
DVB-T2
Encyclopedia
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T
, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television
.
This system transmits compressed digital audio, video, and other data in "physical layer pipes" (PLPs), using OFDM modulation with concatenated channel coding and interleaving. The higher offered bit rate, with respect to its predecessor DVB-T, makes it a suited system for carrying HDTV signals on the terrestrial TV channel (though many broadcasters still use plain DVB-T for this purpose).
It is currently broadcasting in UK (Freeview HD, four channels), Italy
(Europa 7 HD
, twelve channels), Sweden
(five channels), Ukraine (32 SD and HD channels in four nationwide multiplexes) and some other countries.
According to the commercial requirements and call for technologies issued in April 2007, the first phase of DVB-T2 would be devoted to provide optimum reception for stationary (fixed) and portable receivers (i.e., units which can be nomadic, but not fully mobile) using existing aerials, whereas a second and third phase would study methods to deliver higher payloads (with new aerials) and the mobile reception issue. The novel system should provide a minimum 30% increase in payload, under similar channel conditions already used for DVB-T.
The BBC
, ITV
, Channel 4
and Five agreed with the regulator Ofcom
to convert one UK multiplex (B, or PSB3) to DVB-T2 to increase capacity for HDTV via DTT. They expected the first TV region to use the new standard would be Granada in November 2009 (with existing switched over regions being changed at the same time). It was expected that over time there would be enough DVB-T2 receivers sold to switch all DTT transmissions to DVB-T2, and H.264.
Ofcom
published its final decision on April 3, 2008 for HDTV using DVB-T2 and H.264: BBC HD
would have one HD slot after digital switchover (DSO) at Granada. ITV and C4 had, as expected, applied to Ofcom for the 2 additional HD slots available from 2009 to 2012.
Ofcom indicated that it found an unused channel covering 3.7 million households in London, which could be used to broadcast the DVB-T2 HD multiplex from 2010, i.e., before DSO in London. Ofcom indicated that they would look for more unused UHF channels in other parts of the UK, that can be used for the DVB-T2 HD multiplex from 2010 until DSO.
The ETSI process resulted in the DVB-T2 standard being adopted on September 9, 2009. The ETSI process had several phases, but the only changes were text clarifications.
Since the DVB-T2 physical layer specification was complete, and there would be no further technical enhancements, receiver VLSI chip design started with confidence in stability of specification. A draft PSI/SI (program and system information) specification document was also agreed with the DVB-TM-GBS group.
, Harris, Pace, Rohde & Schwarz, Tandberg, Thomson Broadcast and TeamCast. Other manufacturers planning DVB-T2 equipment launches include Alitronika, CellMetric, Cisco, Digital TV Labs, Humax, NXP Semiconductors, Panasonic, ProTelevision Technologies, Screen Service, SIDSA, Sony, ST Microelectronics and T-VIPS.
The first test from a real TV transmitter was performed by the BBC Research & Innovation in the last weeks of June 2008 using channel 53 from the Guildford
transmitter, southwest of London: BBC had developed and built the modulator/demodulator prototype in parallel with the DVB-T2 standard being drafted. Other companies like ENKOM or IfN develop software (processor) based decoding.
NORDIG published a DVB-T2 receiver specification and performance requirement on the July 1, 2009.
In March 2009 the Digital TV Group
(DTG), the industry association for digital TV in the UK, published the technical specification for high definition services on digital terrestrial television (Freeview) using the new DVB-T2 standard. The DTG's test house: DTG Testing are testing Freeview HD products against this specification.
For instance, a UK MFN DVB-T profile (64-QAM, 2k mode, coding rate 2/3, guard interval 1/32) and a DVB-T2 equivalent (256-QAM, 32k, coding rate 3/5, guard interval 1/128) allows for an increase in bit rate from 24.13 Mbit/s to 35.4 Mbit/s (+46.5%).
Another example, for an Italian SFN
DVB-T profile (64-QAM, 8k, coding rate 2/3, guard interval 1/4) and a DVB-T2 equivalent (256-QAM, 32k, coding rate 3/5, guard interval 1/16), achieves an increase in bit rate from 19.91 Mbit/s to 33.3 Mbit/s (+67%).
The earliest introductions of T2 have usually been tied with a launch of high-definition television. There are however some countries where HDTV is broadcast using the old DVB-T standard with no immediate plans to switch those broadcasts to DVB-T2. Among countries using DVB-T for nationwide broadcasts of HDTV are France, Ireland, Italy, Norway
and Denmark
, though usually with MPEG4. Possibly only Australia is using DVB-T with MPEG2 for HD.
Countries where DVB-T2 is in use include:
The Southern African Development Community
announced in November 2010 that DVB-T2 would be the preferred standard for the region. In Serbia, both SD and HD broadcasts will air in DVB-T2.
It has been trialled in Spain and Germany. Sri Lanka and Austria is also expected to use it.
Currently Malaysia, which has yet to officially launch its DVB-T transmission, is running tests on DVB-T2.. Whether the system will be adopted only for HD channels or will replace its existing trial DVB-T system, if adopted at all, remains unannounced.
Freeview HD started its "technical launch" on December 2, 2009, hosting BBC HD
, and ITV1 HD. On March 30, 2010, Freeview HD had its official launch, and added Channel 4 HD to its broadcasts. The fourth channel hosted is BBC One HD
, while as of March 2010 the remaining fifth slot is still to be assigned.
, Freeview covers 77% of UK population, and plans to finally reach 98.5% in 2012, following the region by region digital switchover all over the country.
A 5th HD channel looks likely to launch in April 2012. Public service broadcasters have been invited to apply for the fifth slot, the closing date for applications October 17, 2011: http://www.broadcastnow.co.uk/technology/fifth-dtt-hd-channel-to-launch-early-2012/5031537.article
Also in October 2011 OiV - Transmitters & Communications started testing on UHF channel 53 from Sljeme and Zagreb - Prisavlje 3.
obtained a national multiplex (the slot corresponging to one channel in analog broadcasting and to many channels in digital broadcasting) in spring 2010, and decided to use it for transmitting in DVB-T2. Europa 7 HD
was the name chosen to the offer of digital TV channels. Having a full multiplex for itself, Europa 7 HD hosts twelve alternating channels, of which eight in HD.
Europa 7 HD began testing broadcasts on July 2010, and started broadcasting from October 2010. While BBC, ITV1 and Channel 4 have only one or two of their channels in DVB-T2, Europa 7 HD transmits all of its channels with this technology; it has been announced as "the first broadcaster in the world to broadcast with this new technology."
Europa 7 HD is the first Italian broadcaster to adopt the DVB-T2 technology, and is doing so as an unilateral initialive, as there is not a general plan in Italy to adopt DVB-T2 for the other broadcasters. The two dominating broadcasters Rai (public) and Mediaset (private) still use DVB-T for their HDTV channels. Rai has planned some tests with DVB-T2, but has not a short-term plan for the general public to switch to DVB-T2, and the country is not yet fully switched from analog to DVB-T. Europa7 HD owner Francesco Di Stefano declared that all broadcasters will eventually have to move from T1 to T2, because of the higher quality.
Broadcasts started on November 1, 2010, with five channels available initially: SVT1 HD, SVT2 HD, MTVN HD, National Geographic HD and Canal+ Sport HD
. From this date a coverage of 70% of the population is achieved, with 90% expected by mid 2011 and nationwide coverage by 2012.
(TRT) is testing TRT HD
in Ankara
-Dikmen UHF channel 31.
multiplexes, for both SD and HD broadcasts. Before settling for DVB-T2, Ukraine was testing both DVB-T/MPEG-2 and DVB-T/MPEG-4 options, and some experimental transmitters operating in those standards are still live. Ukraine has never had a full-fledged nationwide DVB-T network, thus not having to do a DVB-T-to-DVB-T2 migration.
Zeonbud's network consists of 167 transmitter sites, each carrying four DVB-T2 multiplexes, with transmitter power ranging from 2 kW to 50 W (all in in MFN
mode). As of October 10, 2011, 150 of the 167 transmitter sites have officially gone live. The biggest problem of Ukraine's DVB-T2 rollout for now is the acute shortage of inexpensive DVB-T2 set-top-boxes.
The four multiplexes carry in total 28 nationwide channels (same for all transmitter sites, distributed via satellite) and 4 local channels. Up to 8 of those 28 nationwide channels can broadcast in HD format.
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television
Digital terrestrial television
Digital terrestrial television is the technological evolution of broadcast television and advance from analog television, which broadcasts land-based signals...
.
This system transmits compressed digital audio, video, and other data in "physical layer pipes" (PLPs), using OFDM modulation with concatenated channel coding and interleaving. The higher offered bit rate, with respect to its predecessor DVB-T, makes it a suited system for carrying HDTV signals on the terrestrial TV channel (though many broadcasters still use plain DVB-T for this purpose).
It is currently broadcasting in UK (Freeview HD, four channels), Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
(Europa 7 HD
Europa 7 HD
Europa 7 HD its an Italian group of channels aired since 11 October 2010. It's one of the first broadcasters in the world to use the DVB-T2 technology, after United Kingdom's channels BBC HD, ITV1 HD and Channel 4 HD.-Legal battle:...
, twelve channels), Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
(five channels), Ukraine (32 SD and HD channels in four nationwide multiplexes) and some other countries.
Preliminary investigation
In March 2006 DVB decided to study options for an upgraded DVB-T standard. In June 2006, a formal study group named TM-T2 (Technical Module on Next Generation DVB-T) was established by the DVB Group to develop an advanced modulation scheme that could be adopted by a second generation digital terrestrial television standard, to be named DVB-T2.According to the commercial requirements and call for technologies issued in April 2007, the first phase of DVB-T2 would be devoted to provide optimum reception for stationary (fixed) and portable receivers (i.e., units which can be nomadic, but not fully mobile) using existing aerials, whereas a second and third phase would study methods to deliver higher payloads (with new aerials) and the mobile reception issue. The novel system should provide a minimum 30% increase in payload, under similar channel conditions already used for DVB-T.
The BBC
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation is a British public service broadcaster. Its headquarters is at Broadcasting House in the City of Westminster, London. It is the largest broadcaster in the world, with about 23,000 staff...
, ITV
ITV
ITV is the major commercial public service TV network in the United Kingdom. Launched in 1955 under the auspices of the Independent Television Authority to provide competition to the BBC, it is also the oldest commercial network in the UK...
, Channel 4
Channel 4
Channel 4 is a British public-service television broadcaster which began working on 2 November 1982. Although largely commercially self-funded, it is ultimately publicly owned; originally a subsidiary of the Independent Broadcasting Authority , the station is now owned and operated by the Channel...
and Five agreed with the regulator Ofcom
Ofcom
Ofcom is the government-approved regulatory authority for the broadcasting and telecommunications industries in the United Kingdom. Ofcom was initially established by the Office of Communications Act 2002. It received its full authority from the Communications Act 2003...
to convert one UK multiplex (B, or PSB3) to DVB-T2 to increase capacity for HDTV via DTT. They expected the first TV region to use the new standard would be Granada in November 2009 (with existing switched over regions being changed at the same time). It was expected that over time there would be enough DVB-T2 receivers sold to switch all DTT transmissions to DVB-T2, and H.264.
Ofcom
Ofcom
Ofcom is the government-approved regulatory authority for the broadcasting and telecommunications industries in the United Kingdom. Ofcom was initially established by the Office of Communications Act 2002. It received its full authority from the Communications Act 2003...
published its final decision on April 3, 2008 for HDTV using DVB-T2 and H.264: BBC HD
BBC HD
BBC HD is a high-definition television network provided by the BBC. The service was initially run as a trial from 15 May 2006 until becoming a full service on 1 December 2007...
would have one HD slot after digital switchover (DSO) at Granada. ITV and C4 had, as expected, applied to Ofcom for the 2 additional HD slots available from 2009 to 2012.
Ofcom indicated that it found an unused channel covering 3.7 million households in London, which could be used to broadcast the DVB-T2 HD multiplex from 2010, i.e., before DSO in London. Ofcom indicated that they would look for more unused UHF channels in other parts of the UK, that can be used for the DVB-T2 HD multiplex from 2010 until DSO.
The DVB-T2 specification
The DVB-T2 draft standard was ratified by the DVB Steering Board on June 26, 2008, and published on the DVB homepage as DVB-T2 standard BlueBook,. It was handed over to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) by DVB.ORG on June 20, 2008.The ETSI process resulted in the DVB-T2 standard being adopted on September 9, 2009. The ETSI process had several phases, but the only changes were text clarifications.
Since the DVB-T2 physical layer specification was complete, and there would be no further technical enhancements, receiver VLSI chip design started with confidence in stability of specification. A draft PSI/SI (program and system information) specification document was also agreed with the DVB-TM-GBS group.
Tests
Prototype receivers were shown in September IBC 2008 and more recent version at the IBC 2009 in Amsterdam. A number of other manufacturers demonstrated DVB-T2 at IBC 2009 including Albis Technologies, Arqiva, DekTec, Enensys TechnologiesEnensys Technologies
ENENSYS is a manufacturer of Broadcast Network Equipment and Test & Monitoring Equipment for digital broadcast. The company provides products for the following fields:* Mobile TV...
, Harris, Pace, Rohde & Schwarz, Tandberg, Thomson Broadcast and TeamCast. Other manufacturers planning DVB-T2 equipment launches include Alitronika, CellMetric, Cisco, Digital TV Labs, Humax, NXP Semiconductors, Panasonic, ProTelevision Technologies, Screen Service, SIDSA, Sony, ST Microelectronics and T-VIPS.
The first test from a real TV transmitter was performed by the BBC Research & Innovation in the last weeks of June 2008 using channel 53 from the Guildford
Guildford
Guildford is the county town of Surrey. England, as well as the seat for the borough of Guildford and the administrative headquarters of the South East England region...
transmitter, southwest of London: BBC had developed and built the modulator/demodulator prototype in parallel with the DVB-T2 standard being drafted. Other companies like ENKOM or IfN develop software (processor) based decoding.
NORDIG published a DVB-T2 receiver specification and performance requirement on the July 1, 2009.
In March 2009 the Digital TV Group
Digital TV Group
The Digital TV Group is the industry association for Digital Television in the United Kingdom : The Group was formed in 1995 to set technical standards for the implementation of digital terrestrial television in the UK and now encompasses all digital TV platforms and convergence issues...
(DTG), the industry association for digital TV in the UK, published the technical specification for high definition services on digital terrestrial television (Freeview) using the new DVB-T2 standard. The DTG's test house: DTG Testing are testing Freeview HD products against this specification.
The standard
The following characteristics have been devised for the T2 standard:- COFDM modulation with QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM, or 256-QAM constellations.
- OFDM modes are 1k, 2k, 4k, 8k, 16k, and 32k. The symbol length for 32k mode is about 4 ms.
- Guard intervals are 1/128, 1/32, 1/16, 19/256, 1/8, 19/128, and 1/4. (For 32k mode, the maximum is 1/8.)
- FECForward error correctionIn telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels....
is concatenated LDPC and BCHBCH codeIn coding theory the BCH codes form a class of parameterised error-correcting codes which have been the subject of much academic attention in the last fifty years. BCH codes were invented in 1959 by Hocquenghem, and independently in 1960 by Bose and Ray-Chaudhuri...
codes (as in DVB-S2DVB-S2Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite - Second Generation is a digital television broadcast standard that has been designed as a successor for the popular DVB-S system. It was developed in 2003 by the , an international industry consortium, and ratified by ETSI in March 2005...
), with rates 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, and 5/6. - There are fewer pilots, in 8 different pilot-patterns, and equalization can be based also on the RAI CD3 system.
- In the 32k mode, a larger part of the standard 8 MHz channel can be used, adding about 2% extra capacity.
- DVB-T2 is specified for 1.7, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 10 MHz channel bandwidth.
- MISOMisois a traditional Japanese seasoning produced by fermenting rice, barley and/or soybeans, with salt and the fungus , the most typical miso being made with soy. The result is a thick paste used for sauces and spreads, pickling vegetables or meats, and mixing with dashi soup stock to serve as miso...
(Multiple-Input Single-Output) may be used (AlamoutiSiavash AlamoutiSiavash Alamouti is an Iranian-American engineer who is best known for the invention of the so-called Alamouti space–time block code, filed in 1997 and patented jointly with Vahid Tarokh. Alamouti's code is a 2 transmit antenna space-time block code and has been adopted in various global standards...
scheme), but MIMOMIMOIn radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
will not be used. Diversity receivers can be used (as they are with DVB-T). - Multiple PLP to enable service specific robustness.
- Bundling of more channels into a SuperMUX (called TFS) is not in the standard, but may be added later.
System differences with DVB-T
The following table reports a comparison of available modes in DVB-T and DVB-T2.| DVB-T | DVB-T2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Error Correction Forward error correction In telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels.... (FEC) |
Convolutional Coding + Reed Solomon 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8 | LDPC + BCH 1/2, 3/5, 2/3, 3/4, 4/5, 5/6 |
| Modulations | QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM | QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM |
| Guard Interval Guard interval In telecommunications, guard intervals are used to ensure that distinct transmissions do not interfere with one another. These transmissions may belong to different users or to the same user .... |
1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32 | 1/4, 19/256, 1/8, 19/128, 1/16, 1/32, 1/128 |
| Discrete Fourier transform Discrete Fourier transform In mathematics, the discrete Fourier transform is a specific kind of discrete transform, used in Fourier analysis. It transforms one function into another, which is called the frequency domain representation, or simply the DFT, of the original function... (DFT) size |
2k, 8k | 1k, 2k, 4k, 8k, 16k, 32k |
| Scattered Pilot Pilot signal In telecommunications, a pilot is a signal, usually a single frequency, transmitted over a communications system for supervisory, control, equalization, continuity, synchronization, or reference purposes.... s |
8% of total | 1%, 2%, 4%, 8% of total |
| Continual Pilots | 2.6% of total | 0.35% of total |
For instance, a UK MFN DVB-T profile (64-QAM, 2k mode, coding rate 2/3, guard interval 1/32) and a DVB-T2 equivalent (256-QAM, 32k, coding rate 3/5, guard interval 1/128) allows for an increase in bit rate from 24.13 Mbit/s to 35.4 Mbit/s (+46.5%).
Another example, for an Italian SFN
Single-frequency network
A single-frequency network or SFN is a broadcast network where several transmitters simultaneously send the same signal over the same frequency channel.-Overview:...
DVB-T profile (64-QAM, 8k, coding rate 2/3, guard interval 1/4) and a DVB-T2 equivalent (256-QAM, 32k, coding rate 3/5, guard interval 1/16), achieves an increase in bit rate from 19.91 Mbit/s to 33.3 Mbit/s (+67%).
Technical details
The processing workflow is as follows:- Input pre-processing
- Physical Layer Pipe (PLP) creation: adaptation of Transport Stream (TS), Generic Stream Encapsulation (GSE), Generic Continuous Stream (GCS), or Generic Fixed-length Packetized Stream (GFPS)
- Input processing
- Mode adaptation
- Single PLP (mode 'A'): data are assembled in groups called BaseBand Frames (BBFRAMEs), with lengths of
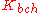 bits, defined by modulation and coding (MODCOD) parameters, in a 'normal' length or 'short' length version
bits, defined by modulation and coding (MODCOD) parameters, in a 'normal' length or 'short' length version
- Input interface
- CRC-8 encoding
- BaseBand (BB) header insertion
- Multiple PLPs (mode 'B')
- Input interface
- Input stream synchronization
- Delay compensation
- Null packets deletion
- CRC-8 encoding
- BB header insertion
- Single PLP (mode 'A'): data are assembled in groups called BaseBand Frames (BBFRAMEs), with lengths of
- Stream adaptation
- Single PLP (mode 'A')
- Padding insertion
- BB scrambling: a Pseudo Random Binary Sequence (PRBS) with generator
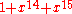 is used to scramble completely every BBFRAME
is used to scramble completely every BBFRAME
- Multiple PLPs (mode 'B')
- PLP scheduling
- Frame delay
- In-band signaling or padding insertion
- BB scrambling
- Single PLP (mode 'A')
- Mode adaptation
- Bit Interleaved Coding and Modulation (BICM)
- Forward Error Correction (FEC) encoding: each BBFRAME is converted into a FECFRAME of
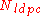 bits, by adding parity data. Normal FECFRAMEs are 64,800 bits long, whereas short FECFRAMEs are 16,200 bits long. The effective code rates are 32,208/64,800 (1/2), 38,688/64,800 (3/5), 43,040/64,800 (2/3), 48,408/64,800 (3/4), 51,648/64,800 (4/5), 53,840/64,800 (5/6)
bits, by adding parity data. Normal FECFRAMEs are 64,800 bits long, whereas short FECFRAMEs are 16,200 bits long. The effective code rates are 32,208/64,800 (1/2), 38,688/64,800 (3/5), 43,040/64,800 (2/3), 48,408/64,800 (3/4), 51,648/64,800 (4/5), 53,840/64,800 (5/6)
- Outer encoding: a BCH codeBCH codeIn coding theory the BCH codes form a class of parameterised error-correcting codes which have been the subject of much academic attention in the last fifty years. BCH codes were invented in 1959 by Hocquenghem, and independently in 1960 by Bose and Ray-Chaudhuri...
, capable to correct 10 or 12 errors per FECFRAME, is used to compute parity data for the information data field. The BCH generator polynomial is of the 160th, 168th, or 192nd grade - Inner encoding: a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code is cascaded to the BCH
- Outer encoding: a BCH code
- Bit interleaving
- Parity bits block interleaving
- Twist column interleaving
- Bit demultiplexing to cell words
- Gray mapping of cell words to constellations: either QPSK (4-QAM), 16-QAM, 64-QAM, or 256-QAM maps are used
- Constellation rotation and cyclic quadrature (Q) delay: optionally, the constellations may be tilted counterclockwise by an amount of up to 30 degrees. Furthermore, the quadrature (imaginary) part of the cells is cyclically shifted by one cell
- Cell interleaving
- Time interleaving
- Forward Error Correction (FEC) encoding: each BBFRAME is converted into a FECFRAME of
- Frame building: the transmitted stream is organized in super frames, which are composed by T2 frames and FEF (Future Extension Frame) parts
- Cell mapping: cells are mapped to OFDM symbols. A T2 frame is composed by a P1 symbol, one or more P2 symbols, regular data symbols, and a Frame Closing symbol (for certain configuration parameters). The P1 symbol is used for synchronization purposes, the P2 symbols convey L1 parameter configuration signaling, whereas the data symbols carry PLP data (there are three types: common PLPs, type 1 PLPs, and type 2 PLPs), auxiliary streams, and dummy symbols used as space filler
- Frequency interleaving: random interleaving is done on every OFDM symbol (except P1)
- OFDM generation
- Multiple-Input Single-Output (MISO) processing: Alamouti pre-processing is optionally applied to pairs of OFDM symbol cells. Given
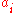 the input cells,
the input cells, 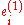 and
and 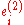 transmitter group 1 and 2 cells, the mapping is done as
transmitter group 1 and 2 cells, the mapping is done as 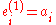 and
and  for group 1, and as
for group 1, and as 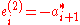 and
and 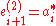 for group 2
for group 2 - Pilot insertion and dummy tone reservation: three classes of pilot tones are added. They are either continual (fixed position), scattered (cyclically moving position), or edge (boundary positions). There are 8 different configuration for scattered pilots (PP1 ... PP8). Moreover, a number of dummy carriers are not modulated and reserved to reduce the dynamic range of the DVB-T2 output signal (it helps to combat nonlinear phenomena in power amplifiers during broadcast).
- Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform (IDFT): classic IDFT is used to switch from the frequency domain into the time domain, after having adjusted carrier position relevant to the central transmit frequency. 1k (1024) to 32k (32768) carriers are available. There is also an extended mode, which allows to fill more data in the available bandwidth, using more active carriers and reducing the number of guard band (null) carriers.
- Peak-to-Average-Power-Ratio (PAPR) reduction
- Guard interval insertion: a cyclic prefix is inserted before the IDFT symbol, to recover from transmit channel echoes (multipath). Lengths from 1/128 to 1/4 of the IDFT length are allowed.
- P1 symbol insertion: the P1 symbol is a particularly crafted 1k OFDM symbol, always inserted at the head of a T2 frame. It conveys few bits of information (spread, scrambled and DBPSK modulated), as it is mainly dedicated to fast synchronization (both in time and in frequency) at the receiver side. It is prepended and postpended by frequency shifted repetitions of itself, to ease receiver lock even if the nominal center frequency of the T2 signal is up to 500 kHz off.
- Digital-to-Analog Conversion (DAC): the T2 samples are converted into an analog BB complex (I&Q) signal at a sample rate that depends on the channelization bandwidth. For instance, in 8 MHz wide channels, the complex sample time is 7/64 μs.
- Multiple-Input Single-Output (MISO) processing: Alamouti pre-processing is optionally applied to pairs of OFDM symbol cells. Given
Market adoption
When the digital terrestrial HDTV service Freeview HD was launched in December 2009, it was the first DVB-T2 service intended for the general public. As of November 2010, DVB-T2 broadcasts were available in a couple of European countries.The earliest introductions of T2 have usually been tied with a launch of high-definition television. There are however some countries where HDTV is broadcast using the old DVB-T standard with no immediate plans to switch those broadcasts to DVB-T2. Among countries using DVB-T for nationwide broadcasts of HDTV are France, Ireland, Italy, Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
and Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, though usually with MPEG4. Possibly only Australia is using DVB-T with MPEG2 for HD.
Countries where DVB-T2 is in use include:
- United Kingdom: one multiplex, soft launch in December 2009, full launch in April 2010
- ItalyItalyItaly , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
: one multiplex, soft launch in October 2010 - SwedenSwedenSweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
: two multiplexes, full launch in November 2010 - FinlandFinlandFinland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
: five multiplexes, soft launch in January 2011, full launch in February 2011 - Ukraine: four DVB-T2 multiplexes × 167 transmission sites, 150 of which have been officially launched on October 10, 2011
- DenmarkDenmarkDenmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
: one multiplex, with TV2 Danmark in HD will launch April 2012
The Southern African Development Community
Southern African Development Community
The Southern African Development Community is an inter-governmental organization headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana. Its goal is to further socio-economic cooperation and integration as well as political and security cooperation among 15 southern African states...
announced in November 2010 that DVB-T2 would be the preferred standard for the region. In Serbia, both SD and HD broadcasts will air in DVB-T2.
It has been trialled in Spain and Germany. Sri Lanka and Austria is also expected to use it.
Currently Malaysia, which has yet to officially launch its DVB-T transmission, is running tests on DVB-T2.. Whether the system will be adopted only for HD channels or will replace its existing trial DVB-T system, if adopted at all, remains unannounced.
UK
, in the UK terrestrial television system, there is only one multiplex (the slot corresponding to one channel in analog broadcasting and to many channels in digital broadcasting) assigned to digital broadcasting in the DVB-T2 standard. This multiplex is controlled by the service company Freeview HD, which has offered to host up to five DVB-T2 HD channels on it.Freeview HD started its "technical launch" on December 2, 2009, hosting BBC HD
BBC HD
BBC HD is a high-definition television network provided by the BBC. The service was initially run as a trial from 15 May 2006 until becoming a full service on 1 December 2007...
, and ITV1 HD. On March 30, 2010, Freeview HD had its official launch, and added Channel 4 HD to its broadcasts. The fourth channel hosted is BBC One HD
BBC One
BBC One is the flagship television channel of the British Broadcasting Corporation in the United Kingdom. It was launched on 2 November 1936 as the BBC Television Service, and was the world's first regular television service with a high level of image resolution...
, while as of March 2010 the remaining fifth slot is still to be assigned.
, Freeview covers 77% of UK population, and plans to finally reach 98.5% in 2012, following the region by region digital switchover all over the country.
A 5th HD channel looks likely to launch in April 2012. Public service broadcasters have been invited to apply for the fifth slot, the closing date for applications October 17, 2011: http://www.broadcastnow.co.uk/technology/fifth-dtt-hd-channel-to-launch-early-2012/5031537.article
Croatia
On October 13, 2011, the Croatian Post and Electronic Communications Agency (HAKOM) granted license for MUX C and MUX E, both in DVB-T2 standard.Also in October 2011 OiV - Transmitters & Communications started testing on UHF channel 53 from Sljeme and Zagreb - Prisavlje 3.
Italy
In Italy, Europa 7Europa 7
Europa 7 is an Italian production centre of television channels owned by Francesco Di Stefano. Europa 7 produces and runs TV syndication nationwide in Italy.-History:In 1997, Europa 7 attempted for the first time to broadcast nationwide...
obtained a national multiplex (the slot corresponging to one channel in analog broadcasting and to many channels in digital broadcasting) in spring 2010, and decided to use it for transmitting in DVB-T2. Europa 7 HD
Europa 7 HD
Europa 7 HD its an Italian group of channels aired since 11 October 2010. It's one of the first broadcasters in the world to use the DVB-T2 technology, after United Kingdom's channels BBC HD, ITV1 HD and Channel 4 HD.-Legal battle:...
was the name chosen to the offer of digital TV channels. Having a full multiplex for itself, Europa 7 HD hosts twelve alternating channels, of which eight in HD.
Europa 7 HD began testing broadcasts on July 2010, and started broadcasting from October 2010. While BBC, ITV1 and Channel 4 have only one or two of their channels in DVB-T2, Europa 7 HD transmits all of its channels with this technology; it has been announced as "the first broadcaster in the world to broadcast with this new technology."
Europa 7 HD is the first Italian broadcaster to adopt the DVB-T2 technology, and is doing so as an unilateral initialive, as there is not a general plan in Italy to adopt DVB-T2 for the other broadcasters. The two dominating broadcasters Rai (public) and Mediaset (private) still use DVB-T for their HDTV channels. Rai has planned some tests with DVB-T2, but has not a short-term plan for the general public to switch to DVB-T2, and the country is not yet fully switched from analog to DVB-T. Europa7 HD owner Francesco Di Stefano declared that all broadcasters will eventually have to move from T1 to T2, because of the higher quality.
Russia
In September 2011 Russian governmental authorities have approved the decision that since this date all newly built terrestrial digital TV networks will use the DVB-T2 standard. In some regions of Russia DVB-T/MPEG-4 networks (mostly consisting of one multiplex) have already been deployed before this decision was made.Serbia
On May 2009, the Serbian Ministry of Telecommunications and Information Society officially announced that the DVB-T2 standard will be the national digital terrestrial broadcasting standard for both SD and HD. Serbia has become one of the first countries to commit to the DVB-T2 standard. First public test with DVB-T2 signal in Serbia was during Telfor 2009 conference in Belgrade. Analog switch off has been planned for April 4, 2012. But it was postponed to 2013 or 2014.South Africa
On January 14, 2011, the South African Department of Communication officially announced that the DVB-T2 standard will be the national digital terrestrial broadcasting standard. Analog switch off has been planned for December 2013.Sweden
On June 17, 2010, the Swedish Radio and TV Authority and the Swedish Government granted a total of nine licenses to broadcast channels in HDTV spread over two multiplexes using DVB-T2.Broadcasts started on November 1, 2010, with five channels available initially: SVT1 HD, SVT2 HD, MTVN HD, National Geographic HD and Canal+ Sport HD
Canal+ Sport HD
Canal+ Sport HD is a premium high-definition television channel owned by C More Entertainment, which is a part of TV4 AB. It broadcasts sports in high definition....
. From this date a coverage of 70% of the population is achieved, with 90% expected by mid 2011 and nationwide coverage by 2012.
Turkey
Turkish Radio and Television CorporationTurkish Radio and Television Corporation
The Turkish Radio and Television Corporation, also known as TRT , is the national public broadcaster of Turkey and was founded in 1964. Around 70% of TRT's funding comes from a tax levied on electricity bills and a sales tax on television and radio receivers...
(TRT) is testing TRT HD
TRT HD
TRT HD is the second High definition channel of TRT after TRT 3 HD. It was launched on 24 May 2010. It broadcasts events such as the Eurovision Song Contest in HD....
in Ankara
Ankara
Ankara is the capital of Turkey and the country's second largest city after Istanbul. The city has a mean elevation of , and as of 2010 the metropolitan area in the entire Ankara Province had a population of 4.4 million....
-Dikmen UHF channel 31.
Ukraine
Ukraine's national terrestrial TV network (built and maintained by the Zeonbud company) uses the DVB-T2 standard for all four nationwide FTAFree-to-air
Free-to-air describes television and radio services broadcast in clear form, allowing any person with the appropriate receiving equipment to receive the signal and view or listen to the content without requiring a subscription or one-off fee...
multiplexes, for both SD and HD broadcasts. Before settling for DVB-T2, Ukraine was testing both DVB-T/MPEG-2 and DVB-T/MPEG-4 options, and some experimental transmitters operating in those standards are still live. Ukraine has never had a full-fledged nationwide DVB-T network, thus not having to do a DVB-T-to-DVB-T2 migration.
Zeonbud's network consists of 167 transmitter sites, each carrying four DVB-T2 multiplexes, with transmitter power ranging from 2 kW to 50 W (all in in MFN
Multi-frequency network
-Introduction:Data networks, such as wireless communication networks, have to trade off between services customized for a single terminal and services provided to a large number of terminals. For example, the distribution of multimedia content to a large number of resource limited portable devices ...
mode). As of October 10, 2011, 150 of the 167 transmitter sites have officially gone live. The biggest problem of Ukraine's DVB-T2 rollout for now is the acute shortage of inexpensive DVB-T2 set-top-boxes.
The four multiplexes carry in total 28 nationwide channels (same for all transmitter sites, distributed via satellite) and 4 local channels. Up to 8 of those 28 nationwide channels can broadcast in HD format.

