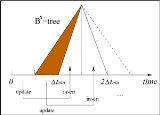
Bx-tree Moving Object Index
Encyclopedia
In computer science
, the Bx tree is a query and update efficient B+ tree
-based index structure for moving objects.
s serve as a directory, each containing a pointer to its right sibling. In the earlier version of the Bx-tree, the leaf nodes contained the moving-object
locations being indexed and corresponding index time. In the optimized version, each leaf node entry contains the id, velocity, single-dimensional mapping value and the latest update time of the object. The fanout is increased by not storing the locations of moving objects, as these can be derived from the mapping
values.
 As for many other moving objects indexes, a 2-dimensional moving object is modeled
As for many other moving objects indexes, a 2-dimensional moving object is modeled
as a linear function as O = ((x, y), (vx, vy), t ), where (x, y) and (vx, vy) are location and velocity
of the object at a given time instance t, i.e., the time of last update. The B+ tree is a structure for indexing single dimensional data. In order to adopt the B+ tree as a moving object index, the Bx-tree uses a linearization
technique which helps to integrate objects' location at time t into single dimensional value. Specifically, objects are first partitioned according to their update time. For objects within the same partition, the Bx-tree stores their locations at a given time which are estimated by linear interpolation
. By doing so, the Bx-tree keeps a consistent view of all objects within the same partition without storing the update time of an objects.
Secondly, the space is partitioned by a grid and the location of an object is linearized within the partitions according to a space-filling curve, e.g., the Peano
or Hilbert curve
s.
Finally, with the combination of the partition number (time information) and the linear order (location information), an object is indexed in Bx-tree with a one dimensional index key Bxvalue:
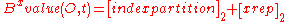
Here index-partition is an index partition determined by the update time and xrep is the space-filling curve value of the object position at the indexed time,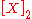 denotes the binary value of x, and “+” means concatenation.
denotes the binary value of x, and “+” means concatenation.
Given an object O ((7, 2), (-0.1,0.05), 10), tmu = 120, the Bxvalue for O can be computed as follows.
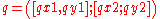 at time
at time 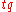 not prior to the current time.
not prior to the current time.
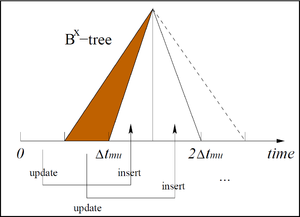
The Bx-tree uses query-window enlargement technique to answer queries. Since the Bx-tree stores an object's location as of sometime after its update time, the enlargement involves two cases: a location must either be brought back to an earlier time or forward to a later time. The main idea is to enlarge the query window so that it encloses all objects whose positions are not within query window at its label timestamp but will enter the query window at the query timestamp.
After the enlargement, the partitions of the Bx-tree need to be traversed to find objects falling in the enlarged query window. In each partition, the use of a space-filling curve means that a range query in the native, two-dimensional space becomes a set of range queries in the transformed, one-dimensional space.
To avoid excessively large query region after expansion in skewed datasets, an optimization of the query algorithm exists, which improves the query efficiency by avoiding unnecessary query enlargement.
.
.
SpADE is moving object management system built on top of a popular relational database system MySQL
, which uses the Bx-tree for indexing the objects. In the implementation, moving object data is transformed and stored directly on MySQL, and queries are transformed into standard SQL statements which are efficiently processed in the relational engine. Most importantly, all these are achieved neatly and independently without infiltrating into the MySQL core.
The Bx-tree have multiple partitions regarding different time intervals. As time elapsed, each partition grows and shrinks alternately. The ST2B-tree utilizes this feature to tune the index online in order to adjust the space partitioning to make itself accommodate to the data changes with time. In particular, as a partition shrinks to empty and starts growing, it chooses a new set of reference points and new grid for each reference point according to the latest data density. The tuning is based on the latest statistics collected during a given period of time, so that the way of space partitioning is supposed to fit the latest data distribution best. By this means, the ST2B-tree is expected to minimize the effect caused by data skew in space and data changes with time.
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, the Bx tree is a query and update efficient B+ tree
B+ tree
In computer science, a B+ tree or B plus tree is a type of tree which represents sorted data in a way that allows for efficient insertion, retrieval and removal of records, each of which is identified by a key. It is a dynamic, multilevel index, with maximum and minimum bounds on the number of...
-based index structure for moving objects.
Index structure
The base structure of the Bx-tree is a B+ tree in which the internal nodeNode (computer science)
A node is a record consisting of one or more fields that are links to other nodes, and a data field. The link and data fields are often implemented by pointers or references although it is also quite common for the data to be embedded directly in the node. Nodes are used to build linked, often...
s serve as a directory, each containing a pointer to its right sibling. In the earlier version of the Bx-tree, the leaf nodes contained the moving-object
Object (computer science)
In computer science, an object is any entity that can be manipulated by the commands of a programming language, such as a value, variable, function, or data structure...
locations being indexed and corresponding index time. In the optimized version, each leaf node entry contains the id, velocity, single-dimensional mapping value and the latest update time of the object. The fanout is increased by not storing the locations of moving objects, as these can be derived from the mapping
Map (mathematics)
In most of mathematics and in some related technical fields, the term mapping, usually shortened to map, is either a synonym for function, or denotes a particular kind of function which is important in that branch, or denotes something conceptually similar to a function.In graph theory, a map is a...
values.
Utilize the B+ tree for moving objects

Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
as a linear function as O = ((x, y), (vx, vy), t ), where (x, y) and (vx, vy) are location and velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
of the object at a given time instance t, i.e., the time of last update. The B+ tree is a structure for indexing single dimensional data. In order to adopt the B+ tree as a moving object index, the Bx-tree uses a linearization
Linearization
In mathematics and its applications, linearization refers to finding the linear approximation to a function at a given point. In the study of dynamical systems, linearization is a method for assessing the local stability of an equilibrium point of a system of nonlinear differential equations or...
technique which helps to integrate objects' location at time t into single dimensional value. Specifically, objects are first partitioned according to their update time. For objects within the same partition, the Bx-tree stores their locations at a given time which are estimated by linear interpolation
Linear interpolation
Linear interpolation is a method of curve fitting using linear polynomials. Lerp is an abbreviation for linear interpolation, which can also be used as a verb .-Linear interpolation between two known points:...
. By doing so, the Bx-tree keeps a consistent view of all objects within the same partition without storing the update time of an objects.
Secondly, the space is partitioned by a grid and the location of an object is linearized within the partitions according to a space-filling curve, e.g., the Peano
Space-filling curve
In mathematical analysis, a space-filling curve is a curve whose range contains the entire 2-dimensional unit square...
or Hilbert curve
Hilbert curve
A Hilbert curve is a continuous fractal space-filling curve first described by the German mathematician David Hilbert in 1891, as a variant of the space-filling curves discovered by Giuseppe Peano in 1890....
s.
Finally, with the combination of the partition number (time information) and the linear order (location information), an object is indexed in Bx-tree with a one dimensional index key Bxvalue:
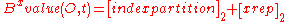
Here index-partition is an index partition determined by the update time and xrep is the space-filling curve value of the object position at the indexed time,
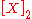 denotes the binary value of x, and “+” means concatenation.
denotes the binary value of x, and “+” means concatenation.Given an object O ((7, 2), (-0.1,0.05), 10), tmu = 120, the Bxvalue for O can be computed as follows.
- O is indexed in partition 0 as mentioned. Therefore, indexpartition = (00)2.
- O’s position at the label timestamp of partition 0 is (1,5).
- Using Z-curve with order = 3, the Z-value of O, i.e., xrep is (010011)2.
- Concatenating indexpartition and xrep, Bxvalue (00010011)2=19.
Insertion, Update and Deletion
Given a new object, its index key is computed and then the object is inserted into the Bx-tree as in the B+ tree. An update consists of a deletion followed by an insertion. An auxiliary structure is employed to keep the latest key of each index so that an object can be deleted by searching for the key. The indexing key is computed before affecting the tree. In this way, the Bx-tree directly inherits the good properties of the B+ tree, and achieves efficient update performance.Range query
A range query retrieves all objects whose location falls within the rectangular range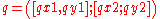 at time
at time 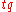 not prior to the current time.
not prior to the current time.The Bx-tree uses query-window enlargement technique to answer queries. Since the Bx-tree stores an object's location as of sometime after its update time, the enlargement involves two cases: a location must either be brought back to an earlier time or forward to a later time. The main idea is to enlarge the query window so that it encloses all objects whose positions are not within query window at its label timestamp but will enter the query window at the query timestamp.
After the enlargement, the partitions of the Bx-tree need to be traversed to find objects falling in the enlarged query window. In each partition, the use of a space-filling curve means that a range query in the native, two-dimensional space becomes a set of range queries in the transformed, one-dimensional space.
To avoid excessively large query region after expansion in skewed datasets, an optimization of the query algorithm exists, which improves the query efficiency by avoiding unnecessary query enlargement.
K nearest neighbor query
K nearest neighbor query is computed by iteratively performing range queries with an incrementally enlarged search region until k answers are obtained. Another possibility is to employ similar queryig ideas in The iDistance TechniqueThe iDistance Technique
In pattern recognition, the iDistance is an indexing and query processing technique for k-nearest neighbor queries on point data in multi-dimensional metric spaces. The kNN query is one of the hardest problems on multi-dimensional data, especially when the dimensionality of the data is high...
.
Other queries
The range query and K Nearest Neighbor query algorithms can be easily extended to support interval queries, continuous queries, etc.Adapting relational database engines to accommodate moving objects
Since the Bx-tree is an index built on top of a B+ tree index, all operations in the Bx-tree, including the insertion, deletion and search, are the same as those in the B+ tree. There is no need to change the implementations of these operations. The only difference is to implement the procedure of deriving the indexing key as a stored procedure in an existing DBMS. Therefore the Bx-tree can be easily integrated into existing DBMS without touching the kernelKernel (mathematics)
In mathematics, the word kernel has several meanings. Kernel may mean a subset associated with a mapping:* The kernel of a mapping is the set of elements that map to the zero element , as in kernel of a linear operator and kernel of a matrix...
.
SpADE is moving object management system built on top of a popular relational database system MySQL
MySQL
MySQL officially, but also commonly "My Sequel") is a relational database management system that runs as a server providing multi-user access to a number of databases. It is named after developer Michael Widenius' daughter, My...
, which uses the Bx-tree for indexing the objects. In the implementation, moving object data is transformed and stored directly on MySQL, and queries are transformed into standard SQL statements which are efficiently processed in the relational engine. Most importantly, all these are achieved neatly and independently without infiltrating into the MySQL core.
Potential problem with data skew
The Bx tree uses a grid for space partitioning while mapping two-dimensional location into one-dimensional key. This may introduce performance degradation to both query and update operations while dealing with skewed data. If grid cell is oversize, many objects are contained in a cell. Since objects in a cell are indistinguishable to the index, there will be some overflow nodes in the underlying B+ tree. The existing of overflow pages not only destroys the balancing of the tree but also increases the update cost. As for the queries, for the given query region, large cell incurs more false positives and increases the processing time. On the other hand, if the space is partitioned with finer grid, i.e. smaller cells, each cell contains few objects. There is hardly overflow pages so that the update cost is minimized. Fewer false positives are retrieved in a query. However, more cells are needed to be searched. The increase in the number of cells searched also increases the workload of a query.Index tuning
The ST2B-tree introduces a self-tuning framework for tuning the performance of the Bx-tree while dealing with data skew in space and data change with time. In order to deal with data skew in space, the ST2B-tree splits the entire space into regions of different object density using a set of reference points. Each region uses an individual grid whose cell size is determined by the object density inside of it.The Bx-tree have multiple partitions regarding different time intervals. As time elapsed, each partition grows and shrinks alternately. The ST2B-tree utilizes this feature to tune the index online in order to adjust the space partitioning to make itself accommodate to the data changes with time. In particular, as a partition shrinks to empty and starts growing, it chooses a new set of reference points and new grid for each reference point according to the latest data density. The tuning is based on the latest statistics collected during a given period of time, so that the way of space partitioning is supposed to fit the latest data distribution best. By this means, the ST2B-tree is expected to minimize the effect caused by data skew in space and data changes with time.

