
Charlotte Forten Grimké
Encyclopedia

Poet
A poet is a person who writes poetry. A poet's work can be literal, meaning that his work is derived from a specific event, or metaphorical, meaning that his work can take on many meanings and forms. Poets have existed since antiquity, in nearly all languages, and have produced works that vary...
, and educator.
Biography
Forten was born in PhiladelphiaPhiladelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Philadelphia County, with which it is coterminous. The city is located in the Northeastern United States along the Delaware and Schuylkill rivers. It is the fifth-most-populous city in the United States,...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
to Mary Woods and Robert Bridges Forten, members of the prominent black Forten-Purvis families of Philadelphia. Robert Forten and his brother-in-law Robert Purvis
Robert Purvis
Robert Purvis was an African-American abolitionist in the United States. He was born in Charleston, South Carolina, educated at Amherst College, and lived most of his life in Philadelphia. Purvis and his brothers were three-quarters European by ancestry and inherited considerable wealth from...
were abolitionists and members of the Philadelphia Vigilant Committee, an anti-slavery network that rendered assistance to escaped slaves. Forten's paternal aunt Margaretta Forten worked in the Philadelphia Female Anti-Slavery Society along with her sisters Harriet Forten Purvis and Sarah Louisa Forten Purvis. Forten's grandparents were Philadelphia abolitionists James Forten
James Forten
James Forten was an African-American abolitionist and wealthy businessman. He worked at many jobs, including dentist, carpenter, pastor and minuteman....
, Sr. and his wife Charlotte Vandine Forten, who were also active in the Philadelphia Female Anti-Slavery Society.
In 1854, Forten attended the Higginson Grammar School in Salem
Salem, Massachusetts
Salem is a city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 40,407 at the 2000 census. It and Lawrence are the county seats of Essex County...
, Massachusetts
Massachusetts
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States of America. It is bordered by Rhode Island and Connecticut to the south, New York to the west, and Vermont and New Hampshire to the north; at its east lies the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2010...
. She was the only non-white student in a class of 200. Known for emphasis in critical thinking, the school focused classes on history, geography, drawing and cartography. After Higginson, Forten studied literature and teaching at the Salem Normal School. Forten cited William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon"...
, John Milton
John Milton
John Milton was an English poet, polemicist, a scholarly man of letters, and a civil servant for the Commonwealth of England under Oliver Cromwell...
, Margaret Fuller
Margaret Fuller
Sarah Margaret Fuller Ossoli, commonly known as Margaret Fuller, was an American journalist, critic, and women's rights advocate associated with the American transcendentalism movement. She was the first full-time American female book reviewer in journalism...
and William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth was a major English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with the 1798 joint publication Lyrical Ballads....
as some of her favorite authors.
Forten became a member of the Salem Female Anti-Slavery Society
Anti-Slavery Society
The Anti-Slavery Society or A.S.S. was the everyday name of two different British organizations.The first was founded in 1823 and was committed to the abolition of slavery in the British Empire. Its official name was the Society for the Mitigation and Gradual Abolition of Slavery Throughout the...
, where she was involved in coalition building and money-raising. She proved to be influential as an activist and leader on civil rights. She occasionally spoke to public groups on abolitionist issues. In addition, she arranged for lectures by prominent speakers and writers, including Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson was an American essayist, lecturer, and poet, who led the Transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century...
and Senator Charles Sumner
Charles Sumner
Charles Sumner was an American politician and senator from Massachusetts. An academic lawyer and a powerful orator, Sumner was the leader of the antislavery forces in Massachusetts and a leader of the Radical Republicans in the United States Senate during the American Civil War and Reconstruction,...
. Forten was acquainted with many other anti-slavery proponents, including William Lloyd Garrison
William Lloyd Garrison
William Lloyd Garrison was a prominent American abolitionist, journalist, and social reformer. He is best known as the editor of the abolitionist newspaper The Liberator, and as one of the founders of the American Anti-Slavery Society, he promoted "immediate emancipation" of slaves in the United...
, editor of The Liberator, and the orators and activists Wendell Phillips
Wendell Phillips
Wendell Phillips was an American abolitionist, advocate for Native Americans, and orator. He was an exceptional orator and agitator, advocate and lawyer, writer and debater.-Education:...
, Maria Weston Chapman
Maria Weston Chapman
Maria Weston or Maria Weston Chapman was an American abolitionist. She was elected to the executive committee of the American Anti-Slavery Society in 1839 and from 1839 until 1842, she served as editor of the anti-slavery journal, Non-Resistant.-Family:Weston was born in 1806 in Weymouth,...
and William Wells Brown
William Wells Brown
William Wells Brown was a prominent African-American abolitionist lecturer, novelist, playwright, and historian. Born into slavery in the Southern United States, Brown escaped to the North in 1834, where he worked for abolitionist causes and was a prolific writer...
.
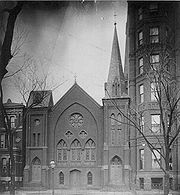
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body...
. At this point, Forten began writing poetry, much of which was activist in theme. Her work was published in The Liberator and Anglo African magazines.
Forten was the first black teacher to join the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
's Sea Islands mission. During her time in South Carolina
South Carolina
South Carolina is a state in the Deep South of the United States that borders Georgia to the south, North Carolina to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Originally part of the Province of Carolina, the Province of South Carolina was one of the 13 colonies that declared independence...
, she worked with many former slaves who were enthusiastic about her teaching. She chronicled this time in her essays titled, "Life on the Sea Islands", which were published in the Atlantic Monthly in the May and June issues of 1864. Forten struck up a deep friendship with Robert Gould Shaw, the Commander of the all black 54th Massachusetts Regiment during the Sea Islands Campaign and was present when the 54th stormed Fort Wagner on the night of July 18, 1863. Shaw was killed in the battle and Forten volunteered as a nurse to the surviving members of the 54th. In the late 1860s, Forten worked for the U.S. Treasury Department in Washington, DC recruiting teachers. In 1873 she became a clerk at the Treasury Department.
In December 1878, when Forten was 41, she married Presbyterian minister Francis J. Grimké
Francis J. Grimké
Francis James Grimké was a Presbyterian minister who was prominent in working for equal rights for African Americans...
, the nephew of abolitionists Sarah and Angelina Grimké
Grimké sisters
Sarah Grimké and Angelina Grimké , known as the Grimké sisters, were 19th-century American Quakers, educators and writers who were early advocates of abolitionism and women's rights....
. Francis J. Grimké was also the brother of Archibald Grimké
Archibald Grimke
Archibald Henry Grimké was an American lawyer, intellectual, journalist, diplomat and community leader in the 19th and early 20th century...
, who served as U.S. consul in the Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
from 1894-1898. While her father served in the Dominican Republic, Angelina Grimké lived with Charlotte and Francis Grimke. Angelina Weld Grimké
Angelina Weld Grimke
Angelina Weld Grimké was an African-American journalist, teacher, playwright and poet who was part of the Harlem Renaissance and was one of the first African-American women to have a play performed.- Biography :...
later became an author in her own right.
In 1880, Charlotte and Francis Grimké's daughter Theodora Cornelia was born. She died as an infant.
Charlotte Forten Grimké helped her husband in his ministry at the Fifteenth Street Presbyterian Church in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
, organized a women's missionary group, and continued her "racial uplift" efforts.
Charlotte Forten Grimké's last literary effort was in response to an Evangelist editorial, "Relations of Blacks and Whites: Is There a Color Line in New England?" It asserted that blacks were not discriminated against in New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
society. Forten Grimké stated that black Americans achieved success over extraordinary social odds, and they simply wanted fair and respectful treatment.
Charlotte Forten Grimké was a regular journal writer until she returned north after teaching in South Carolina. After her return, her entries were less frequent. While she did write about her daughter's death and her busy life with her husband, her writing was less frequent than the daily entries she made when younger. Her diary is one of the few extant documents detailing the life of a free black female in the antebellum North.
The Charlotte Forten Grimke House
Charlotte Forten Grimke House
The Charlotte Forten Grimké House is a historic home in the Dupont Circle neighborhood of Northwest Washington, D.C., United States. From 1881 to 1886, the house was owned by Charlotte Forten Grimké , one of the first Northern educators who entered Union-controlled areas of the South during the...
in Washington D.C. is listed on the National Register of Historic Places
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places is the United States government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures, and objects deemed worthy of preservation...
.

