
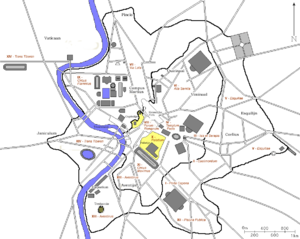
14 regions of the Augustan Rome
Encyclopedia
Augustus
Augustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
divided the city of Rome
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
into 14 administrative regions (Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
regiones). These replaced the four regiones or "quarters" traditionally attributed to Servius Tullius
Servius Tullius
Servius Tullius was the legendary sixth king of ancient Rome, and the second of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned 578-535 BC. Roman and Greek sources describe his servile origins and later marriage to a daughter of Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, Rome's first Etruscan king, who was assassinated in 579 BC...
, sixth King of Rome
King of Rome
The King of Rome was the chief magistrate of the Roman Kingdom. According to legend, the first king of Rome was Romulus, who founded the city in 753 BC upon the Palatine Hill. Seven legendary kings are said to have ruled Rome until 509 BC, when the last king was overthrown. These kings ruled for...
. They were further divided into official neighborhoods (vici
Vicus (Rome)
In ancient Rome, the vicus was a neighborhood. During the Republican era, the four regiones of the city of Rome were subdivided into vici. In the 1st century BC, Augustus reorganized the city for administrative purposes into 14 regions, comprising 265 vici. Each vicus had its own board of...
). Originally designated by number, the regions acquired nicknames from major landmarks or topographical features
Topography of ancient Rome
The topography of ancient Rome is a multidisciplinary field of study that draws on archaeology, epigraphy, cartography and philology.The classic English-language work of scholarship is A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome , written by Samuel Ball Platner, completed and published after his...
within them.
I: Porta Capena
Regio I took its name from the Porta CapenaPorta Capena
The Porta Capena was a gate in the Servian Wall near the Caelian Hill, in Rome, Italy according to Roman tradition the sacred grove where Numa Pompilius and the nymph Egeria used to meet. It was one of the main entries to the city of Rome, since it opened on the Appian Way...
("Gate to Capua"), a gate through the Servian Wall
Servian Wall
The Servian Wall was a defensive barrier constructed around the city of Rome in the early 4th century BC. The wall was up to 10 metres in height in places, 3.6 metres wide at its base, 11 km long, and is believed to had 16 main gates, though many of these are mentioned only from...
s which the Appian Way
Appian Way
The Appian Way was one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, Apulia, in southeast Italy...
takes to get into the city. Beginning from this to the south of the Caelian Hill
Caelian Hill
The Caelian Hill is one of the famous Seven Hills of Rome. Under reign of Tullus Hostilius, the entire population of Alba Longa was forcibly resettled on the Caelian Hill...
, it runs to the future track of the Aurelian Walls
Aurelian Walls
The Aurelian Walls is a line of city walls built between 271 and 275 in Rome, Italy, during the reign of the Roman Emperors Aurelian and Probus....
.
III: Isis et Serapis
Regio III took its name from the sanctuary of IsisIsis
Isis or in original more likely Aset is a goddess in Ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. She was worshipped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic...
, in the area of the modern Labicana street, containing the valley which was to be the future site of the Colosseum
Colosseum
The Colosseum, or the Coliseum, originally the Flavian Amphitheatre , is an elliptical amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, the largest ever built in the Roman Empire...
, and parts of the Oppian
Oppian Hill
The Oppian Hill is the southern spur of the Esquiline Hill , one of the famous Seven Hills of Rome. It is separated from the Cispius on the north by the valley of the Subura, and from the Caelian Hill on the south by the valley of the Colosseum...
and Esquiline
Esquiline Hill
The Esquiline Hill is one of the celebrated Seven Hills of Rome. Its southern-most cusp is the Oppius .-Etymology:The origin of the name Esquilino is still under much debate. One view is that the Hill was named after the abundance of holm-oaks, exculi, that resided there...
hills.
IV: Templum Pacis
Region IV took its name from the Temple of Peace built in the region by VespasianVespasian
Vespasian , was Roman Emperor from 69 AD to 79 AD. Vespasian was the founder of the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for a quarter century. Vespasian was descended from a family of equestrians, who rose into the senatorial rank under the Emperors of the Julio-Claudian dynasty...
. It includes the valley between the Esquiline and the Viminal
Viminal Hill
The Viminal Hill is the smallest of the famous seven hills of Rome. A finger-shape cusp pointing toward central Rome between the Quirinal Hill to the northwest and the Esquiline Hill to the southeast, it is home to the Teatro dell'Opera and the Termini Railway Station.At the top of Viminal Hill...
hills, the popular area of the Subura, and the Velian Hill
Velian Hill
The Velia — or Velian Hill or Velian Ridge — is a saddle or spur stretching out from the middle of the north side of the Palatine Hill towards the Oppian Hill ....
(the hill between the Palatine
Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill is the centermost of the Seven Hills of Rome and is one of the most ancient parts of the city...
and the Oppian Hill, removed in the early 20th century to make way for the via dei Fori Imperiali, the street passing between the Forum Romanum and the Forum of Augustus).
V: Esquiliae
The name of Regio V derives from the Esquiline hill. It contains parts of the Oppian and Cispian (two minor hills close to the city center) and of the Esquiline, plus the plain just outside the Servian walls.VI: Alta Semita
The name of Regio VI derives from the street (Alta Semita, "High Path") passing over the Quirinal HillQuirinal Hill
The Quirinal Hill is one of the Seven Hills of Rome, at the north-east of the city center. It is the location of the official residence of the Italian Head of State, who resides in the Quirinal Palace; by metonymy "the Quirinal" has come to stand for the Italian President.- History :It was...
. The regio contains parts of the Quirinal and Viminal hills.
VII: Via Lata
The name of Regio VII was derived from the via FlaminiaVia Flaminia
The Via Flaminia was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to Ariminum on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had for travel between Etruria, Latium and Campania and the Po Valley...
which runs between the Servian walls and the future Aurelian Walls
Aurelian Walls
The Aurelian Walls is a line of city walls built between 271 and 275 in Rome, Italy, during the reign of the Roman Emperors Aurelian and Probus....
. This was a wide urban street (Via Lata, "Broadway"), corresponding to the modern via del Corso
Via del Corso
The Via del Corso , commonly known as the Corso, is a main street in the historical centre of Rome. It is remarkable for being absolutely straight in an area characterized by narrow meandering alleys and small piazzas...
. The regio contained part of the Campus Martius
Campus Martius
The Campus Martius , was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome...
on the east of the street plus the Collis Hortulorum (Hill of the Hortuli), the Pincian Hill
Pincian Hill
The Pincian Hill is a hill in the northeast quadrant of the historical center of Rome. The hill lies to the north of the Quirinal, overlooking the Campus Martius...
(modern Pincio).
VIII: Forum Romanum
The central region contains the Capitoline HillCapitoline Hill
The Capitoline Hill , between the Forum and the Campus Martius, is one of the seven hills of Rome. It was the citadel of the earliest Romans. By the 16th century, Capitolinus had become Capitolino in Italian, with the alternative Campidoglio stemming from Capitolium. The English word capitol...
, the valley between the Palatine and the Capitoline hills (where the Forum Romanum is located), and the area between Velian Hill
Velian Hill
The Velia — or Velian Hill or Velian Ridge — is a saddle or spur stretching out from the middle of the north side of the Palatine Hill towards the Oppian Hill ....
and the Palatine up to the Arch of Titus
Arch of Titus
The Arch of Titus is a 1st-century honorific arch located on the Via Sacra, Rome, just to the south-east of the Roman Forum. It was constructed in c.82 AD by the Roman Emperor Domitian shortly after the death of his older brother Titus to commemorate Titus' victories, including the Siege of...
and the Temple of Venus and Roma
Temple of Venus and Roma
The Temple of Venus and of Rome — in Latin, Templum Veneris et Romae — is thought to have been the largest temple in Ancient Rome. Located on the Velian Hill, between the eastern edge of the Forum Romanum and the Colosseum, it was dedicated to the goddesses Venus Felix and Roma Aeterna...
.
IX: Circus Flaminius
The name derives from the racecourseCircus Flaminius
The Circus Flaminius was a large, circular area of land in Rome that contained a small race-track reserved for mysterious games, and various other buildings and monuments. It was located in the southern end of the Campus Martius, near the Tiber River. It was ‘built,’ or sectioned off, by Flaminius...
located in the southern end of the Campus Martius
Campus Martius
The Campus Martius , was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome...
, close to Tiber Island
Tiber Island
The Tiber Island , is a boat-shaped island which has long been associated with healing. It is an ait, and is one of the two islands in the Tiber river, which runs through Rome; the other one, much larger, is near the mouth. The island is located in the southern bend of the Tiber. It is...
. The region contains part of the Campus Martius
Campus Martius
The Campus Martius , was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome...
, on the west side of via Lata
Via del Corso
The Via del Corso , commonly known as the Corso, is a main street in the historical centre of Rome. It is remarkable for being absolutely straight in an area characterized by narrow meandering alleys and small piazzas...
.
XI: Circus Maximus
Regio XI took its name from the Circus MaximusCircus Maximus
The Circus Maximus is an ancient Roman chariot racing stadium and mass entertainment venue located in Rome, Italy. Situated in the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and largest stadium in ancient Rome and its later Empire...
, located in the valley between the Palatine and the Aventine
Aventine Hill
The Aventine Hill is one of the seven hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the twelfth rione, or ward, of Rome.-Location and boundaries:The Aventine hill is the southernmost of Rome's seven hills...
. It contained the Circus Maximus
Circus Maximus
The Circus Maximus is an ancient Roman chariot racing stadium and mass entertainment venue located in Rome, Italy. Situated in the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and largest stadium in ancient Rome and its later Empire...
, the Velabrum
Velabrum
The Velabrum is the low valley in the city of Rome that connects the Forum with the Forum Boarium, and the Capitoline Hill with the western slope of the Palatine Hill. Before the construction of the Cloaca Maxima, which probably follows the course of an ancient stream, the area was a swamp...
(the valley between the Palatine and Capitoline), as well as the areas next to the Forum Boarium
Forum Boarium
The Forum Boarium was the cattle forum venalium of Ancient Rome and the oldest forum that Rome possessed. It was located on a level piece of land near the Tiber between the Capitoline, the Palatine and Aventine hills. Here, too, is where the first bridges were built...
and the Forum Holitorium
Forum Holitorium
The Forum Holitorium was the market for vegetables, herbs and oil forum venalium of early ancient Rome, by the Tiber at the foot of the Capitoline and Palatine hills...
.
XII: Piscina Publica
Regio XII took its name from the Piscina PublicaPiscina Publica
In ancient Rome, the Piscina Publica was a public reservoir and swimming pool located in Regio XII. The region itself came to be called informally Piscina Publica from the landmark...
, a monument that disappeared during the Empire. It had the high ground where the church of San Saba is at present, plus its ramifications towards the Appian Way
Appian Way
The Appian Way was one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, Apulia, in southeast Italy...
, where Caracalla's baths
Baths of Caracalla
The Baths of Caracalla in Rome, Italy were Roman public baths, or thermae, built in Rome between AD 212 and 216, during the reign of the Emperor Caracalla.- History :...
were.
In the 180s, a bank and exchange for Christians operated in the area.
XIII: Aventinus
Regio XIII contained the Aventine HillAventine Hill
The Aventine Hill is one of the seven hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the twelfth rione, or ward, of Rome.-Location and boundaries:The Aventine hill is the southernmost of Rome's seven hills...
and the plain in front of it, along the Tiber. Here was the Emporium
Marketplace
A marketplace is the space, actual, virtual or metaphorical, in which a market operates. The term is also used in a trademark law context to denote the actual consumer environment, ie. the 'real world' in which products and services are provided and consumed.-Marketplaces and street markets:A...
, the first port on the river.
XIV: Transtiberim
Regio XIV (the region "across the Tiber") contained Tiber IslandTiber Island
The Tiber Island , is a boat-shaped island which has long been associated with healing. It is an ait, and is one of the two islands in the Tiber river, which runs through Rome; the other one, much larger, is near the mouth. The island is located in the southern bend of the Tiber. It is...
and all the parts of Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
west beyond the Tiber. This is modern Trastevere
Trastevere
Trastevere is rione XIII of Rome, on the west bank of the Tiber, south of Vatican City. Its name comes from the Latin trans Tiberim, meaning literally "beyond the Tiber". The correct pronunciation is "tras-TEH-ve-ray", with the accent on the second syllable. Its logo is a golden head of a lion on a...
.
Source
- DISCRIPTIO XIIII REGIONVM VRBIS ROMÆ, Curiosum - Notitia. 4th century descriptions of the regions of Rome and their main buildings

