
Effects of alcohol on memory
Encyclopedia
Ethanol
is the type of alcohol
found in alcoholic beverages. It is a volatile
, flammable, colorless liquid that acts as a central nervous system
depressant
. Ethanol can impair different types of memory
.

 Alcohol
Alcohol
acts as a positive allosteric modulator of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA
) receptors, specifically the GABAA subtype. Upon activation, these GABA receptors conduct Cl-, resulting in neuron
al hyperpolarization
. This hyperpolarization decreases the chance of an action potential
occurring and thus has an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission
of the central nervous system
.
At higher doses, ethanol also affects NMDA receptor
s by inhibiting the ion
current induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA
), a glutamate receptor
agonist
. This prevents excitatory synaptic transmissions from occurring, affecting synaptic plasticity
and, in turn, memory
and learning
.
layers of the hippocampus
. This impairs memory encoding since the hippocampus plays an important role in the formation of new memories. Alcohol also impairs and alters functioning in the cerebellum
Alcohol also impairs and alters functioning in the cerebellum
, which affects motor function and coordination. It has a notable inhibitory effect on neurons of the cerebral cortex
, affecting and altering thought processes, decreasing inhibition, and increasing the pain threshold. It also decreases sexual performance by depressing nerve centres in the hypothalamus
. Alcohol also has an effect on urine excretion via inhibition of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH
) secretion of the pituitary gland
. Lastly, it depresses breathing and heart rate by inhibiting neuronal functioning of the medulla
.
(LTM) has a long duration and large capacity. Memories stored in LTM can last from a few days to a lifetime. LTM consists of explicit memory
(requiring conscious awareness) and implicit memory
(unconscious awareness). Information selected for LTM goes through three processes. First, in the encoding stage, information from the senses is incorporated into mental activity in the form of a memory. Secondly, storage
involves taking this information and holding it indefinitely in memory. Lastly, retrieval is the ability to recall information from the long term memory storage. Each of these processes can be affected by alcohol.
requires conscious and intentional effort for recall. It includes both episodic memory
(for everyday events) and semantic memory
(for factual information).
Alcohol impairs episodic encoding, specifically for cued recall, recognition of completed word fragments, and free recall. A blackout
is an example of a difficulty in encoding episodic memories due to alcohol
. Blackouts are caused by a rapid increase in blood alcohol concentration (BAC) which in turn distorts the neurons in the hippocampus
. This distortion impairs a person's ability to form new episodic memories.
High doses of alcohol
severely disrupt the storage process of semantic memories. Alcohol
was found to impair the storage of novel stimuli but not that of previously learned information. Since alcohol affects the central nervous system
, it hinders semantic storage functioning by restricting the consolidation of the information from encoding.
Retrieval of explicit memory
is significantly impaired by alcohol
. When compared to sober participants, intoxicated participants performed quite poorly on a recall task for everyday events (episodic memory). Intoxicated participants are also slower to respond in reaction time tasks. Alcohol also impairs retrieval in word recognition tasks. When both encoding and retrieval take place during intoxication, there are surprisingly more impairments for cued recall than for free recall. In terms of gender differences in retrieval processes, females tend to score lower than males on recall tasks when intoxicated.
does not require conscious effort or intention for recall. It occurs when previous experience influences performance on a certain task. This is evident in priming
experiments. Implicit memory
includes procedural memory
, which influences our everyday behaviours, such as riding a bike or tying shoes. People can perform these abilities without thinking about them, which means procedural memory
functions automatically. While retrieval of explicit memory
is severely impaired by alcohol, retrieval of implicit memory
is not. Intoxicated subjects score higher on recognition tasks (involving implicit memory
) than on recall tasks (involving explicit memory
).
refers to temporary storage of small amounts of information over short delays. Digit span refers to the proposed number of pieces of information (5-9) that can be held in short-term memory. This is also referred to as the magic number seven – plus or minus two. Any more pieces of information than this, and newer items replace previous items. Alcohol intoxication has been found to have dissociative effects on short-term memory and cognitive functioning.
changes occurring in the anterior cingulate are correlated with altered short-term memory functions in the brains of young alcoholic men. fMRIs of alcohol-dependent women displayed significantly less blood oxygen in the frontal and parietal regions, especially in the right hemisphere. This is supported by findings of short-term memory impairment by lesions of the parietal lobe
and prefrontal cortex. Associations between third ventricular volume and cognitive performance on memory tests have been found in alcoholics. Specifically, increases in third ventricular volume correlate with a decline in memory performance.
(a type of visual short-term memory). With BACs between 80–84 mg/dl, more intrusion errors occur in a delayed recall task compared to a control group. Intrusion errors, which represent reflective cognitive functioning, occur when irrelevant information is produced. Alcoholics have less control of inhibiting intrusions. Acute alcohol intoxication in social drinkers caused more intrusion errors in delayed recall tasks than in immediate free recall tasks. Acute alcohol intoxication increases susceptibility to interference, which allows for more intrusion errors when there is a short delay. Free recall
(given list of words then asked to recall list) is significantly lower and therefore impaired by alcohol intoxication. Encoding deficits were found in verbal free recall and recognition tasks under the influence of alcohol. A discrimination task found significant alcohol-related impairments in depth perception
and in visual short-term memory. State-dependent learning
and relearning studies in male heavy drinkers demonstrate that the condition of intoxication while learning and sobriety when tested caused a performance deficit in free recall tasks. These findings are supportive of alcohol-induced storage deficits (not retrieval deficits). The effects of acute alcohol consumption on visual short-term memory, stereoscopic depth perception, and attention were studied. A 33% alcohol condition showed significant impairments in depth perception and in visual short-term memory (assessed by the vernier discrimination task).
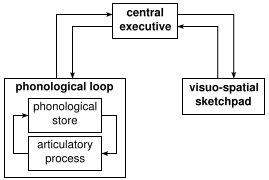
allows one to keep things in mind while simultaneously performing complex tasks. It involves a system for the temporary storage and manipulation of information, forming a crucial link between perception and controlled action. Evidence suggests that working memory involves three components: the central executive which controls attention, the visuo-spatial sketchpad which holds and manipulates spatial information, and the phonological loop which performs a similar function for auditory and speech-based information.
. One finding regarding the effects of alcohol on working memory points out that alcohol reduces working memory only in individuals with a high baseline working memory capacity., suggesting a universal suffering of working memory functionality is non-existent. Alcohol appears to impair the capacity of working memory to modulate response inhibition. Alcohol disinhibits behaviour, but only in individuals with a low baseline working memory capacity. An interesting finding is that incentive to perform well with working memory measurement tasks while under the influence of alcohol does in fact have some effect on working memory, in that it boosts scores in rate of mental scanning and reaction time to stimulus, but did not reduce number of errors compared to subjects with no incentive to perform well. Even acute alcohol intoxication (a blood alcohol concentration of 0.08-0.09%) produces a substantial impairment of working memory processes that require mnemonic rehearsal strategies. Alcohol is less likely to impair a working memory task that does not rely on memory rehearsal
or associated mnemonic strategies. Because of this, working memory is very susceptible to falter when a person is participating in tasks involving retention concerning auditory and visual sequences. A real world and interesting example of this is failure of guitarists or other musicians performing concerts to cue in on auditory patterns and make it known that their performance is hindered by intoxication, whereas professional basketball (a less sequence-heavy activity for working memory) standout Ron Artest
recently admitted in an interview with Sporting News to drinking heavily during half-time in the early days of his career and it having little if any recognizable effect on his working memory. His former coach Fran Fraschilla has gone on record saying:
is associated with impairment in sustained attention and visual working memory. Thus, alcoholics have reduced ability, but not necessarily inability, to perform these executive tasks, assumed to be subserved by regions of prefrontal cortex
. While it may not serve as a surprise that chronic alcoholism has been linked to decreased cognitive function including working memory, one surprising finding is not only that even moderate levels of alcohol consumption during pregnancy were shown to have an adverse affect on the child's working memory when tested at 7.5 years of age, but that working memory may be the most important aspect of attention that is adversely affected by prenatal alcohol exposure.
involves remembering to carry out an intended action in the future without an explicit reminder. Alcohol has been found to impair this ability. Chronic heavy alcohol users report significantly more prospective forgetting compared to low-dose and alcohol-free controls. The Prospective Memory Questionnaire assesses short-term habitual prospective memory, long-term episodic prospective memory, and internally cued prospective memory. Chronic heavy alcohol users reported significantly greater deficits for all three aspects of prospective memory. Individuals that report heavy alcohol use report 24% more difficulties with prospective memory than those who report that they are light drinkers and 30% more difficulties than those who report that they never drink. The effects of alcohol on prospective memory can also be assessed in the laboratory by simulating prospective memory tasks that individuals face in everyday life. Individuals who are given 0.6 g/kg alcohol prior to performing prospective memory tasks do significantly poorer than a placebo
group. Alcohol can damage the prefrontal and frontal areas of the brain, and this may be responsible for prospective memory impairments since prospective memory performance is highly correlated with frontal executive functions.
 A recent movie is The Hangover. Three groomsmen lose the groom during a bachelor party in Las Vegas, so they retrace their steps to find him. The characters still had functioning implicit/procedural memory, which allowed them to carry out the many acts they performed that night, but their episodic memory was impaired and thus they had no recollection of the events occurring.
A recent movie is The Hangover. Three groomsmen lose the groom during a bachelor party in Las Vegas, so they retrace their steps to find him. The characters still had functioning implicit/procedural memory, which allowed them to carry out the many acts they performed that night, but their episodic memory was impaired and thus they had no recollection of the events occurring.
Another movie is What Happens in Vegas. After an intoxicated night in “Sin City,” two people wake-up to find they got married.
Songs such as Waking Up in Vegas by Katy Perry
and Last Name by Carrie Underwood
also depict characters waking up and not remembering the night before due to alcohol consumption.
Our culture has been infiltrated by light-hearted images and perceptions of memory loss or decline at the hands of alcohol consumption, but there are also more serious dimensions of alcohol consumption and memory that come into the limelight. The most namely being in legal issues in terms of memory loss due to alcohol consumption as a defense. R. v. Daviault
[1994], is amongst many poignant cases where alcohol's effect on memory has been the crux of a much publicized trial in Canada.
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
is the type of alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
found in alcoholic beverages. It is a volatile
Volatility (chemistry)
In chemistry and physics, volatility is the tendency of a substance to vaporize. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. At a given temperature, a substance with higher vapor pressure vaporizes more readily than a substance with a lower vapor pressure.The term is primarily...
, flammable, colorless liquid that acts as a central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
depressant
Depressant
A depressant, or central depressant, is a drug or endogenous compound that depresses the function or activity of a specific part of the brain...
. Ethanol can impair different types of memory
Memory
In psychology, memory is an organism's ability to store, retain, and recall information and experiences. Traditional studies of memory began in the fields of philosophy, including techniques of artificially enhancing memory....
.


Neurochemistry

Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
acts as a positive allosteric modulator of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA
Gabâ
Gabâ or gabaa, for the people in many parts of the Philippines), is the concept of a non-human and non-divine, imminent retribution. A sort of negative karma, it is generally seen as an evil effect on a person because of their wrongdoings or transgressions...
) receptors, specifically the GABAA subtype. Upon activation, these GABA receptors conduct Cl-, resulting in neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
al hyperpolarization
Hyperpolarization
Hyperpolarization has several meanings:* Hyperpolarization occurs when the strength of the electric field across the width of a cell membrane increases...
. This hyperpolarization decreases the chance of an action potential
Action potential
In physiology, an action potential is a short-lasting event in which the electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and...
occurring and thus has an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission
Neurotransmission
Neurotransmission , also called synaptic transmission, is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by a neuron , and bind to and activate the receptors of another neuron...
of the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
.
At higher doses, ethanol also affects NMDA receptor
NMDA receptor
The NMDA receptor , a glutamate receptor, is the predominant molecular device for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function....
s by inhibiting the ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
current induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA
NMDA
N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid or N-Methyl-D-aspartate is an amino acid derivative which acts as a specific agonist at the NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor...
), a glutamate receptor
Glutamate receptor
Glutamate receptors are synaptic receptors located primarily on the membranes of neuronal cells. Glutamate is one of the 20 amino acids used to assemble proteins and as a result is abundant in many areas of the body, but it also functions as a neurotransmitter and is particularly abundant in the...
agonist
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell. Agonists often mimic the action of a naturally occurring substance...
. This prevents excitatory synaptic transmissions from occurring, affecting synaptic plasticity
Synaptic plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of the connection, or synapse, between two neurons to change in strength in response to either use or disuse of transmission over synaptic pathways. Plastic change also results from the alteration of the number of receptors located on a synapse...
and, in turn, memory
Memory
In psychology, memory is an organism's ability to store, retain, and recall information and experiences. Traditional studies of memory began in the fields of philosophy, including techniques of artificially enhancing memory....
and learning
Learning
Learning is acquiring new or modifying existing knowledge, behaviors, skills, values, or preferences and may involve synthesizing different types of information. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, animals and some machines. Progress over time tends to follow learning curves.Human learning...
.
Neurophysiology
Alcohol acts as a general central nervous system depressant, but it also affects specific areas of the brain to a more profound degree than others. At higher doses, it significantly inhibits neuronal activity in the CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cellPyramidal cell
Pyramidal neurons are a type of neuron found in areas of the brain including cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and in the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cortex and the corticospinal tract. Pyramidal neurons were first discovered and...
layers of the hippocampus
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a major component of the brains of humans and other vertebrates. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in...
. This impairs memory encoding since the hippocampus plays an important role in the formation of new memories.

Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language, and in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established...
, which affects motor function and coordination. It has a notable inhibitory effect on neurons of the cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
, affecting and altering thought processes, decreasing inhibition, and increasing the pain threshold. It also decreases sexual performance by depressing nerve centres in the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions...
. Alcohol also has an effect on urine excretion via inhibition of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH
Vasopressin
Arginine vasopressin , also known as vasopressin, argipressin or antidiuretic hormone , is a neurohypophysial hormone found in most mammals, including humans. Vasopressin is a peptide hormone that controls the reabsorption of molecules in the tubules of the kidneys by affecting the tissue's...
) secretion of the pituitary gland
Pituitary gland
In vertebrate anatomy the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 g , in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain, and rests in a small, bony cavity covered by a dural fold...
. Lastly, it depresses breathing and heart rate by inhibiting neuronal functioning of the medulla
Medulla
Medulla refers to the middle of something and derives from the Latin word for marrow. Its anatomical uses include:* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland...
.
Long-term memory
Long-term memoryLong-term memory
Long-term memory is memory in which associations among items are stored, as part of the theory of a dual-store memory model. According to the theory, long term memory differs structurally and functionally from working memory or short-term memory, which ostensibly stores items for only around 20–30...
(LTM) has a long duration and large capacity. Memories stored in LTM can last from a few days to a lifetime. LTM consists of explicit memory
Explicit memory
Explicit memory is the conscious, intentional recollection of previous experiences and information. People use explicit memory throughout the day, such as remembering the time of an appointment or recollecting an event from years ago....
(requiring conscious awareness) and implicit memory
Implicit memory
Implicit memory is a type of memory in which previous experiences aid in the performance of a task without conscious awareness of these previous experiences. Evidence for implicit memory arises in priming, a process whereby subjects show improved performance on tasks for which they have been...
(unconscious awareness). Information selected for LTM goes through three processes. First, in the encoding stage, information from the senses is incorporated into mental activity in the form of a memory. Secondly, storage
Storage
Storage may refer to:-Storage of goods:* Warehouse, a commercial building for storage of goods* Self storage, public storage facility-Containers:* Dry cask storage, storing high-level radioactive waste* Food storage...
involves taking this information and holding it indefinitely in memory. Lastly, retrieval is the ability to recall information from the long term memory storage. Each of these processes can be affected by alcohol.
Explicit memory
Explicit memoryExplicit memory
Explicit memory is the conscious, intentional recollection of previous experiences and information. People use explicit memory throughout the day, such as remembering the time of an appointment or recollecting an event from years ago....
requires conscious and intentional effort for recall. It includes both episodic memory
Episodic memory
Episodic memory is the memory of autobiographical events that can be explicitly stated. Semantic and episodic memory together make up the category of declarative memory, which is one of the two major divisions in memory...
(for everyday events) and semantic memory
Semantic memory
Semantic memory refers to the memory of meanings, understandings, and other concept-based knowledge unrelated to specific experiences. The conscious recollection of factual information and general knowledge about the world is generally thought to be independent of context and personal relevance...
(for factual information).
Alcohol impairs episodic encoding, specifically for cued recall, recognition of completed word fragments, and free recall. A blackout
Blackout (alcohol-related amnesia)
A blackout is a phenomenon caused by the intake of alcohol or other substance in which long term memory creation is impaired or there is a complete inability to recall the past. Blackouts are frequently described as having effects similar to that of anterograde amnesia, in which the subject cannot...
is an example of a difficulty in encoding episodic memories due to alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
. Blackouts are caused by a rapid increase in blood alcohol concentration (BAC) which in turn distorts the neurons in the hippocampus
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a major component of the brains of humans and other vertebrates. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in...
. This distortion impairs a person's ability to form new episodic memories.
High doses of alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
severely disrupt the storage process of semantic memories. Alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
was found to impair the storage of novel stimuli but not that of previously learned information. Since alcohol affects the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
, it hinders semantic storage functioning by restricting the consolidation of the information from encoding.
Retrieval of explicit memory
Explicit memory
Explicit memory is the conscious, intentional recollection of previous experiences and information. People use explicit memory throughout the day, such as remembering the time of an appointment or recollecting an event from years ago....
is significantly impaired by alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
. When compared to sober participants, intoxicated participants performed quite poorly on a recall task for everyday events (episodic memory). Intoxicated participants are also slower to respond in reaction time tasks. Alcohol also impairs retrieval in word recognition tasks. When both encoding and retrieval take place during intoxication, there are surprisingly more impairments for cued recall than for free recall. In terms of gender differences in retrieval processes, females tend to score lower than males on recall tasks when intoxicated.
Implicit memory
Implicit memoryImplicit memory
Implicit memory is a type of memory in which previous experiences aid in the performance of a task without conscious awareness of these previous experiences. Evidence for implicit memory arises in priming, a process whereby subjects show improved performance on tasks for which they have been...
does not require conscious effort or intention for recall. It occurs when previous experience influences performance on a certain task. This is evident in priming
Priming
Priming may refer to:* Priming , a process in which the processing of a target stimulus is aided or altered by the presentation of a previously presented stimulus....
experiments. Implicit memory
Implicit memory
Implicit memory is a type of memory in which previous experiences aid in the performance of a task without conscious awareness of these previous experiences. Evidence for implicit memory arises in priming, a process whereby subjects show improved performance on tasks for which they have been...
includes procedural memory
Procedural memory
Procedural memory is memory for how to do things. Procedural memory guides the processes we perform and most frequently resides below the level of conscious awareness. When needed, procedural memories are automatically retrieved and utilized for the execution of the integrated procedures involved...
, which influences our everyday behaviours, such as riding a bike or tying shoes. People can perform these abilities without thinking about them, which means procedural memory
Procedural memory
Procedural memory is memory for how to do things. Procedural memory guides the processes we perform and most frequently resides below the level of conscious awareness. When needed, procedural memories are automatically retrieved and utilized for the execution of the integrated procedures involved...
functions automatically. While retrieval of explicit memory
Explicit memory
Explicit memory is the conscious, intentional recollection of previous experiences and information. People use explicit memory throughout the day, such as remembering the time of an appointment or recollecting an event from years ago....
is severely impaired by alcohol, retrieval of implicit memory
Implicit memory
Implicit memory is a type of memory in which previous experiences aid in the performance of a task without conscious awareness of these previous experiences. Evidence for implicit memory arises in priming, a process whereby subjects show improved performance on tasks for which they have been...
is not. Intoxicated subjects score higher on recognition tasks (involving implicit memory
Implicit memory
Implicit memory is a type of memory in which previous experiences aid in the performance of a task without conscious awareness of these previous experiences. Evidence for implicit memory arises in priming, a process whereby subjects show improved performance on tasks for which they have been...
) than on recall tasks (involving explicit memory
Explicit memory
Explicit memory is the conscious, intentional recollection of previous experiences and information. People use explicit memory throughout the day, such as remembering the time of an appointment or recollecting an event from years ago....
).
Short-term memory
Short-term memoryShort-term memory
Short-term memory is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in mind in an active, readily available state for a short period of time. The duration of short-term memory is believed to be in the order of seconds. A commonly cited capacity is 7 ± 2 elements...
refers to temporary storage of small amounts of information over short delays. Digit span refers to the proposed number of pieces of information (5-9) that can be held in short-term memory. This is also referred to as the magic number seven – plus or minus two. Any more pieces of information than this, and newer items replace previous items. Alcohol intoxication has been found to have dissociative effects on short-term memory and cognitive functioning.
Brain areas affected by alcohol
Alcohol affects brain functioning. NeurochemicalNeurochemical
A neurochemical is an organic molecule, such as serotonin, dopamine, or nerve growth factor, that participates in neural activity. The science of neurochemistry studies the functions of neurochemicals.-Prominent neurochemicals:...
changes occurring in the anterior cingulate are correlated with altered short-term memory functions in the brains of young alcoholic men. fMRIs of alcohol-dependent women displayed significantly less blood oxygen in the frontal and parietal regions, especially in the right hemisphere. This is supported by findings of short-term memory impairment by lesions of the parietal lobe
Parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is a part of the Brain positioned above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe.The parietal lobe integrates sensory information from different modalities, particularly determining spatial sense and navigation. For example, it comprises somatosensory cortex and the...
and prefrontal cortex. Associations between third ventricular volume and cognitive performance on memory tests have been found in alcoholics. Specifically, increases in third ventricular volume correlate with a decline in memory performance.
Tasks and intoxication findings
Short-term memory is commonly tested with visual tasks. Short-term memory, especially for non-verbal and spatial material, are impaired by intoxication. Alcohol decreases iconic memoryIconic memory
Iconic memory is the visual sensory memory register pertaining to the visual domain. It is a component of the visual memory system which also includes visual short term memory and long term memory . Iconic memory is described as a very brief . A small decrease in visual persistence occurs with age...
(a type of visual short-term memory). With BACs between 80–84 mg/dl, more intrusion errors occur in a delayed recall task compared to a control group. Intrusion errors, which represent reflective cognitive functioning, occur when irrelevant information is produced. Alcoholics have less control of inhibiting intrusions. Acute alcohol intoxication in social drinkers caused more intrusion errors in delayed recall tasks than in immediate free recall tasks. Acute alcohol intoxication increases susceptibility to interference, which allows for more intrusion errors when there is a short delay. Free recall
Free recall
Free recall is a basic paradigm in the psychological study of memory. In this paradigm, participants study a list of items on each trial, and then are prompted to recall the items in any order...
(given list of words then asked to recall list) is significantly lower and therefore impaired by alcohol intoxication. Encoding deficits were found in verbal free recall and recognition tasks under the influence of alcohol. A discrimination task found significant alcohol-related impairments in depth perception
Depth perception
Depth perception is the visual ability to perceive the world in three dimensions and the distance of an object. Depth sensation is the ability to move accurately, or to respond consistently, based on the distances of objects in an environment....
and in visual short-term memory. State-dependent learning
State-dependent learning
State-dependent learning is a notion that learning and recalling are based upon the physiological and mental state of the organism....
and relearning studies in male heavy drinkers demonstrate that the condition of intoxication while learning and sobriety when tested caused a performance deficit in free recall tasks. These findings are supportive of alcohol-induced storage deficits (not retrieval deficits). The effects of acute alcohol consumption on visual short-term memory, stereoscopic depth perception, and attention were studied. A 33% alcohol condition showed significant impairments in depth perception and in visual short-term memory (assessed by the vernier discrimination task).

Effects on working memory
Working memoryWorking memory
Working memory has been defined as the system which actively holds information in the mind to do verbal and nonverbal tasks such as reasoning and comprehension, and to make it available for further information processing...
allows one to keep things in mind while simultaneously performing complex tasks. It involves a system for the temporary storage and manipulation of information, forming a crucial link between perception and controlled action. Evidence suggests that working memory involves three components: the central executive which controls attention, the visuo-spatial sketchpad which holds and manipulates spatial information, and the phonological loop which performs a similar function for auditory and speech-based information.
In the short term
Alcohol consumption has substantial, measurable effects on working memory, though these effects vary greatly between individual responses. Little is known about the neural mechanisms that underlie these individual differences. It is also found that alcohol impairs working memory by affecting mnemonic strategies and executive processes rather than by shrinking the basic holding capacity of working memory. Isolated acute-moderate levels of alcohol intoxication do not profoundly physically alter the structures which are critical for working memory function, such as the frontal cortex, parietal cortex, anterior cingulate, and parts of the basal gangliaBasal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
. One finding regarding the effects of alcohol on working memory points out that alcohol reduces working memory only in individuals with a high baseline working memory capacity., suggesting a universal suffering of working memory functionality is non-existent. Alcohol appears to impair the capacity of working memory to modulate response inhibition. Alcohol disinhibits behaviour, but only in individuals with a low baseline working memory capacity. An interesting finding is that incentive to perform well with working memory measurement tasks while under the influence of alcohol does in fact have some effect on working memory, in that it boosts scores in rate of mental scanning and reaction time to stimulus, but did not reduce number of errors compared to subjects with no incentive to perform well. Even acute alcohol intoxication (a blood alcohol concentration of 0.08-0.09%) produces a substantial impairment of working memory processes that require mnemonic rehearsal strategies. Alcohol is less likely to impair a working memory task that does not rely on memory rehearsal
Memory rehearsal
Memory rehearsal is a term for the role of repetition in the retention of memories, e.g., working memory rehearsal tasks.In the Baddeley's model of working memory, this ability comprises a central executive and two buffers - the phonological loop and the visuo—spatial sketch pad. Both storage...
or associated mnemonic strategies. Because of this, working memory is very susceptible to falter when a person is participating in tasks involving retention concerning auditory and visual sequences. A real world and interesting example of this is failure of guitarists or other musicians performing concerts to cue in on auditory patterns and make it known that their performance is hindered by intoxication, whereas professional basketball (a less sequence-heavy activity for working memory) standout Ron Artest
Ron Artest
Metta World Peace is an American professional basketball player and rapper who is currently with the Los Angeles Lakers in the NBA. World Peace gained a reputation as one of the league's premier defenders as he won the NBA Defensive Player of the Year Award in 2004...
recently admitted in an interview with Sporting News to drinking heavily during half-time in the early days of his career and it having little if any recognizable effect on his working memory. His former coach Fran Fraschilla has gone on record saying:
In the long term
Alcohol has shown to have some long term effect on working memory. Findings have shown that for working memory to be substantially affected, long-term, heavy drinking must be sustained over a long period of time as up to one drink per day does not impair cognitive function and may actually decrease the risk of cognitive decline. Furthermore, chronic alcoholismAlcoholism
Alcoholism is a broad term for problems with alcohol, and is generally used to mean compulsive and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, usually to the detriment of the drinker's health, personal relationships, and social standing...
is associated with impairment in sustained attention and visual working memory. Thus, alcoholics have reduced ability, but not necessarily inability, to perform these executive tasks, assumed to be subserved by regions of prefrontal cortex
Prefrontal cortex
The prefrontal cortex is the anterior part of the frontal lobes of the brain, lying in front of the motor and premotor areas.This brain region has been implicated in planning complex cognitive behaviors, personality expression, decision making and moderating correct social behavior...
. While it may not serve as a surprise that chronic alcoholism has been linked to decreased cognitive function including working memory, one surprising finding is not only that even moderate levels of alcohol consumption during pregnancy were shown to have an adverse affect on the child's working memory when tested at 7.5 years of age, but that working memory may be the most important aspect of attention that is adversely affected by prenatal alcohol exposure.
Prospective memory
Prospective memoryProspective memory
Prospective memory is a form of memory that involves remembering to perform a planned action or intention at the appropriate time. Prospective memory tasks are highly prevalent in daily life and range from relatively simple tasks to extreme life-or-death situations...
involves remembering to carry out an intended action in the future without an explicit reminder. Alcohol has been found to impair this ability. Chronic heavy alcohol users report significantly more prospective forgetting compared to low-dose and alcohol-free controls. The Prospective Memory Questionnaire assesses short-term habitual prospective memory, long-term episodic prospective memory, and internally cued prospective memory. Chronic heavy alcohol users reported significantly greater deficits for all three aspects of prospective memory. Individuals that report heavy alcohol use report 24% more difficulties with prospective memory than those who report that they are light drinkers and 30% more difficulties than those who report that they never drink. The effects of alcohol on prospective memory can also be assessed in the laboratory by simulating prospective memory tasks that individuals face in everyday life. Individuals who are given 0.6 g/kg alcohol prior to performing prospective memory tasks do significantly poorer than a placebo
Placebo
A placebo is a simulated or otherwise medically ineffectual treatment for a disease or other medical condition intended to deceive the recipient...
group. Alcohol can damage the prefrontal and frontal areas of the brain, and this may be responsible for prospective memory impairments since prospective memory performance is highly correlated with frontal executive functions.
In popular culture
The memory inhibiting effects of alcohol are often a prominent topic in popular culture. It appears in movies, books, and television shows. Several movies exists with the characters drinking alcohol to the point of memory loss and awakening the next morning with a host of problems due to actions they performed while intoxicated.
Another movie is What Happens in Vegas. After an intoxicated night in “Sin City,” two people wake-up to find they got married.
Songs such as Waking Up in Vegas by Katy Perry
Katy Perry
Katy Perry is an American singer, songwriter and actress. Born in Santa Barbara, California, and raised by Christian pastor parents, Perry grew up listening to only gospel music and sang in her local church as a child. After earning a GED during her first year of high school, she began to pursue a...
and Last Name by Carrie Underwood
Carrie Underwood
Carrie Marie Underwood is an American country singer-songwriter and actress who rose to fame as the winner of the fourth season of American Idol, in 2005...
also depict characters waking up and not remembering the night before due to alcohol consumption.
Our culture has been infiltrated by light-hearted images and perceptions of memory loss or decline at the hands of alcohol consumption, but there are also more serious dimensions of alcohol consumption and memory that come into the limelight. The most namely being in legal issues in terms of memory loss due to alcohol consumption as a defense. R. v. Daviault
R. v. Daviault
R. v. Daviault [1994] 3 S.C.R. 63, is a Supreme Court of Canada decision on the availability of the defence of intoxication for "general intent" criminal offences. The Leary rule which eliminated the defence was found unconstitutional in violation of both section 7 and 11 of the Canadian Charter of...
[1994], is amongst many poignant cases where alcohol's effect on memory has been the crux of a much publicized trial in Canada.

