Dorset culture
Encyclopedia
The Dorset culture was a Paleo-Eskimo
culture (500 BCE - CE 1500) that preceded the Inuit
culture in Arctic
North America
. It has been defined as having four phases, with distinct technology related to the people's hunting and tool making. They made distinctive triangular end-blades, soapstone
lamps, and burin
s.
The Dorset were identified as a separate culture in 1925. Archaeology
has been critical to adding to knowledge about them, as the Dorset were essentially extinct by 1500. They had difficulty adapting to the Medieval Warm Period
and were later displaced by the Thule
, who migrated east from present-day Alaska
. However a small, isolated community of Dorset culture people known as the Sadlermiut
survived until 1902-1903 at Hudson Bay
on Coats
, Walrus, and Southampton
islands. DNA
testing has confirmed the people were directly related to Dorset culture.
Inuit legends recount their driving away the people they called Tuniit (singular Tuniq) or Sivullirmiut (First Inhabitants). According to legend, the First Inhabitants were "giants", people who were taller and stronger than the Inuit, but who were easily scared off. Scholars believe that the Dorset and the later Thule people
were the peoples encountered by the Norse
who visited the area. The Norse called these native peoples skræling
.
Diamond Jenness
received some odd artifacts
from Cape Dorset, Nunavut
. As they were quite different than that of the Inuit, he speculated that they were indicative of an ancient, preceding culture. Jenness named the culture Dorset after the location of the find. These artifacts showed a consistent and distinct cultural pattern that included sophisticated art distinct from that of the Inuit. For example, the carvings featured uniquely large hairstyles for women; and figures of both sexes wearing hoodless parkas with large, tall collars. Much research since then has revealed many details of the Dorset people and their culture.
, Saqqaq
or (less likely) Independence I
. There are, however, problems with this theory: these earlier cultures had bow and arrow technology (which the Dorsets lacked). Possibly due to a shift from terrestrial to aquatic hunting, the bow and arrow became lost to the Dorset. Another piece of technology that is missing from the Dorset are drills
: there are no drill holes in Dorset artifacts. Instead, the Dorset gouged lenticular holes. For example, bone needles are common in Dorset sites, but they have long and narrow holes that have been painstakingly carved or gouged. Both the Pre-Dorset and Thule (Inuit) had drills.
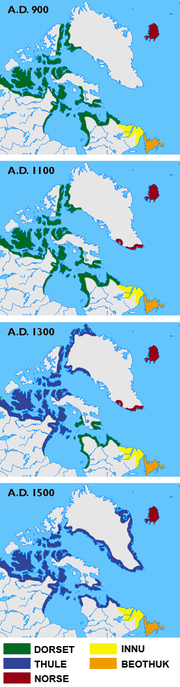
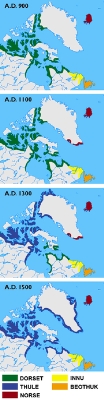
Dorset culture and history is divided into four periods: the Early (which began around 500 BCE), Middle, Late (starting around CE 800), and Terminal (CE 1000 to 1500) phases. The Terminal phase was already in progress when the Thule entered the Canadian Arctic, migrating east from Alaska. It is probably closely related to the onset of the Medieval Warm Period
, which started to warm the Arctic considerably around AD 800. With the warmer climates, the sea ice became less predictable and was isolated from the High Arctic.
The Dorset were highly adapted to living in a very cold climate, and much of their food came from hunting sea mammals through holes in the ice. The massive decline in sea-ice which the Medieval Warm Period produced would have had a devastating impact upon their way of life. They seem to have had great difficulty adapting to this change. They apparently followed the ice north. During the Late and Terminal periods, they concentrated their settlements in the High Arctic. As mentioned below, an isolated remnant of the Dorset may have survived on a few small Hudson Bay
islands until 1902. Most of the evidence demonstrates that by 1500 they had essentially disappeared.
-based Thule Inuit. Specifically, the Dorset did little hunting of land animals, such as polar bear
s and caribou. They lacked bow and arrow technology. Instead, they relied upon sea mammals (mostly seal), which they hunted from holes in the ice. Their clothing was well adapted to extremely cold weather.
Technological diagnostics of the Dorset culture include small, triangular end-blades; soapstone; and burin
s. The end-blades were hafted onto harpoon heads. They primarily used the harpoons to hunt seal, but also hunted larger sea mammals such as walrus
and narwhal
s. They used soapstone
to make lamps, which when filled with seal oil, would heat the Dorset dwellings during the cold and dark months. The distinctive burin
s were a special type of stone flake with a chisel-like edge. They were probably used for engraving, or for carving wood or bone. The burins were also used by Pre-Dorset groups; they usually had a distinctive mitten shape.
The Dorset were highly skilled at making refined miniature carvings, and striking masks. Both indicate an active shamanistic tradition. The Dorset culture was remarkably homogeneous across the Canadian Arctic, but there were some important variations which have been noted in both Greenland
and Newfoundland/Labrador regions.
connection between the Dorset and the Thule
. Archaeological, cultural and legend
ary evidence supports Thule-Dorset interaction. For instance, the Thule engaged in seal-hole hunting, which was not known from their culture in Alaska. The Dorset extensively used this hunting technique, likely a form of technology that they could teach the Thule.
Further, the speed and direction of the Thule migration may imply Dorset-Thule connections. The Thule made an almost direct migration from Alaska, across the continent through foreign lands all the way to Greenland, in the span of a few centuries. For the Thule to have accomplished this, they likely required directions and assistance, which the Dorset may have provided. The details of Thule/Dorset interactions are mostly unknown and generate questions: did the Thule carry new diseases, how much direct conflict was there between the two peoples, and what was the nature of their social interactions?
Much can be inferred from Inuit legends, archaeology and the genetic studies mentioned above. The Thule were a strong people with a history of warfare, and they had better weapons than the Dorset. The process of "driving off" the Dorset, which is recounted in their legends, would likely have involved direct conflict. As there was almost no interbreeding between them, social interactions did not appear to go much beyond trading. Although archaeological evidence indicates that the Dorset were in steep decline when the Thule arrived, conflicts with the Inuit would have hastened that decline.
were a people living in near isolation mainly on and around Coats Island
, Walrus Island, and Southampton Island
in Hudson Bay
up until 1902-1903. Encounters with Europeans and exposure to infectious disease
caused the deaths of the last people. Scholars believe they were the last remnants of the Dorset culture, as they had a culture and dialect distinct from the mainland Inuit
. In addition, recent mitochondrial DNA research has shown that the Sadlermiut were directly related to the Tuniit.
Paleo-Eskimo
The Paleo-Eskimo were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka in present-day Russia across North America to Greenland prior to the rise of the modern Inuit and/or Eskimo and related cultures...
culture (500 BCE - CE 1500) that preceded the Inuit
Inuit
The Inuit are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic regions of Canada , Denmark , Russia and the United States . Inuit means “the people” in the Inuktitut language...
culture in Arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. It has been defined as having four phases, with distinct technology related to the people's hunting and tool making. They made distinctive triangular end-blades, soapstone
Soapstone
Soapstone is a metamorphic rock, a talc-schist. It is largely composed of the mineral talc and is thus rich in magnesium. It is produced by dynamothermal metamorphism and metasomatism, which occurs in the areas where tectonic plates are subducted, changing rocks by heat and pressure, with influx...
lamps, and burin
Burin
Burin from the French burin meaning "cold chisel" has two specialised meanings for types of tools in English, one meaning a steel cutting tool which is the essential tool of engraving, and the other, in archaeology, meaning a special type of lithic flake with a chisel-like edge which was probably...
s.
The Dorset were identified as a separate culture in 1925. Archaeology
Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
has been critical to adding to knowledge about them, as the Dorset were essentially extinct by 1500. They had difficulty adapting to the Medieval Warm Period
Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period , Medieval Climate Optimum, or Medieval Climatic Anomaly was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region, that may also have been related to other climate events around the world during that time, including in China, New Zealand, and other countries lasting from...
and were later displaced by the Thule
Thule people
The Thule or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by AD 1000 and expanded eastwards across Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people of the earlier Dorset culture that had previously inhabited the region...
, who migrated east from present-day Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
. However a small, isolated community of Dorset culture people known as the Sadlermiut
Sadlermiut
The Sadlermiut were an Eskimo group living in near isolation mainly on and around Coats Island, Walrus Island, and Southampton Island in Hudson Bay...
survived until 1902-1903 at Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
on Coats
Coats Island
Coats Island lies at the northern end of Hudson Bay in the Kivalliq Region of Nunavut. At in size, it is the 107th largest island in the world, and Canada's 24th largest island....
, Walrus, and Southampton
Southampton Island
Southampton Island is a large island at the entrance to Hudson Bay at Foxe Basin. One of the larger members of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Southampton Island is part of the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut, Canada. The area of the island is stated as by Statistics Canada . It is the 34th largest...
islands. DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
testing has confirmed the people were directly related to Dorset culture.
Inuit legends recount their driving away the people they called Tuniit (singular Tuniq) or Sivullirmiut (First Inhabitants). According to legend, the First Inhabitants were "giants", people who were taller and stronger than the Inuit, but who were easily scared off. Scholars believe that the Dorset and the later Thule people
Thule people
The Thule or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by AD 1000 and expanded eastwards across Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people of the earlier Dorset culture that had previously inhabited the region...
were the peoples encountered by the Norse
Norsemen
Norsemen is used to refer to the group of people as a whole who spoke what is now called the Old Norse language belonging to the North Germanic branch of Indo-European languages, especially Norwegian, Icelandic, Faroese, Swedish and Danish in their earlier forms.The meaning of Norseman was "people...
who visited the area. The Norse called these native peoples skræling
Skræling
Skræling is the name the Norse Greenlanders used for the indigenous peoples they encountered in North America and Greenland. In surviving sources it is first applied to the Thule people, the Eskimo group with whom the Norse coexisted in Greenland after about the 13th century...
.
Discovery
In 1925 anthropologistAnthropology
Anthropology is the study of humanity. It has origins in the humanities, the natural sciences, and the social sciences. The term "anthropology" is from the Greek anthrōpos , "man", understood to mean mankind or humanity, and -logia , "discourse" or "study", and was first used in 1501 by German...
Diamond Jenness
Diamond Jenness
Diamond Jenness, CC was one of Canada's greatest early scientists and a pioneer of Canadian anthropology.-Biography:...
received some odd artifacts
Artifact (archaeology)
An artifact or artefact is "something made or given shape by man, such as a tool or a work of art, esp an object of archaeological interest"...
from Cape Dorset, Nunavut
Cape Dorset, Nunavut
Cape Dorset is an Inuit hamlet located on Dorset Island near Foxe Peninsula at the southern tip of Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada...
. As they were quite different than that of the Inuit, he speculated that they were indicative of an ancient, preceding culture. Jenness named the culture Dorset after the location of the find. These artifacts showed a consistent and distinct cultural pattern that included sophisticated art distinct from that of the Inuit. For example, the carvings featured uniquely large hairstyles for women; and figures of both sexes wearing hoodless parkas with large, tall collars. Much research since then has revealed many details of the Dorset people and their culture.
Origins
The origins of the Dorset people are not well understood. They may have developed from the previous cultures of Pre-DorsetPre-Dorset
The "Pre-Dorset culture" was a Paleo-Eskimo culture that lived in the Eastern Arctic from 2500 to 500 BC....
, Saqqaq
Saqqaq culture
The Saqqaq culture was a Paleo-Eskimo culture in Greenland.-Timeframe:...
or (less likely) Independence I
Independence I culture
The Independence I culture was a Paleo-Eskimo culture of peoples who lived in northern Greenland from 2,400 to 1,000 B.C. It is named after Independence Fjord. During this time they coexisted with the Saqqaq culture of southern Greenland...
. There are, however, problems with this theory: these earlier cultures had bow and arrow technology (which the Dorsets lacked). Possibly due to a shift from terrestrial to aquatic hunting, the bow and arrow became lost to the Dorset. Another piece of technology that is missing from the Dorset are drills
Bow drill
The bow drill is an ancient tool. While it was usually used to make fire, it was also used for primitive woodworking and dentistry. It consists of a bearing block or handhold, a spindle or drill, a hearth or fireboard, and a simple bow...
: there are no drill holes in Dorset artifacts. Instead, the Dorset gouged lenticular holes. For example, bone needles are common in Dorset sites, but they have long and narrow holes that have been painstakingly carved or gouged. Both the Pre-Dorset and Thule (Inuit) had drills.
Historical and cultural periods

Dorset culture and history is divided into four periods: the Early (which began around 500 BCE), Middle, Late (starting around CE 800), and Terminal (CE 1000 to 1500) phases. The Terminal phase was already in progress when the Thule entered the Canadian Arctic, migrating east from Alaska. It is probably closely related to the onset of the Medieval Warm Period
Medieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period , Medieval Climate Optimum, or Medieval Climatic Anomaly was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region, that may also have been related to other climate events around the world during that time, including in China, New Zealand, and other countries lasting from...
, which started to warm the Arctic considerably around AD 800. With the warmer climates, the sea ice became less predictable and was isolated from the High Arctic.
The Dorset were highly adapted to living in a very cold climate, and much of their food came from hunting sea mammals through holes in the ice. The massive decline in sea-ice which the Medieval Warm Period produced would have had a devastating impact upon their way of life. They seem to have had great difficulty adapting to this change. They apparently followed the ice north. During the Late and Terminal periods, they concentrated their settlements in the High Arctic. As mentioned below, an isolated remnant of the Dorset may have survived on a few small Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
islands until 1902. Most of the evidence demonstrates that by 1500 they had essentially disappeared.
Technology
Scholars credit the Dorset with a faultless understanding of their local environment (which they may have shared with the newly arrived Inuit). But, their adaptation was different from that of the whalingWhaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales mainly for meat and oil. Its earliest forms date to at least 3000 BC. Various coastal communities have long histories of sustenance whaling and harvesting beached whales...
-based Thule Inuit. Specifically, the Dorset did little hunting of land animals, such as polar bear
Polar Bear
The polar bear is a bear native largely within the Arctic Circle encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the world's largest land carnivore and also the largest bear, together with the omnivorous Kodiak Bear, which is approximately the same size...
s and caribou. They lacked bow and arrow technology. Instead, they relied upon sea mammals (mostly seal), which they hunted from holes in the ice. Their clothing was well adapted to extremely cold weather.
Technological diagnostics of the Dorset culture include small, triangular end-blades; soapstone; and burin
Burin
Burin from the French burin meaning "cold chisel" has two specialised meanings for types of tools in English, one meaning a steel cutting tool which is the essential tool of engraving, and the other, in archaeology, meaning a special type of lithic flake with a chisel-like edge which was probably...
s. The end-blades were hafted onto harpoon heads. They primarily used the harpoons to hunt seal, but also hunted larger sea mammals such as walrus
Walrus
The walrus is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous circumpolar distribution in the Arctic Ocean and sub-Arctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the Odobenidae family and Odobenus genus. It is subdivided into three subspecies: the Atlantic...
and narwhal
Narwhal
The narwhal, Monodon monoceros, is a medium-sized toothed whale that lives year-round in the Arctic. One of two living species of whale in the Monodontidae family, along with the beluga whale, the narwhal males are distinguished by a characteristic long, straight, helical tusk extending from their...
s. They used soapstone
Soapstone
Soapstone is a metamorphic rock, a talc-schist. It is largely composed of the mineral talc and is thus rich in magnesium. It is produced by dynamothermal metamorphism and metasomatism, which occurs in the areas where tectonic plates are subducted, changing rocks by heat and pressure, with influx...
to make lamps, which when filled with seal oil, would heat the Dorset dwellings during the cold and dark months. The distinctive burin
Burin
Burin from the French burin meaning "cold chisel" has two specialised meanings for types of tools in English, one meaning a steel cutting tool which is the essential tool of engraving, and the other, in archaeology, meaning a special type of lithic flake with a chisel-like edge which was probably...
s were a special type of stone flake with a chisel-like edge. They were probably used for engraving, or for carving wood or bone. The burins were also used by Pre-Dorset groups; they usually had a distinctive mitten shape.
The Dorset were highly skilled at making refined miniature carvings, and striking masks. Both indicate an active shamanistic tradition. The Dorset culture was remarkably homogeneous across the Canadian Arctic, but there were some important variations which have been noted in both Greenland
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for...
and Newfoundland/Labrador regions.
Interaction with the Inuit
There appears to have been minimal (if any) geneticGenetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
connection between the Dorset and the Thule
Thule people
The Thule or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by AD 1000 and expanded eastwards across Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people of the earlier Dorset culture that had previously inhabited the region...
. Archaeological, cultural and legend
Legend
A legend is a narrative of human actions that are perceived both by teller and listeners to take place within human history and to possess certain qualities that give the tale verisimilitude...
ary evidence supports Thule-Dorset interaction. For instance, the Thule engaged in seal-hole hunting, which was not known from their culture in Alaska. The Dorset extensively used this hunting technique, likely a form of technology that they could teach the Thule.
Further, the speed and direction of the Thule migration may imply Dorset-Thule connections. The Thule made an almost direct migration from Alaska, across the continent through foreign lands all the way to Greenland, in the span of a few centuries. For the Thule to have accomplished this, they likely required directions and assistance, which the Dorset may have provided. The details of Thule/Dorset interactions are mostly unknown and generate questions: did the Thule carry new diseases, how much direct conflict was there between the two peoples, and what was the nature of their social interactions?
Much can be inferred from Inuit legends, archaeology and the genetic studies mentioned above. The Thule were a strong people with a history of warfare, and they had better weapons than the Dorset. The process of "driving off" the Dorset, which is recounted in their legends, would likely have involved direct conflict. As there was almost no interbreeding between them, social interactions did not appear to go much beyond trading. Although archaeological evidence indicates that the Dorset were in steep decline when the Thule arrived, conflicts with the Inuit would have hastened that decline.
The Sadlermiut
The SadlermiutSadlermiut
The Sadlermiut were an Eskimo group living in near isolation mainly on and around Coats Island, Walrus Island, and Southampton Island in Hudson Bay...
were a people living in near isolation mainly on and around Coats Island
Coats Island
Coats Island lies at the northern end of Hudson Bay in the Kivalliq Region of Nunavut. At in size, it is the 107th largest island in the world, and Canada's 24th largest island....
, Walrus Island, and Southampton Island
Southampton Island
Southampton Island is a large island at the entrance to Hudson Bay at Foxe Basin. One of the larger members of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Southampton Island is part of the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut, Canada. The area of the island is stated as by Statistics Canada . It is the 34th largest...
in Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
up until 1902-1903. Encounters with Europeans and exposure to infectious disease
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
caused the deaths of the last people. Scholars believe they were the last remnants of the Dorset culture, as they had a culture and dialect distinct from the mainland Inuit
Inuit
The Inuit are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic regions of Canada , Denmark , Russia and the United States . Inuit means “the people” in the Inuktitut language...
. In addition, recent mitochondrial DNA research has shown that the Sadlermiut were directly related to the Tuniit.
Dorset in culture
- CanadianCanadaCanada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
poet Al PurdyAl PurdyAlfred Wellington Purdy, OC, O.Ont was one of the most popular and important Canadian poets of the 20th century. Purdy's writing career spanned more than fifty years. His works include over thirty books of poetry; a novel; two volumes of memoirs and four books of correspondence...
wrote a poem entitled "Lament for the Dorsets" which starts "Animal bones and some mossy tent rings... all that remains of Dorset giants, who drove the Vikings back to their longships..." This poem laments the loss of their culture and describes them and their end.
External links
- "Dorset Culture in Nunavik", Avataq
- "In the bones of the world", Nuntsiaq News
- "Sadlermiut", Canadian Encyclopedia
- "Dorset Paleoeskimo Culture", Canada.ca.

