
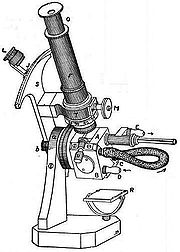
Abbe refractometer
Encyclopedia
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
.
Details
Ernst Abbe (1840–1905), working for the Zeiss Company in Jena, Germany in the late 19th century, was the first to develop a laboratory refractometer. These first instruments had built-in thermometers and required circulating water to control instrument and fluid temperatures. They also had adjustments for eliminating the effects of dispersionDispersion (optics)
In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency, or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency.Media having such a property are termed dispersive media...
and analog scales from which the readings were taken.
In the Abbe' refractometer the liquid sample is sandwiched into a thin layer between an illuminating prism and a refracting prism. The refracting prism is made of a glass with a high refractive index (e.g., 1.75) and the refractometer is designed to be used with samples having a refractive index smaller than that of the refracting prism. A light source is projected through the illuminating prism, the bottom surface of which is ground (i.e., roughened like a ground-glass joint), so each point on this surface can be thought of as generating light rays traveling in all directions. A detector placed on the back side of the refracting prism would show a light and a dark region.
Over a century after Abbe's work, the usefulness and precision of refractometers has improved, although their principle of operation has changed very little. They are also possibly the easiest device to use for measuring the refractive index of solid samples, such as glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
, plastics, and polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
films. Some modern Abbe refractometers use a digital
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
display for measurement, eliminating the need for discerning between small graduations. However, the user still has to adjust the view to get a final reading.
The first truly digital laboratory refractometers began appearing in the late 1970s and early 1980s, and no longer depended on the user's eye to determine the reading. They still required the use of circulating water baths to control instrument and fluid temperature. They did, however, have the ability to electronically compensate for the temperature differences of many fluids where there is a known concentration-to-refractive-index conversion. Most digital laboratory refractometers, while much more accurate and versatile than their analog Abbe counterparts, are incapable of readings on solid samples.
In the late 1990s, Abbe refractometers became available with the capability of measurements at wavelengths other than the standard 589 nanometers. These instruments use special filters to reach the desired wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
, and can extend measurements well into the near infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
(though a special viewer is required to see the infrared rays). Multi-wavelength Abbe refractometers can be used to easily determine a sample's Abbe number
Abbe number
In physics and optics, the Abbe number, also known as the V-number or constringence of a transparent material, is a measure of the material's dispersion in relation to the refractive index...
.

See also
- Refractive indexRefractive indexIn optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
- Traditional handheld refractometerTraditional handheld refractometerA traditional handheld refractometer is an analog instrument for measuring a liquid's refractive index. It works on the critical angle principle by which lenses and prisms project a shadow line onto a small glass reticle inside the instrument, which is then viewed by the user through a magnifying...
- Digital handheld refractometerDigital handheld refractometerA digital handheld refractometer is an instrument for measuring the refractive index of materials.-Principle of operation:Most operate on the same general critical angle principle as a traditional handheld refractometer. The difference is that light from an LED light source is focused on the...
- Inline process refractometerInline process refractometerInline process refractometers are a type of refractometer designed for the continuous measurement of a fluid flowing through a pipe or inside a tank. These refractometers typically consist of a sensor, placed inline with the fluid flow, coupled to a control box...
External links
- refractometer after Ernst Abbe by Carl Zeiss made in 1904
- improved Abbe refractometer by Carl Zeiss made in 1928

