 1,807 wind turbines generating 2440 MW of power. A lack of locations with constant wind, environmental restrictions, and emphasis by power utilities on fossil and nuclear power hinders the employment of more wind power in Japan.
As of September 2011, Japan had 1,198 small hydropower plants producing 3,225 MW of power. The smaller plants accounted ro 6.6 percent of Japan's total hydropower capacity. The remaining capacity was filled by large and medium hydropower stations, typically sited at large dams. Cost per killowat-hour for power from smaller plants was high at ¥15-100, hindering further development of the energy source.
As of September 2011, Japan had 190 generators attached to municipal waste units and 70 independent plants using biomass
fuel to produce energy. In addition, 14 other generators were used to burn both coal and biomass fuel. In 2008, Japan produced 322 million tons of biomass fuel and converted 76% of it into energy.
In 2003 Japan was the 5th largest producer of carbon emissions, generating 5% of the world total. In 2003 Japan ranked 36 in the list of countries by carbon dioxide emissions per capita.
Reports indicate Japan is having difficulty in meeting its 6% reduction target under the Kyoto Protocol
in part because Japanese businesses are already very energy efficient. Despite this, former Prime Minister Shinzo Abe
has called for a 50% cut in world emissions by 2050, and expects Japan to play a leading role in such an effort.
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
lacks significant domestic sources of fossil energy except coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
and must import substantial amounts of crude oil, natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, and other energy resources, including uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
. In 1990 Japan's dependence on import
Import
The term import is derived from the conceptual meaning as to bring in the goods and services into the port of a country. The buyer of such goods and services is referred to an "importer" who is based in the country of import whereas the overseas based seller is referred to as an "exporter". Thus...
s for primary energy
Primary energy
Primary energy is an energy form found in nature that has not been subjected to any conversion or transformation process. It is energy contained in raw fuels, and other forms of energy received as input to a system...
stood at more than 85%, and the country had a total energy requirement of 428.2 million tons of petroleum equivalent.
Overview
| Energy in Japan | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capita | Prim. energy | Production | Import | Electricity | CO2-emission | |
| Million | TWh | TWh | TWh | TWh | Mt | |
| 2004 | 127.7 | 6,201 | 1,125 | 5,126 | 1,031 | 1,215 |
| 2007 | 127.8 | 5,972 | 1,052 | 5,055 | 1,083 | 1,236 |
| 2008 | 127.7 | 5,767 | 1,031 | 4,872 | 1,031 | 1,151 |
| 2009 | 127.3 | 5,489 | 1,091 | 4,471 | 997 | 1,093 |
| Change 2004-2009 | 0 % | -11.5 % | -3.1 % | -12.8 % | -3.3 % | -10.1 % |
| Mtoe = 11.63 TWh, Prim. energy includes energy losses that are 2/3 for nuclear power | ||||||
Energy use
Japan's rapid industrial growth since the end of World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
doubled the nation's energy consumption every five years into the 1990s. During the 1960–72 period of accelerated growth, energy consumption grew much faster than GNP, doubling Japan's consumption of world energy. By 1976, with only 3% of the world's population, Japan was consuming 6% of global energy supplies.
In 1990, consumption totaled 298 million tons: 46.7% of which was used by industry; 23.3% by the transportation sector; 26.6% for agricultural, residential, services, and other uses; and 3.3% for non-energy uses, such as lubricating oil or asphalt
Asphalt
Asphalt or , also known as bitumen, is a sticky, black and highly viscous liquid or semi-solid that is present in most crude petroleums and in some natural deposits, it is a substance classed as a pitch...
. (source?)
Compared with other nations, electricity in Japan is relatively expensive.
Electricity generation
In 2008, JapanJapan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
ranked third in the world in electricity production, after the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, with 1.025×1012 kWh produced during that year.
In terms of per capita electricity consumption, the average person in Japan consumed 8,459 Kilowatt-Hours in 2004 compared to 14,240 for the average American. In that respect it ranked 18th among the countries of the world. Its per capita electricity consumption increased by 21.8% between 1990 and 2004.
With 53 active nuclear power generating reactor units in 2009, Japan ranked third in the world in that respect, after the United States (104 reactors) and France (59). Almost one quarter (24.93%) of its electricity production was from nuclear plants, compared to 76.18% for France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and 19.66% for the United States.
In 1989 Japan was the world's third largest producer of electricity. About 75% of the available power was controlled by the ten major regional power utilities, of which Tokyo Electric Power Company was the world's largest. Electricity rates in Japan were among the world's highest.
Electrical power supply
Japan doesn't have a single national gridNational Grid
-Electric power transmission systems:*National Grid , the electricity transmission network of Great Britain.*National Grid , the electricity transmission network of Malaysia....
like most other industrial countries have, but has separate eastern and western grids. The standard voltage at power outlets is 100 V, but the grids operate at different frequencies: 50 Hz in Eastern Japan and 60 Hz in Western Japan. The grids are connected together by 3 frequency converter stations
Frequency changer
A frequency changer or frequency converter is an electronic device that converts alternating current of one frequency to alternating current of another frequency. The device may also change the voltage, but if it does, that is incidental to its principal purpose.Traditionally, these devices were...
(Higashi-Shimizu, Shin Shinano and Sakuma), but these can only handle 1 GW. The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
The 2011 earthquake off the Pacific coast of Tohoku, also known as the 2011 Tohoku earthquake, or the Great East Japan Earthquake, was a magnitude 9.0 undersea megathrust earthquake off the coast of Japan that occurred at 14:46 JST on Friday, 11 March 2011, with the epicenter approximately east...
resulted in 11 reactors being taken offline with a loss of 9.7GW. The 3 converter stations did not have the capacity to transfer enough power from Japan's western power grid to significantly help the eastern grid.
The two grids were originally developed by separate companies. Tokyo Electric Light Co was established in 1883 which also established electric power in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. In 1885 demand had grown enough that TELCO bought generation equipment from AEG
AEG
Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft was a German producer of electrical equipment founded in 1883 by Emil Rathenau....
of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. The same happened in the western parts of Japan with General Electric
General Electric
General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States...
being the supplier to Osaka Electric Lamp. GE's equipment used the US standard 60Hz while AEG's equipment used the European standard of 50Hz.
Utilities
In Japan, the electricity market is divided up into 10 regulated companies:- Chugoku Electric Power CompanyChugoku Electric Power Companyis an electric utility with its exclusive operational area of Chūgoku region of Japan. It is the sixth largest by electricity sales among Japan’s ten regional power utilities...
(CEPCO) - Chubu Electric Power (Chuden)
- Hokuriku Electric Power CompanyHokuriku Electric Power CompanyThe Hokuriku Electric Power Company supplies power by a regulated monopoly to the Toyama Prefecture, Ishikawa Prefecture, the northern part of Fukui Prefecture, and northwestern parts of Gifu Prefecture...
(HEPCO) - Hokkaido Electric Power CompanyHokkaido Electric Power CompanyThe , or for short, is the monopoly electric company of Hokkaidō, Japan. It is also known as Hokuden, Dōden, and HEPCO. The company is traded on the Tokyo Stock Exchange , Osaka Securities Exchange , and Sapporo Securities Exchange....
(Hokuden) - Kyushu Electric Power (Kyuden)
- Kansai Electric Power CompanyKansai Electric Power Company, also known as , is an electric utility with its operational area of Kansai region, Japan . The company is regarded as one of the leading companies in Kansai, as well as a leader of the Japanese electric power industry....
(KEPCO) - Okinawa Electric Power CompanyOkinawa Electric Power Company, OEPC or for short, is an electric utility with its exclusive operational area of Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. It is the smallest by electricity sales among Japan’s ten regional power utilities, indeed, its electricity sales is approximately 1⁄40 of that of The Tokyo Electric Power Company, though...
(Okiden) - The Tokyo Electric Power CompanyThe Tokyo Electric Power Company, also known as or TEPCO, is an electric utility servicing Japan's Kantō region, Yamanashi Prefecture, and the eastern portion of Shizuoka Prefecture. This area includes Tokyo...
(TEPCO) - Tohoku Electric Power (Tohokuden)
- Shikoku Electric Power CompanyShikoku Electric Power CompanyThe is the electric provider for the 4 prefectures of the Shikoku island in Japan with few exceptions. Their image character is .On April 12, 1991 the company instituted Akari-chan as their image character and at the same time introduced the romanized nickname of Yonden .The company is also an...
(Yonden)
Energy supply

In 1950 coal supplied half of Japan's energy needs, hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy...
one-third, and oil the rest. In 1988 oil provided Japan with 57.3% of energy needs, coal 18.1%, natural gas 10.1%, nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
9.0%, hydroelectic power 4.6%, geothermal power
Geothermal power
Geothermal energy is thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. Earth's geothermal energy originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of minerals...
0.1%, and 1.3% came from other sources. By 2001 the contribution of oil had declined to 50.2% of the total, with rises in the use of nuclear power and natural gas.
| Japan—primary energy use | |||
| Fuel | 1950 | 1988 | 2001 |
| Coal | 50% | 18.1% | 16.8% |
| Hydro | 33% | 4.6% | 4.0% |
| Oil | 17% | 57.3% | 50.2% |
| Natural gas | - | 10.1% | 13.6% |
| Nuclear | - | 9.0% | 14.4% |
| Other | - | 1.3% | 1.0% |
Petroleum and diversification
In accordance with the two oil crises of the 1970s (19731973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis started in October 1973, when the members of Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries or the OAPEC proclaimed an oil embargo. This was "in response to the U.S. decision to re-supply the Israeli military" during the Yom Kippur war. It lasted until March 1974. With the...
and 1979
1979 energy crisis
The 1979 oil crisis in the United States occurred in the wake of the Iranian Revolution. Amid massive protests, the Shah of Iran, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, fled his country in early 1979 and the Ayatollah Khomeini soon became the new leader of Iran. Protests severely disrupted the Iranian oil...
), Japan made efforts to diversify to other forms of energy resources in order to increase energy security
Energy security
Energy security is a term for an association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led...
. Japan's domestic oil consumption dropped slightly, from around 5.1 Moilbbl of oil per day in the late 1970s to 4.9 Moilbbl per day in 1990. While the country's use of oil declined, its consumption of nuclear power and LNG rose substantially. Several Japanese industries, including electric power companies and steelmakers
Steelmaking
Steelmaking is the second step in producing steel from iron ore. In this stage, impurities such as sulfur, phosphorus, and excess carbon are removed from the raw iron, and alloying elements such as manganese, nickel, chromium and vanadium are added to produce the exact steel required.-Older...
, switched from petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
to coal, most of which is imported.
The state stockpile equals about 92 days of consumption and the privately held stockpiles equal another 77 days of consumption for a total of 169 days or 579 Moilbbl. The Japanese SPR is run by the Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corporation.
Natural gas
Because domestic natural gas production is minimal, rising demand is met by greater imports. Japan's main LNG suppliers in 1987 were IndonesiaIndonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
(51.3%), Malaysia (20.4%), Brunei
Brunei
Brunei , officially the State of Brunei Darussalam or the Nation of Brunei, the Abode of Peace , is a sovereign state located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, in Southeast Asia...
(17.8%), United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates, abbreviated as the UAE, or shortened to "the Emirates", is a state situated in the southeast of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia on the Persian Gulf, bordering Oman, and Saudi Arabia, and sharing sea borders with Iraq, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, and Iran.The UAE is a...
(7.3%), and the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
(3.2%).
Nuclear power
The Japanese were working to increase the availability of nuclear power in 1985. Although Japan was a late starter in this field, it finally imported technology from the United States and obtained uranium from CanadaCanada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, and Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
. By 1991 the country had 42 nuclear reactor
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
s in operation, with a total generating capacity of approximately 33 gigawatts. The ratio of nuclear power generation to total electricity production increased from 2% in 1973 to 23.6% in 1990.
During the 1980s, Japan's nuclear power program was strongly opposed by environmental groups, particularly after the Three Mile Island accident
Three Mile Island accident
The Three Mile Island accident was a core meltdown in Unit 2 of the Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station in Dauphin County, Pennsylvania near Harrisburg, United States in 1979....
in the United States. Other problems for the program were the rising costs of nuclear reactors and fuel, the huge investments necessary for fuel enrichment
Enriched uranium
Enriched uranium is a kind of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Natural uranium is 99.284% 238U isotope, with 235U only constituting about 0.711% of its weight...
and reprocessing plants, reactor failures
Nuclear and radiation accidents
A nuclear and radiation accident is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency as "an event that has led to significant consequences to people, the environment or the facility...
, and nuclear waste disposal
Radioactive waste
Radioactive wastes are wastes that contain radioactive material. Radioactive wastes are usually by-products of nuclear power generation and other applications of nuclear fission or nuclear technology, such as research and medicine...
. Nevertheless, Japan continued to build nuclear power plants. After the 2011 earthquake and tsunami some nuclear reactors were damaged, causing much uncertainty and fear about the release of radioactive material, as well as highlighting the ongoing concerns over Japanese nuclear seismic design standards.
Renewable energy
Of alternative energy sources, Japan has partially exploited geothermal energyGeothermal power
Geothermal energy is thermal energy generated and stored in the Earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. Earth's geothermal energy originates from the original formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of minerals...
. The country had six geothermal power stations with a combined capacity of 133 megawatts in 1989. By 2011, the country had 18 geothermal plants.
In addition, although it only makes a minor contribution to the total, Japan was the world's second largest producer of photovoltaic electricity
Photovoltaics
Photovoltaics is a method of generating electrical power by converting solar radiation into direct current electricity using semiconductors that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. Photovoltaic power generation employs solar panels composed of a number of solar cells containing a photovoltaic material...
until overtaken by Germany in 2005, a year in which it had 38% of the world supply compared to Germany's 39%.
As of September 2011, Japan had 1,807 wind turbines generating 2440 MW of power. A lack of locations with constant wind, environmental restrictions, and emphasis by power utilities on fossil and nuclear power hinders the employment of more wind power in Japan.
As of September 2011, Japan had 1,198 small hydropower plants producing 3,225 MW of power. The smaller plants accounted ro 6.6 percent of Japan's total hydropower capacity. The remaining capacity was filled by large and medium hydropower stations, typically sited at large dams. Cost per killowat-hour for power from smaller plants was high at ¥15-100, hindering further development of the energy source.
As of September 2011, Japan had 190 generators attached to municipal waste units and 70 independent plants using biomass
Biomass
Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel....
fuel to produce energy. In addition, 14 other generators were used to burn both coal and biomass fuel. In 2008, Japan produced 322 million tons of biomass fuel and converted 76% of it into energy.
Carbon emissions


In 2003 Japan was the 5th largest producer of carbon emissions, generating 5% of the world total. In 2003 Japan ranked 36 in the list of countries by carbon dioxide emissions per capita.
Reports indicate Japan is having difficulty in meeting its 6% reduction target under the Kyoto Protocol
Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol is a protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change , aimed at fighting global warming...
in part because Japanese businesses are already very energy efficient. Despite this, former Prime Minister Shinzo Abe
Shinzo Abe
was the 90th Prime Minister of Japan, elected by a special session of the National Diet on 26 September 2006. He was Japan's youngest post–World War II prime minister and the first born after the war. Abe served as prime minister for nearly twelve months, before resigning on 12 September 2007...
has called for a 50% cut in world emissions by 2050, and expects Japan to play a leading role in such an effort.
| Carbon dioxide emissions (thousands of metric tons Tonne The tonne, known as the metric ton in the US , often put pleonastically as "metric tonne" to avoid confusion with ton, is a metric system unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. The tonne is not an International System of Units unit, but is accepted for use with the SI... of CO2) |
||
| Year | CO2 | Change |
| 1990 | 1,072,420 | 0% |
| 1991 | 1,094,350 | 2.04% |
| 1992 | 1,106,500 | 3.18% |
| 1993 | 1,081,490 | 0.85% |
| 1994 | 1,132,560 | 5.61% |
| 1995 | 1,138,750 | 9.19% |
| 1996 | 1,169,550 | 9.06% |
| 1997 | 1,170,120 | 9.11% |
| 1998 | 1,130,600 | 5.43% |
| 1999 | 1,165,720 | 8.7% |
| 2000 | 1,207,980 | 12.64% |
| 2001 | 1,191,390 | 11.09% |
| 2002 | 1,205,480 | 12.41% |
| 2003 | 1,233,640 | 15.03% |
See also
- EnergyEnergyIn physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
- Energy Law - Japan
- Japan Electric AssociationJapan Electric AssociationThe is a membership organisation for the electricity sector in Japan and, although it has roots dating back to 1892, was founded in October 1921...
- Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National CorporationJapan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corporation, also known as JOGMEC, is a Japanese government Independent Administrative Institution which was created in 2004 when the former Japan National Oil Corporation merged with the former Metal Mining Agency of Japan.-History:...
- Nuclear power in JapanNuclear power in JapanNuclear energy was a national strategic priority in Japan, but there has been concern about the ability of Japan's nuclear plants to withstand seismic activity...
- World energy resources and consumptionWorld energy resources and consumption]World energy consumption in 2010: over 5% growthEnergy markets have combined crisis recovery and strong industry dynamism. Energy consumption in the G20 soared by more than 5% in 2010, after the slight decrease of 2009. This strong increase is the result of two converging trends...
External links
- http://www.enecho.meti.go.jp/english/index.htmAgency for Natural Resources and EnergyAgency for Natural Resources and EnergyThe Agency for Natural Resources and Energy is an agency of Japan' Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and is responsible for Japan's policies in regard to energy and natural resources....
]

