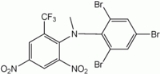
Bromethalin
Encyclopedia
Bromethalin is a rodenticide which poisons the central nervous system
by uncoupling mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation
, which causes a decrease in adenosine triphosphate
(ATP) synthesis. Decreased ATP ultimately results in increased intracranial pressure
, which damages neuronal axon
s. This damage to the central nervous system can cause paralysis
, convulsion
s, and death
.
s, hyperexcitability, fits, extreme sensitivity to being touched (hyperesthesia
) and seizure
s that appear to be caused by light or noise. Secondary bromethalin poisoning can occur in dogs or cats who eat a mouse killed by Bromethalin. In such cases, the pet owner may notice the "mild" symptoms such as loss of ability to bark, loss of appetite, depression, lethargy and coma
.
There is no antidote for bromethalin, but symptoms can be treated with corticosteroid
s. Clinical studies indicate that symptoms return as soon as the corticosteroids are discontinued.
The mechanism of bromethalin toxicity differs from that of popular rodent poisons, which are anticoagulants related to warfarin
(Coumadin). These drugs, such as diphacinone and bromadiolone
eaten by the mouse as an overdose, inhibiting vitamin K
and leading to a loss of clotting activity over several days (clotting factors require vitamin K), and ultimately hemorrhage.
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
by uncoupling mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
, which causes a decrease in adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
(ATP) synthesis. Decreased ATP ultimately results in increased intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
, which damages neuronal axon
Axon
An axon is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body or soma....
s. This damage to the central nervous system can cause paralysis
Paralysis
Paralysis is loss of muscle function for one or more muscles. Paralysis can be accompanied by a loss of feeling in the affected area if there is sensory damage as well as motor. A study conducted by the Christopher & Dana Reeve Foundation, suggests that about 1 in 50 people have been diagnosed...
, convulsion
Convulsion
A convulsion is a medical condition where body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in an uncontrolled shaking of the body. Because a convulsion is often a symptom of an epileptic seizure, the term convulsion is sometimes used as a synonym for seizure...
s, and death
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
.
Risk of poisoning
There are no tests that will diagnose bromethalin poisoning in pets, but signs to watch for include severe muscle tremorTremor
A tremor is an involuntary, somewhat rhythmic, muscle contraction and relaxation involving to-and-fro movements of one or more body parts. It is the most common of all involuntary movements and can affect the hands, arms, eyes, face, head, vocal folds, trunk, and legs. Most tremors occur in the...
s, hyperexcitability, fits, extreme sensitivity to being touched (hyperesthesia
Hyperesthesia
Hyperesthesia is a condition that involves an abnormal increase in sensitivity to stimuli of the sense. "When a non-noxious stimulus causes the sensation of pain the area will be termed hyperaesthetic". Stimuli of the senses can include sound that one hears, foods that one tastes, textures that...
) and seizure
Seizure
An epileptic seizure, occasionally referred to as a fit, is defined as a transient symptom of "abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain". The outward effect can be as dramatic as a wild thrashing movement or as mild as a brief loss of awareness...
s that appear to be caused by light or noise. Secondary bromethalin poisoning can occur in dogs or cats who eat a mouse killed by Bromethalin. In such cases, the pet owner may notice the "mild" symptoms such as loss of ability to bark, loss of appetite, depression, lethargy and coma
Coma
In medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
.
There is no antidote for bromethalin, but symptoms can be treated with corticosteroid
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex. Corticosteroids are involved in a wide range of physiologic systems such as stress response, immune response and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte...
s. Clinical studies indicate that symptoms return as soon as the corticosteroids are discontinued.
The mechanism of bromethalin toxicity differs from that of popular rodent poisons, which are anticoagulants related to warfarin
Warfarin
Warfarin is an anticoagulant. It is most likely to be the drug popularly referred to as a "blood thinner," yet this is a misnomer, since it does not affect the thickness or viscosity of blood...
(Coumadin). These drugs, such as diphacinone and bromadiolone
Bromadiolone
Bromadiolone is a potent rodenticide. It is a second-generation 4-hydroxycoumarin derivative, often called a "super-warfarin" for its added potency and tendency to accumulate in the liver of the poisoned organism...
eaten by the mouse as an overdose, inhibiting vitamin K
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is a group of structurally similar, fat soluble vitamins that are needed for the posttranslational modification of certain proteins required for blood coagulation and in metabolic pathways in bone and other tissue. They are 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives...
and leading to a loss of clotting activity over several days (clotting factors require vitamin K), and ultimately hemorrhage.

