
Advanced Test Reactor
Encyclopedia
The Advanced Test Reactor (ATR) is a research reactor
at the Idaho National Laboratory
, located east of Arco, Idaho
. This reactor is primarily designed and used to test materials to be used in other, larger-scale and prototype
reactors. It can operate at a maximum power of 250 MW and has a "Four Leaf Clover" design that allows for a variety of testing locations. The unique design allows for different flux
in various locations and specialized systems also allow for certain experiments to be run at their own temperature and pressure.
The ATR is light water moderated
and cooled
, with a beryllium
neutron reflector
. It is pressurized and housed in a stainless steel
tank.
 As well as its role in materials irradiation
As well as its role in materials irradiation
work, ATR is the USA's only source of Cobalt-60
for medical applications.
 Since 1951, fifty-two reactors have existed on the grounds of the Idaho National Laboratory's National Reactor Testing Station. Constructed in 1967, the ATR is the second-oldest of three reactors still in operation at the site. Its primary function is to intensely bombard samples of materials and fuels with neutron
Since 1951, fifty-two reactors have existed on the grounds of the Idaho National Laboratory's National Reactor Testing Station. Constructed in 1967, the ATR is the second-oldest of three reactors still in operation at the site. Its primary function is to intensely bombard samples of materials and fuels with neutron
s to simulate long-term exposure to high levels of radiation
, as would be present in a commercial nuclear reactor. The ATR is one of only four test reactors in the world with this capability. The reactor also produces rare isotope
s for use in medicine
and industry
.
, laboratories
, and industry. This status is intended to stimulate experiments to extend the life of existing commercial reactors and encourage nuclear power development. These experiments will test "materials, nuclear fuel
, and instruments that operate in the reactors." Under this program, experimenters will not have to pay to perform experiments at the reactor, but are required to publish their findings. The interest from the academic community was seen at the 2009 ATR NSUF User's Week Conference, held in Idaho Falls, that attracted 32 different universities. There were five different university experiments assigned to the ATR in 2008, and another two in 2009.
and pressure
, and require a large amount of nuclear fuel. A typical commercial reactor has a volume of 48 cubic meters with 5400 kg of uranium
at 288 °C (550.4 °F) and 177 atm. Because of their large size and stored energy, commercial reactors require a robust "containment structure" to prevent the release of radioactive material in the event of an emergency situation.
By contrast, the ATR does not require a large containment structure—it has a volume of 1.4 cubic meters, contains 43 kg of uranium, and operates at 60 °C (140 °F) and 26.5 atm (conditions similar to a water heater). The reactor vessel itself, which is made of stainless steel surrounded by concrete that extends more than 20 feet (6.1 m) underground, is hardened against accidental or intentional damage. The entire reactor area is also surrounded by a confinement structure (as opposed to a "containment structure") designed to further protect the surrounding environment from any potential release of radioactivity.
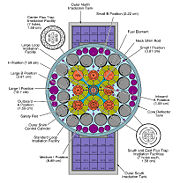 The ATR core is designed to be as flexible as possible for research
The ATR core is designed to be as flexible as possible for research
needs. It can be brought online and powered down safely as often as necessary to change experiments or perform maintenance. The reactor is also powered down automatically in the event of abnormal experimental conditions or power failure.
Components of the reactor core are replaced as necessary every 7–10 years to prevent fatigue
due to exposure to radiation and to ensure experimenters always have a new reactor to work with. The neutron flux
provided by the reactor can be either constant or variable, and each lobe of the four-leaf-clover design can be controlled independently to produce up to 1015 thermal neutrons per second per square centimeter or 5·1014 fast neutrons s−1 cm−2. There are 77 different testing locations inside the reflector and another 34 low-intensity locations outside the core (see figure at right), allowing many experiments to run simultaneously in different test environments. Test volumes up to 5 inches (127 mm) in diameter and 4 feet (1.2 m) long can be accommodated. Experiments are changed on average every seven weeks, and the reactor is in nominal operation (110 MW) 75% of the year.
Three types of experiments can be performed in the reactor:
Research experiments at the reactor include:
Research reactor
Research reactors are nuclear reactors that serve primarily as a neutron source. They are also called non-power reactors, in contrast to power reactors that are used for electricity production, heat generation, or maritime propulsion.-Purpose:...
at the Idaho National Laboratory
Idaho National Laboratory
Idaho National Laboratory is an complex located in the high desert of eastern Idaho, between the town of Arco to the west and the cities of Idaho Falls and Blackfoot to the east. It lies within Butte, Bingham, Bonneville and Jefferson counties...
, located east of Arco, Idaho
Arco, Idaho
Arco is a city in Butte County, Idaho, United States. The population was 995 at the 2010 census. The city is the county seat of Butte County.Craters of the Moon National Monument is located along U.S. Route 20, southwest of the city. The Idaho National Laboratory is located east of Arco...
. This reactor is primarily designed and used to test materials to be used in other, larger-scale and prototype
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
reactors. It can operate at a maximum power of 250 MW and has a "Four Leaf Clover" design that allows for a variety of testing locations. The unique design allows for different flux
Flux
In the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
in various locations and specialized systems also allow for certain experiments to be run at their own temperature and pressure.
The ATR is light water moderated
Neutron moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, thereby turning them into thermal neutrons capable of sustaining a nuclear chain reaction involving uranium-235....
and cooled
Nuclear reactor coolant
A nuclear reactor coolant is a coolant in a nuclear reactor used to remove heat from the nuclear reactor core and transfer it to electrical generators and the environment....
, with a beryllium
Beryllium
Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl...
neutron reflector
Neutron reflector
A neutron reflector is any material that reflects neutrons. This refers to elastic scattering rather than to a specular reflection. The material may be graphite, beryllium, steel, and tungsten carbide, or other materials...
. It is pressurized and housed in a stainless steel
Stainless steel
In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable", is defined as a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5 or 11% chromium content by mass....
tank.

Irradiation
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. The exposure can originate from various sources, including natural sources. Most frequently the term refers to ionizing radiation, and to a level of radiation that will serve a specific purpose, rather than radiation exposure to...
work, ATR is the USA's only source of Cobalt-60
Cobalt-60
Cobalt-60, , is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt. Due to its half-life of 5.27 years, is not found in nature. It is produced artificially by neutron activation of . decays by beta decay to the stable isotope nickel-60...
for medical applications.
History

Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s to simulate long-term exposure to high levels of radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
, as would be present in a commercial nuclear reactor. The ATR is one of only four test reactors in the world with this capability. The reactor also produces rare isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
s for use in medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
and industry
Industry
Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,...
.
National Scientific User Facility
In April 2007, the ATR was designated a "National Scientific User Facility" to encourage use of the reactor by universitiesUniversity
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees in a variety of subjects. A university is an organisation that provides both undergraduate education and postgraduate education...
, laboratories
Laboratory
A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. The title of laboratory is also used for certain other facilities where the processes or equipment used are similar to those in scientific laboratories...
, and industry. This status is intended to stimulate experiments to extend the life of existing commercial reactors and encourage nuclear power development. These experiments will test "materials, nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available...
, and instruments that operate in the reactors." Under this program, experimenters will not have to pay to perform experiments at the reactor, but are required to publish their findings. The interest from the academic community was seen at the 2009 ATR NSUF User's Week Conference, held in Idaho Falls, that attracted 32 different universities. There were five different university experiments assigned to the ATR in 2008, and another two in 2009.
ATR compared with commercial reactors
Test reactors are very different in appearance and design from commercial, nuclear power reactors. Commercial reactors are large, operate at high temperatureTemperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
, and require a large amount of nuclear fuel. A typical commercial reactor has a volume of 48 cubic meters with 5400 kg of uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
at 288 °C (550.4 °F) and 177 atm. Because of their large size and stored energy, commercial reactors require a robust "containment structure" to prevent the release of radioactive material in the event of an emergency situation.
By contrast, the ATR does not require a large containment structure—it has a volume of 1.4 cubic meters, contains 43 kg of uranium, and operates at 60 °C (140 °F) and 26.5 atm (conditions similar to a water heater). The reactor vessel itself, which is made of stainless steel surrounded by concrete that extends more than 20 feet (6.1 m) underground, is hardened against accidental or intentional damage. The entire reactor area is also surrounded by a confinement structure (as opposed to a "containment structure") designed to further protect the surrounding environment from any potential release of radioactivity.
Reactor design and experimental capabilities

Research
Research can be defined as the scientific search for knowledge, or as any systematic investigation, to establish novel facts, solve new or existing problems, prove new ideas, or develop new theories, usually using a scientific method...
needs. It can be brought online and powered down safely as often as necessary to change experiments or perform maintenance. The reactor is also powered down automatically in the event of abnormal experimental conditions or power failure.
Components of the reactor core are replaced as necessary every 7–10 years to prevent fatigue
Fatigue (material)
'In materials science, fatigue is the progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading. The nominal maximum stress values are less than the ultimate tensile stress limit, and may be below the yield stress limit of the material.Fatigue occurs...
due to exposure to radiation and to ensure experimenters always have a new reactor to work with. The neutron flux
Neutron flux
The neutron flux is a quantity used in reactor physics corresponding to the total length travelled by all neutrons per unit time and volume . The neutron fluence is defined as the neutron flux integrated over a certain time period....
provided by the reactor can be either constant or variable, and each lobe of the four-leaf-clover design can be controlled independently to produce up to 1015 thermal neutrons per second per square centimeter or 5·1014 fast neutrons s−1 cm−2. There are 77 different testing locations inside the reflector and another 34 low-intensity locations outside the core (see figure at right), allowing many experiments to run simultaneously in different test environments. Test volumes up to 5 inches (127 mm) in diameter and 4 feet (1.2 m) long can be accommodated. Experiments are changed on average every seven weeks, and the reactor is in nominal operation (110 MW) 75% of the year.
Three types of experiments can be performed in the reactor:
- Static Capsule Experiment: The material to be tested is placed in a sealed tube made of aluminum, stainless steel, or zircaloyZircaloyZirconium alloys are solid solutions of zirconium or other metals, a common subgroup having the trade mark Zircaloy. Zirconium has very low absorption cross-section of thermal neutrons, high hardness, ductility and corrosion resistance...
, which is then inserted in the desired reactor location. If the tube is less than the full 48" reactor height, several capsules may be stacked. In some cases, it is desirable to test materials (such as fuel elements) in direct contact with the reactor coolantNuclear reactor coolantA nuclear reactor coolant is a coolant in a nuclear reactor used to remove heat from the nuclear reactor core and transfer it to electrical generators and the environment....
, in which case, the test capsule is not sealed.
Very limited monitoring and temperature control are available for the static capsule configuration, and any instances would have to be built into the capsule experiment (such as temperature melt wires or an insulating air gap).
- Instrumented Lead Experiment: Similar to the Static Capsule configuration, this type of experiment allows for real-time monitoring of temperature and gas conditions inside the capsule. An umbilical connects the test capsule to a control station to report test conditions. The control station automatically regulates the temperature inside the test capsule as desired by pumping a combination of heliumHeliumHelium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
(conducting) and neonNeonNeon is the chemical element that has the symbol Ne and an atomic number of 10. Although a very common element in the universe, it is rare on Earth. A colorless, inert noble gas under standard conditions, neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in either low-voltage neon glow lamps or...
or argonArgonArgon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
(nonconducting) gases through the capsule. The circulated gas can be examined though gas-liquid chromatographyGas-liquid chromatographyGas chromatography , is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analysing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture...
to test for failure or oxidation of the material being tested.
- Pressurized Water Loop Experiment: More complex than the Instrumented Lead configuration, this type of experiment is available in only five of the flux tubes. Test material is isolated from the primary ATR coolant by a secondary coolant system, allowing for precise conditions of a commercial reactor to be simulated. Extensive instrumentation and control systems in this type of experiment generate a large amount of data, which is available to the experimenter in real-time so that changes can be made to the experiment as required.
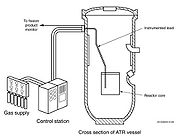
Research experiments at the reactor include:
- Advanced Graphite Capsule: This experiment will test the effects of radiation on several types of graphite under consideration for the Next Generation Nuclear PlantNext Generation Nuclear PlantA Next Generation Nuclear Plant is a generation IV version of the Very High Temperature Reactor that could be coupled to a neighboring hydrogen production facility. It could also produce electricity and supply process heat...
program that currently have no high-flux temperature data available. - Advanced Fuel Cycle Initiative / Light Water Reactor: The goal of the AFCI is to transmute longer-life fuels into shorter-life ones which would be able to be used in commercial light water reactors, to reduce the amount of wasteRadioactive wasteRadioactive wastes are wastes that contain radioactive material. Radioactive wastes are usually by-products of nuclear power generation and other applications of nuclear fission or nuclear technology, such as research and medicine...
that must be stored while increasing the fuel available for commercial reactors. - Cobalt-60Cobalt-60Cobalt-60, , is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt. Due to its half-life of 5.27 years, is not found in nature. It is produced artificially by neutron activation of . decays by beta decay to the stable isotope nickel-60...
Production: The least complex of current uses of the Advanced Test Reactor is the production of the Co-60 isotopeIsotopeIsotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
for medical uses. Disks of Cobalt-59 1 mm -diameter by 1 mm thick are inserted into the reactor (Static Capsule Experiment), which bombards the sample with neutrons, producing Cobalt-60. Approximately 200 kCi are produced per year, entirely for medical uses.
External links
- ATR factsheet (PDFPortable Document FormatPortable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
, 868KB). - ATR Capabilities and Future Operating Plans (PDFPortable Document FormatPortable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
, 800KB) - ATR Irradiation Facilities and Capabilities (PDFPortable Document FormatPortable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
, 2.4MB)

