
Anal sac adenocarcinoma
Encyclopedia
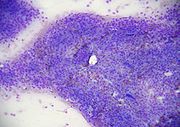
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
found in dog
Dog
The domestic dog is a domesticated form of the gray wolf, a member of the Canidae family of the order Carnivora. The term is used for both feral and pet varieties. The dog may have been the first animal to be domesticated, and has been the most widely kept working, hunting, and companion animal in...
s that arises from the apocrine glandular tissue of anal sac
Anal glands
The anal glands or anal sacs are small glands found near the anus in many mammals, including dogs and cats. They are not found in humans or other primates. They are paired sacs located on either side of the anus between the external and internal sphincter muscles. Sebaceous glands within the...
. At least one case has been reported in a cat
Cat
The cat , also known as the domestic cat or housecat to distinguish it from other felids and felines, is a small, usually furry, domesticated, carnivorous mammal that is valued by humans for its companionship and for its ability to hunt vermin and household pests...
. They are the second most common cancerous cause of hypercalcaemia
Hypercalcaemia
Hypercalcaemia is an elevated calcium level in the blood. . It can be an asymptomatic laboratory finding, but because an elevated calcium level is often indicative of other diseases, a workup should be undertaken if it persists...
(high serum calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
) in dogs, following T-cell lymphoma.
Signs and symptoms
Apocrine gland anal sac adenocarcinomas first appear as small lumps associated with one of the anal sacs (rarely bilateral), but they can grow to a large size. Smaller tumors are undetectable without a rectal examinationRectal examination
A rectal examination or rectal exam is an internal examination of the rectum such as by a physician or other healthcare professional.-Procedure:...
, while larger tumors can cause pain and straining to defecate. Between 25-50 percent of dogs with these tumors will also develop hypercalcaemia through secretion of parathyroid hormone-related protein
Parathyroid hormone-related protein
Parathyroid hormone-related protein is a protein member of the parathyroid hormone family. It is occasionally secreted by cancer cells . However, it also has normal functions.- Function :PTHrP acts as an endocrine, autocrine, paracrine, and intracrine hormone...
by the tumor. Symptoms of hypercalcaemia include increased drinking and urination, vomiting, loss of appetite, weight loss, and bradycardia
Bradycardia
Bradycardia , in the context of adult medicine, is the resting heart rate of under 60 beats per minute, though it is seldom symptomatic until the rate drops below 50 beat/min. It may cause cardiac arrest in some patients, because those with bradycardia may not be pumping enough oxygen to their heart...
(slow heart rate). Apocrine gland anal sac adenocarcinomas also have a tendency to metastasize
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
to the regional lymph node
Lymph node
A lymph node is a small ball or an oval-shaped organ of the immune system, distributed widely throughout the body including the armpit and stomach/gut and linked by lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes are garrisons of B, T, and other immune cells. Lymph nodes are found all through the body, and act as...
s, spleen
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrate animals with important roles in regard to red blood cells and the immune system. In humans, it is located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood in case of hemorrhagic shock...
, and lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s. The sublumbar (iliac) lymph nodes are the most common site of metastasis and can become larger than the original tumor.
Diagnosis
Anal sac adenocarcinomas are often suspected due to location and behavior, but a biopsyBiopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
is necessary for a definitive diagnosis. Needle aspiration biopsy
Needle aspiration biopsy
Needle aspiration biopsy , may refer to fine needle aspiration cytology , fine needle aspiration biopsy and fine needle aspiration , is a diagnostic procedure sometimes used to investigate superficial lumps or masses...
is a common first step. Cytopathology
Cytopathology
Cytopathology is a branch of pathology that studies and diagnoses diseases on the cellular level. The discipline was founded by Rudolf Virchow in 1858. A common application of cytopathology is the Pap smear, used as a screening tool, to detect precancerous cervical lesions and prevent cervical...
reveals clusters of cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s with uniform round nuclei
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
. These cells do not have many of the features usually associated with malignancy, such as a high nucleus to cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
ratio or prominent nucleoli
Nucleolus
The nucleolus is a non-membrane bound structure composed of proteins and nucleic acids found within the nucleus. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed and assembled within the nucleolus...
. Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasonography
Diagnostic sonography is an ultrasound-based diagnostic imaging technique used for visualizing subcutaneous body structures including tendons, muscles, joints, vessels and internal organs for possible pathology or lesions...
and radiography
Radiography
Radiography is the use of X-rays to view a non-uniformly composed material such as the human body. By using the physical properties of the ray an image can be developed which displays areas of different density and composition....
are performed to look for metastasis.
Treatment and prognosis
Aggressive surgical removal of the tumor and any enlarged sublumbar lymph nodes is essential for treatment of the tumor and associated hypercalcaemia. There is a high recurrence rate, although removal of lymph nodes with metastasis may improve survival time. Radiation therapyRadiation therapy
Radiation therapy , radiation oncology, or radiotherapy , sometimes abbreviated to XRT or DXT, is the medical use of ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control malignant cells.Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control...
and chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
may be helpful in treatment. Severe hypercalcaemia is treated with aggressive IV fluid therapy
Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy or IV therapy is the infusion of liquid substances directly into a vein. The word intravenous simply means "within a vein". Therapies administered intravenously are often called specialty pharmaceuticals...
using sodium chloride
Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaCl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of the ocean and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms...
and medications such as loop diuretic
Loop diuretic
Loop diuretics are diuretics that act on the ascending loop of Henle in the kidney. They are primarily used in medicine to treat hypertension and edema often due to congestive heart failure or renal insufficiency...
s (increased kidney excretion of calcium) and aminobisphosphonate
Bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone mass, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases...
s (decreased calcium release from bones). A poorer prognosis is associated with large tumor size (greater than 10 cm), hypercalcaemia, and distante metastasis.
Commonly affected breeds
Breeds that may be more commonly affected include the English Cocker SpanielEnglish Cocker Spaniel
The English Cocker Spaniel is a breed of gun dog. The English Cocker Spaniel is an active, good-natured, sporting dog, standing well up at the withers and compactly built. There are "field" or "working" cockers and "show" cockers...
, German Shepherd Dog
German Shepherd Dog
The German Shepherd Dog , also known as an Alsatian or just the German Shepherd, is a breed of large-sized dog that originated in Germany. The German Shepherd is a relatively new breed of dog, with its origin dating to 1899. As part of the Herding Group, the German Shepherd is a working dog...
, Alaskan Malamute
Alaskan Malamute
The Alaskan Malamute is a generally large breed of domestic dog originally bred for use as a utilitarian dog and later an Alaskan sled dog. They are sometimes mistaken for a Siberian Husky, but in fact are quite different in many ways...
, Dachshund
Dachshund
The dachshund is a short-legged, long-bodied dog breed belonging to the hound family. The standard size dachshund was bred to scent, chase, and flush out badgers and other burrow-dwelling animals, while the miniature dachshund was developed to hunt smaller prey such as rabbits...
, and . It is a disease of middle-age to older dogs and even though early reports described spayed females as more commonly affected, multiple recents studies have shown no gender overrepresentation.

