Bone segment navigation
Encyclopedia
Bone segment navigation is a surgical method used in the field to find the anatomical position of displaced bone fragments in fractures, allowing a good fixation by osteosynthesis
. It has been developed for the first time in oral and maxillofacial surgery
.
After an accident or injury, a fracture can be produced and the resulting bony fragments can be displaced. In the oral and maxillofacial area, such a discplacement could have a major effect both on facial aesthetics and organ function: a fracture occurring in a bone that delimits the orbit
can lead to diplopia
; a mandibular fracture can induce significant modifications of the dental occlusion
; in the same manner, a skull (neurocranium) fracture can produce an increased intracranial pressure
.
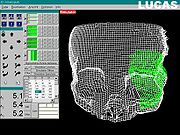
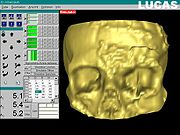
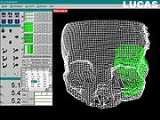
is a surgical intervention that consists of cutting through bone and repositioning the resulting fragments in the correct anatomical place. To insure optimal repositioning of the bony structures by osteotomy
, the intervention can be planned in advance and simulated. The surgical simulation is a key factor in reducing the actual operating time. Often, during this kind of operation, the surgical access to the bone segments is very limited by the presence of the soft tissues: muscles, fat tissue and skin - thus, the correct anatomical repositioning is very difficult to assess, or even impossible. This led to the necessity of a preoperative planning and simulation on models of the bare bony structures.
are classically planned on cast models of the tooth-bearing jaws, fixed in an articulator
. For edentulous patients, the surgical planning is made by using stereolithographic models
. These tridimensional models are then cut along the planned osteothomy line, slid and fixed in the new position.
Since the 1990’s, modern techniques of presurgical planning were developed – allowing the surgeon to plan and simulate the osteotomy in a virtual environment, based on a preoperative CT
or MRI; this procedure reduces the costs and the duration of creating, positioning, cutting, repositioning and refixing the cast models for each patient. The first system that allowed such a surgical simulation environment is the Laboratory Unit for Computer Assisted Surgery
(LUCAS), that was developed in 1998 at the University of Regensburg, Germany
, with the support of the Carl Zeiss Company.
in the surgical field. The transfer of the planning was mainly based on the surgeon’s visual skills. Different guiding headframes were further developed to mechanically guide bone fragment repositioning. Such a headframe is attached to the patient’s head, during CT or MRI, and surgery. There are certain difficulties in using this device. First, exact reproducibility of the headframe position on the patient’s head is needed, both during CT or MRI registration, and during surgery. The headframe is relatively uncomfortable to wear, and very difficult or even impossible to use on small children, who can be uncooperative during medical procedures.
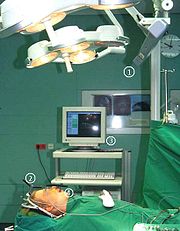
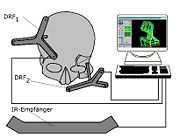
(SSN), developed in 1997 at the University of Regensburg, Germany
, with the support of the Carl Zeiss Company. This new system does not need any mechanical surgical guides (such as a headframe). It is based on an infrared (IR)
camera and IR transmitters attached to the skull. At least three IR transmitters are attached in the neurocranium area to compensate the movements of the patient’s head. There are three or more IR transmitters are attached to the bones where the osteotomy and bone repositioning is about to be performed onto. The 3D
position of each transmitter is measured by the IR camera, using the same principle as in satellite navigation. The workstation of the Surgical Segment Navigator
(SSN) is constantly visualizing the actual position of the bone fragments, compared with the predetermined position, and also makes real-time spatial determinations of the free-moving bony segments resulting from the osteotomy.
Thus, fragments can be very accurately positioned into the target position, predetermined by surgical simulation.
.
Osteosynthesis
Osteosynthesis is the reduction and fixation of a bone fracture with implantable devices that are usually made of metal. It is a surgical procedure with an open or percutaneous approach to the fractured bone. Osteosynthesis aims to bring the fractured bone ends together and immobilize the fracture...
. It has been developed for the first time in oral and maxillofacial surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is surgery to correct a wide spectrum of diseases, injuries and defects in the head, neck, face, jaws and the hard and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial region. It is an internationally recognized surgical specialty...
.
After an accident or injury, a fracture can be produced and the resulting bony fragments can be displaced. In the oral and maxillofacial area, such a discplacement could have a major effect both on facial aesthetics and organ function: a fracture occurring in a bone that delimits the orbit
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents...
can lead to diplopia
Diplopia
Diplopia, commonly known as double vision, is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced horizontally, vertically, or diagonally in relation to each other...
; a mandibular fracture can induce significant modifications of the dental occlusion
Occlusion (dentistry)
Occlusion, in a dental context, means simply the contact between teeth. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary and mandibular teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest....
; in the same manner, a skull (neurocranium) fracture can produce an increased intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid . The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF...
.


Surgical planning and surgical simulation
An osteotomyOsteotomy
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten, lengthen, or change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum...
is a surgical intervention that consists of cutting through bone and repositioning the resulting fragments in the correct anatomical place. To insure optimal repositioning of the bony structures by osteotomy
Osteotomy
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten, lengthen, or change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum...
, the intervention can be planned in advance and simulated. The surgical simulation is a key factor in reducing the actual operating time. Often, during this kind of operation, the surgical access to the bone segments is very limited by the presence of the soft tissues: muscles, fat tissue and skin - thus, the correct anatomical repositioning is very difficult to assess, or even impossible. This led to the necessity of a preoperative planning and simulation on models of the bare bony structures.
Materials and devices needed for preoperative planning and simulation
The osteotomies performed in orthognathic surgeryOrthognathic surgery
Orthognathic surgery is surgery to correct conditions of the jaw and face related to structure, growth, sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion problems owing to skeletal disharmonies, or other orthodontic problems that cannot be easily treated with braces. Originally coined by Dr. Harold...
are classically planned on cast models of the tooth-bearing jaws, fixed in an articulator
Articulator
An articulator is a mechanical device used in dentistry to which casts of the maxillary and mandibular teeth are fixed, reproducing recorded positions of the mandible in relation to the maxilla...
. For edentulous patients, the surgical planning is made by using stereolithographic models
Stereolithography
Stereolithography is an additive manufacturing technology for producing models, prototypes, patterns, and in some cases, production parts.-Technology description:...
. These tridimensional models are then cut along the planned osteothomy line, slid and fixed in the new position.
Since the 1990’s, modern techniques of presurgical planning were developed – allowing the surgeon to plan and simulate the osteotomy in a virtual environment, based on a preoperative CT
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
or MRI; this procedure reduces the costs and the duration of creating, positioning, cutting, repositioning and refixing the cast models for each patient. The first system that allowed such a surgical simulation environment is the Laboratory Unit for Computer Assisted Surgery
Laboratory Unit for Computer Assisted Surgery
Laboratory Unit for Computer Assisted Surgery is a system used for virtual surgical planning. Starting with 1998, LUCAS was developed at the University of Regensburg, Germany, with the support of the Carl Zeiss Company. The resulting surgical planning is then reproduced onto the patient by using a...
(LUCAS), that was developed in 1998 at the University of Regensburg, Germany
University of Regensburg
The University of Regensburg is a public research university located in the medieval city of Regensburg, Bavaria, a city that is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The university was founded on July 18, 1962 by the Landtag of Bavaria as the fourth full-fledged university in Bavaria...
, with the support of the Carl Zeiss Company.
Transferring the preoperative planning to the operating theatre
The usefulness of the preoperative planning, no matter how accurate, depends on the accuracy of the reproduction of the simulated osteotomyOsteotomy
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten, lengthen, or change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum...
in the surgical field. The transfer of the planning was mainly based on the surgeon’s visual skills. Different guiding headframes were further developed to mechanically guide bone fragment repositioning. Such a headframe is attached to the patient’s head, during CT or MRI, and surgery. There are certain difficulties in using this device. First, exact reproducibility of the headframe position on the patient’s head is needed, both during CT or MRI registration, and during surgery. The headframe is relatively uncomfortable to wear, and very difficult or even impossible to use on small children, who can be uncooperative during medical procedures.


Surgical Segment Navigator
The first system that allowed a seamless bone segment navigation for preoperative planning was the Surgical Segment NavigatorSurgical Segment Navigator
The Surgical Segment Navigator is a computer-based system for use in surgical navigation. It is integrated into a common platform, together with the Surgical Tool Navigator , the Surgical Microscope Navigator and the 6DOF Manipulator , developed by Carl Zeiss.- SSN :The SSN has been developed as...
(SSN), developed in 1997 at the University of Regensburg, Germany
University of Regensburg
The University of Regensburg is a public research university located in the medieval city of Regensburg, Bavaria, a city that is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The university was founded on July 18, 1962 by the Landtag of Bavaria as the fourth full-fledged university in Bavaria...
, with the support of the Carl Zeiss Company. This new system does not need any mechanical surgical guides (such as a headframe). It is based on an infrared (IR)
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
camera and IR transmitters attached to the skull. At least three IR transmitters are attached in the neurocranium area to compensate the movements of the patient’s head. There are three or more IR transmitters are attached to the bones where the osteotomy and bone repositioning is about to be performed onto. The 3D
Three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space is a geometric 3-parameters model of the physical universe in which we live. These three dimensions are commonly called length, width, and depth , although any three directions can be chosen, provided that they do not lie in the same plane.In physics and mathematics, a...
position of each transmitter is measured by the IR camera, using the same principle as in satellite navigation. The workstation of the Surgical Segment Navigator
Surgical Segment Navigator
The Surgical Segment Navigator is a computer-based system for use in surgical navigation. It is integrated into a common platform, together with the Surgical Tool Navigator , the Surgical Microscope Navigator and the 6DOF Manipulator , developed by Carl Zeiss.- SSN :The SSN has been developed as...
(SSN) is constantly visualizing the actual position of the bone fragments, compared with the predetermined position, and also makes real-time spatial determinations of the free-moving bony segments resulting from the osteotomy.
Thus, fragments can be very accurately positioned into the target position, predetermined by surgical simulation.
Indications for the hard tissue segment navigation method
The hard tissue segment navigation is more and more frequently used in orthognatic surgery (correction of the anomalies of the jaws and skull), in temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) surgery, or in the reconstruction of the mid-face and orbitOrbit (anatomy)
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents...
.

