
Bone marrow biopsy
Encyclopedia
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic
analysis of samples of bone marrow
obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called a trephine
biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditions, including leukemia
, multiple myeloma
, lymphoma
, anemia
, and pancytopenia
. The bone marrow produces the cellular elements of the blood
, including platelet
s, red blood cell
s and white blood cell
s. While much information can be gleaned by testing the blood itself (drawn from a vein by phlebotomy
), it is sometimes necessary to examine the source of the blood cells in the bone marrow to obtain more information on hematopoiesis; this is the role of bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
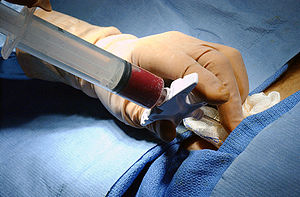 Bone marrow samples can be obtained by aspiration and trephine biopsy. Sometimes, a bone marrow examination will include both an aspirate and a biopsy. The aspirate yields semi-liquid bone marrow, which can be examined by a pathologist under a light microscope as well as analyzed by flow cytometry
Bone marrow samples can be obtained by aspiration and trephine biopsy. Sometimes, a bone marrow examination will include both an aspirate and a biopsy. The aspirate yields semi-liquid bone marrow, which can be examined by a pathologist under a light microscope as well as analyzed by flow cytometry
, chromosome analysis
, or polymerase chain reaction
(PCR). Frequently, a trephine biopsy is also obtained, which yields a narrow, cylindrically shaped solid piece of bone marrow, 2mm wide and 2 cm long (80 μL), which is examined microscopically (sometimes with the aid of immunohistochemistry
) for cellularity and infiltrative processes. An aspiration, using a 20 mL syringe, yields approximately 300 μL of bone marrow. A volume greater than 300 μL is not recommended, since it may dilute the sample with peripheral blood.
Aspiration doesn't always represent all cells since, as some such as lymphoma
stick to the trabecula, and would thus be missed by a simple aspiration.
. However, an aspirate can also be obtained from the sternum (breastbone). A trephine biopsy should never be performed on the sternum, due to the risk of injury to blood vessel
s, lung
s or the heart
.
for the procedure is typically required. The patient is asked to lie on his or her abdomen (prone position) or on his/her side (lateral decubitus
position). The skin is cleansed, and a local anesthetic
such as lidocaine
is injected to numb the area. Patients may also be pretreated with analgesic
s and/or anti-anxiety medications
, although this is not a routine practice.
Typically, the aspirate is performed first. An aspirate needle is inserted through the skin using manual pressure and force until it abuts the bone
. Then, with a twisting motion of clinician's hand and wrist, the needle is advanced through the bony cortex
(the hard outer layer of the bone) and into the marrow cavity. Once the needle is in the marrow cavity, a syringe is attached and used to aspirate ("suck out") liquid bone marrow. A twisting motion is performed during the aspiration to avoid excess content of blood in the sample, which might be the case if an excessively large sample from one single point is taken.
Subsequently, the biopsy is performed if indicated. A different, larger trephine
needle is inserted and anchored in the bony cortex. The needle is then advanced with a twisting motion and rotated to obtain a solid piece of bone marrow. This piece is then removed along with the needle. The entire procedure, once preparation is complete, typically takes 10–15 minutes.
If several samples are taken, the needle is removed between the samples to avoid blood coagulation.
In March of 2010, Vidacare Corporation introduced a new technology to facilitate faster
and easier insertion when compared to manual insertions with comparable or better core
sample quality. The OnControl™ Bone Marrow Biopsy and Aspiration
System provides the first advance in bone marrow biopsy and aspiration procedures in
over 50 years by combining a specially designed needle with a powered driver to obtain
high quality core samples.Validation testing completed prior to the product’s launch on
the OnControl™ System showed the following results:
Mean length of core sample of 1.32 cm, Median time to core extraction of 81 seconds, Needle insertion success rate of 94%, Biopsy core acquisition success rate of 90%, Zero complications.
In addition, an article dated April 19, 2010 published in the Journal of Clinical Pathology
(Swords, Ronan, et al.) made the following conclusion about the System: “As
clinicians, we feel that the speed and ease of use of this new powered system could
change the way that bone marrow aspiration and biopsy is carried out in the future,
particularly in large centres where this procedure is commonly performed.”
(acetaminophen) or other simple analgesics can be used to ease soreness, which is common for 2–3 days after the procedure. Any worsening pain, redness, fever, bleeding or swelling may suggest a complication. Patients are also advised to avoid washing the procedure site for at least 24 hours after the procedure is completed.
(low platelet
count).
are extremely rare. In a large review, an estimated 55,000 bone marrow examinations were performed, with 26 serious adverse event
s (0.05%), including one fatality. The same author collected data on over 19,000 bone marrow examinations performed in the United Kingdom
in 2003, and found 16 adverse event
s (0.08% of total procedures), the most common of which was bleeding. In this report, complications, while rare, were serious in individual cases.
Pathology
Pathology is the precise study and diagnosis of disease. The word pathology is from Ancient Greek , pathos, "feeling, suffering"; and , -logia, "the study of". Pathologization, to pathologize, refers to the process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological, e.g. pathological gambling....
analysis of samples of bone marrow
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is the flexible tissue found in the interior of bones. In humans, bone marrow in large bones produces new blood cells. On average, bone marrow constitutes 4% of the total body mass of humans; in adults weighing 65 kg , bone marrow accounts for approximately 2.6 kg...
obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called a trephine
Trephine
A trephine is a surgical instrument with a cylindrical blade. It can be of one of several dimensions and designs depending on what it is going to be used for. They may be specially designed for obtaining a cylindrically shaped core of bone that can be used for tests and bone studies, cutting holes...
biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditions, including leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
, multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma , also known as plasma cell myeloma or Kahler's disease , is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell normally responsible for the production of antibodies...
, lymphoma
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer in the lymphatic cells of the immune system. Typically, lymphomas present as a solid tumor of lymphoid cells. Treatment might involve chemotherapy and in some cases radiotherapy and/or bone marrow transplantation, and can be curable depending on the histology, type, and stage...
, anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin...
, and pancytopenia
Pancytopenia
Pancytopenia is a medical condition in which there is a reduction in the number of red and white blood cells, as well as platelets.If only two parameters from the full blood count are low, the term bicytopenia can be used...
. The bone marrow produces the cellular elements of the blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
, including platelet
Platelet
Platelets, or thrombocytes , are small,irregularly shaped clear cell fragments , 2–3 µm in diameter, which are derived from fragmentation of precursor megakaryocytes. The average lifespan of a platelet is normally just 5 to 9 days...
s, red blood cell
Red blood cell
Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues via the blood flow through the circulatory system...
s and white blood cell
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
s. While much information can be gleaned by testing the blood itself (drawn from a vein by phlebotomy
Phlebotomy
Phlebotomy is the process of making an incision in a vein.It is associated with the following concepts:* Venipuncture, the practice of collecting venous blood samples* The main practice of a phlebotomist, an individual trained to draw blood...
), it is sometimes necessary to examine the source of the blood cells in the bone marrow to obtain more information on hematopoiesis; this is the role of bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.
Components of the procedure

Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique for counting and examining microscopic particles, such as cells and chromosomes, by suspending them in a stream of fluid and passing them by an electronic detection apparatus. It allows simultaneous multiparametric analysis of the physical and/or chemical...
, chromosome analysis
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is a branch of genetics that is concerned with the study of the structure and function of the cell, especially the chromosomes. It includes routine analysis of G-Banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as fluorescent in situ...
, or polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
(PCR). Frequently, a trephine biopsy is also obtained, which yields a narrow, cylindrically shaped solid piece of bone marrow, 2mm wide and 2 cm long (80 μL), which is examined microscopically (sometimes with the aid of immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry or IHC refers to the process of detecting antigens in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno," in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and...
) for cellularity and infiltrative processes. An aspiration, using a 20 mL syringe, yields approximately 300 μL of bone marrow. A volume greater than 300 μL is not recommended, since it may dilute the sample with peripheral blood.
| Aspiration | Biopsy | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
|
| Drawbacks | Doesn't represent all cells | Slow processing |
Aspiration doesn't always represent all cells since, as some such as lymphoma
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer in the lymphatic cells of the immune system. Typically, lymphomas present as a solid tumor of lymphoid cells. Treatment might involve chemotherapy and in some cases radiotherapy and/or bone marrow transplantation, and can be curable depending on the histology, type, and stage...
stick to the trabecula, and would thus be missed by a simple aspiration.
Site of procedure
Bone marrow aspiration and trephine biopsy are usually performed on the back of the hipbone, or posterior iliac crestIliac crest
-External links: - "Superficial muscles of the gluteal region and posterior thigh." - "Anterior Abdominal Wall: Osteology and Surface Anatomy " - "The Back, Posterior View" * *...
. However, an aspirate can also be obtained from the sternum (breastbone). A trephine biopsy should never be performed on the sternum, due to the risk of injury to blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s, lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s or the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
.
How the test is performed
A bone marrow biopsy may be done in a health care provider's office or in a hospital. Informed consentInformed consent
Informed consent is a phrase often used in law to indicate that the consent a person gives meets certain minimum standards. As a literal matter, in the absence of fraud, it is redundant. An informed consent can be said to have been given based upon a clear appreciation and understanding of the...
for the procedure is typically required. The patient is asked to lie on his or her abdomen (prone position) or on his/her side (lateral decubitus
Decubitus
Commonly used in medicine, the word decubitus is used to mean "lying down". It is derived from the Latin verb “decumbere” meaning "to lie down"....
position). The skin is cleansed, and a local anesthetic
Local anesthetic
A local anesthetic is a drug that causes reversible local anesthesia, generally for the aim of having local analgesic effect, that is, inducing absence of pain sensation, although other local senses are often affected as well...
such as lidocaine
Lidocaine
Lidocaine , Xylocaine, or lignocaine is a common local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug. Lidocaine is used topically to relieve itching, burning and pain from skin inflammations, injected as a dental anesthetic or as a local anesthetic for minor surgery.- History :Lidocaine, the first amino...
is injected to numb the area. Patients may also be pretreated with analgesic
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
s and/or anti-anxiety medications
Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic is a drug used for the treatment of anxiety, and its related psychological and physical symptoms...
, although this is not a routine practice.
Typically, the aspirate is performed first. An aspirate needle is inserted through the skin using manual pressure and force until it abuts the bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
. Then, with a twisting motion of clinician's hand and wrist, the needle is advanced through the bony cortex
Cortical bone
Cortical bone, synonymous with compact bone, is one of the two types of osseous tissue that form bones. Cortical bone facilitates bone's main functions: to support the whole body, protect organs, provide levers for movement, and store and release chemical elements, mainly calcium. As its name...
(the hard outer layer of the bone) and into the marrow cavity. Once the needle is in the marrow cavity, a syringe is attached and used to aspirate ("suck out") liquid bone marrow. A twisting motion is performed during the aspiration to avoid excess content of blood in the sample, which might be the case if an excessively large sample from one single point is taken.
Subsequently, the biopsy is performed if indicated. A different, larger trephine
Trephine
A trephine is a surgical instrument with a cylindrical blade. It can be of one of several dimensions and designs depending on what it is going to be used for. They may be specially designed for obtaining a cylindrically shaped core of bone that can be used for tests and bone studies, cutting holes...
needle is inserted and anchored in the bony cortex. The needle is then advanced with a twisting motion and rotated to obtain a solid piece of bone marrow. This piece is then removed along with the needle. The entire procedure, once preparation is complete, typically takes 10–15 minutes.
If several samples are taken, the needle is removed between the samples to avoid blood coagulation.
In March of 2010, Vidacare Corporation introduced a new technology to facilitate faster
and easier insertion when compared to manual insertions with comparable or better core
sample quality. The OnControl™ Bone Marrow Biopsy and Aspiration
System provides the first advance in bone marrow biopsy and aspiration procedures in
over 50 years by combining a specially designed needle with a powered driver to obtain
high quality core samples.Validation testing completed prior to the product’s launch on
the OnControl™ System showed the following results:
Mean length of core sample of 1.32 cm, Median time to core extraction of 81 seconds, Needle insertion success rate of 94%, Biopsy core acquisition success rate of 90%, Zero complications.
In addition, an article dated April 19, 2010 published in the Journal of Clinical Pathology
(Swords, Ronan, et al.) made the following conclusion about the System: “As
clinicians, we feel that the speed and ease of use of this new powered system could
change the way that bone marrow aspiration and biopsy is carried out in the future,
particularly in large centres where this procedure is commonly performed.”
After the procedure
After the procedure is complete, the patient is typically asked to lie flat for 5–10 minutes to provide pressure over the procedure site. After that, assuming no bleeding is observed, the patient can get up and go about their normal activities. ParacetamolParacetamol
Paracetamol INN , or acetaminophen USAN , is a widely used over-the-counter analgesic and antipyretic . It is commonly used for the relief of headaches and other minor aches and pains and is a major ingredient in numerous cold and flu remedies...
(acetaminophen) or other simple analgesics can be used to ease soreness, which is common for 2–3 days after the procedure. Any worsening pain, redness, fever, bleeding or swelling may suggest a complication. Patients are also advised to avoid washing the procedure site for at least 24 hours after the procedure is completed.
Contraindications
There are few contraindications to bone marrow examination. The only absolute reason to avoid performing a bone marrow examination is the presence of a severe bleeding disorder which may lead to serious bleeding after the procedure. If there is a skin or soft tissue infection over the hip, a different site should be chosen for bone marrow examination. Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy can be safely performed even in the setting of extreme thrombocytopeniaThrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a relative decrease of platelets in blood.A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. These limits are determined by the 2.5th lower and upper percentile, so values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease...
(low platelet
Platelet
Platelets, or thrombocytes , are small,irregularly shaped clear cell fragments , 2–3 µm in diameter, which are derived from fragmentation of precursor megakaryocytes. The average lifespan of a platelet is normally just 5 to 9 days...
count).
Complications
While mild soreness lasting 12–24 hours is common after a bone marrow examination, serious complicationsComplication (medicine)
Complication, in medicine, is an unfavorable evolution of a disease, a health condition or a medical treatment. The disease can become worse in its severity or show a higher number of signs, symptoms or new pathological changes, become widespread throughout the body or affect other organ systems. A...
are extremely rare. In a large review, an estimated 55,000 bone marrow examinations were performed, with 26 serious adverse event
Serious adverse event
A serious adverse event in human drug trials are defined as any untowardmedical occurrence that at any dose#results in death,#is life-threatening#requires inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization...
s (0.05%), including one fatality. The same author collected data on over 19,000 bone marrow examinations performed in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
in 2003, and found 16 adverse event
Adverse event
An adverse event is any adverse change in health or side effect that occurs in a person who participates in a clinical trial while the patient is receiving the treatment or within a previously specified period of time after the treatment has been completed.AEs in patients participating in...
s (0.08% of total procedures), the most common of which was bleeding. In this report, complications, while rare, were serious in individual cases.

