Pilot signal
Encyclopedia
In telecommunication
s, a pilot is a signal, usually a single frequency
, transmitted over a communications system
for supervisory, control, equalization
, continuity, synchronization
, or reference
purposes.
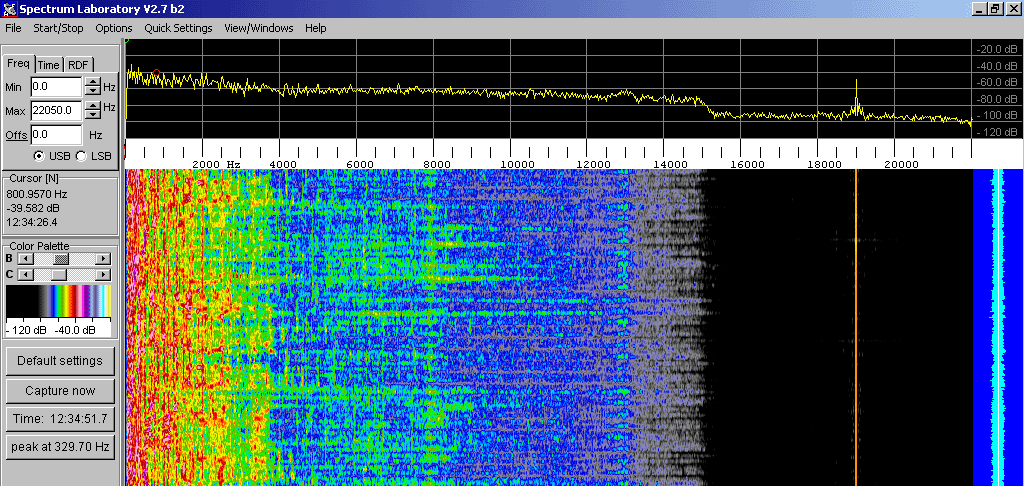 In FM stereo broadcasting
In FM stereo broadcasting
, a pilot tone of 19 kHz indicates that there is stereophonic information at 38 kHz (19×2, the second harmonic
of the pilot). The receiver doubles the frequency of the pilot tone and uses it as a phase reference to demodulate the stereo information.
If no 19 kHz pilot tone is present, then any signals in the 25-53 kHz range are ignored by a stereo receiver. A guard band
of ±4 kHz (15-23 kHz) protects the pilot tone from interference
from the baseband
audio
signal (50 Hz-15 kHz) and from the lower sideband
of the double sideband stereo information (23-53 kHz). The third harmonic of the pilot (19×3, or 57 kHz) is used for Radio Data System
.
In AM stereo
, the bandwidth is too narrow
to accommodate subcarriers, so the modulation
itself is changed, and the pilot tone is infrasonic
(below the normal hearing
range, instead of above it).
In color television
, the color burst placed between each video field is the pilot signal to indicate that there are color subcarriers present.
In the NTSC
television system, a pilot tone of 15.734 kHz is used to indicate the presence of MTS
stereo.
In some analog video formats (Frequency modulation is the standard method for recording the luminance part of the signal, and is used to record a composite video signal in Direct colour systems), e.g. Video 2000
and some Hi-band formats a pilot tone is added to the signal to detect and correct timebase errors
.
Note: Sometimes it is necessary to employ several independent pilot frequencies. Most radio relay
systems use radio or continuity pilots of their own but transmit also the pilot frequencies belonging to the carrier frequency
multiplex system.
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
s, a pilot is a signal, usually a single frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, transmitted over a communications system
Communications system
In telecommunication, a communications system is a collection of individual communications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and data terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole...
for supervisory, control, equalization
Equalization
Equalization, is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used...
, continuity, synchronization
Synchronization
Synchronization is timekeeping which requires the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. The familiar conductor of an orchestra serves to keep the orchestra in time....
, or reference
Reference
Reference is derived from Middle English referren, from Middle French rèférer, from Latin referre, "to carry back", formed from the prefix re- and ferre, "to bear"...
purposes.

Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio and video content to a dispersed audience via any audio visual medium. Receiving parties may include the general public or a relatively large subset of thereof...
, a pilot tone of 19 kHz indicates that there is stereophonic information at 38 kHz (19×2, the second harmonic
Harmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
of the pilot). The receiver doubles the frequency of the pilot tone and uses it as a phase reference to demodulate the stereo information.
If no 19 kHz pilot tone is present, then any signals in the 25-53 kHz range are ignored by a stereo receiver. A guard band
Guard band
-Radio and electronic signalling:In radio, a guard band is an unused part of the radio spectrum between radio bands, for the purpose of preventing interference....
of ±4 kHz (15-23 kHz) protects the pilot tone from interference
Adjacent-channel interference
Adjacent-channel interference is interference caused by extraneous power from a signal in an adjacent channel. ACI may be caused by inadequate filtering , improper tuning or poor frequency control .ACI is distinguished from crosstalk.Broadcast...
from the baseband
Baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is an adjective that describes signals and systems whose range of frequencies is measured from close to 0 hertz to a cut-off frequency, a maximum bandwidth or highest signal frequency; it is sometimes used as a noun for a band of frequencies...
audio
Audio frequency
An audio frequency or audible frequency is characterized as a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human...
signal (50 Hz-15 kHz) and from the lower sideband
Sideband
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, containing power as a result of the modulation process. The sidebands consist of all the Fourier components of the modulated signal except the carrier...
of the double sideband stereo information (23-53 kHz). The third harmonic of the pilot (19×3, or 57 kHz) is used for Radio Data System
Radio Data System
Radio Data System, or RDS, is a communications protocol standard for embedding small amounts of digital information in conventional FM radio broadcasts. RDS standardises several types of information transmitted, including time, station identification and programme information.Radio Broadcast Data...
.
In AM stereo
AM stereo
AM stereo is a term given to a series of mutually incompatible techniques for wireless radio broadcasting stereo audio in the AM band in a manner that is compatible with standard AM receivers...
, the bandwidth is too narrow
Narrowband
In radio, narrowband describes a channel in which the bandwidth of the message does not significantly exceed the channel's coherence bandwidth. It is a common misconception that narrowband refers to a channel which occupies only a "small" amount of space on the radio spectrum.The opposite of...
to accommodate subcarriers, so the modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
itself is changed, and the pilot tone is infrasonic
Infrasound
Infrasound is sound that is lower in frequency than 20 Hz or cycles per second, the "normal" limit of human hearing. Hearing becomes gradually less sensitive as frequency decreases, so for humans to perceive infrasound, the sound pressure must be sufficiently high...
(below the normal hearing
Hearing (sense)
Hearing is the ability to perceive sound by detecting vibrations through an organ such as the ear. It is one of the traditional five senses...
range, instead of above it).
In color television
Color television
Color television is part of the history of television, the technology of television and practices associated with television's transmission of moving images in color video....
, the color burst placed between each video field is the pilot signal to indicate that there are color subcarriers present.
In the NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
television system, a pilot tone of 15.734 kHz is used to indicate the presence of MTS
Multichannel television sound
Multichannel television sound, better known as MTS , is the method of encoding three additional channels of audio into an NTSC-format audio carrier.- History :...
stereo.
In some analog video formats (Frequency modulation is the standard method for recording the luminance part of the signal, and is used to record a composite video signal in Direct colour systems), e.g. Video 2000
Video 2000
Video 2000 was a consumer videocassette recorder system and analog recording videocassette standard developed by Philips and Grundig to compete with JVC's VHS and Sony's Betamax video technologies...
and some Hi-band formats a pilot tone is added to the signal to detect and correct timebase errors
Timebase correction
Time base correction is a technique to reduce or eliminate errors caused by mechanical instability present in analog recordings on mechanical media. Without time base correction, a signal from a videotape recorder or videocassette recorder cannot be mixed with other, more time stable devices...
.
Note: Sometimes it is necessary to employ several independent pilot frequencies. Most radio relay
Radio relay
Radio stations that cannot communicate directly due to distance, terrain or other difficulties sometimes use an intermediate radio relay station to relay the signals. Examples include airborne radio relay, microwave radio relay, and communications satellite...
systems use radio or continuity pilots of their own but transmit also the pilot frequencies belonging to the carrier frequency
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
multiplex system.

