
Affluence in the United States
Encyclopedia
Reference group
A reference group is a concept referring to a group to which an individual or another group is compared.Sociologists call any group that individuals use as a standard for evaluating themselves and their own behavior a reference group....
. While there are no precise guidelines or thresholds for what may be considered affluent, the United States Department of Commerce
United States Department of Commerce
The United States Department of Commerce is the Cabinet department of the United States government concerned with promoting economic growth. It was originally created as the United States Department of Commerce and Labor on February 14, 1903...
's Bureau of the Census does provide detailed statistical data on the economic state of America's population. Income
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
, measured either by household
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
or individual
Personal income in the United States
Personal income is an individual’s total earnings from wages, investment interest, and other sources. In the United States the most widely cited personal income statistics are the Bureau of Economic Analysis’s personal income and the Census Bureau’s per capita money income...
, is perhaps the most commonly used measure for whether or not a given entity may be considered affluent. The term's usage varies greatly depending on context and speaker. Both an upper middle class person with a personal income of $77,500 annually and a billionaire may be referred to as affluent. If the average American with a median income of roughly $32,000 ($39,000 for those employed full-time between the ages of 25 and 64) was used as a reference group, the upper middle class person with a personal income in the tenth percentile of $77,500 may indeed be referred to as affluent. If compared to an executive of the Fortune 500
Fortune 500
The Fortune 500 is an annual list compiled and published by Fortune magazine that ranks the top 500 U.S. closely held and public corporations as ranked by their gross revenue after adjustments made by Fortune to exclude the impact of excise taxes companies collect. The list includes publicly and...
, however, the upper middle class person would be poor. Currently, marketing corporations and investment houses classify those with household incomes exceeding $75,000 as mass affluent
Mass affluent
Mass affluent and emerging affluent are marketing terms used to refer to the high end of the mass market. It is most commonly used by the financial services industry to refer to individuals with US$100,000 to US$1,000,000 of liquid financial assets, although the exact definition varies...
, while sociologist Leonard Beeghley
Leonard Beeghley
Leonard Beeghley is Professor Emeritus of sociology at the University of Florida since 1975. He received his Ph.D. from the University of California at Riverside in 1975 and has since published seven books over the course of his career...
identifies all those with a net worth of $1 million or more as "rich." The upper class
American upper class
See: millionaire for more details-Millionaires:See also: MillionairesHouseholds with net worths of $1 million or more may be identified as members of the upper-most socio-economic demographic, depending on the class model used...
is most commonly defined as the top 1% with household incomes commonly exceeding $250,000 annually. These two figures should be seen only as guidelines based upon the top 1% of a population because net worth exceeding $1 million may be increasingly inaccurate as an upper class
Upper class
In social science, the "upper class" is the group of people at the top of a social hierarchy. Members of an upper class may have great power over the allocation of resources and governmental policy in their area.- Historical meaning :...
indicator as the value of the dollar falls and inflation along with interest and the turn of the 21st century's real estate boom causes more and more people to self-classify as millionaires.
The U.S. Census Bureau offers income data
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
by household and individual. 42% of households have two income earners; thus making households' income levels higher than personal income levels. The 2005 economic survey revealed the income distribution for households and individuals whereby the top 5% of individuals had six figure incomes (exceeding $100,000) and the top 10% of individuals had incomes exceeding $75,000. The top 5% of households, three quarters of whom had two income earners, had incomes of $166,200 (about 10 time the 2009 minimum wage in the US) or more, with the top 10% having incomes well in excess of $100,000. The top 1.5% of households had incomes exceeding $250,000 with 146,000 households, the top 0.12%, having incomes exceeding $1,600,000 annually. Households may also be differentiated among each other, depending on whether or not they have one or multiple income earners. While many middle-middle class
American middle class
The American middle class is a social class in the United States. While the concept is typically ambiguous in popular opinion and common language use, contemporary social scientists have put forward several, more or less congruent, theories on the American middle class...
households rely on two income earners to merely make ends meet, those in the upper middle class may be able to do so on just one income. In 2005 for example, the median households income
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
for a two income earner households was $67,000. The median income for an individual employed full-time with a graduate degree
Educational attainment in the United States
The educational attainment of the U.S. population is similar to that of many other industrialized countries with the vast majority of the population having completed secondary education and a rising number of college graduates that outnumber high school dropouts. As a whole, the population of the...
was in excess of $60,000, concluding that nearly half of those with graduate degree
Educational attainment in the United States
The educational attainment of the U.S. population is similar to that of many other industrialized countries with the vast majority of the population having completed secondary education and a rising number of college graduates that outnumber high school dropouts. As a whole, the population of the...
are able to out-earn most dual income households with one-income.
Overall the term affluent may be applied to a variety of individuals, households or other entities depending on context. Data from the U.S. Census Bureau serves as the main guideline for defining affluence. U.S. government data not only reveals the nation's income distribution
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
but also provides data regarding the demographic characteristics of those to whom the term, affluent, may be applied.
Top percentiles
Affluence and economic standing within society is often expressed in terms of percentile ranking. Economic ranking is conducted either in terms of giving lower thresholds for a designated group (e.g. the top 5%, 10%, 15%, etc.) or in terms of the percentage of households/individuals with incomes above a certain thresholds (e.g. above $75,000, $100,000, $150,000, etc.). The table below presents 2006 income data in terms of the lower thresholds for the given percentages (e.g. the top 25.6% of households had incomes exceeding $80,000, compared to $47,000 for the top quarter of individuals).| Data | Top third | Top quarter | Top quintile | Top 15% | Top 10% | Top 5% | Top 3% | Top 1.5% | Top 0.1% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Household income Household income in the United States Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support... |
||||||||||
| Lower threshold (annual gross income) | $65,000 | $80,000 | $91,202 | $100,000 | $118,200 | $166,200 | $200,000 | $250,000 | $1,600,000 | |
| Exact Percentage of households | 34.72% | 25.60% | 20.00% | 17.80% | 10.00% | 5.00% | 2.67% | 1.50% | 0.12% | |
| Personal income Personal income in the United States Personal income is an individual’s total earnings from wages, investment interest, and other sources. In the United States the most widely cited personal income statistics are the Bureau of Economic Analysis’s personal income and the Census Bureau’s per capita money income... (age 25+) |
||||||||||
| Lower threshold (annual gross income) | $37,500 | $47,500 | $52,500 | $62,500 | $75,000 | $100,000 | N/A | |||
| Exact Percentage of individuals | 33.55% | 24.03% | 19.74% | 14.47% | 10.29% | 5.63% | N/A | |||
Source: U.S. Census Bureau, 2006
Over time
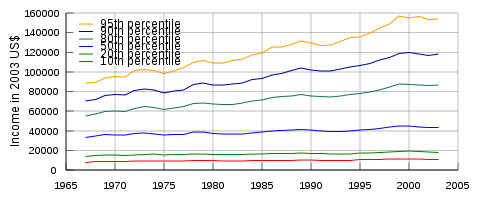
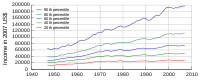
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
changes over the course of time, with income gains being substantially larger for the upper, than for the lower, percentiles. All areas of the income strata saw their incomes rise since the late 1960s, especially during the late 1990s. The overall increase in household income is largely the result of an increased percentage of households with more than one income earner. While households with just one income earner, most commonly the male, were the norm in the middle of the 20th century, 42% of all households and the vast majority of married couple households now have two or more income earners. With so many present day households having two income earners, a substantial increase in household income is easy to explain.
Two income earner households are far more common among the top quintile of households than the general population. 2006 U.S. Census Bureau data indicates that over three quarters, 76%, of households in the top quintile, with annual incomes
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
exceeding $91,200, had two or more income earners compared to just 42% among the general population and a small minority in the bottom three quintiles. As a result much of the rising income
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
inequity between the upper and lower percentiles can be explained through the increasing percentage of households with two or more incomes.
| Data | 2003 | 2000 | 1997 | 1994 | 1991 | 1988 | 1985 | 1982 | 1979 | 1976 | 1973 | 1970 | 1967 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20th percentile | $17,984 | $19,142 | $17,601 | $16,484 | $16,580 | $17,006 | $16,306 | $15,548 | $16,457 | $15,615 | $15,844 | $15,126 | $14,002 |
| Median (50th) | $43,318 | $44,853 | $42,294 | $39,613 | $39,679 | $40,678 | $38,510 | $36,811 | $38,649 | $36,155 | $37,700 | $35,832 | $33,338 |
| 80th percentile | $86,867 | $87,341 | $81,719 | $77,154 | $74,759 | $75,593 | $71,433 | $66,920 | $68,318 | $63,247 | $64,500 | $60,148 | $55,265 |
| 95th percentile | $154,120 | $155,121 | $144,636 | $134,835 | $126,969 | $127,958 | $119,459 | $111,516 | $111,445 | $100,839 | $102,243 | $95,090 | $88,678 |
Source: U.S. Census Bureau (2004): "Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2003", p. 36 et seq. All figures are inflation-adjusted and given in 2003 dollars.
Median income levels
Professions
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
derived from an occupation is largely determined by scarcity and the economic law of supply and demand
Supply and demand
Supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers will equal the quantity supplied by producers , resulting in an...
. The more demand for a certain specialty and the less supply, the higher the income. There has been shown to be a correlation between increases in income and increases in worker satisfaction. The decrease in worker dissatisfaction, however, is not solely a result of the increase in income. Workers in more complex and higher level
Social structure of the United States
Social class is a controversial issue in the United States, having many competing definitions, models, and even disagreements over its very existence. Many Americans believe in a simple three-class model that includes the "rich", the "middle class", and the "poor"...
occupations tend to have attained higher levels of education
Educational attainment in the United States
The educational attainment of the U.S. population is similar to that of many other industrialized countries with the vast majority of the population having completed secondary education and a rising number of college graduates that outnumber high school dropouts. As a whole, the population of the...
and thus are more likely to have a greater degree of autonomy in the workplace. Additionally higher level workers with advanced degrees are hired to share their personal knowledge, to conceptualize, and to consult. Higher-level workers suffer less job alienation and reap not only external benefits in terms of income from their jobs, but also enjoy high levels of intrinsic motivation and satisfaction.
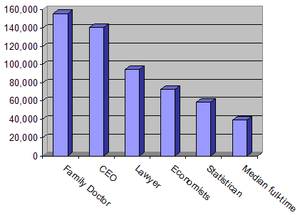
In the United States the highest earning occupational group is white collar professionals. Individuals in this occupational classification tend to experience the highest job satisfaction and highest incomes. Defining income based on title of a profession is fairly inaccurate, given that a professional title may indicate the type of education received, but does not always correlate with the actual day to day income producing endeavors that are pursued. Some sources cite the profession of physician in the United States as the highest paying, Physician (M.D.and D.O.) compensation ranks as the highest median annual earnings of any profession. Median annual earnings ranged from $156,010 for family physicians to $321,686 for anesthesiologists. Surgeons post a median annual income of $282,504. However, the annual salary for Chief Executive Officer (C.E.O.) is projected quite differently based on source: Salary.com reports a median salary of $634,941, while the U.S. Department of Labor in May 2004 reported the median as $140,350. This is primarily due to a methodological difference in terms of which companies were surveyed. Overall annual earnings among the nation's top 25 professions ranged from the $70,000s to the $300,000s. In addition to physicians, lawyers, physicists, and nuclear engineers were all among the nation's 20 highest paid occupations with incomes in excess of $78,410. Some of the other occupations in the high five-figure range were economists with a median of $72,780, mathematicians with $81,240, financial managers with $81,880, and software publishers with median annual earnings of $73,060. Median annual of wage-and-salary pharmacists in May 2006 were $94,520. The middle 50 percent earned between $83,180 and $108,140 a year (as in the Occupational Outlook Handbook, 2008–09 Edition by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics).
Education
Educational attainmentEducational attainment in the United States
The educational attainment of the U.S. population is similar to that of many other industrialized countries with the vast majority of the population having completed secondary education and a rising number of college graduates that outnumber high school dropouts. As a whole, the population of the...
plays a major factor in determining an individual's economic disposition. Personal income varied greatly according to an individual's education, as did household income. Incomes for those employed, full-time, year-round and over the age of twenty-five ranged from $20,826 ($17,422 if including those who worked part-time) for those with less than a ninth grade education to $100,000 for those with professional degrees ($82,473 if including those who work part-time). This median income for individuals with doctorates was $79,401 ($70,853 if including those who work part-time). These statistics reveal that the majority of those employed full-time with professional or doctoral degrees are among the overall top 10% (15% if including those who work part time) of income earners. Of those with a master's degree, nearly 50% were among the top quarter of income earners (top third if including those who work part time).
Race
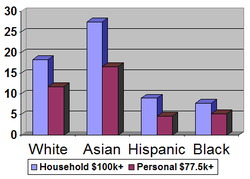
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
quintile, households with incomes exceeding $91,200, Asian American
Asian American
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian descent. The U.S. Census Bureau definition of Asians as "Asian” refers to a person having origins in any of the original peoples of the Far East, Southeast Asia, or the Indian subcontinent, including, for example, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Japan,...
s and Whites
White American
White Americans are people of the United States who are considered or consider themselves White. The United States Census Bureau defines White people as those "having origins in any of the original peoples of Europe, the Middle East, or North Africa...
were overrepresented, whereas Hispanics and African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
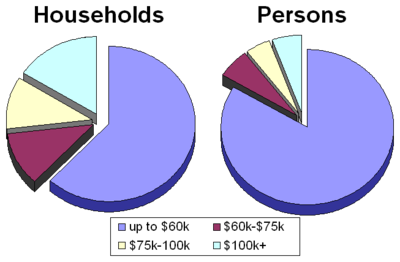
s were underrepresented. The household income for Asian Americans was, at $61,094, by far the highest, exceeding that of Whites ($48,554) by 26%. Over a quarter, 27.5%, of Asian American households had incomes exceeding $100,000 , and another 40% had incomes of over $75,000. Among White households, who remained near the national median, 18.3% had six figure incomes, while 28.9% had incomes exceeding $75,000. The percentages of households with incomes exceeding $100,000 and $75,000 were far below the national medians for Hispanic and African American households. Among Hispanic households, for example, only 9% had six figure incomes, and 17% had incomes exceeding $75,000. The race gap remained when considering personal income. In 2005, roughly 11% of Asian Americans and 7% of White individuals had six figure incomes, compared to 2.6% among Hispanics and 2.3% among African Americans.
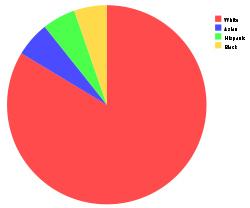
The racial breakdowns of income brackets further illustrate the racial disparities associated with affluence. in 2005, 81.8% of all 114 million households were White
White American
White Americans are people of the United States who are considered or consider themselves White. The United States Census Bureau defines White people as those "having origins in any of the original peoples of Europe, the Middle East, or North Africa...
(including White Hispanics), 12.2% were African American
African American
African Americans are citizens or residents of the United States who have at least partial ancestry from any of the native populations of Sub-Saharan Africa and are the direct descendants of enslaved Africans within the boundaries of the present United States...
, 10.9% were Hispanic and 3.7% were Asian American
Asian American
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian descent. The U.S. Census Bureau definition of Asians as "Asian” refers to a person having origins in any of the original peoples of the Far East, Southeast Asia, or the Indian subcontinent, including, for example, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Japan,...
. While White households are always near the national median
Household income in the United States
Household income is a measure commonly used by the United States government and private institutions, that counts the income of all residents over the age of 18 in each household, including not only all wages and salaries, but such items as unemployment insurance, disability payments, child support...
due to Whites being the by far most prevalent racial demographic, the percentages of minority households with incomes exceeding $100,000 strayed considerably from their percentage of the overall population. Asian Americans, who represent the smallest surveyed racial demographic in the overall population, were the found to be the prevalent minority among six figure income households. Among the nearly twenty million households with six figure incomes, 86.9% were White, 5.9% were Asian American, 5.6% were Hispanic and 5.5% were African American. Among the general individual population with earnings, 82.1% were White, 12.7% were Hispanic, 11.0% were African American and 4.6% were Asian American. Of the top 10% of income earners, those nearly 15 million individuals with incomes exceeding $77,500, Whites and Asians were once again overrepresented with the percentages of African Americans and Hispanics trailing behind considerably. Of the top 10% of earners, 86.7% were White. Asian Americans were the prevalent minority, constituting 6.8% of top 10% income earners, nearly twice the percentage of Asian Americans among the general population. Hispanics, who were the prevalent minority in the general population of income earners
Personal income in the United States
Personal income is an individual’s total earnings from wages, investment interest, and other sources. In the United States the most widely cited personal income statistics are the Bureau of Economic Analysis’s personal income and the Census Bureau’s per capita money income...
, constituted only 5.2% of those in the top 10%, with African Americans being the least represented with 5.1%.
| Race | Overall Median | High School | Some College | College Graduate | Bachelor's Degree | Master's Degree | Doctorate Degree | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total population | All, age 25+ | 32,140 | 26,505 | 31,054 | 49,303 | 43,143 | 52,390 | 70,853 |
| Full-time workers, age 25–64 | 39,509 | 31,610 | 37,150 | 56,027 | 50,959 | 61,324 | 79,292 | |
| White alone | All, age 25+ | 33,030 | 27,311 | 31,564 | 49,972 | 43,833 | 52,318 | 71,268 |
| Full-time workers, age 25–64 | 40,422 | 32,427 | 38,481 | 56,903 | 51,543 | 61,441 | 77,906 | |
| Asian alone | All, age 25+ | 36,152 | 25,285 | 29,982 | 51,481 | 42,466 | 61,452 | 69,653 |
| Full-time workers, age 25–64 | 42,109 | 27,041 | 33,120 | 60,532 | 51,040 | 71,316 | 91,430 | |
| African American | All, age 25+ | 27,101 | 22,379 | 27,648 | 44,534 | 41,572 | 48,266 | 61,894 |
| Full-time workers, age 25–64 | 32,021 | 26,230 | 32,392 | 47,758 | 45,505 | 52,858 | N/A | |
| Hispanic or Latino | All, age 25+ | 23,613 | 22,941 | 28,698 | 41,596 | 37,819 | 50,901 | 67,274 |
| Full-time workers, age 25–64 | 27,266 | 26,461 | 33,120 | 46,594 | 41,831 | 53,880 | N/A | |
Source: U.S. Census Bureau, 2006
Status and stratification
Economic well-being is often associated with high societal statusSocial structure of the United States
Social class is a controversial issue in the United States, having many competing definitions, models, and even disagreements over its very existence. Many Americans believe in a simple three-class model that includes the "rich", the "middle class", and the "poor"...
, yet income and economic compensation
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
are a function of scarcity and act as only one of a number of indicators of social class. It is in the interest of all of society that open positions are adequately filled with a competent occupant enticed to do his or her best. As a result, an occupation that requires a scarce skill, the attainment of which is often documented through an educational degree
Educational attainment in the United States
The educational attainment of the U.S. population is similar to that of many other industrialized countries with the vast majority of the population having completed secondary education and a rising number of college graduates that outnumber high school dropouts. As a whole, the population of the...
, and entrusts its occupant with a high degree of influence will generally offer high economic compensation. The high income is meant to ensure that the desired individuals obtain the necessary skills (e.g. medical or graduate school) and complete their tasks with the necessary valor. Differences in income may, however, be found among occupations of similar sociological nature. The median annual earnings of a physican were in excess of $150,000 in May 2004, compared to $95,000 for an attorney. Both occupations require finely tuned and scarce skill sets and both are essential to the well-being of society. Yet, physicians outearned attorneys and other upper middle class professionals by a wide margin as their skill-sets are deemed especially scarce. Overall, high status positions tend to be those requiring a scarce skill and are therefore commonly far better compensated than those in the middle of the occupational strata.
It is important to note that the above is an ideal type
Ideal type
Ideal type , also known as pure type, is a typological term most closely associated with antipositivist sociologist Max Weber . For Weber, the conduct of social science depends upon the construction of hypothetical concepts in the abstract...
, a simplified model or reality using optimal circumstances. In reality other factors such as discrimination based on race, ethnicity and gender as well as aggressive political lobbying by certain professional organizations also influence personal income. An individual's personal career decisions as well as his or her personal connections within the nation's economic institutions are also likely to have an effect on income, status
Social structure of the United States
Social class is a controversial issue in the United States, having many competing definitions, models, and even disagreements over its very existence. Many Americans believe in a simple three-class model that includes the "rich", the "middle class", and the "poor"...
and whether or not an individual may be referred to as affluent. In contemporary America it is a combination of all these factors, with scarcity remaining the by far most prominent one, determine a person's economic compensation. Due to higher status professions requiring advanced and thus less commonly found skill sets (including the ability to supervise and work with a considerable autonomy) are better compensated through the means of income, making high status individuals affluent, depending on reference group
Reference group
A reference group is a concept referring to a group to which an individual or another group is compared.Sociologists call any group that individuals use as a standard for evaluating themselves and their own behavior a reference group....
.
While the two paragraphs above only describe the relationship between status and personal income, household income is also often used to infer status. As a result, the dual income phenomenon presents yet another problem in equating affluence with high societal status
Social structure of the United States
Social class is a controversial issue in the United States, having many competing definitions, models, and even disagreements over its very existence. Many Americans believe in a simple three-class model that includes the "rich", the "middle class", and the "poor"...
. As mentioned earlier in the article 42% of households have two or more income earners, 76% of households with six figure incomes have two or more income earner
Income earner
Income earner refers to an individual who through work, investments or a combination of both derives income, which has a fixed and very fixed value of his/her income...
s. Furthermore people are most likely to marry their professional and societal equals. It therefore becomes apparent that the majority of households with incomes
Income in the United States
Income in the United States is measured by the United States Department of Commerce either by household or individual. The differences between household and personal income is considerable since 42% of households, the majority of those in the top two quintiles with incomes exceeding $57,658, now...
exceeding the six figure mark are the result of an economic as well as personal union between two economic equals. Today, two nurses, each making $55,000 a year, can easily outearn a single attorney who makes the median of $95,000 annually. Despite household income rising drastically through the union of two economic equals, neither individual has advanced his or her function and position within society. Yet the household (not individual) may have become more affluent, assuming an increase in household members
Median income per household member
The median income per member of household is a measure used by statisticians and the US Census Bureau to determine the median income that exists in a household for each of its members. In order to obtain this number the median household income is divided by the median number of persons in...
does not off-set the dual-income derived gains.
Extreme affluence
As of 2005, there were approximately 146,000 (0.1%) households with incomes exceeding $1,500,000, while the top 0.01% or 11,000 households had incomes exceeding $5,500,000. The 400 highest tax payers in the nation had gross annual household incomes exceeding $87,000,000. Household incomes for this group have risen more dramatically than for any other. As a result the gap between those who make less than one and half million dollars annually (99.9% of households) and those who make more (0.1%) has been steadily increasing, prompting The New York TimesThe New York Times
The New York Times is an American daily newspaper founded and continuously published in New York City since 1851. The New York Times has won 106 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any news organization...
to proclaim that the "Richest Are Leaving Even the Rich Far Behind." Indeed the income disparities within the top 1.5% are quite drastic. While households in the top 1.5% of households had incomes exceeding $250,000, 443% above the national median, their incomes were still 2200% lower than those of the top .01% of households. One can therefore conclude that almost any household, even those with incomes of $250,000 annually are poor when compared to the top .1%, who in turn are poor compared to the top 0.000267%, the top 400 taxpaying households.
See also
- The Affluent SocietyThe Affluent SocietyThe Affluent Society is a 1958 book by Harvard economist John Kenneth Galbraith. The book sought to clearly outline the manner in which the post-World War II America was becoming wealthy in the private sector but remained poor in the public sector, lacking social and physical infrastructure, and...
- Economy of the United StatesEconomy of the United StatesThe economy of the United States is the world's largest national economy. Its nominal GDP was estimated to be nearly $14.5 trillion in 2010, approximately a quarter of nominal global GDP. The European Union has a larger collective economy, but is not a single nation...
- International Ranking of Household Income
- List of Average Wages per Country
- States of the United States of America by income
External links
- Alternate income measures forum
- Americans Underestimate U.S. Wealth Inequality - audio report by NPRNPRNPR, formerly National Public Radio, is a privately and publicly funded non-profit membership media organization that serves as a national syndicator to a network of 900 public radio stations in the United States. NPR was created in 1970, following congressional passage of the Public Broadcasting...
- 15 Mind-Blowing Facts About Wealth And Inequality In America - charts by The Business Insider
- US Census Bureau, personal income forum *US Census Bureau, household income forum
- It's the Inequality, Stupid: 11 Charts that Explain Everything that's Wrong with America - March 2011 issue of Mother JonesMother Jones (magazine)Mother Jones is an American independent news organization, featuring investigative and breaking news reporting on politics, the environment, human rights, and culture. Mother Jones has been nominated for 23 National Magazine Awards and has won six times, including for General Excellence in 2001,...

