
Cyclotron radiation
Encyclopedia
Cyclotron radiation is electromagnetic radiation
emitted by moving charge
d particles deflected by a magnetic field
. The Lorentz force
on the particles acts perpendicular to both the magnetic field lines and the particles' motion through them, creating an acceleration of charged particles that causes them to emit radiation (and to spiral around the magnetic field lines).
The name of this radiation derives from the cyclotron
, a type of particle accelerator
used since the 1930s to create highly energetic particles for study. The cyclotron makes use of the circular orbits that charged particles exhibit in a uniform magnetic field. Furthermore, the period of the orbit is independent of the energy of the particles, allowing the cyclotron to operate at a set frequency
, and not worry about the energy of the particles at a given time. Cyclotron radiation is emitted by all charged particles travelling through magnetic fields, however, not just those in cyclotrons. Cyclotron radiation from plasma
in the interstellar medium
or around black hole
s and other astronomical phenomena is an important source of information about distant magnetic fields. The power
(energy per unit time) of the emission of each electron can be calculated using:
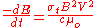
where E is energy, t is time,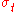 is the Thomson cross section (total, not differential), B is the magnetic field strength, V is the velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field, c is the speed of light and
is the Thomson cross section (total, not differential), B is the magnetic field strength, V is the velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field, c is the speed of light and 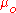 is the permeability of free space. In the context of magnetic fusion energy, cyclotron radiation losses translate into a requirement for a minimum plasma energy density in relation to the magnetic field energy density (see Aneutronic fusion#Power density and energy balance).
is the permeability of free space. In the context of magnetic fusion energy, cyclotron radiation losses translate into a requirement for a minimum plasma energy density in relation to the magnetic field energy density (see Aneutronic fusion#Power density and energy balance).
Cyclotron radiation would likely be produced in a high altitude nuclear explosion. Gamma ray
s produced by the explosion would ionize
atom
s in the upper atmosphere and those free electrons would interact with the Earth's magnetic field to produce cyclotron radiation in the form of an electromagnetic pulse
(EMP). This phenomenon is of concern to the military as the EMP may damage solid state equipment.
Cyclotron radiation has a spectrum with its main spike at the
same fundamental frequency as the particle's orbit, and harmonic
s at higher integral factors. Harmonics are the result of imperfections in the actual emission environment, which also create a broadening of the spectral line
s. The most obvious source of line broadening is non-uniformities in the magnetic field; as an electron passes
from one area of the field to another, its emission frequency will change with the strength of the field. Other sources of broadening include collisional broadening from the electron failing to follow a perfect orbit, distortions of the emission caused by interactions with the surrounding plasma, and relativistic
effects if the charged particles are sufficiently energetic. When the electrons are moving at relativistic speeds, cyclotron radiation is known as synchrotron radiation
.
The recoil experienced by a particle emitting cyclotron radiation is called radiation reaction. Radiation reaction acts as a resistance to motion in a cyclotron; and the work necessary to overcome it is the main energetic cost of accelerating a particle in a cyclotron. Cyclotrons are prime examples of systems which experience radiation reaction.
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
emitted by moving charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
d particles deflected by a magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
. The Lorentz force
Lorentz force
In physics, the Lorentz force is the force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields. It is given by the following equation in terms of the electric and magnetic fields:...
on the particles acts perpendicular to both the magnetic field lines and the particles' motion through them, creating an acceleration of charged particles that causes them to emit radiation (and to spiral around the magnetic field lines).
The name of this radiation derives from the cyclotron
Cyclotron
In technology, a cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator. In physics, the cyclotron frequency or gyrofrequency is the frequency of a charged particle moving perpendicularly to the direction of a uniform magnetic field, i.e. a magnetic field of constant magnitude and direction...
, a type of particle accelerator
Particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and to contain them in well-defined beams. An ordinary CRT television set is a simple form of accelerator. There are two basic types: electrostatic and oscillating field accelerators.In...
used since the 1930s to create highly energetic particles for study. The cyclotron makes use of the circular orbits that charged particles exhibit in a uniform magnetic field. Furthermore, the period of the orbit is independent of the energy of the particles, allowing the cyclotron to operate at a set frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, and not worry about the energy of the particles at a given time. Cyclotron radiation is emitted by all charged particles travelling through magnetic fields, however, not just those in cyclotrons. Cyclotron radiation from plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
in the interstellar medium
Interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter that exists in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, dust, and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space...
or around black hole
Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that...
s and other astronomical phenomena is an important source of information about distant magnetic fields. The power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
(energy per unit time) of the emission of each electron can be calculated using:
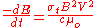
where E is energy, t is time,
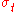 is the Thomson cross section (total, not differential), B is the magnetic field strength, V is the velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field, c is the speed of light and
is the Thomson cross section (total, not differential), B is the magnetic field strength, V is the velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field, c is the speed of light and 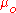 is the permeability of free space. In the context of magnetic fusion energy, cyclotron radiation losses translate into a requirement for a minimum plasma energy density in relation to the magnetic field energy density (see Aneutronic fusion#Power density and energy balance).
is the permeability of free space. In the context of magnetic fusion energy, cyclotron radiation losses translate into a requirement for a minimum plasma energy density in relation to the magnetic field energy density (see Aneutronic fusion#Power density and energy balance).Cyclotron radiation would likely be produced in a high altitude nuclear explosion. Gamma ray
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
s produced by the explosion would ionize
Ionization
Ionization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s in the upper atmosphere and those free electrons would interact with the Earth's magnetic field to produce cyclotron radiation in the form of an electromagnetic pulse
Electromagnetic pulse
An electromagnetic pulse is a burst of electromagnetic radiation. The abrupt pulse of electromagnetic radiation usually results from certain types of high energy explosions, especially a nuclear explosion, or from a suddenly fluctuating magnetic field...
(EMP). This phenomenon is of concern to the military as the EMP may damage solid state equipment.
Cyclotron radiation has a spectrum with its main spike at the
same fundamental frequency as the particle's orbit, and harmonic
Harmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
s at higher integral factors. Harmonics are the result of imperfections in the actual emission environment, which also create a broadening of the spectral line
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
s. The most obvious source of line broadening is non-uniformities in the magnetic field; as an electron passes
from one area of the field to another, its emission frequency will change with the strength of the field. Other sources of broadening include collisional broadening from the electron failing to follow a perfect orbit, distortions of the emission caused by interactions with the surrounding plasma, and relativistic
Special relativity
Special relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
effects if the charged particles are sufficiently energetic. When the electrons are moving at relativistic speeds, cyclotron radiation is known as synchrotron radiation
Synchrotron radiation
The electromagnetic radiation emitted when charged particles are accelerated radially is called synchrotron radiation. It is produced in synchrotrons using bending magnets, undulators and/or wigglers...
.
The recoil experienced by a particle emitting cyclotron radiation is called radiation reaction. Radiation reaction acts as a resistance to motion in a cyclotron; and the work necessary to overcome it is the main energetic cost of accelerating a particle in a cyclotron. Cyclotrons are prime examples of systems which experience radiation reaction.
See also
- Auroral kilometric radiationAuroral kilometric radiationAuroral kilometric radiation is the intense radio radiation emitted in the acceleration zone of the polar lights. The radiation mainly comes from cyclotron radiation from electrons orbiting around the magnetic field lines of the Earth...
(AKR) - BremsstrahlungBremsstrahlungBremsstrahlung is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon because energy is conserved. The term is...
- Free electron laserFree electron laserA free-electron laser, or FEL, is a laser that shares the same optical properties as conventional lasers such as emitting a beam consisting of coherent electromagnetic radiation which can reach high power, but which uses some very different operating principles to form the beam...
- Larmor formulaLarmor formulaIn physics, in the area of electrodynamics, the Larmor formula is used to calculate the total power radiated by a nonrelativistic point charge as it accelerates. It was first derived by J. J...

