
Abbe number
Encyclopedia
In physics
and optics
, the Abbe number, also known as the V-number or constringence of a transparent material, is a measure of the material's dispersion
(variation of refractive index with wavelength) in relation to the refractive index
. It is named after Ernst Abbe (1840–1905), the German physicist who defined it.
The Abbe number V of a material is defined as
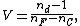
where nd, nF and nC are the refractive indices of the material at the wavelengths of the Fraunhofer
d-, F- and C- spectral line
s (587.6 nm
, 486.1 nm and 656.3 nm respectively). Low dispersion (low chromatic aberration) materials have high values of V.
Abbe numbers are used to classify glass
and other optically transparent materials. For example, flint glass
has V < 50 and crown glass
has V > 50. Typical values of V range from around 20 for very dense flint glass, around 30 for polycarbonate
plastics, and up to 65 for very light crown glass, and up to 85 for fluor
-crown glass. Abbe numbers are only a useful measure of dispersion for visible light, and for other wavelengths, or for higher precision work, the group velocity dispersion
is used.
Alternate definitions of the Abbe number are used in some contexts. The value Vd is given by
which defines the Abbe number with respect to the yellow Fraunhofer d (or D3) helium
line at 587.5618 nm wavelength. It can also be defined at the green mercury
E-line at 546.073 nm:
where F' and C' are the blue and red cadmium
lines at 480.0 nm and 643.8 nm, respectively.
An Abbe diagram is produced by plotting the Abbe number Vd of a material versus its refractive index nd. Glasses can then be categorised by their composition and position on the diagram. This can be a letter-number code, as used in the Schott Glass
catalogue, or a 6-digit glass code
.
Abbe numbers are used to calculate the necessary focal length
s of achromatic doublet
lenses
to minimize chromatic aberration
.
The following table lists standard wavelengths at which n is usually determined, indicated by subscripts. For example, nD is measured at 589.3 nm:
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
and optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, the Abbe number, also known as the V-number or constringence of a transparent material, is a measure of the material's dispersion
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
(variation of refractive index with wavelength) in relation to the refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
. It is named after Ernst Abbe (1840–1905), the German physicist who defined it.
The Abbe number V of a material is defined as
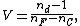
where nd, nF and nC are the refractive indices of the material at the wavelengths of the Fraunhofer
Fraunhofer lines
In physics and optics, the Fraunhofer lines are a set of spectral lines named for the German physicist Joseph von Fraunhofer . The lines were originally observed as dark features in the optical spectrum of the Sun....
d-, F- and C- spectral line
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
s (587.6 nm
Nanometre
A nanometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one billionth of a metre. The name combines the SI prefix nano- with the parent unit name metre .The nanometre is often used to express dimensions on the atomic scale: the diameter...
, 486.1 nm and 656.3 nm respectively). Low dispersion (low chromatic aberration) materials have high values of V.
Abbe numbers are used to classify glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
and other optically transparent materials. For example, flint glass
Flint glass
Flint glass is optical glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number. Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45 and 2.00...
has V < 50 and crown glass
Crown glass (optics)
Crown glass is type of optical glass used in lenses and other optical components. It has relatively low refractive index and low dispersion...
has V > 50. Typical values of V range from around 20 for very dense flint glass, around 30 for polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
PolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%...
plastics, and up to 65 for very light crown glass, and up to 85 for fluor
Fluorite
Fluorite is a halide mineral composed of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It is an isometric mineral with a cubic habit, though octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon...
-crown glass. Abbe numbers are only a useful measure of dispersion for visible light, and for other wavelengths, or for higher precision work, the group velocity dispersion
Dispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
is used.
Alternate definitions of the Abbe number are used in some contexts. The value Vd is given by

which defines the Abbe number with respect to the yellow Fraunhofer d (or D3) helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
line at 587.5618 nm wavelength. It can also be defined at the green mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
E-line at 546.073 nm:

where F' and C' are the blue and red cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
lines at 480.0 nm and 643.8 nm, respectively.
An Abbe diagram is produced by plotting the Abbe number Vd of a material versus its refractive index nd. Glasses can then be categorised by their composition and position on the diagram. This can be a letter-number code, as used in the Schott Glass
Schott Glass
SCHOTT AG is a German manufacturer of high-quality industrial glass products, its main markets are household appliances, pharmaceutical industries, solar energy, electronics, optics as well as automotive...
catalogue, or a 6-digit glass code
Glass code
A glass code is a method of classifying glasses for optical use, such as the manufacture of lenses and prisms. There are many different types of glass with different compositions and optical properties, and a glass code is used to distinguish between them....
.
Abbe numbers are used to calculate the necessary focal length
Focal length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light. For an optical system in air, it is the distance over which initially collimated rays are brought to a focus...
s of achromatic doublet
Achromatic lens
An achromatic lens or achromat is a lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to bring two wavelengths into focus in the same plane....
lenses
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
to minimize chromatic aberration
Chromatic aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration is a type of distortion in which there is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same convergence point. It occurs because lenses have a different refractive index for different wavelengths of light...
.
The following table lists standard wavelengths at which n is usually determined, indicated by subscripts. For example, nD is measured at 589.3 nm:
| λ in nm | Fraunhofer's symbol Fraunhofer lines In physics and optics, the Fraunhofer lines are a set of spectral lines named for the German physicist Joseph von Fraunhofer . The lines were originally observed as dark features in the optical spectrum of the Sun.... |
Light source | Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| 365.01 | i | Hg | UV |
| 404.66 | h | Hg | violet |
| 435.84 | g | Hg | blue |
| 479.99 | F' | Cd | blue |
| 486.13 | F | H | blue |
| 546.07 | e | Hg | green |
| 587.56 | d | He | yellow |
| 589.3 | D | Na | yellow |
| 643.85 | C' | Cd | red |
| 656.27 | C | H | red |
| 706.52 | r | He | red |
| 768.2 | A' | K | IR |
| 852.11 | s | Cs | IR |
| 1013.98 | t | Hg | IR |
See also
- Abbe prismAbbe prismIn optics, an Abbe prism, named for its inventor, the German physicist Ernst Abbe, is a type of constant deviation dispersive prism similar to a Pellin–Broca prism.-Structure:...
- Abbe refractometerAbbe refractometerAn Abbe refractometer is a bench-top device for the high-precision measurement of an index of refraction.- Details :Ernst Abbe , working for the Zeiss Company in Jena, Germany in the late 19th century, was the first to develop a laboratory refractometer...
- Calculation of glass propertiesCalculation of glass propertiesThe calculation of glass properties is used to predict glass properties of interest or glass behavior under certain conditions without experimental investigation, based on past data and experience, with the intention to save time, material, financial, and environmental resources, or to gain...
, including Abbe number - Glass codeGlass codeA glass code is a method of classifying glasses for optical use, such as the manufacture of lenses and prisms. There are many different types of glass with different compositions and optical properties, and a glass code is used to distinguish between them....

