1890 Atlantic hurricane season
Encyclopedia
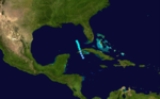
The 1890 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1890.
The 1890 season was fairly inactive, with only four storms forming. Two became hurricanes, two were tropical storms. However, due to scarce technology and the fact that only storms that affected land or ships were recorded, the actual total could be higher.
No hurricanes made landfall in the United States
in 1890. It wouldn't be till 1990
, 100 years later, that a hurricane, or even a tropical storm didn't make landfall in the United States.
, and went north across it with 50 mph (80 km/h) winds. It dissipated soon after leaving Cuban land on May 29.
on August 18. It continued west-northwest, and hit near the northeastern tip of the Yucatán Peninsula
with 50 mph (80 km/h) winds. It continued north and hit the southeastern part of Louisiana. It continued up into Mississippi, where it dissipated on August 28.
. It formed to the northeast of the Lesser Antilles
, and continued northwest. When it got to a position northeast of the Bahamas, it reached a peak of 115 mph winds, turned northwest and headed toward Nova Scotia
. It traveled right over the southeastern coast of Nova Scotia, causing ship damage and fatalities. It then continued on its northeast path, and dissipated on September 3. It caused 9 deaths from a boat sinking.
on October 31. It traveled west, and hit Nicaragua with 80 mph (129 km/h) winds.
The 1890 season was fairly inactive, with only four storms forming. Two became hurricanes, two were tropical storms. However, due to scarce technology and the fact that only storms that affected land or ships were recorded, the actual total could be higher.
No hurricanes made landfall in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
in 1890. It wouldn't be till 1990
1990 Atlantic hurricane season
The 1990 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active Atlantic hurricane season since 1969. It officially began on June 1, 1990, and lasted until November 30, 1990. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin...
, 100 years later, that a hurricane, or even a tropical storm didn't make landfall in the United States.
Tropical Storm One
The season began unusually early, on May 27. This storm formed directly below CubaCuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
, and went north across it with 50 mph (80 km/h) winds. It dissipated soon after leaving Cuban land on May 29.
Tropical Storm Two
The season continued with the second storm forming very close to the west coast of the Lesser AntillesLesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
on August 18. It continued west-northwest, and hit near the northeastern tip of the Yucatán Peninsula
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
with 50 mph (80 km/h) winds. It continued north and hit the southeastern part of Louisiana. It continued up into Mississippi, where it dissipated on August 28.
Hurricane Three
The next storm was first detected on August 26, possibly forming earlier as a Cape Verde-type hurricaneCape Verde-type hurricane
A Cape Verde-type hurricane is an Atlantic hurricane that develops near the Cape Verde islands, off the west coast of Africa. The average hurricane season has about two Cape Verde-type hurricanes, which are usually the largest and most intense storms of the season because they often have plenty of...
. It formed to the northeast of the Lesser Antilles
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
, and continued northwest. When it got to a position northeast of the Bahamas, it reached a peak of 115 mph winds, turned northwest and headed toward Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
. It traveled right over the southeastern coast of Nova Scotia, causing ship damage and fatalities. It then continued on its northeast path, and dissipated on September 3. It caused 9 deaths from a boat sinking.
Hurricane Four
The last storm formed to the east of NicaraguaNicaragua
Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
on October 31. It traveled west, and hit Nicaragua with 80 mph (129 km/h) winds.
See also
- List of tropical cyclones
- List of Atlantic hurricane seasons

