
Carboxylesterase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a carboxylesterase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are carboxylic ester and H2O
, whereas its two products
are alcohol
and carboxylate.
Most enzymes from this group belong to the superfamily of hydrolase
s with alpha/beta protein fold
(so called Alpha/beta hydrolase fold
), specifically those acting on carboxylic ester
bonds. Some exceptions include an esterase with beta-lactamase
like structure . The carboxylesterase family
of evolutionarily related proteins (those with clear sequence homology to each other) includes a number of proteins with different substrate specificities, such as acetylcholinesterase
s.
The systematic name of this enzyme class is carboxylic-ester hydrolase. Examples of carboxyesterases include:
The last enzyme also participates in alkaloid
biosynthesis.
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
accession codes , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and .
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- a carboxylic ester + H2O
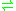 an alcohol + a carboxylate
an alcohol + a carboxylate
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are carboxylic ester and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
and carboxylate.
Most enzymes from this group belong to the superfamily of hydrolase
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond. For example, an enzyme that catalyzed the following reaction is a hydrolase:-Nomenclature:...
s with alpha/beta protein fold
Structural Classification of Proteins
The Structural Classification of Proteins database is a largely manual classification of protein structural domains based on similarities of their structures and amino acid sequences. A motivation for this classification is to determine the evolutionary relationship between proteins...
(so called Alpha/beta hydrolase fold
Alpha/beta hydrolase fold
In molecular biology, the alpha/beta hydrolase fold is common to a number of hydrolytic enzymes of widely differing phylogenetic origin and catalytic function. The core of each enzyme is an alpha/beta-sheet , containing 8 strands connected byhelices...
), specifically those acting on carboxylic ester
Ester
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH group is replaced by an -O-alkyl group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and...
bonds. Some exceptions include an esterase with beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamase
Beta-lactamases are enzymes produced by some bacteria and are responsible for their resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillins, cephamycins, and carbapenems . These antibiotics have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam...
like structure . The carboxylesterase family
Carboxylesterase family
Carboxylesterase, type B is a family of evolutionarily related proteins.Higher eukaryotes have many distinct esterases. Among the different types are those which act on carboxylic esters . Carboxyl-esterases have been classified into three categories on the basis of differential patterns of...
of evolutionarily related proteins (those with clear sequence homology to each other) includes a number of proteins with different substrate specificities, such as acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase
"Acetylcholinesterase, also known as AChE or acetylcholine acetylhydrolase, is an enzyme that degrades the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, producing choline and an acetate group. It is mainly found at neuromuscular junctions and cholinergic nervous system, where its activity serves to terminate...
s.
Nomenclature
Carboxylesterase is an enzyme that capable of hydrolyzing a wide variety of carboxylic acid esters. Although its metabolic function is unclear, the enzyme is widely distributed in nature, being especially common in mammalian liver. Carboxylesterase belongs to the class of serine hydrolases which includes Chymotrypsin and Acetylcholinesterase.The systematic name of this enzyme class is carboxylic-ester hydrolase. Examples of carboxyesterases include:
- ali-esterase,
- alpha-carboxylesterase,
- B-esterase,
- butyrate esterase,
- butyryl esterase,
- carboxyesterase,
- carboxyl ester hydrolase,
- carboxylate esterase,
- carboxylic acid esterase,
- carboxylic esterase,
- esterase A,
- esterase B,
- esterase D,
- methylbutyrase,
- methylbutyrase,
- methylbutyrate esterase,
- monobutyrase,
- nonspecific carboxylesterase,
- procaine esterase,
- propionyl esterase,
- serine esterase,
- triacetin esterase,
- vitamin A esterase, and
- cocaine esterase.
The last enzyme also participates in alkaloid
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a group of naturally occurring chemical compounds that contain mostly basic nitrogen atoms. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Also some synthetic compounds of similar structure are attributed to alkaloids...
biosynthesis.
Genes
Humans genes that encode carboxylesterase enzymes include:- CES1
- CES2
- CES3
- CES4
- CES7
- CES8
Structural studies
As of late 2007, 38 structuresTertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
accession codes , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and .

