
Countersink
Encyclopedia
A countersink is a conical
hole cut into a manufactured object, or the cutter used to cut such a hole. A common usage is to allow the head of a countersunk bolt or screw, when placed in the hole, to sit flush with or below the surface of the surrounding material. (By comparison, a counterbore
makes a flat-bottomed hole that might be used with a hex-headed capscrew.) A countersink may also be used to remove the burr left from a drilling or tapping
operation thereby improving the finish of the product and removing any hazardous sharp edges.
The basic geometry of a countersink (cutter) inherently can be applied to the plunging applications described above (axial feed only) and also to other milling applications (sideways traversal). Therefore countersinks overlap in form, function, and sometimes name with chamfering endmills (endmill
s with angled tips). Regardless of the name given to the cutter, the surface being generated may be a conical chamfer (plunging applications) or a beveled corner for the intersection of two planes (traversing applications).
s, drill presses, milling machine
s, and lathe
s.
 A cross-hole countersink is a cone-shaped tool with a cutting edge provided by a hole that goes through the side of the cone. The intersection of the hole and cone form the cutting edge on the tool. The cone is not truly symmetrical as it is essential that the cone retreats away from the cutting edge as the tool rotates. If this does not occur the cutting edge will lack clearance and rub rather than bite into the material. This clearance is referred to as cutting relief.
A cross-hole countersink is a cone-shaped tool with a cutting edge provided by a hole that goes through the side of the cone. The intersection of the hole and cone form the cutting edge on the tool. The cone is not truly symmetrical as it is essential that the cone retreats away from the cutting edge as the tool rotates. If this does not occur the cutting edge will lack clearance and rub rather than bite into the material. This clearance is referred to as cutting relief.
These tools are best used as deburring tools, where the burr from a previous machining operation needs to be removed for cosmetic and safety reasons, however they may be used in softer materials (such as wood or plastic) to create a countersunk hole for a screw.
 The fluted countersink cutter is used to provide a heavy chamfer
The fluted countersink cutter is used to provide a heavy chamfer
in the entrance to a drilled hole. This may be required to allow the correct seating for a countersunk-head screw or to provide the lead in for a second machining operation such as tapping
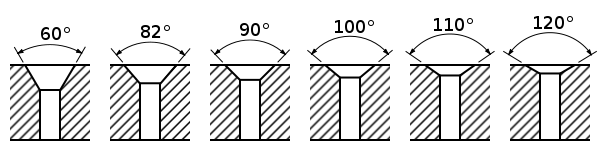
. Countersink cutters are manufactured with six common angles, which are 60°, 82°, 90°, 100°, 110°, or 120°, with the two most common of those being 82° and 90°. Countersunk-head screws that follow the Unified Thread Standard
very often have an 82° angle, and screws that follow the ISO standard
very often have a 90° angle. Throughout the aerospace industry, countersunk fasteners typically have an angle of 100°.
painstakingly).
action and leaving an undulated surface. This surface ripple is also dependent on the surface speed of the cutting edges, material type, and applied pressure (or feed rate); once started it is hard to remove. Too light a feed tends to increase chatter risk. As in many other machining operations, an appropriate response to the chatter may be to decrease speed and increase feed. On a drill press, the slowest available spindle speed is usually best. With a variable-speed handheld power drill, the trigger is best squeezed lightly to yield a low spindle speed.
Very good chatter-free results can usually be had by countersinking by hand (as opposed to running the tool in a powered spindle). The slow speed and sensitive feed tend to obviate chatter. With a quarter-inch-hex shank, the countersink cutter can be held with a screwdriver handle of the indexable-bit type.
to increase the strength of a structure as the countersinks of multiple pieces nest together. There are two processes for producing formed countersinks: coin dimpling and modified radius dimpling. Such dimples in fairly thick sheet can even be tapped to yield a threaded hardpoint
on the sheet without the bother and expense of welding a nut
to the sheet. This style of construction is often seen in modern household appliance design, because it allows the product to be lower-priced, and the quality can still be good as long as the sheet is thick enough.
Cone (geometry)
A cone is an n-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a base to a point called the apex or vertex. Formally, it is the solid figure formed by the locus of all straight line segments that join the apex to the base...
hole cut into a manufactured object, or the cutter used to cut such a hole. A common usage is to allow the head of a countersunk bolt or screw, when placed in the hole, to sit flush with or below the surface of the surrounding material. (By comparison, a counterbore
Counterbore
A counterbore can refer to a cylindrical flat-bottomed hole, which enlarges another hole, or the tool used to create that feature. A spot face is a very shallow counterbore...
makes a flat-bottomed hole that might be used with a hex-headed capscrew.) A countersink may also be used to remove the burr left from a drilling or tapping
Taps and dies
Taps and dies are cutting tools used to create screw threads, which is called threading. A tap is used to cut the female portion of the mating pair . A die is used to cut the male portion of the mating pair . The process of cutting threads using a tap is called tapping, whereas the process using a...
operation thereby improving the finish of the product and removing any hazardous sharp edges.
The basic geometry of a countersink (cutter) inherently can be applied to the plunging applications described above (axial feed only) and also to other milling applications (sideways traversal). Therefore countersinks overlap in form, function, and sometimes name with chamfering endmills (endmill
Endmill
An endmill is a type of milling cutter, a cutting tool used in industrial milling applications. It is distinguished from the drill bit, in its application, geometry, and manufacture...
s with angled tips). Regardless of the name given to the cutter, the surface being generated may be a conical chamfer (plunging applications) or a beveled corner for the intersection of two planes (traversing applications).

Types
| Type of Thread | Normal CS Angle |
|---|---|
| ISO Metric ISO metric screw thread The ISO metric screw threads are the world-wide most commonly used type of general-purpose screw thread. They were one of the first international standards agreed when the International Organization for Standardization was set up in 1947.-Basic profile:... |
90° |
| Imperial BA British Association screw threads British Association or BA screw threads are a largely obsolete set of small screw threads, the largest being 0BA at 6 mm diameter. They were, and to some extent still are, used for miniature instruments and modelling.... , BSF, BSW etc |
90° |
| UNC, UNF Unified Thread Standard The Unified Thread Standard defines a standard thread form and series—along with allowances, tolerances, and designations—for screw threads commonly used in the United States and Canada... |
82° |
| Aviation fasteners | 100° |
Machining
A countersink may be used in many tools, such as drillDrill
A drill or drill motor is a tool fitted with a cutting tool attachment or driving tool attachment, usually a drill bit or driver bit, used for drilling holes in various materials or fastening various materials together with the use of fasteners. The attachment is gripped by a chuck at one end of...
s, drill presses, milling machine
Milling machine
A milling machine is a machine tool used to machine solid materials. Milling machines are often classed in two basic forms, horizontal and vertical, which refers to the orientation of the main spindle. Both types range in size from small, bench-mounted devices to room-sized machines...
s, and lathe
Lathe
A lathe is a machine tool which rotates the workpiece on its axis to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, or deformation with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object which has symmetry about an axis of rotation.Lathes are used in woodturning,...
s.
Cross-hole countersink cutter

These tools are best used as deburring tools, where the burr from a previous machining operation needs to be removed for cosmetic and safety reasons, however they may be used in softer materials (such as wood or plastic) to create a countersunk hole for a screw.
Fluted countersink cutter

Chamfer
A chamfer is a beveled edge connecting two surfaces. If the surfaces are at right angles, the chamfer will typically be symmetrical at 45 degrees. A fillet is the rounding off of an interior corner. A rounding of an exterior corner is called a "round" or a "radius"."Chamfer" is a term commonly...
in the entrance to a drilled hole. This may be required to allow the correct seating for a countersunk-head screw or to provide the lead in for a second machining operation such as tapping
Taps and dies
Taps and dies are cutting tools used to create screw threads, which is called threading. A tap is used to cut the female portion of the mating pair . A die is used to cut the male portion of the mating pair . The process of cutting threads using a tap is called tapping, whereas the process using a...
. Countersink cutters are manufactured with six common angles, which are 60°, 82°, 90°, 100°, 110°, or 120°, with the two most common of those being 82° and 90°. Countersunk-head screws that follow the Unified Thread Standard
Unified Thread Standard
The Unified Thread Standard defines a standard thread form and series—along with allowances, tolerances, and designations—for screw threads commonly used in the United States and Canada...
very often have an 82° angle, and screws that follow the ISO standard
ISO metric screw thread
The ISO metric screw threads are the world-wide most commonly used type of general-purpose screw thread. They were one of the first international standards agreed when the International Organization for Standardization was set up in 1947.-Basic profile:...
very often have a 90° angle. Throughout the aerospace industry, countersunk fasteners typically have an angle of 100°.
Back countersink
A back countersink, also known as an inserted countersink, is a two piece countersink used on tough to reach areas. One component is a rod that is inserted into the existing hole in the workpieces; the other component is the cutter, which is attached to the rod, or extends out of it, after it is in position. This is comparable to other types of "back-" machining, such as back-spotfacing, back-boring, back-counterboring, back-milling, and back-deburring. The common theme is accomplishing machining operations on the far side of the workpiece from the spindle face, which obviates a "second operation" setup. This reduces setup time and frustration in several ways. Not only does it obviate the flipping over, cleaning, reclamping, etc, but it also can allow effortless high concentricity, parallelism, and squareness with the first setup's datum without the hassle of reestablishing it on another setup (via indicatingDial indicator
Dial indicators, also known as dial gauges and probe indicators, are instruments used to accurately measure small linear distances, and are frequently used in industrial and mechanical processes...
painstakingly).
Speeds, feeds, and avoiding chatter
It can often be difficult to avoid chatter when cutting with countersink cutters. As usual in machining, the shorter and more rigid the setup, the better. Better-quality fluted countersink cutters sometimes have the flutes (or at least one flute) at an irregular pitching. This variation in pitching reduces the chance of the cutting edges setting up a harmonicHarmonic
A harmonic of a wave is a component frequency of the signal that is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency, i.e. if the fundamental frequency is f, the harmonics have frequencies 2f, 3f, 4f, . . . etc. The harmonics have the property that they are all periodic at the fundamental...
action and leaving an undulated surface. This surface ripple is also dependent on the surface speed of the cutting edges, material type, and applied pressure (or feed rate); once started it is hard to remove. Too light a feed tends to increase chatter risk. As in many other machining operations, an appropriate response to the chatter may be to decrease speed and increase feed. On a drill press, the slowest available spindle speed is usually best. With a variable-speed handheld power drill, the trigger is best squeezed lightly to yield a low spindle speed.
Very good chatter-free results can usually be had by countersinking by hand (as opposed to running the tool in a powered spindle). The slow speed and sensitive feed tend to obviate chatter. With a quarter-inch-hex shank, the countersink cutter can be held with a screwdriver handle of the indexable-bit type.
Form countersinking
Form countersinking, also known as dimpling, is a countersink that is formed into sheet metalSheet metal
Sheet metal is simply metal formed into thin and flat pieces. It is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking, and can be cut and bent into a variety of different shapes. Countless everyday objects are constructed of the material...
to increase the strength of a structure as the countersinks of multiple pieces nest together. There are two processes for producing formed countersinks: coin dimpling and modified radius dimpling. Such dimples in fairly thick sheet can even be tapped to yield a threaded hardpoint
Hardpoint
A hardpoint, or weapon station, is any part of an airframe designed to carry an external load. This includes a point on the wing or fuselage of military aircraft where external ordnance, countermeasures, gun pods, targeting pods or drop tanks can be mounted.-Rail launchers:Large missiles and...
on the sheet without the bother and expense of welding a nut
Nut (hardware)
A nut is a type of hardware fastener with a threaded hole. Nuts are almost always used opposite a mating bolt to fasten a stack of parts together. The two partners are kept together by a combination of their threads' friction, a slight stretch of the bolt, and compression of the parts...
to the sheet. This style of construction is often seen in modern household appliance design, because it allows the product to be lower-priced, and the quality can still be good as long as the sheet is thick enough.

